Abstract
1. On fractionation of guinea-pig forebrain homogenates by differential and gradient-density centrifugation most of the polyphosphoinositides were recovered in the myelin-rich particles. 2. The phospholipids of pure preparations of myelin contained di- and tri-phosphoinositide in proportions 2–3 times greater than in the whole-brain phospholipids. 3. Di- and tri-phosphoinositide appeared in young rat brain during the period of myelination. 4. After the administration of [32P]phosphate to guinea pigs the labelling of the polyphosphoinositides in isolated pure myelin was as great as in the whole brain, whereas little synthesis of the other myelin phospholipids had occurred. 5. When brain subcellular fractions were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP, some triphosphoinositide labelling occurred in the myelin-rich fraction whereas the active labelling of diphosphoinositide was localized mainly in the mitochondrial fraction. 6. The Na+, K+ and Mg2+ plus Ca2+ concentrations in purified myelin have been determined. The Mg2+ plus Ca2+ content present showed close acid–base equivalence to the polyphosphoinositides. 7. It is concluded that di- and tri-phosphoinositide are rapidly-metabolizing components of the myelin sheath or intimately associated structures.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMADUCCI L., PAZZAGLI A., PESSINA G. The relation of proteolipids and phosphatidopeptides to tissue elements in the bovine nervous system. J Neurochem. 1962 Sep-Oct;9:509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMES A., 3rd, NESBETT F. B. A method for multiple electrolyte analyses on small samples of nervous tissue. J Neurochem. 1958 Dec;3(2):116–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANSELL G. B., SPANNER S. The effect of insulin on the formation of phosphorylcholine and phosphorylethanolamine in the brain. J Neurochem. 1959 Oct;4:325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb13213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUGUST C., DAVISON A. N., MAURICE-WILLIAMS F. Phospholipid metabolism in nervous tissue. 4. Incorporation of P32 into the lipids of subcellular fractions of the brain. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:8–12. doi: 10.1042/bj0810008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
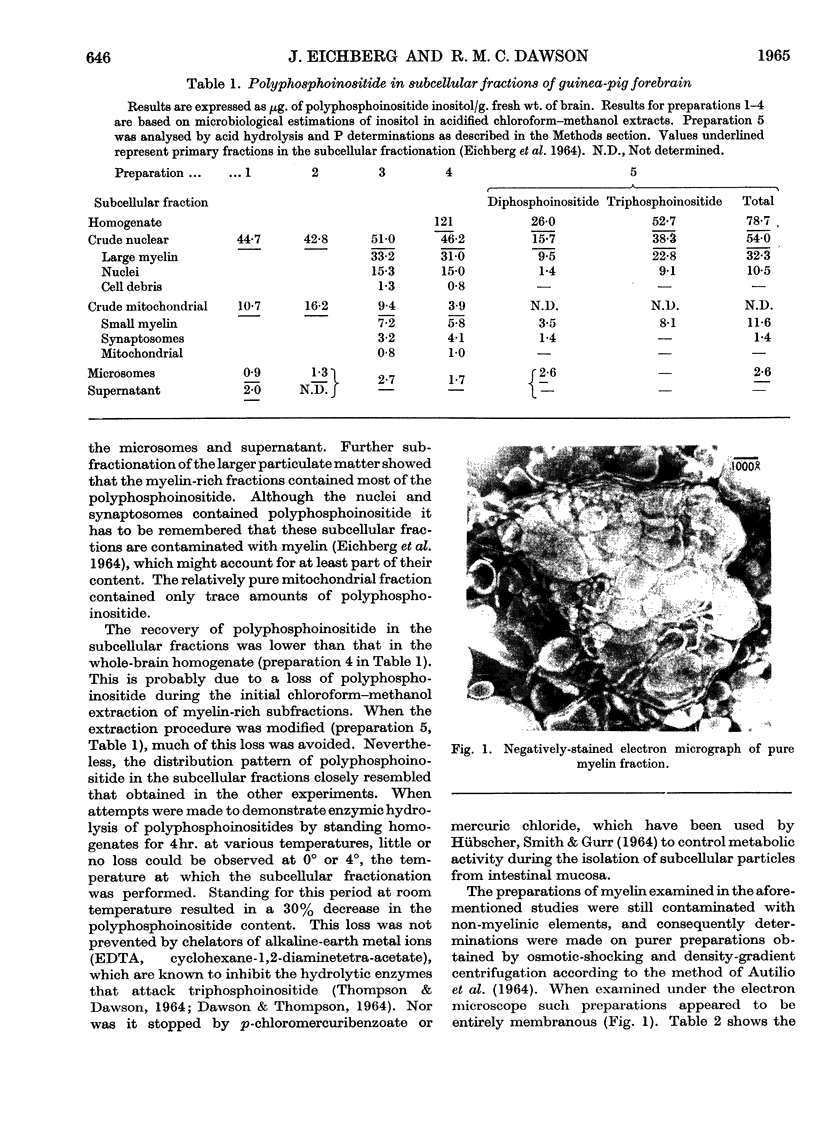
- AUTILIO L. A., NORTON W. T., TERRY R. D. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF PURIFIED MYELIN FROM THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. J Neurochem. 1964 Jan;11:17–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKERHOFF H., BALLOU C. E. Phosphate incorporation in brain phosphionositides. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins J. T., McIlwain H. Electrical pulses and the potassium and other ions of isolated cerebral tissues. Biochem J. 1961 May;79(2):330–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0790330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N., DOBBING J. Phospholipid metabolism in nervous tissue. 2. Metabolic stability. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:565–570. doi: 10.1042/bj0750565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N., DOBBING J. Phospolipid metabolism in nervous tissue. 3. The anatomical distribution of metabolically inert phospholipid in the central nervous system. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:571–574. doi: 10.1042/bj0750571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the labelling of brain phospholipids with radioactive phosphorus. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):237–245. doi: 10.1042/bj0570237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., DAWSON R. M. The isolation of a new lipid, triphosphoinositide, and monophosphoinositide from ox brain. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj0810535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., DAWSON R. M. The isolation of a new lipid, triphosphoinositide, and monophosphoinositide from ox brain. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj0810535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Eichberg J. Diphosphoinositide and triphosphoinositide in animal tissues. Extraction, estimation and changes post mortem. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):634–643. doi: 10.1042/bj0960634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Thompson W. The triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):244–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0910244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Whittaker V. P., Dawson R. M. Distribution of lipids in subcellular particles of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):91–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0920091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., CASALS J., POPE A., MEATH J. A., LEBARON F. N., LEES M. Chemistry of myelin development. Prog Neurobiol. 1959;4:122–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. The mechanism of phosphate exchange in phosphatidic acid in response to acetylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1387–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The intracellular calcium contents of some invertebrate nerves. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):399–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LE BARON F. N., KISTLER J. P., HAUSER G. Incorporation of 32P in vivo into phosphatidopeptides of rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Oct 21;44:170–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBARON F. N., MCDONALD C. P., RAMARAO B. S. THE AMOUNTS AND DISTRIBUTION OF FREE INOSITOL AND FREE AND PROTEIN-BOUND PHOSPHOINOSITIDES IN BRAIN TISSUES. J Neurochem. 1963 Oct;10:677–683. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRICKLAND K. P. Nucleic acids and other protein-bound phosphorus compounds of cat brain; incorporation of P32 after an intracisternal injection. Can J Med Sci. 1952 Dec;30(6):484–493. doi: 10.1139/cjms52-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Dawson R. M. The triphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj0910237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]