Abstract
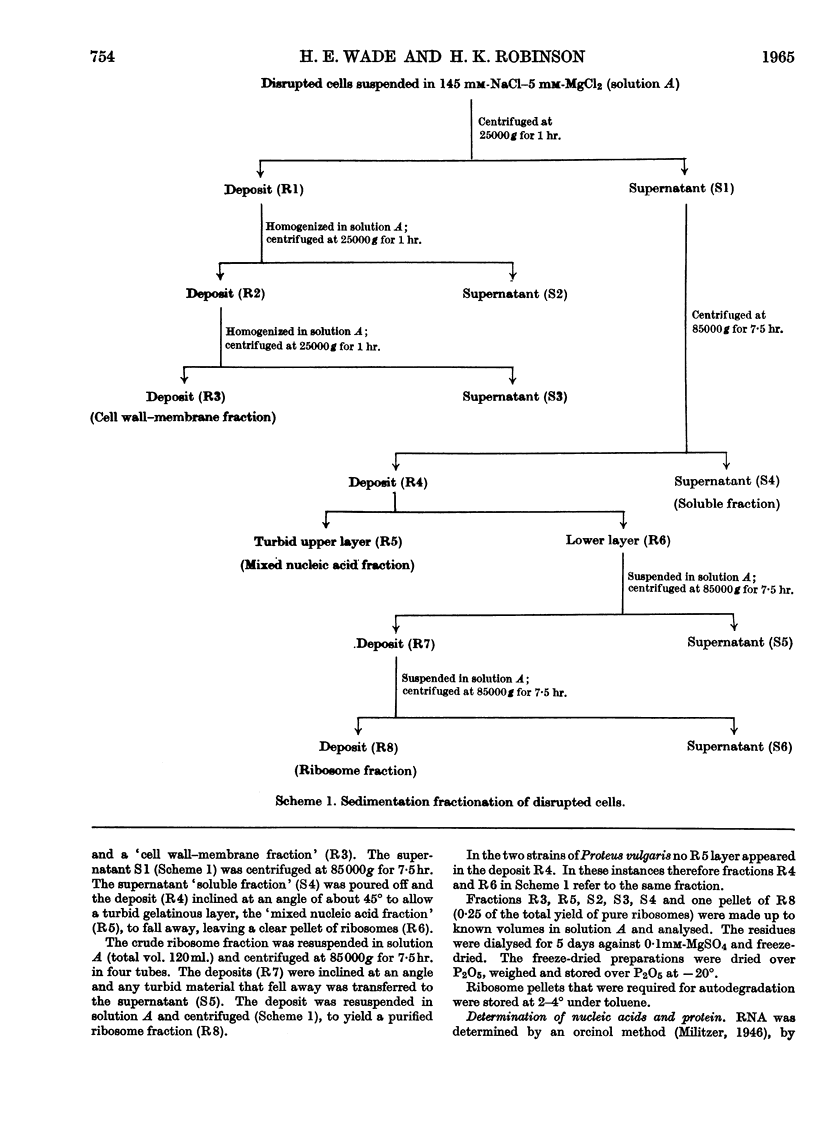
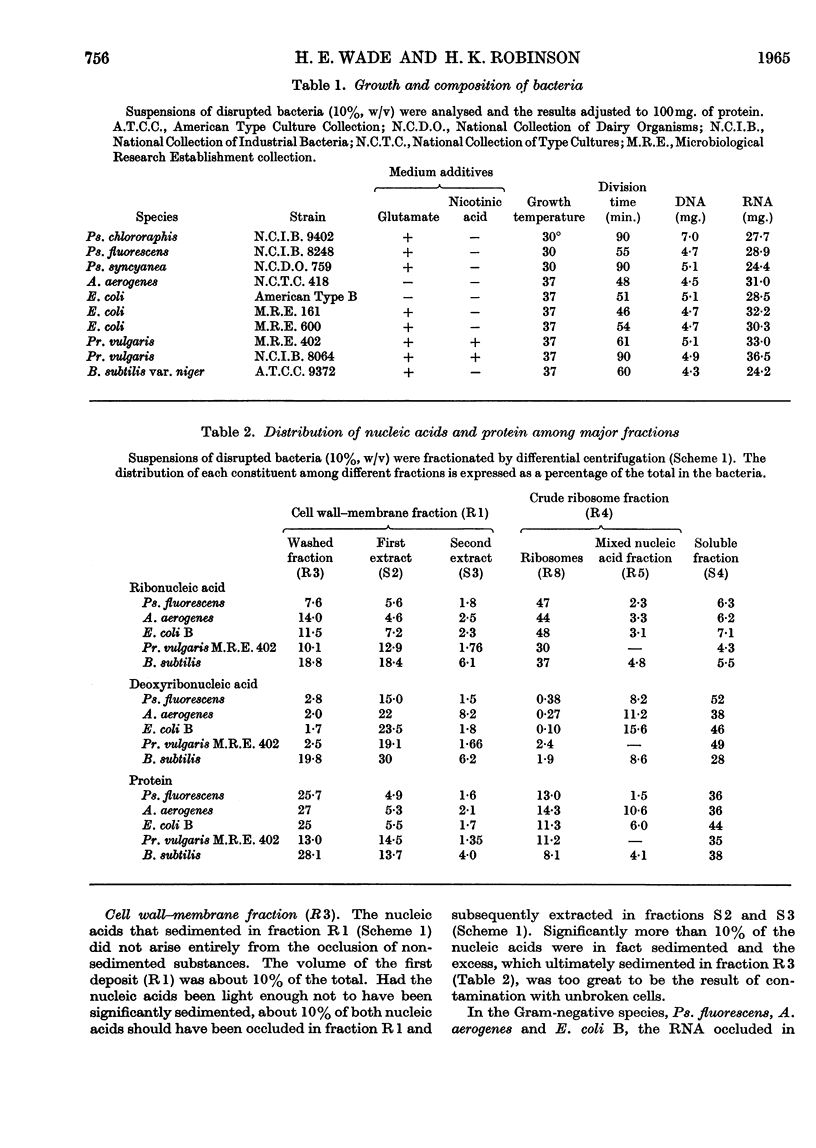
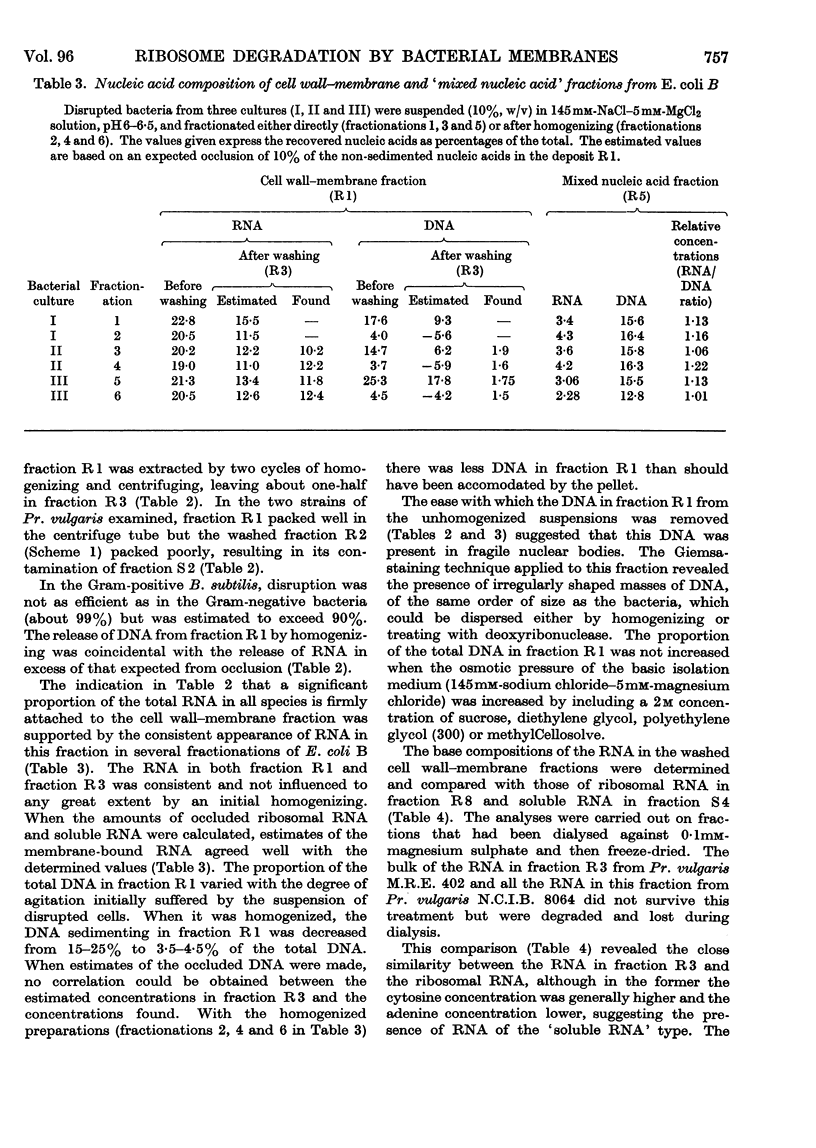
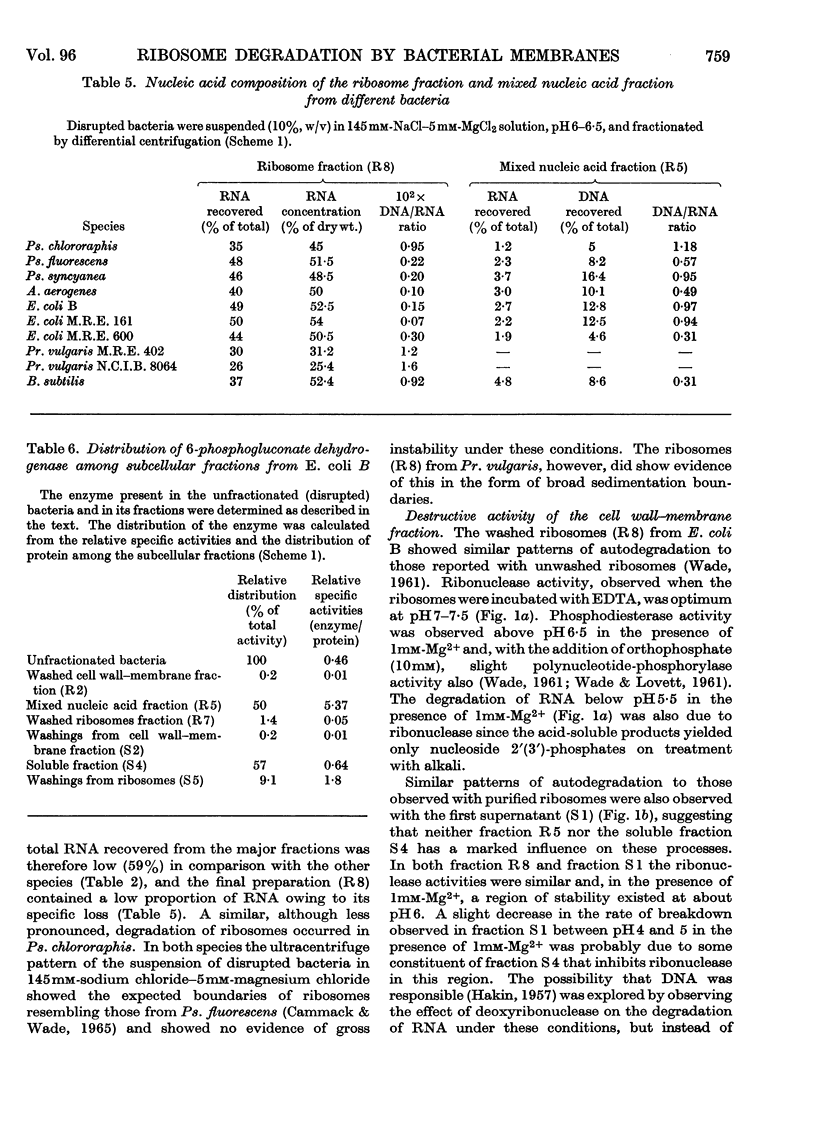
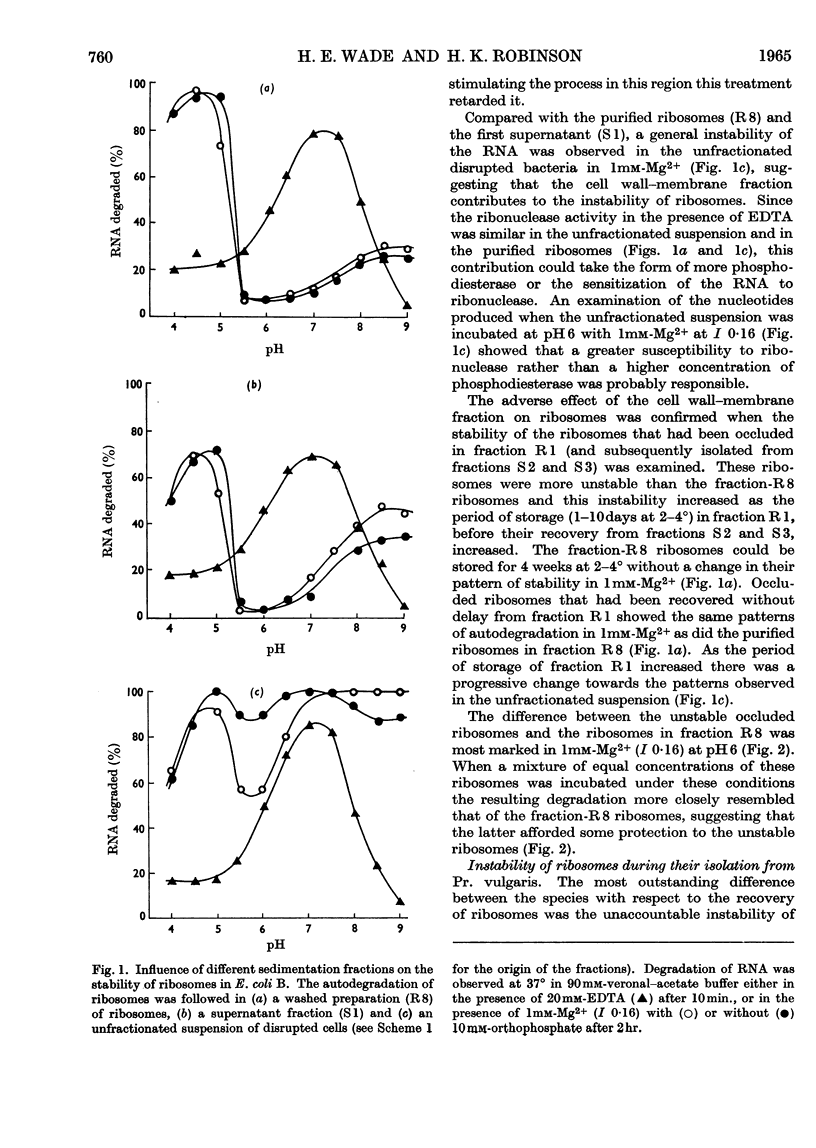
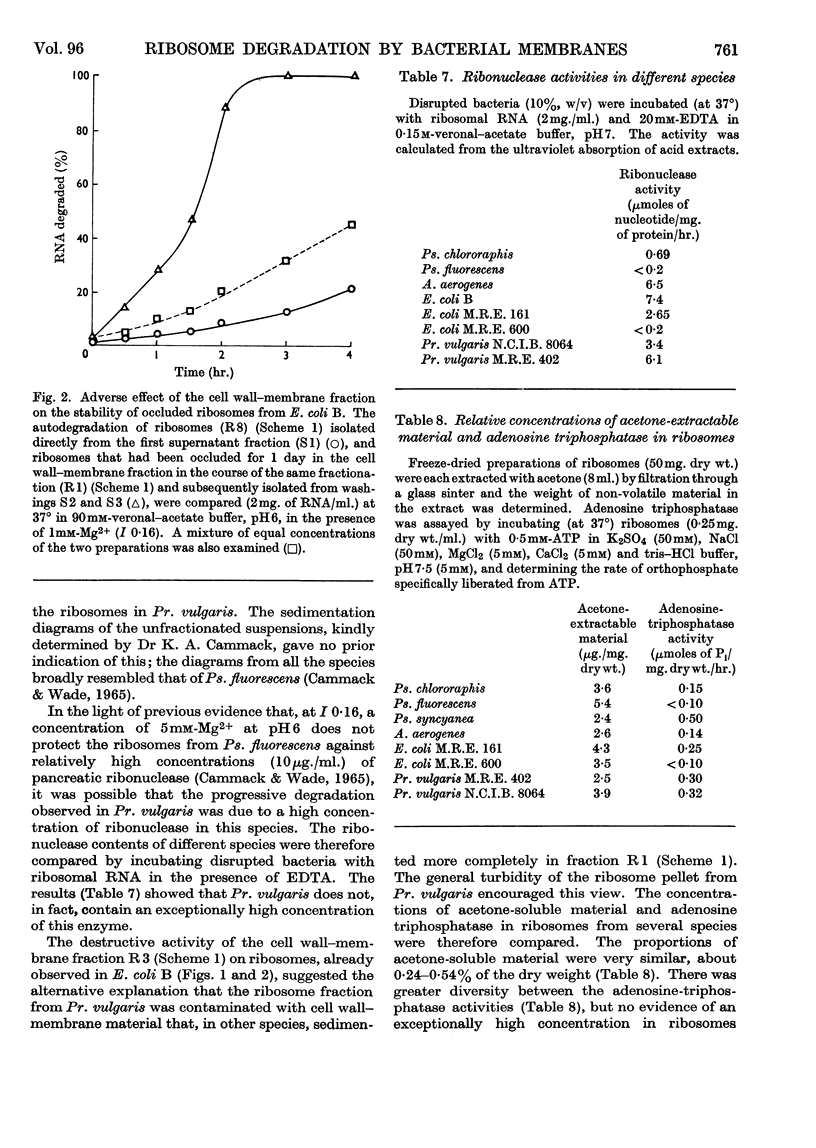
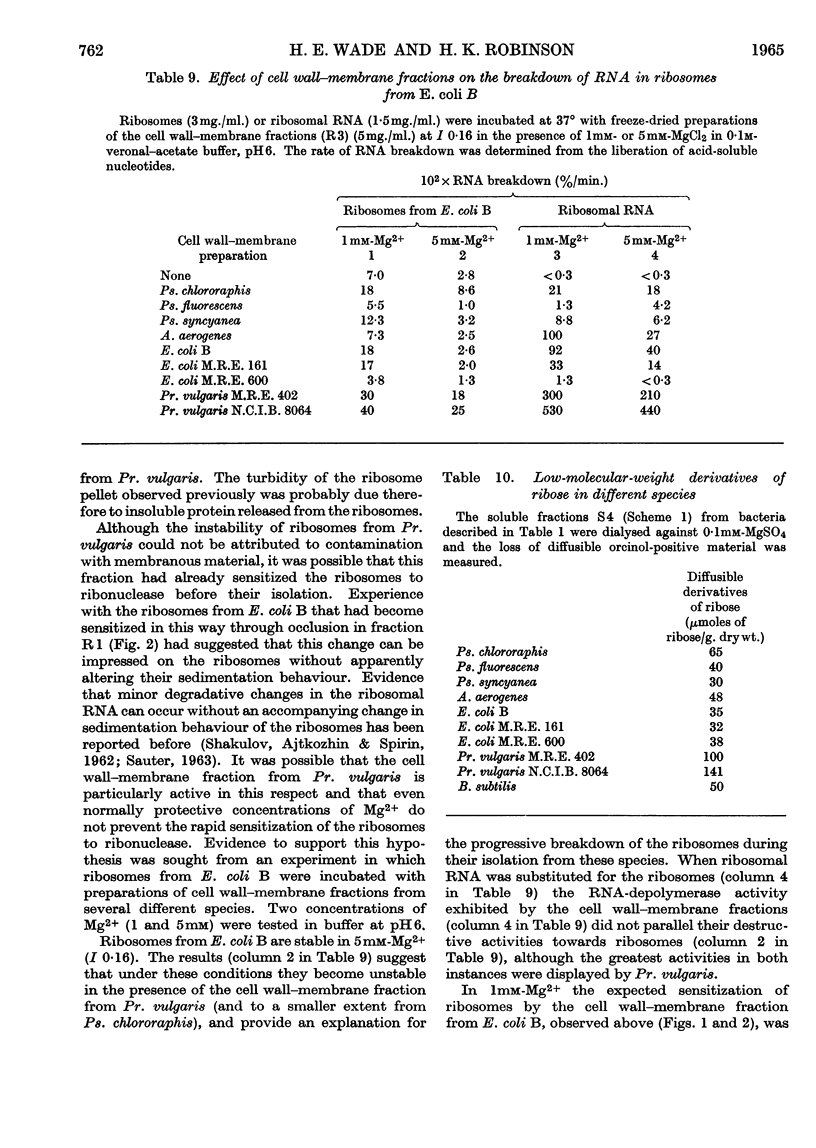
1. The distributions of nucleic acids and protein among fractions obtained by differential centrifugation from species of Pseudomonas, Aerobacter, Escherichia, Proteus and Bacillus have been studied. 2. The DNA in a cell wall–membrane fraction obtained by low-speed centrifugation from the Gram-negative species could be removed by homogenizing and subsequent washing. About 7–14% of the total RNA remained firmly attached and resembled ribosomal RNA in base composition. A similar fraction from the Gram-positive B. subtilis contained about one-half of the total bacterial DNA and only 60% of this could be removed by homogenizing and subsequent washing. 3. A deposit obtained by high-speed centrifugation could be separated into a heavy ribosome layer and a light turbid layer. In E. coli B the latter contained about equal concentrations of RNA and DNA and accounted for about one-half of the total bacterial NADP-activated 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. 4. The washed cell wall–membrane fraction from most species accelerated the degradation of ribosomes. In Pr. vulgaris the activity of this fraction was exceptionally high and resulted in the progressive degradation of ribosomes during their isolation from this species. 5. A possible connexion between ribosome degradation and the synthesis of flagella is discussed in the light of these results.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAM D., KOFFLER H. IN VITRO FORMATION OF FLAGELLA-LIKE FILAMENTS AND OTHER STRUCTURES FROM FLAGELLIN. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:168–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAMS A., NIELSEN L., THAEMERT J. RAPIDLY SYNTHESIZED RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN MEMBRANE GHOSTS FROM STREPTOCOCCUS FECALIS PROTOPLASTS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:325–337. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDOH T., MIZUNO D. Molecular heterogeneity of RNA in ribosomes of E. coli with respect to turnover rate in the maximum concentration of the cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Nov 1;6:104–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL J. J., HOGGLA, STRASDINE G. A. Enzyme distribution in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:1155–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.1155-1160.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack K. A., Wade H. E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0960671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJISAWA Y., SIBATANI A. Is there any quantitative relationship between the synthesis and the breakdown of nucleic acids in living cells? Experientia. 1954 Apr 15;10(4):178–180. doi: 10.1007/BF02157200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODSON G. N., HUNTER G. D., BUTLER J. A. Cellular components of Bacillus megaterium and their role in protein biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:59–68. doi: 10.1042/bj0810059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN A., BROWN B. J. Effect of sonic oscillation upon "old" and "new" nucleic acids in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:19–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90790-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Butler J. A. Biosynthesis of nucleic acids in Bacillus megaterium. 4. Roles of the 'nuclear' cytoplasmic and cytoplasmic-membrane components of the cell in the biosynthesis of ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):573–583. doi: 10.1042/bj0930573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKIM A. A. Enzymic heterogeneity of crystalline ribonuclease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Aug;70(2):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANZON V., HERMODSSON L. H., TOSCHI G. Ultrastructural organization of cytoplasmic nucleoprotein in the exocrine pancreas cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1959 Dec;3:216–227. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(59)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDLER R. W., BANFIELD W. G., TANI J., KUFFEL ON THE CYTOLOGICAL UNIT FOR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN VIVO IN E. COLI. III. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC AND ULTRACENTRIFUGAL EXAMINATION OF INTACT CELLS AND FRACTIONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L., van ITERSON W. Electron microscopical observations on bacterial cytology; a study on flagellation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Mar;5(1):10–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SKUTCH E. T., SCHADE A. L. Effect of cobalt on the phosphorus turnover rate in the nucleic acids of Proteus vulgaris. Arch Biochem. 1949 Nov;24(1):206–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANSON L. A. The metabolism of ribonucleic acid in normal and bacteriophage infected Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):703–711. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.703-711.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTAKA E., OSAWA S., OOTA Y., ISHIHAMA A., MITSUI H. Synthesis of ribonucleic acids in microbial cells. I. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis in growing bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:310–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90786-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. NUCLEIC ACID PRECURSORS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 May;40(5):263–270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.5.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J. S. Ribonuclease. III. Ribonuclease activity in rat liver and kidney. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):181–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M. RIBOSOMAL RNA ON THE SURFACE OF RIBOSOMES. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1049–1050. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLESSINGER D. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY POLYRIBOSOMES ON PROTOPLAST MEMBRANES OF B. MEGATERIUM. J Mol Biol. 1963 Nov;7:569–582. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAKULOV R. S., AITKHOZHIN M. A., SPIRIN A. S. [On latent degradation of ribosomes]. Biokhimiia. 1962 Jul-Aug;27:744–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STICKLAND L. H. The determination of small quantities of bacteria by means of the biuret reaction. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):698–703. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., WADE H. E., NESS A. G. The catabolism of proteins and nucleic acids in starved Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem J. 1963 Feb;86:197–203. doi: 10.1042/bj0860197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUIT J. C. Localization of deoxyribonucleic acid-like ribonucleic acid in a "membrane" fraction of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 30;72:488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANI J., HENDLER R. W. ON THE CYTOLOGICAL UNIT FOR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN VIVO IN E. COLI. I. STUDIES WITH SPHEROPLASTS OF TYPE K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:279–293. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., LOVETT S. Polynucleotide phosphorylase in ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:319–328. doi: 10.1042/bj0810319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., LOVETT S. The incorporation of phosphorus into fractions of Escherichia coli made by centrifuging and by chemical means. Biochem J. 1958 Dec;70(4):697–705. doi: 10.1042/bj0700697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., ROBINSON H. K. ABSENCE OF RIBONUCLEASE FROM THE RIBOSOMES OF PSEUDOMONAS FLUORESCENS. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:661–663. doi: 10.1038/200661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E. The autodegradation of ribonucleoprotein in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:457–472. doi: 10.1042/bj0780457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


