Abstract
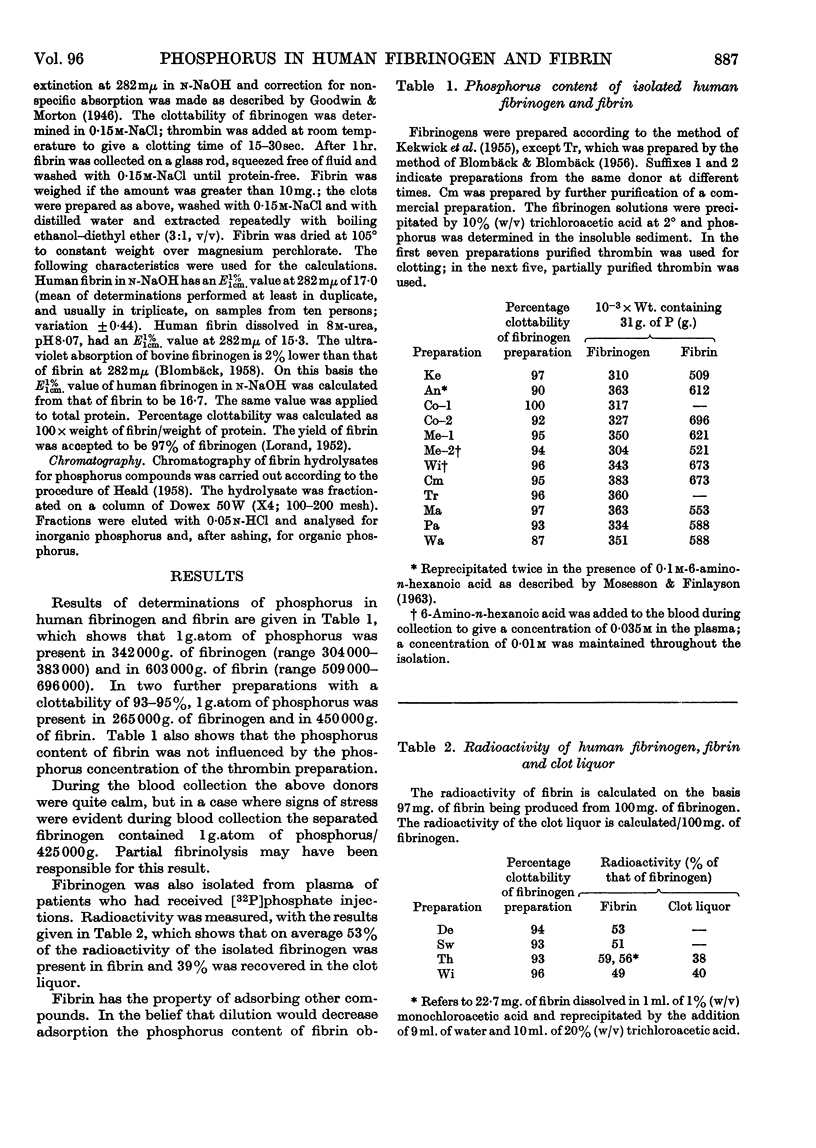
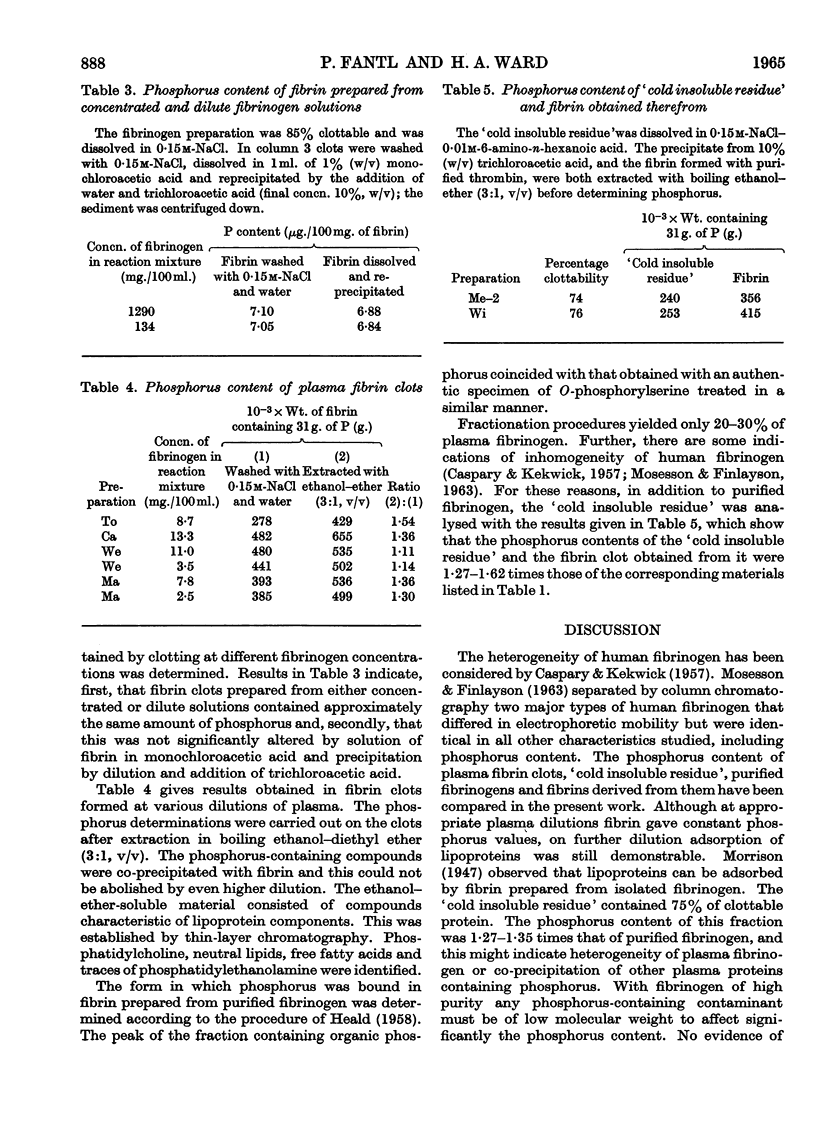
1. Fibrin clots obtained from diluted human plasma with bovine thrombin often contain amounts of phospholipids that cannot be diminished by further plasma dilution. 2. The `cold insoluble residue' obtained during fibrinogen preparation has a higher phosphorus content than the purified fibrinogen. 3. Evidence showed that adsorption of phospholipids or phosphorus-containing fibrinopeptides on purified fibrinogen or fibrin was unlikely. 4. O-Phosphorylserine was detected in acid hydrolysates of human fibrin. 5. On the basis of phosphorus determinations the average molecular weight of human fibrinogen cannot be less than 342000 (304000–383000) for a group of ten donors, and 265000 for two other persons, assuming 1 phosphorus atom/molecule and incomplete splitting of the phosphorus-containing fibrinopeptide. Complete splitting of the phosphopeptide would require molecular weights twice as high. 6. Fibrinolysis was a possible cause of lower phosphorus contents found in isolated fibrinogen and fibrin from a donor who showed apprehension during blood collection and in a fibrinogen preparation that had been submitted to prolonged dialysis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOMBACK B., BLOMBACK M., SEARLE J. On the occurrence of phosphorus in fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 2;74:148–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPARY E. A., KEKWICK R. A. Observations on the molecular weight of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1954 Jan 16;56(325TH):xxxv–xxxvi. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPARY E. A., KEKWICK R. A. Some physicochemical properties of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1957 Sep;67(1):41–48. doi: 10.1042/bj0670041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALD P. J. Phosphorylserine and cerebral phosphoprotein. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):580–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0680580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., MACKAY M. E., NANCE M. H., RECORD B. R. The purification of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):671–683. doi: 10.1042/bj0600671b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L. Fibrino-peptide. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):200–203. doi: 10.1042/bj0520200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSESSON M. W., FINLAYSON J. S. SUBFRACTIONS OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN; PREPARATION AND ANALYSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Oct;62:663–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN P. S. Purification of thrombin by chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


