The title compounds, C10H9Cl2FN2O3, (I), and C11H12Cl2N2O3, (II), are α,α-dihalo-β-diketone urea derivatives, which contain 4-fluorophenyl and p-tolyl groups, respectively. The conformation about the CO—CCl2—CO—Nu (O = keto, Cl2 = dichloro, u = urea) bond is anti in (I) and gauche in (II). In the crystals of both compounds, O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds generate inversion dimers and the dimers are linked into (100) layers by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure; hydrogen bonds; Hirshfeld surface analysis; α,α-dihalo-β-oxoaldehydes; urea
Abstract
The title compounds, C10H9Cl2FN2O3, (I), and C11H12Cl2N2O3, (II), are α,α-dihalo-β-diketone urea derivatives, which contain 4-fluorophenyl and p-tolyl groups, respectively. The conformation about the CO—CCl2—CO—Nu (O = keto, Cl2 = dichloro, u = urea) bond is anti in (I) and gauche in (II). In the crystals of both compounds, O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds generate inversion dimers and the dimers are linked into (100) layers by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The Hirshfeld surface analyses of the crystal structures indicate that the most important contributions for the crystal packings are from H⋯O/O⋯H (22.3%), H⋯H (20.9%), H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H (15.6%) and H⋯C/C⋯H (10.3%) for (I) and H⋯H (31.7%), H⋯O/O⋯H (25.1%), H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H (21.1%) and H⋯C/C⋯H (9.5%) for (II).
1. Chemical context
The replacement of hydrogen atoms with halogen atoms at the active methylene group in β-diketones prevents keto–enol tautomerism and impacts on the reactivity of the corresponding α,α-dihalo-β- diketones (e.g., Guseinov et al., 2006 ▸). For instance, the reaction of α,α-dihalo-β-oxoaldehydes and their derivatives with N-nucleophilic reagents lead to hetero- or macrocyclic compounds (Guseinov et al., 2024 ▸). This class of compounds can be used in the spectrophotometric determination of metal ions (Aliyev et al., 2020 ▸), decoration of the secondary coordination sphere of metal complexes for catalysis (Aliyeva et al., 2024 ▸), crystal growth and design (Naghiyev et al., 2023 ▸) and heterogenous catalysis (Mahmudov et al., 2022 ▸). In fact, the use of N-compounds has many synthetic advantages (Khalilov, 2021 ▸), such as easy modification and functionalization (Huseynov et al., 2021 ▸), immobilization on solid materials through supramolecular interactions (Mamedov et al., 2006 ▸), and crystal engineering (Hajiyeva et al., 2024 ▸).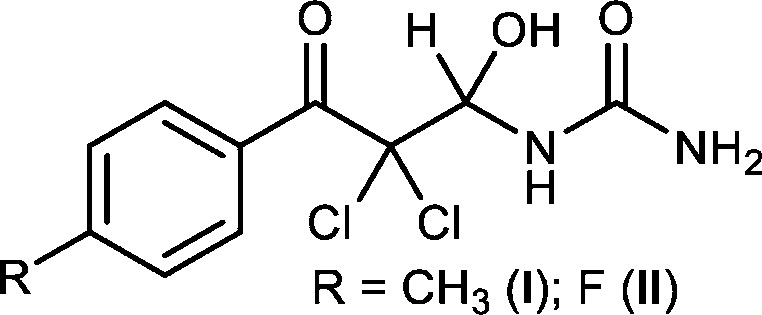
Herein, we describe the syntheses and crystal structures of the two title compounds, C10H9Cl2FN2O3 (I) and C11H12Cl2N2O3 (II), which differ in the substituent at the para position of the phenyl group.
2. Structural commentary
In (I) (Fig. 1 ▸), the dihedral angle between the C7–C12 phenyl group and the C2/N1/N3/O2 urea moiety is 65.19 (8)°. The key torsion angles for the backbone of the molecule are C7—C6—C5—C4 = −179.65 (13), C6—C5—C4—N3 = −171.20 (12), C4—C5—C6—O6 = 2.95 (19) and C6—C5—C4—O4 = 66.65 (15)°. Atom C4 is a stereogenic centre: in the arbitrarily chosen asymmetric unit it has R configuration, but crystal symmetry generates a racemic mixture. Atoms F1, C6, C5 are displaced by −0.0244 (11), −0.0602 (15) and −0.0879 (15) Å, respectively, from the plane of the phenyl group. The N1—C2—O2, N3—C4—O4, N3—C4—C5, Cl1—C5—Cl2 and C4—C5—C6 bond angles in (I) are enlarged, while the O2—C2—N3 bond angle in (I) is narrowed compared to the corresponding values in (II): these small differences might arise due to steric reasons or ’packing effects’.
Figure 1.
The asymmetric units of compounds (a) (I) and (b) (II) with 50% probability ellipsoids.
In (II) (Fig. 1 ▸), the corresponding dihedral angle between the C7–C12 and C2/N1/N3/O2 planes is 62.70 (9)° and the equivalent backbone torsion angles are C7—C6—C5—C4 = 162.65 (14), C6—C5—C4—N3 = −62.41 (16), C4—C5—C6—O6 = −17.42 (19) and C6—C5—C4—O4 = 176.34 (12)°. Thus it may be seen that the conformation of the atoms about the C4—C5 bond is quite different in the two structures. The stereogenic atom C4 in (II) was arbitrarily assigned to have an R configuration, but crystal symmetry generates a racemic mixture.
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystals of both compounds, O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸) generate inversion dimers featuring  (12) loops. In both structures, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the dimers into (100) layers, although they are not isostuctural. The hydrogen-bond network encloses
(12) loops. In both structures, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the dimers into (100) layers, although they are not isostuctural. The hydrogen-bond network encloses  (14) loops in (I) (Fig. 2 ▸a) and
(14) loops in (I) (Fig. 2 ▸a) and  (8) and
(8) and  (8) loops in (II) (Fig. 2 ▸b).
(8) loops in (II) (Fig. 2 ▸b).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O4i | 0.90 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.9488 (19) | 172 (2) |
| N1—H1B⋯O2ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.48 (2) | 3.297 (2) | 158 (2) |
| N3—H3⋯O6iii | 0.87 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.9055 (18) | 167 (2) |
| O4—H4⋯O2iv | 0.78 (3) | 1.91 (3) | 2.6596 (16) | 161 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O4i | 0.82 (3) | 2.27 (3) | 3.0261 (19) | 153 (2) |
| N1—H1B⋯O4ii | 0.84 (3) | 2.14 (3) | 2.9798 (18) | 177 (2) |
| N3—H3⋯O2iii | 0.81 (3) | 2.19 (3) | 2.9445 (18) | 156 (2) |
| O4—H4⋯O2iv | 0.78 (3) | 1.83 (3) | 2.5979 (16) | 168 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Figure 2.
The partial packing diagrams of compounds (a) (I) and (b) (II). Intermolecular O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in these interactions have been omitted for clarity.
4. Hirshfeld surface analysis
For visualizing the intermolecular interactions in the crystals of (I) and (II), Hirshfeld surface (HS) analyses were carried out using Crystal Explorer 17.5 (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸). In the HSs plotted over dnorm (Fig. 3 ▸a and b), the contact distances equal, shorter and longer with respect to the sum of van der Waals radii are shown by the white, red and blue colours, respectively. According to the two-dimensional fingerprint plots, H⋯O/O⋯H, H⋯H and H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H contacts make the most important contributions to the HSs (Table 3 ▸, Figs. 4 ▸ and 5 ▸), and they have significant differences due to the different numbers and values of the close contacts in (I) and (II).
Figure 3.
Views of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surfaces of compounds (a) (I) and (b) (II) plotted over dnorm.
Table 3. Comparison of the fingerprint percentages for compounds (I) and (II).
| Contacts | (I) | (II) |
|---|---|---|
| H⋯O/O⋯H | 22.3 | 25.1 |
| H⋯H | 20.9 | 31.7 |
| H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H | 15.6 | 21.1 |
| H⋯C/C⋯H | 10.3 | 9.5 |
| H⋯F/F⋯H | 8.3 | – |
| C⋯Cl/Cl⋯C | 6.4 | 2.8 |
| C⋯F/F⋯C | 3.1 | – |
| F⋯Cl/Cl⋯F | 2.8 | – |
| Cl⋯Cl | 2.4 | 1.9 |
| H⋯N/N⋯H | 2.4 | 1.3 |
| C⋯C | 1.8 | 3.0 |
| O⋯O | 1.4 | – |
| F⋯F | 0.7 | – |
| O⋯Cl/Cl⋯O | 0.7 | 0.2 |
| C⋯O/O⋯C | 0.6 | 1.9 |
| N⋯O/O⋯N | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| C⋯N/N⋯C | 0.1 | – |
| N⋯Cl/Cl⋯N | 0.1 | 1.3 |
Figure 4.
The two-dimensional fingerprint plots for compound (I), showing (a) all interactions, and delineated into different contact types (b)–(i). The di and de values are the closest internal and external distances (in Å) from given points on the Hirshfeld surface.
Figure 5.
The two-dimensional fingerprint plots for compound (II), showing (a) all interactions, and delineated into different contact types (b)–(i). The di and de values are the closest internal and external distances (in Å) from given points on the Hirshfeld surface.
5. Synthesis and crystallization
A solution of 2,2-dichloro-3-oxo-3-(p-tolyl)propanal (231 mg) for (I) or 2,2-dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-oxopropanal (235 mg) for (II) and urea (60 mg) in 15 ml of dry acetonitrile was stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The solvent was removed in vacuo, and the remaining white powder was recrystallized from acetone solution and the title compounds were isolated. The reaction scheme is shown in Fig. 6 ▸.
Figure 6.
The synthesis of the title compounds.
(I): yield 82%; m.p. 378–380 K. Analysis calculated (%) for C11H12Cl2N2O3: C 45.38, H 4.15, N 9.62; found C 45.36, H 4.11, N 9.60. 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-d6): 2.41 (s, CH3), 5.94 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.01–6.08 (d.d, CH), 6.72 (d, OH), 6.85 (d. NH), 7.38 (d. 2H, Ar), 7.95 (d, 2H, Ar). 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): 21.32, 88.03, 104.05, 128.74, 128.91, 133.77, 142.81, 162.72, 186.95.
(II): yield 78%; m.p. 397–398 K. Analysis calculated (%) for C10H9Cl2FN2O3: C 40.70, H 3.07, N 9.49; found C 40.65, H 3.02, N 9.45. 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-d6): 5.96 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.03–6.08 (d.d, CH), 6.78 (d, OH), 6.93 (d, NH), 7.46 (t, 2H, Ar), 8.12 (d.d, 2H, Ar). 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): 88.10, 104.12, 115.46, 130.49, 132.37, 162.74, 167.35, 186.92.
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 4 ▸. The OH and NH2 hydrogen atoms were located in difference-Fourier maps, and refined isotropically. The C-bond hydrogen-atom positions were placed geometrically (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and refined using a riding model by applying the constraint Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(methyl C).
Table 4. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C10H9Cl2FN2O3 | C11H12Cl2N2O3 |
| M r | 295.09 | 291.13 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 15.6136 (1), 7.2214 (1), 10.7929 (1) | 12.62183 (13), 8.77585 (9), 11.59930 (11) |
| β (°) | 104.622 (1) | 94.8294 (9) |
| V (Å3) | 1177.51 (2) | 1280.26 (2) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 5.14 | 4.60 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.32 × 0.15 × 0.05 | 0.45 × 0.35 × 0.16 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | XtaLAB Synergy, Dualflex, HyPix | XtaLAB Synergy, Dualflex, HyPix |
| Absorption correction | Gaussian (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2024 ▸) | Gaussian (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2024 ▸) |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.408, 1.000 | 0.277, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 16149, 2562, 2494 | 17344, 2808, 2738 |
| R int | 0.035 | 0.050 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.640 | 0.640 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.031, 0.082, 1.06 | 0.037, 0.104, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 2562 | 2808 |
| No. of parameters | 179 | 180 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.40, −0.31 | 0.51, −0.43 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127sup1.cif
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127Isup4.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127Isup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127IIsup5.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127IIsup5.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The crystal structure determinations were performed in the Department of Structural Studies of Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, Moscow. This work was supported by the Western Caspian University and Azerbaijan Medical University in Azerbaijan. The authors’ contributions are as follows. Conceptualization, FIG, TH and ANB; synthesis, KAA, EVS and LMG; X-ray analysis, AIS; Hirshfeld surface analyses, crystal voids, interaction energies and energy frameworks, TH; writing (review and editing of the manuscript) FIG and TH; funding acquisition, KIH; supervision, FIG, TH and ANB.
supplementary crystallographic information
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Crystal data
| C10H9Cl2FN2O3 | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 295.09 | Dx = 1.665 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 15.6136 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 10775 reflections |
| b = 7.2214 (1) Å | θ = 2.9–80.5° |
| c = 10.7929 (1) Å | µ = 5.14 mm−1 |
| β = 104.622 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1177.51 (2) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.15 × 0.05 mm |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Data collection
| XtaLAB Synergy, Dualflex, HyPix diffractometer | 2562 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, PhotonJet (Cu) X-ray Source | 2494 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.035 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 80.7°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −19→19 |
| Absorption correction: gaussian (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2024) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.408, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −10→13 |
| 16149 measured reflections |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0418P)2 + 0.7639P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2562 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 179 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.75812 (2) | 0.64065 (5) | 0.20981 (3) | 0.02166 (11) | |
| Cl2 | 0.71108 (2) | 0.90786 (5) | 0.38664 (3) | 0.02237 (11) | |
| F1 | 0.45932 (7) | 0.18867 (16) | 0.44559 (10) | 0.0321 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.91429 (7) | 1.16468 (16) | 0.49959 (11) | 0.0231 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.93636 (8) | 0.66517 (16) | 0.38219 (11) | 0.0216 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.9848 (18) | 0.692 (4) | 0.417 (2) | 0.038 (7)* | |
| O6 | 0.83823 (7) | 0.53628 (16) | 0.55147 (10) | 0.0220 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.91321 (10) | 1.2742 (2) | 0.30188 (16) | 0.0279 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.9206 (17) | 1.389 (4) | 0.334 (2) | 0.040 (7)* | |
| H1B | 0.9071 (15) | 1.259 (4) | 0.221 (2) | 0.032 (6)* | |
| N3 | 0.88523 (9) | 0.96745 (19) | 0.32966 (13) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.8796 (15) | 0.958 (4) | 0.248 (2) | 0.035 (6)* | |
| C2 | 0.90498 (10) | 1.1385 (2) | 0.38332 (16) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.87990 (10) | 0.8058 (2) | 0.40405 (14) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| H4A | 0.896975 | 0.839528 | 0.496915 | 0.023* | |
| C5 | 0.78496 (10) | 0.7248 (2) | 0.37028 (13) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.77450 (10) | 0.5688 (2) | 0.46381 (14) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.68898 (10) | 0.4691 (2) | 0.45000 (14) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.61114 (10) | 0.5077 (2) | 0.35608 (15) | 0.0220 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.611405 | 0.600113 | 0.293538 | 0.026* | |
| C9 | 0.53355 (11) | 0.4121 (2) | 0.35358 (16) | 0.0239 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.480694 | 0.437166 | 0.289650 | 0.029* | |
| C10 | 0.53522 (11) | 0.2797 (2) | 0.44634 (16) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.61052 (11) | 0.2368 (2) | 0.54016 (16) | 0.0261 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.609462 | 0.144287 | 0.602320 | 0.031* | |
| C12 | 0.68768 (11) | 0.3321 (2) | 0.54142 (15) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.740343 | 0.304306 | 0.605008 | 0.027* |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.02614 (19) | 0.0226 (2) | 0.01572 (18) | −0.00771 (14) | 0.00426 (13) | −0.00293 (12) |
| Cl2 | 0.02389 (19) | 0.01773 (19) | 0.0245 (2) | 0.00268 (13) | 0.00429 (14) | 0.00032 (13) |
| F1 | 0.0255 (5) | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0395 (6) | −0.0097 (4) | 0.0100 (4) | 0.0007 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0199 (6) | 0.0272 (6) | −0.0036 (4) | 0.0059 (4) | −0.0061 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0172 (5) | 0.0271 (6) | −0.0031 (4) | 0.0057 (4) | −0.0057 (4) |
| O6 | 0.0226 (5) | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0188 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0023 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0359 (8) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0321 (8) | −0.0040 (6) | 0.0103 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0285 (7) | 0.0174 (7) | 0.0200 (6) | −0.0056 (5) | 0.0046 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0147 (6) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0281 (8) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0041 (6) | −0.0038 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0151 (7) | 0.0210 (7) | −0.0024 (6) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0024 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0171 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | −0.0017 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0057 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0218 (7) | 0.0165 (7) | 0.0186 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0063 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0211 (7) | 0.0204 (7) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0237 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0285 (8) | −0.0058 (6) | 0.0093 (6) | −0.0045 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0227 (8) | 0.0269 (8) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0088 (6) | 0.0052 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0231 (7) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0028 (6) |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C5 | 1.7826 (14) | C4—C5 | 1.549 (2) |
| Cl2—C5 | 1.7923 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.549 (2) |
| F1—C10 | 1.3534 (18) | C6—C7 | 1.491 (2) |
| O2—C2 | 1.241 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.400 (2) |
| O4—H4 | 0.78 (3) | C7—C12 | 1.401 (2) |
| O4—C4 | 1.4032 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O6—C6 | 1.2103 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.389 (2) |
| N1—H1A | 0.90 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1B | 0.86 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.380 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.344 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (2) |
| N3—H3 | 0.87 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C2 | 1.366 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.385 (2) |
| N3—C4 | 1.431 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4A | 1.0000 | ||
| C4—O4—H4 | 108.1 (19) | O6—C6—C5 | 116.71 (13) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 119 (2) | O6—C6—C7 | 121.55 (14) |
| C2—N1—H1A | 116.4 (17) | C7—C6—C5 | 121.69 (13) |
| C2—N1—H1B | 124.6 (17) | C8—C7—C6 | 124.60 (14) |
| C2—N3—H3 | 117.2 (17) | C8—C7—C12 | 119.10 (14) |
| C2—N3—C4 | 122.60 (14) | C12—C7—C6 | 116.26 (14) |
| C4—N3—H3 | 120.1 (17) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.7 |
| O2—C2—N1 | 122.99 (15) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.56 (15) |
| O2—C2—N3 | 121.50 (15) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.7 |
| N1—C2—N3 | 115.50 (15) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.9 |
| O4—C4—N3 | 111.59 (13) | C10—C9—C8 | 118.28 (15) |
| O4—C4—H4A | 109.0 | C10—C9—H9 | 120.9 |
| O4—C4—C5 | 106.95 (12) | F1—C10—C9 | 118.43 (15) |
| N3—C4—H4A | 109.0 | F1—C10—C11 | 118.56 (15) |
| N3—C4—C5 | 111.33 (13) | C11—C10—C9 | 123.01 (15) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.0 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| Cl1—C5—Cl2 | 110.35 (8) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.29 (15) |
| C4—C5—Cl1 | 109.49 (10) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C4—C5—Cl2 | 107.43 (10) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—Cl1 | 110.36 (10) | C11—C12—C7 | 120.75 (15) |
| C6—C5—Cl2 | 107.22 (10) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 111.93 (12) | ||
| Cl1—C5—C6—O6 | 125.15 (13) | C4—N3—C2—O2 | −4.3 (2) |
| Cl1—C5—C6—C7 | −57.44 (16) | C4—N3—C2—N1 | 175.81 (14) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—O6 | −114.62 (13) | C4—C5—C6—O6 | 2.95 (19) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—C7 | 62.78 (15) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.65 (13) |
| F1—C10—C11—C12 | −179.17 (15) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.6 (2) |
| O4—C4—C5—Cl1 | −56.04 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C12 | −179.34 (13) |
| O4—C4—C5—Cl2 | −175.90 (10) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −177.53 (15) |
| O4—C4—C5—C6 | 66.65 (15) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | 177.33 (15) |
| O6—C6—C7—C8 | 175.69 (15) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.5 (2) |
| O6—C6—C7—C12 | −2.1 (2) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.5 (2) |
| N3—C4—C5—Cl1 | 66.10 (14) | C8—C9—C10—F1 | 178.80 (15) |
| N3—C4—C5—Cl2 | −53.75 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.8 (3) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | −171.20 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.4 (3) |
| C2—N3—C4—O4 | −124.46 (15) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 0.3 (3) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | 116.12 (15) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.2 (2) |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methylphenyl)-3-oxopropyl]urea (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O4i | 0.90 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.9488 (19) | 172 (2) |
| N1—H1B···O2ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.48 (2) | 3.297 (2) | 158 (2) |
| N3—H3···O6iii | 0.87 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.9055 (18) | 167 (2) |
| O4—H4···O2iv | 0.78 (3) | 1.91 (3) | 2.6596 (16) | 161 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) x, −y+5/2, z−1/2; (iii) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (iv) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1.
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Crystal data
| C11H12Cl2N2O3 | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 291.13 | Dx = 1.510 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 12.62183 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 11708 reflections |
| b = 8.77585 (9) Å | θ = 3.5–80.3° |
| c = 11.59930 (11) Å | µ = 4.60 mm−1 |
| β = 94.8294 (9)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1280.26 (2) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.45 × 0.35 × 0.16 mm |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Data collection
| XtaLAB Synergy, Dualflex, HyPix diffractometer | 2808 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, PhotonJet (Cu) X-ray Source | 2738 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.050 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 80.7°, θmin = 3.5° |
| ω scans | h = −13→16 |
| Absorption correction: gaussian (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2024) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.277, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −14→14 |
| 17344 measured reflections |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.104 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0655P)2 + 0.6302P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2808 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 180 parameters | Δρmax = 0.51 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.43 e Å−3 |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.22629 (3) | 0.88241 (4) | 0.40687 (3) | 0.02066 (13) | |
| Cl2 | 0.24819 (3) | 0.70279 (5) | 0.61915 (3) | 0.02309 (13) | |
| O2 | 0.02392 (10) | 0.37516 (13) | 0.31405 (10) | 0.0221 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.03286 (9) | 0.72384 (13) | 0.48926 (10) | 0.0192 (2) | |
| O6 | 0.27591 (10) | 0.45882 (14) | 0.39418 (11) | 0.0259 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.03826 (12) | 0.49974 (17) | 0.14562 (12) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.08327 (11) | 0.62287 (15) | 0.31617 (12) | 0.0180 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.04683 (12) | 0.49344 (18) | 0.26185 (13) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.10682 (12) | 0.63031 (17) | 0.43899 (13) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| H4A | 0.103457 | 0.525355 | 0.472057 | 0.021* | |
| C5 | 0.22071 (13) | 0.69474 (17) | 0.46569 (13) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.30485 (13) | 0.58690 (19) | 0.41747 (13) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.41441 (13) | 0.6404 (2) | 0.40165 (14) | 0.0225 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.46819 (15) | 0.5634 (2) | 0.31877 (16) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.433483 | 0.484415 | 0.274165 | 0.033* | |
| C9 | 0.57245 (15) | 0.6024 (2) | 0.30150 (17) | 0.0321 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.607516 | 0.551826 | 0.243057 | 0.039* | |
| C10 | 0.62617 (15) | 0.7138 (2) | 0.36820 (18) | 0.0325 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.57243 (15) | 0.7900 (2) | 0.45141 (18) | 0.0326 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.608274 | 0.866470 | 0.497716 | 0.039* | |
| C12 | 0.46717 (15) | 0.7555 (2) | 0.46742 (16) | 0.0275 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.431028 | 0.810101 | 0.523000 | 0.033* | |
| C13 | 0.74130 (16) | 0.7514 (3) | 0.3535 (2) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.762750 | 0.702446 | 0.283178 | 0.066* | |
| H13B | 0.786149 | 0.713990 | 0.420656 | 0.066* | |
| H13C | 0.749543 | 0.862022 | 0.347188 | 0.066* | |
| H1A | 0.059 (2) | 0.574 (3) | 0.110 (2) | 0.030 (6)* | |
| H1B | 0.0183 (19) | 0.420 (3) | 0.110 (2) | 0.028 (6)* | |
| H3 | 0.0725 (18) | 0.701 (3) | 0.280 (2) | 0.023 (5)* | |
| H4 | 0.014 (2) | 0.683 (3) | 0.543 (3) | 0.034 (6)* |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0239 (2) | 0.0173 (2) | 0.0211 (2) | −0.00221 (12) | 0.00407 (14) | 0.00018 (12) |
| Cl2 | 0.0263 (2) | 0.0291 (2) | 0.01385 (19) | 0.00153 (14) | 0.00155 (14) | −0.00215 (13) |
| O2 | 0.0313 (6) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0164 (5) | −0.0060 (4) | 0.0065 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0229 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0150 (5) | 0.0016 (4) | 0.0073 (4) | 0.0021 (4) |
| O6 | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0290 (6) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0057 (5) | −0.0049 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0304 (7) | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0144 (6) | −0.0061 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | −0.0009 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0139 (6) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0179 (7) | 0.0168 (7) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | 0.0001 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0217 (7) | 0.0176 (7) | 0.0139 (7) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0042 (5) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0150 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0005 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0156 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0039 (5) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0258 (8) | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0307 (9) | 0.0258 (8) | 0.0044 (7) | 0.0061 (6) | −0.0006 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0279 (9) | 0.0390 (10) | 0.0308 (9) | 0.0081 (8) | 0.0105 (7) | 0.0065 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0377 (10) | 0.0372 (10) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0063 (7) | 0.0162 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0358 (10) | −0.0041 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0263 (8) | 0.0305 (9) | 0.0260 (8) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0039 (6) | −0.0010 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0258 (10) | 0.0529 (14) | 0.0546 (13) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0104 (9) | 0.0210 (11) |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C5 | 1.7864 (16) | C6—C7 | 1.486 (2) |
| Cl2—C5 | 1.7861 (16) | C7—C8 | 1.397 (2) |
| O2—C2 | 1.248 (2) | C7—C12 | 1.400 (3) |
| O4—C4 | 1.4060 (18) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O4—H4 | 0.78 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.390 (3) |
| O6—C6 | 1.205 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C2 | 1.345 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.388 (3) |
| N1—H1A | 0.82 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.396 (3) |
| N1—H1B | 0.84 (3) | C10—C13 | 1.514 (2) |
| N3—C2 | 1.360 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C4 | 1.432 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.390 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.81 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4A | 1.0000 | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.551 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.561 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C4—O4—H4 | 109 (2) | C8—C7—C6 | 116.30 (16) |
| C2—N1—H1A | 121.9 (18) | C8—C7—C12 | 119.18 (16) |
| C2—N1—H1B | 117.0 (16) | C12—C7—C6 | 124.44 (15) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 121 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 |
| C2—N3—C4 | 122.18 (13) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.07 (18) |
| C2—N3—H3 | 115.9 (17) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.0 |
| C4—N3—H3 | 118.9 (17) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| O2—C2—N1 | 121.23 (15) | C10—C9—C8 | 121.10 (18) |
| O2—C2—N3 | 123.58 (14) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| N1—C2—N3 | 115.19 (14) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.69 (17) |
| O4—C4—N3 | 110.47 (13) | C9—C10—C13 | 121.3 (2) |
| O4—C4—H4A | 109.1 | C11—C10—C13 | 120.0 (2) |
| O4—C4—C5 | 109.93 (12) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.6 |
| N3—C4—H4A | 109.1 | C12—C11—C10 | 120.89 (19) |
| N3—C4—C5 | 109.05 (12) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.1 | C7—C12—H12 | 120.0 |
| Cl2—C5—Cl1 | 109.48 (8) | C11—C12—C7 | 120.02 (17) |
| C4—C5—Cl1 | 108.99 (11) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—Cl2 | 108.20 (10) | C10—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 110.76 (13) | C10—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—Cl1 | 111.85 (11) | C10—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—Cl2 | 107.47 (11) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| O6—C6—C5 | 116.31 (14) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O6—C6—C7 | 122.32 (15) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.38 (14) | ||
| Cl1—C5—C6—O6 | −139.23 (13) | C4—N3—C2—N1 | −173.78 (14) |
| Cl1—C5—C6—C7 | 40.85 (18) | C4—C5—C6—O6 | −17.42 (19) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—O6 | 100.57 (15) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 162.65 (14) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—C7 | −79.35 (16) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −155.04 (15) |
| O4—C4—C5—Cl1 | −60.19 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C12 | 28.2 (2) |
| O4—C4—C5—Cl2 | 58.79 (14) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −177.58 (17) |
| O4—C4—C5—C6 | 176.34 (12) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | 175.43 (17) |
| O6—C6—C7—C8 | 25.0 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 2.2 (3) |
| O6—C6—C7—C12 | −151.71 (18) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −1.2 (3) |
| N3—C4—C5—Cl1 | 61.06 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.9 (3) |
| N3—C4—C5—Cl2 | −179.97 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C13 | 177.11 (18) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | −62.41 (16) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2—N3—C4—O4 | −110.90 (16) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 1.6 (3) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | 128.18 (15) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.6 (3) |
| C4—N3—C2—O2 | 5.2 (2) | C13—C10—C11—C12 | −179.03 (19) |
1-[2,2-Dichloro-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]urea (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O4i | 0.82 (3) | 2.27 (3) | 3.0261 (19) | 153 (2) |
| N1—H1B···O4ii | 0.84 (3) | 2.14 (3) | 2.9798 (18) | 177 (2) |
| N3—H3···O2iii | 0.81 (3) | 2.19 (3) | 2.9445 (18) | 156 (2) |
| O4—H4···O2iv | 0.78 (3) | 1.83 (3) | 2.5979 (16) | 168 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iv) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Aliyeva, V. A., Gurbanov, A. V., Huseynov, F. E., Hajiyeva, S. R., Conceiçao, N. R., Nunes, A. V. M., Pombeiro, A. J. L. & Mahmudov, K. T. (2024). Polyhedron, 255, 116955.
- Aliyev, E. H., Bahmanova, F. N., Hamidov, S. Z. & Chyragov, F. M. (2020). Izvest. Vuzov-Prikladnaya Khim. Biotek.10, 107–113.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst.42, 339–341.
- Guseinov, F. I., Ovsyannikov, V. O., Shuvalova, E. V., Kustov, L. M., Kobrakov, K. I., Samigullina, A. I. & Mahmudov, K. T. (2024). New J. Chem.48, 12869–12872.
- Guseinov, F. N., Burangulova, R. N., Mukhamedzyanova, E. F., Strunin, B. P., Sinyashin, O. G., Litvinov, I. A. & Gubaidullin, A. T. (2006). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd.42, 943–947.
- Hajiyeva, S. R., Huseynov, F. E., Atioğlu, Z., Akkurt, M. & Bhattarai, A. (2024). Acta Cryst. E80, 110–116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Huseynov, F. E., Mahmoudi, G., Hajiyeva, S. R., Shamilov, N. T., Zubkov, F. I., Nikitina, E. V., Prisyazhnyuk, E. D. & Kopylovich, M. N. (2021). Polyhedron, 209, 115453.
- Khalilov, A. N. (2021). Rev. Roum. Chim.66, 719.
- Mahmudov, K. T., Kerimli, F. Sh., Mammadov, E. S., Gurbanov, A. V., Akhmedova, N. F. & Mammadov, S. E. (2022). Pet. Chem.62, 933–941.
- Mamedov, S. E., Akhmedov, E. I., Kerimli, F. S. & Makhmudova, M. I. (2006). Russ. J. Appl. Chem.79, 1723–1725.
- Naghiyev, F. N., Khrustalev, V. N., Akkurt, M., Khalilov, A. N., Bhattarai, A., Kerimli, F. S. & Mamedov, İ. G. (2023). Acta Cryst. E79, 494–498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2024). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst.54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127sup1.cif
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127Isup4.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127Isup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127IIsup5.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025004359/hb8127IIsup5.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report








