In the title compound, one of the oxazolidine rings adopts a twisted conformation and the other is a shallow envelope. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking interactions help to consolidate a three-dimensional architecture.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bond, π-stacking, quinoxaline
Abstract
In the title compound, C18H20N4O6, one of the oxazolidine rings adopts a twisted conformation and the other is a shallow envelope. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking interactions help to consolidate a three-dimensional architecture. The Hirshfeld surface analysis of the crystal structure indicates that the most important contributions for the crystal packing are from H⋯H (48.4%) and H⋯O/O⋯H (29.1%) contacts.
1. Chemical context
Quinoxaline and its derivatives are widely used in various fields, including medicine (Kaushal et al., 2019 ▸; Montana et al., 2019 ▸), pharmacology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, microbiology, agriculture, chemistry, toxicology, materials science, and biochemistry (Balderas-Renteria et al., 2012 ▸; Pereira et al., 2015 ▸; Zeb et al., 2014 ▸; Tangherlini et al., 2019 ▸; Vieira et al., 2014 ▸; Zheng et al., 2002 ▸).
The quinoxaline molecule has been utilized as a precursor for synthesizing bioactive derivatives, with several research teams emphasizing its potential applications in the pharmaceutical and therapeutic fields (Raoa et al., 2010 ▸; Yousra et al., 2023 ▸). Different synthesis methodologies have been detailed in the literature, reflecting extensive research efforts to elucidate these compounds’ properties and applications (e.g., Gu et al., 2017 ▸). Building on our previous research into the synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives (Yousra et al., 2023 ▸), we have synthesized the title compound, C18H20N4O6 (I), and we now describe its synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface.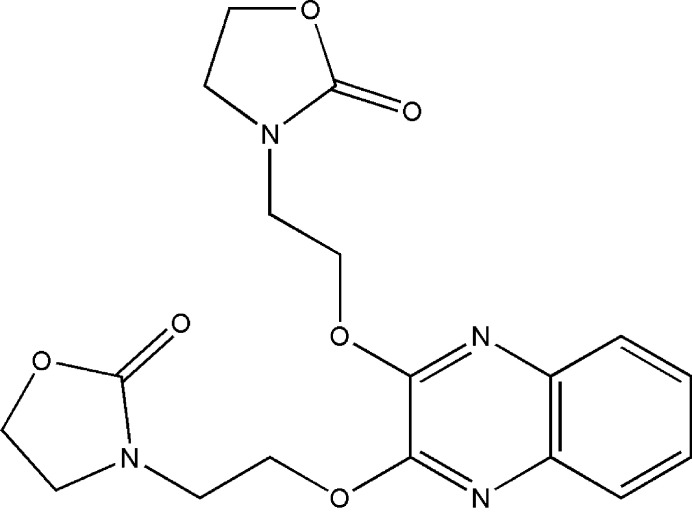
2. Structural commentary
Compound (I) contains an almost planar quinoxaline fused ring and two oxazolidine rings (Fig. 1 ▸), where the oxazolidine (C, N3/O3/C13–C15) and (D, N4/O5/C16–C18) rings are in half-chair [with a puckering parameter value of φ = 305.0 (4)°] and shallow envelope conformations, respectively. In ring D, atom N4 is at the flap position and is 0.0849 (11) Å away from the best least-squares plane of the other four atoms. The almost planar A (N1/N2/C3–C6) and B (C5–C10) rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 1.46 (4)°. Atoms O1, O2 and C11 are −0.094 (1), 0.059 (1) and 0.070 (1) Å, respectively, away from the best least-squares plane of ring A. The side chains both have anti–gauche conformations as indicated by the following torsion angles: C3—O1—C2—C1 = −162.00 (10), O1—C2—C1—N3 = −55.36 (14), C4—O2—C11—C12 = −174.35 (9) and O2—C11—C12—N4 = −57.76 (13)°. The dihedral angles between the quinoxaline ring and the pendant oxazolidine C and D rings (all atoms) are 85.72 (6) and 56.91 (7)°, respectively; the equivalent angle between the oxazolidine rings is 89.98 (9)°.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule with 50% probability ellipsoids.
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystal structure of (I), the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). Aromatic π–π stacking interactions between the quinoxaline A and B rings of adjacent molecules with a shortest intercentroid distance of 3.5155 (7) Å may help to consolidate the packing. No C—H⋯π interactions could be identified.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14A⋯O6i | 0.99 | 2.37 | 3.189 (2) | 140 |
| C10—H10⋯O5ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.4935 (18) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 2.
A partial packing diagram viewed down the a-axis direction. Intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in these interactions are omitted for clarity.
4. Hirshfeld surface analysis
A Hirshfeld surface (HS) analysis was carried out using Crystal Explorer 17.5 (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸) to investigate the intermolecular interactions in the crystal of (I). The HS is shown in Fig. 3 ▸, where the bright-red spots correspond to the respective donors and/or acceptors. According to the two-dimensional fingerprint plots (McKinnon et al., 2007 ▸), the intermolecular H⋯H and H⋯O/O⋯H contacts make the most important contributions to the HS of 48.4% and 29.1%, respectively (Fig. 4 ▸). All other contact types contribute 5% or less to the surface.
Figure 3.
View of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface of the title compound plotted over dnorm.
Figure 4.
The full two-dimensional fingerprint plots for the title compound, showing (a) all interactions, and delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) H⋯O/O⋯H, (d) C⋯C, (e) H⋯C/C⋯H, (f) H⋯N/N⋯H, (g) C⋯N/N⋯C, (h) C⋯O/O⋯C, (i) N⋯N, (j) N⋯O/O⋯N and (k) O⋯O interactions. The di and de values are the closest internal and external distances (in Å) from given points on the Hirshfeld surface.
5. Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) (Groom et al., 2016 ▸; updated to January 2024) using the search fragment (II) yielded 25 hits of which those most similar to the title molecule have the formula (III) with R = Me and R′ = CH2CO2H (CSD refcode DEZJAW; Missioui et al., 2018 ▸) or benzyl (DUSHUV; Ramli et al., 2010 ▸) with R = CF3 and R′ = i-Bu (DUBPUO; Wei et al., 2019 ▸), with R = Ph and R′ = CH2 (cyclo-CHCH2O) and R′ = benzyl (PUGGII; Benzeid et al., 2009 ▸). As expected, in all these hits, the dihydroquinoxaline ring system is essentially planar with the dihedral angle between the constituent rings being less than 1° or having the nitrogen atom bearing the exocyclic substituent less than 0.03 Å from the mean plane of the remaining nine atoms.
6. Synthesis and crystallization
A solution of quinoxaline-2,3-dione (0.29 g, 1.00 mmol) in dimethylformamide (15 ml) was prepared. To this solution, tetra-n-butylammonium bromide (0.1 mmol), 2.2 equivalents of bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride, and 2.00 equivalents of potassium carbonate were added. The mixture was stirred at 353 K for 6 h. After stirring, the salts were removed by filtration, and the solution was evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was dissolved in dichloromethane. The remaining salts were extracted with distilled water. The mixture obtained was then chromatographed on a silica gel column using an eluent of ethyl acetate and hexane in a 4:1 ratio. The solid isolate was recrystallized from an ethanol solution, resulting in crystals of (I) with a yield of 56%.
7. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The C-bound hydrogen-atom positions were calculated geometrically at distances of 0.95 Å (for aromatic CH) and 0.99 Å (for CH2) and they were refined using a riding model by applying the constraint Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C18H20N4O6 |
| M r | 388.38 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 160 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.6576 (1), 17.1463 (2), 15.8105 (2) |
| β (°) | 98.935 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1782.92 (4) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.93 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.21 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | XtaLAB Synergy, Dualflex, HyPix |
| Absorption correction | Analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2024 ▸) |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.845, 0.932 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 23056, 3781, 3577 |
| R int | 0.027 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.633 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.038, 0.099, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 3781 |
| No. of parameters | 254 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.35, −0.29 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134Isup3.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 2447382
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
TH is grateful to Hacettepe University Scientific Research Project Unit (grant No. 013 D04 602 004).
supplementary crystallographic information
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Crystal data
| C18H20N4O6 | F(000) = 816 |
| Mr = 388.38 | Dx = 1.447 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 6.6576 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 17516 reflections |
| b = 17.1463 (2) Å | θ = 3.8–79.5° |
| c = 15.8105 (2) Å | µ = 0.93 mm−1 |
| β = 98.935 (1)° | T = 160 K |
| V = 1782.92 (4) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.21 × 0.10 mm |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Data collection
| XtaLAB Synergy, Dualflex, HyPix diffractometer | 3781 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, PhotonJet (Cu) X-ray Source | 3577 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 77.4°, θmin = 3.8° |
| ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2024) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.845, Tmax = 0.932 | l = −17→19 |
| 23056 measured reflections |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0447P)2 + 0.6483P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.06 | Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3 |
| 3781 reflections | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
| 254 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2019/3 (Sheldrick, 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0023 (2) |
| Primary atom site location: dual |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.34531 (13) | 0.47199 (5) | 0.72202 (5) | 0.02841 (19) | |
| O2 | 0.29395 (12) | 0.35049 (4) | 0.62370 (5) | 0.02608 (19) | |
| O3 | 0.35795 (16) | 0.33324 (6) | 0.96229 (7) | 0.0444 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.66392 (15) | 0.37070 (6) | 0.93404 (7) | 0.0451 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.74284 (18) | 0.16514 (7) | 0.76528 (7) | 0.0527 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.62002 (19) | 0.11202 (8) | 0.63787 (7) | 0.0587 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.28423 (15) | 0.55758 (6) | 0.60819 (6) | 0.0269 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.25336 (14) | 0.42434 (6) | 0.50000 (6) | 0.0253 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.37902 (16) | 0.44689 (6) | 0.89855 (7) | 0.0322 (2) | |
| N4 | 0.44993 (17) | 0.20867 (6) | 0.69704 (7) | 0.0331 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.4760 (2) | 0.51244 (7) | 0.86354 (8) | 0.0342 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.616539 | 0.497667 | 0.857060 | 0.041* | |
| H1B | 0.484189 | 0.556502 | 0.904393 | 0.041* | |
| C2 | 0.3645 (2) | 0.53887 (7) | 0.77796 (8) | 0.0328 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.228380 | 0.559210 | 0.784233 | 0.039* | |
| H2B | 0.441442 | 0.580793 | 0.754216 | 0.039* | |
| C3 | 0.30273 (16) | 0.48736 (7) | 0.63769 (7) | 0.0252 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.28227 (16) | 0.41917 (6) | 0.58255 (7) | 0.0241 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.23938 (16) | 0.49903 (7) | 0.46633 (8) | 0.0261 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.25158 (16) | 0.56504 (7) | 0.51985 (8) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.23349 (18) | 0.64004 (7) | 0.48354 (9) | 0.0316 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.240283 | 0.684707 | 0.519426 | 0.038* | |
| C8 | 0.20594 (18) | 0.64869 (8) | 0.39597 (9) | 0.0354 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.193559 | 0.699445 | 0.371627 | 0.043* | |
| C9 | 0.19602 (19) | 0.58335 (8) | 0.34250 (9) | 0.0358 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.178341 | 0.590080 | 0.282161 | 0.043* | |
| C10 | 0.21172 (18) | 0.50923 (8) | 0.37678 (8) | 0.0314 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.203901 | 0.465090 | 0.340091 | 0.038* | |
| C11 | 0.27737 (18) | 0.28136 (6) | 0.57133 (7) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| H11A | 0.395000 | 0.277258 | 0.540209 | 0.032* | |
| H11B | 0.151217 | 0.282899 | 0.528962 | 0.032* | |
| C12 | 0.27329 (19) | 0.21297 (7) | 0.63101 (8) | 0.0298 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.149795 | 0.216567 | 0.658525 | 0.036* | |
| H12B | 0.263947 | 0.164211 | 0.597081 | 0.036* | |
| C13 | 0.4844 (2) | 0.38405 (7) | 0.93076 (8) | 0.0335 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.1517 (2) | 0.36156 (10) | 0.94072 (11) | 0.0483 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.077858 | 0.356549 | 0.990193 | 0.058* | |
| H14B | 0.077252 | 0.332043 | 0.891836 | 0.058* | |
| C15 | 0.1730 (2) | 0.44643 (9) | 0.91721 (10) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| H15A | 0.073565 | 0.461243 | 0.866518 | 0.051* | |
| H15B | 0.157556 | 0.481479 | 0.965547 | 0.051* | |
| C16 | 0.6022 (2) | 0.15857 (8) | 0.69375 (8) | 0.0366 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.6778 (4) | 0.22219 (12) | 0.82074 (12) | 0.0720 (6) | |
| H17A | 0.773792 | 0.266660 | 0.828125 | 0.086* | |
| H17B | 0.670734 | 0.199276 | 0.877681 | 0.086* | |
| C18 | 0.4690 (3) | 0.24899 (9) | 0.77867 (9) | 0.0520 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.361999 | 0.232637 | 0.811984 | 0.062* | |
| H18B | 0.463720 | 0.306297 | 0.771004 | 0.062* |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0383 (5) | 0.0205 (4) | 0.0264 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0047 (3) | −0.0015 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0325 (4) | 0.0185 (4) | 0.0268 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0032 (3) | 0.0000 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0531 (6) | 0.0357 (5) | 0.0436 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0096 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0414 (6) | 0.0437 (6) | 0.0480 (6) | 0.0111 (4) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0032 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0546 (7) | 0.0533 (6) | 0.0442 (6) | 0.0125 (5) | −0.0111 (5) | 0.0030 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0615 (7) | 0.0665 (8) | 0.0468 (6) | 0.0281 (6) | 0.0044 (5) | −0.0123 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0261 (5) | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0326 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0051 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0236 (5) | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0280 (5) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0028 (4) | 0.0012 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0043 (4) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| N4 | 0.0451 (6) | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0285 (5) | 0.0043 (4) | −0.0010 (4) | −0.0016 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0425 (7) | 0.0263 (6) | 0.0330 (6) | −0.0020 (5) | 0.0034 (5) | −0.0029 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0464 (7) | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0051 (5) | −0.0039 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0220 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0297 (6) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0202 (5) | 0.0262 (6) | 0.0318 (6) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0044 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0342 (6) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0042 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0263 (6) | 0.0252 (6) | 0.0436 (7) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0061 (5) | 0.0059 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0275 (6) | 0.0324 (6) | 0.0464 (7) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0057 (5) | 0.0153 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0417 (7) | 0.0354 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0042 (5) | 0.0130 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0281 (6) | 0.0348 (6) | 0.0310 (6) | −0.0006 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0040 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0305 (6) | 0.0205 (5) | 0.0280 (5) | −0.0003 (4) | 0.0024 (4) | −0.0025 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0343 (6) | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0328 (6) | −0.0017 (4) | 0.0032 (5) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0436 (7) | 0.0298 (6) | 0.0257 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0007 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0453 (8) | 0.0538 (9) | 0.0464 (8) | −0.0081 (7) | 0.0084 (6) | 0.0063 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0377 (7) | 0.0479 (8) | 0.0438 (8) | 0.0052 (6) | 0.0090 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0415 (7) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0043 (5) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0041 (5) |
| C17 | 0.1003 (15) | 0.0538 (10) | 0.0487 (9) | 0.0250 (10) | −0.0297 (10) | −0.0142 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0775 (11) | 0.0436 (8) | 0.0309 (7) | 0.0155 (8) | −0.0045 (7) | −0.0085 (6) |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.4416 (14) | C5—C6 | 1.4079 (17) |
| O1—C3 | 1.3454 (14) | C5—C10 | 1.4100 (17) |
| O2—C4 | 1.3418 (13) | C6—C7 | 1.4057 (16) |
| O2—C11 | 1.4403 (13) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C13 | 1.3589 (17) | C7—C8 | 1.3762 (19) |
| O3—C14 | 1.447 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O4—C13 | 1.2101 (17) | C8—C9 | 1.399 (2) |
| O5—C16 | 1.3563 (17) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O5—C17 | 1.425 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.3792 (18) |
| O6—C16 | 1.2100 (18) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C3 | 1.2901 (15) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C6 | 1.3857 (16) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C4 | 1.2924 (15) | C11—C12 | 1.5080 (16) |
| N2—C5 | 1.3846 (15) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| N3—C1 | 1.4483 (17) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| N3—C13 | 1.3421 (16) | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| N3—C15 | 1.4474 (18) | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| N4—C12 | 1.4480 (16) | C14—C15 | 1.514 (2) |
| N4—C16 | 1.3359 (17) | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| N4—C18 | 1.4522 (17) | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C17—H17A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C17—H17B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.5084 (18) | C17—C18 | 1.516 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C18—H18A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C18—H18B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4521 (15) | ||
| C3—O1—C2 | 115.92 (9) | C5—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C4—O2—C11 | 116.75 (9) | C9—C10—C5 | 119.93 (12) |
| C13—O3—C14 | 108.53 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C16—O5—C17 | 109.50 (12) | O2—C11—H11A | 110.4 |
| C3—N1—C6 | 116.22 (10) | O2—C11—H11B | 110.4 |
| C4—N2—C5 | 116.25 (10) | O2—C11—C12 | 106.71 (9) |
| C13—N3—C1 | 122.03 (11) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.6 |
| C13—N3—C15 | 111.99 (11) | C12—C11—H11A | 110.4 |
| C15—N3—C1 | 125.10 (11) | C12—C11—H11B | 110.4 |
| C12—N4—C18 | 124.44 (11) | N4—C12—C11 | 113.52 (10) |
| C16—N4—C12 | 122.74 (11) | N4—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C16—N4—C18 | 112.25 (11) | N4—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| N3—C1—H1A | 109.0 | C11—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| N3—C1—H1B | 109.0 | C11—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| N3—C1—C2 | 112.93 (11) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.8 | O4—C13—O3 | 121.80 (12) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.0 | O4—C13—N3 | 128.51 (13) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.0 | N3—C13—O3 | 109.68 (12) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 107.19 (10) | O3—C14—H14A | 110.7 |
| O1—C2—H2A | 110.3 | O3—C14—H14B | 110.7 |
| O1—C2—H2B | 110.3 | O3—C14—C15 | 105.00 (12) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.3 | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.8 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.3 | C15—C14—H14A | 110.7 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.5 | C15—C14—H14B | 110.7 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 115.02 (10) | N3—C15—C14 | 100.55 (11) |
| N1—C3—O1 | 122.32 (10) | N3—C15—H15A | 111.7 |
| N1—C3—C4 | 122.65 (11) | N3—C15—H15B | 111.7 |
| O2—C4—C3 | 115.00 (10) | C14—C15—H15A | 111.7 |
| N2—C4—O2 | 122.56 (10) | C14—C15—H15B | 111.7 |
| N2—C4—C3 | 122.44 (10) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| N2—C5—C6 | 121.22 (10) | O6—C16—O5 | 122.03 (13) |
| N2—C5—C10 | 119.43 (11) | O6—C16—N4 | 127.85 (13) |
| C6—C5—C10 | 119.35 (11) | N4—C16—O5 | 110.11 (12) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 121.12 (10) | O5—C17—H17A | 110.4 |
| N1—C6—C7 | 119.09 (11) | O5—C17—H17B | 110.4 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.78 (11) | O5—C17—C18 | 106.47 (13) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.0 | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.6 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.93 (12) | C18—C17—H17A | 110.4 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.0 | C18—C17—H17B | 110.4 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.7 | N4—C18—C17 | 101.14 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.54 (11) | N4—C18—H18A | 111.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.7 | N4—C18—H18B | 111.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.8 | C17—C18—H18A | 111.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.46 (12) | C17—C18—H18B | 111.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.8 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.4 |
| O1—C3—C4—O2 | 4.66 (14) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −0.28 (17) |
| O1—C3—C4—N2 | −175.86 (10) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.10 (18) |
| O2—C11—C12—N4 | −57.76 (13) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.64 (19) |
| O3—C14—C15—N3 | 19.93 (15) | C8—C9—C10—C5 | −0.44 (19) |
| O5—C17—C18—N4 | −6.2 (2) | C10—C5—C6—N1 | −178.23 (10) |
| N1—C3—C4—O2 | −176.22 (10) | C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.82 (16) |
| N1—C3—C4—N2 | 3.25 (18) | C11—O2—C4—N2 | 1.41 (15) |
| N1—C6—C7—C8 | 178.43 (10) | C11—O2—C4—C3 | −179.12 (9) |
| N2—C5—C6—N1 | 1.99 (16) | C12—N4—C16—O5 | −177.58 (11) |
| N2—C5—C6—C7 | −178.96 (10) | C12—N4—C16—O6 | 1.4 (2) |
| N2—C5—C10—C9 | 179.50 (11) | C12—N4—C18—C17 | 178.95 (14) |
| N3—C1—C2—O1 | −55.36 (14) | C13—O3—C14—C15 | −17.07 (15) |
| C1—N3—C13—O3 | 177.45 (11) | C13—N3—C1—C2 | 132.78 (12) |
| C1—N3—C13—O4 | −2.1 (2) | C13—N3—C15—C14 | −17.38 (15) |
| C1—N3—C15—C14 | 173.26 (12) | C14—O3—C13—O4 | −173.94 (13) |
| C2—O1—C3—N1 | 1.41 (16) | C14—O3—C13—N3 | 6.47 (15) |
| C2—O1—C3—C4 | −179.46 (10) | C15—N3—C1—C2 | −58.87 (16) |
| C3—O1—C2—C1 | −162.00 (10) | C15—N3—C13—O3 | 7.71 (15) |
| C3—N1—C6—C5 | 0.10 (16) | C15—N3—C13—O4 | −171.84 (14) |
| C3—N1—C6—C7 | −178.95 (10) | C16—O5—C17—C18 | 3.4 (2) |
| C4—O2—C11—C12 | −174.35 (9) | C16—N4—C12—C11 | −102.91 (14) |
| C4—N2—C5—C6 | −1.41 (16) | C16—N4—C18—C17 | 7.40 (18) |
| C4—N2—C5—C10 | 178.81 (10) | C17—O5—C16—O6 | −177.74 (17) |
| C5—N2—C4—O2 | 178.41 (9) | C17—O5—C16—N4 | 1.34 (19) |
| C5—N2—C4—C3 | −1.03 (16) | C18—N4—C12—C11 | 86.40 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.63 (17) | C18—N4—C16—O5 | −5.86 (17) |
| C6—N1—C3—O1 | 176.48 (9) | C18—N4—C16—O6 | 173.16 (16) |
| C6—N1—C3—C4 | −2.57 (16) |
3-(2-{3-[2-(2-Oxooxazolidin-3-yl)ethoxy]quinoxalin-2-yloxy}ethyl)oxazolidin-2-one. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14A···O6i | 0.99 | 2.37 | 3.189 (2) | 140 |
| C10—H10···O5ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.4935 (18) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
References
- Balderas-Renteria, I., Gonzalez-Barranco, P., Garcia, A., Banik, B. K. & Rivera, G. (2012). Curr. Med. Chem.19, 4377–4398. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Benzeid, H., Saffon, N., Garrigues, B., Essassi, E. M. & Ng, S. W. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst.42, 339–341.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gu, W., Wang, S., Jin, X., Zhang, Y., Hua, D., Miao, T., Tao, X. & Wang, S. (2017). Molecules, 22, 1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, T., Srivastava, G., Sharma, A. & Singh Negi, A. (2019). Bioorg. Med. Chem.27, 16–35. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3814–3816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Missioui, M., El Fal, M., Taoufik, J., Essassi, E. M., Mague, J. T. & Ramli, Y. (2018). IUCrData3, x180882.
- Montana, M., Mathias, F., Terme, T. & Vanelle, P. (2019). Eur. J. Med. Chem.163, 136–147. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J. A., Pessoa, A. M., Cordeiro, M. N. D. S., Fernandes, R., Prudêncio, C., Noronha, J. P. & Vieira, M. (2015). Eur. J. Med. Chem.97, 664–672. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ramli, Y., Moussaif, A., Zouihri, H., Lazar, S. & Essassi, E. M. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Raoa, G. K., Kotnal, R. B. & Sanjay Paib, P. N. (2010). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2, 368–373.
- Rigaku OD (2024). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst.54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tangherlini, G., Kalinin, D. V., Schepmann, D., Che, T., Mykicki, N., Ständer, S., Loser, K. & Wünsch, B. (2019). J. Med. Chem.62, 893–907. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M., Pinheiro, C., Fernandes, R., Noronha, J. P. & Prudêncio, C. (2014). Microbiol. Res.169, 287–293. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z., Qi, S., Xu, Y., Liu, H., Wu, J., Li, H., Xia, C. & Duan, G. (2019). Adv. Synth. Catal.361, 5490–5498.
- Yousra, S., El Ghayati, L., Hökelek, T., Ouazzani Chahdi, F., Mague, J. T., Kandri Rodi, Y. & Sebbar, N. K. (2023). Acta Cryst. E79, 895–898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A., Hameed, A., Khan, L., Khan, I. K., Dalvandi, K., Choudhary, M. I. & Basha, F. Z. (2014). Med. Chem.10, 724–729. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H., Jiang, C., Chiu, M. H., Covey, J. M. & Chan, K. K. (2002). Drug Metab. Dispos.30, 344–348. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134Isup3.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025003755/hb8134Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 2447382
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






