Abstract
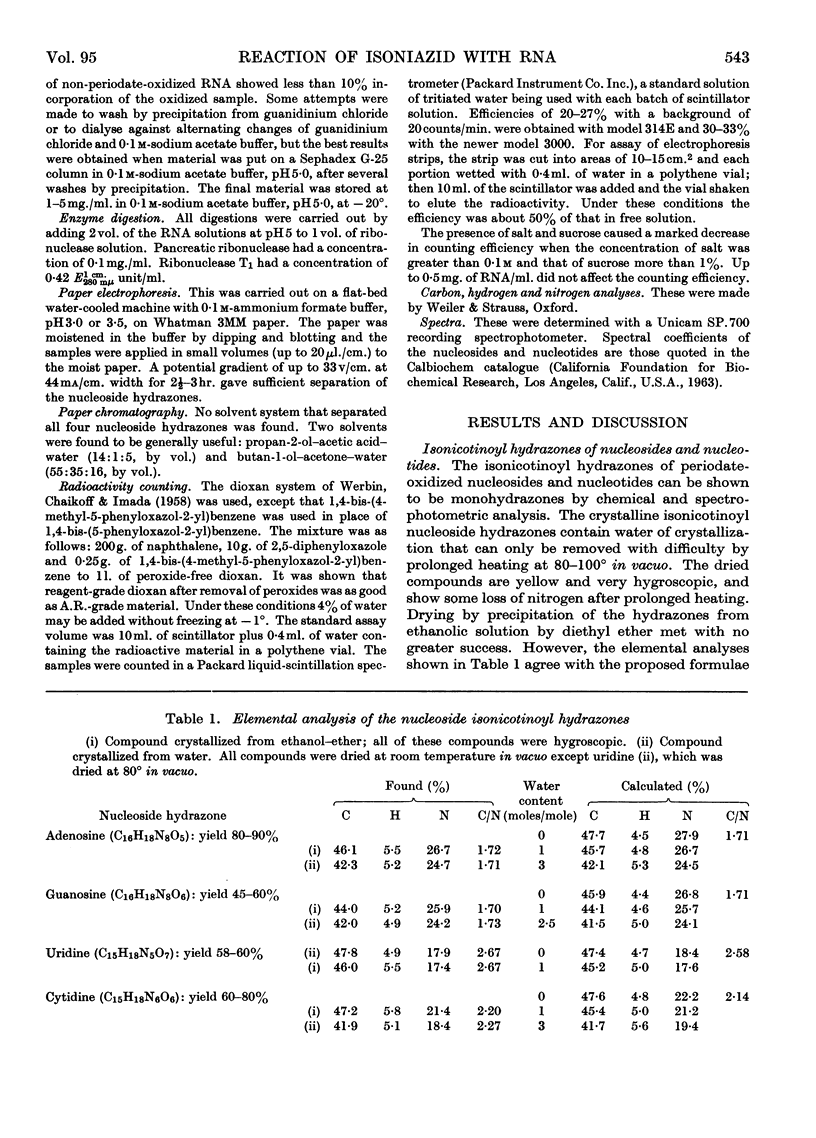
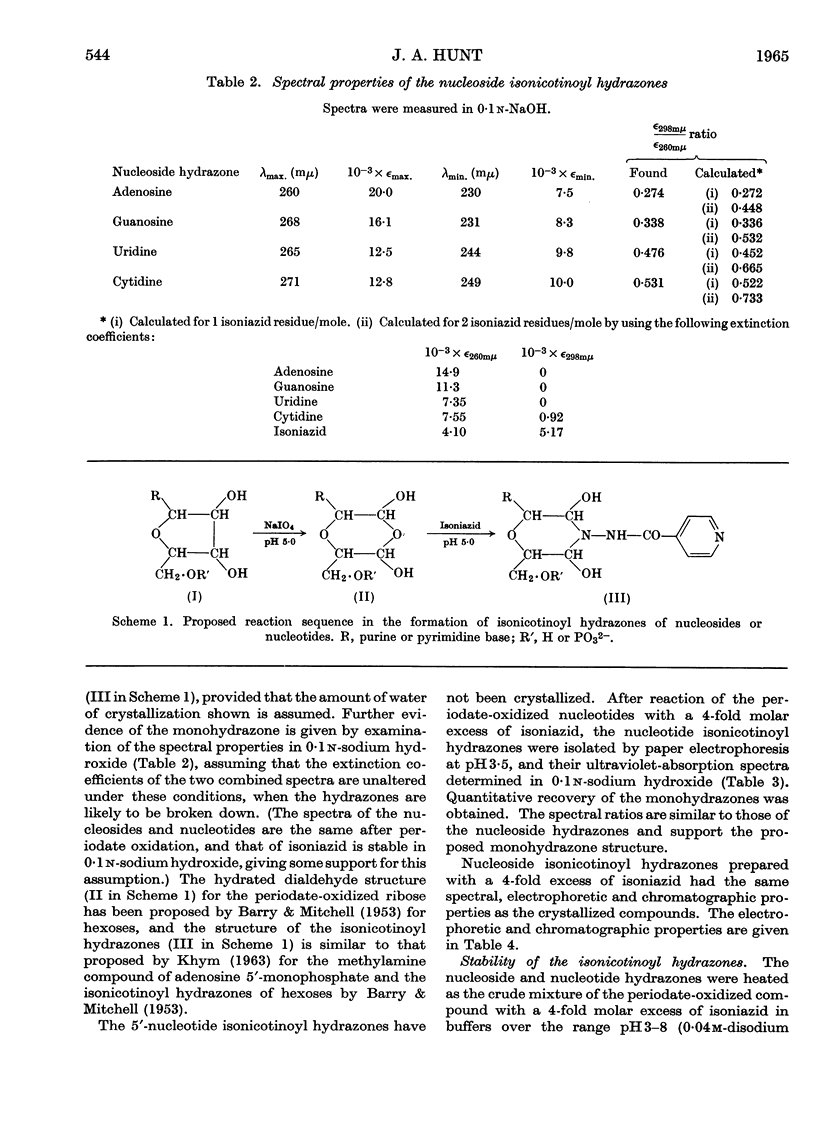
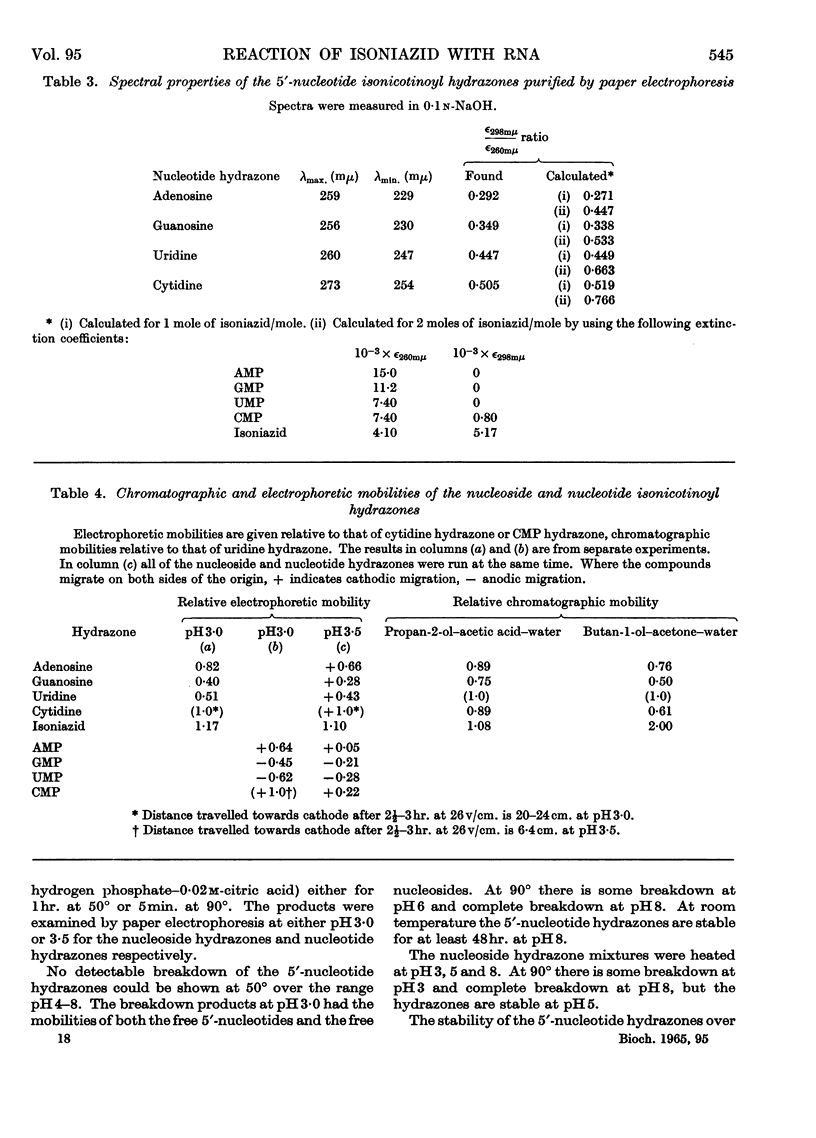
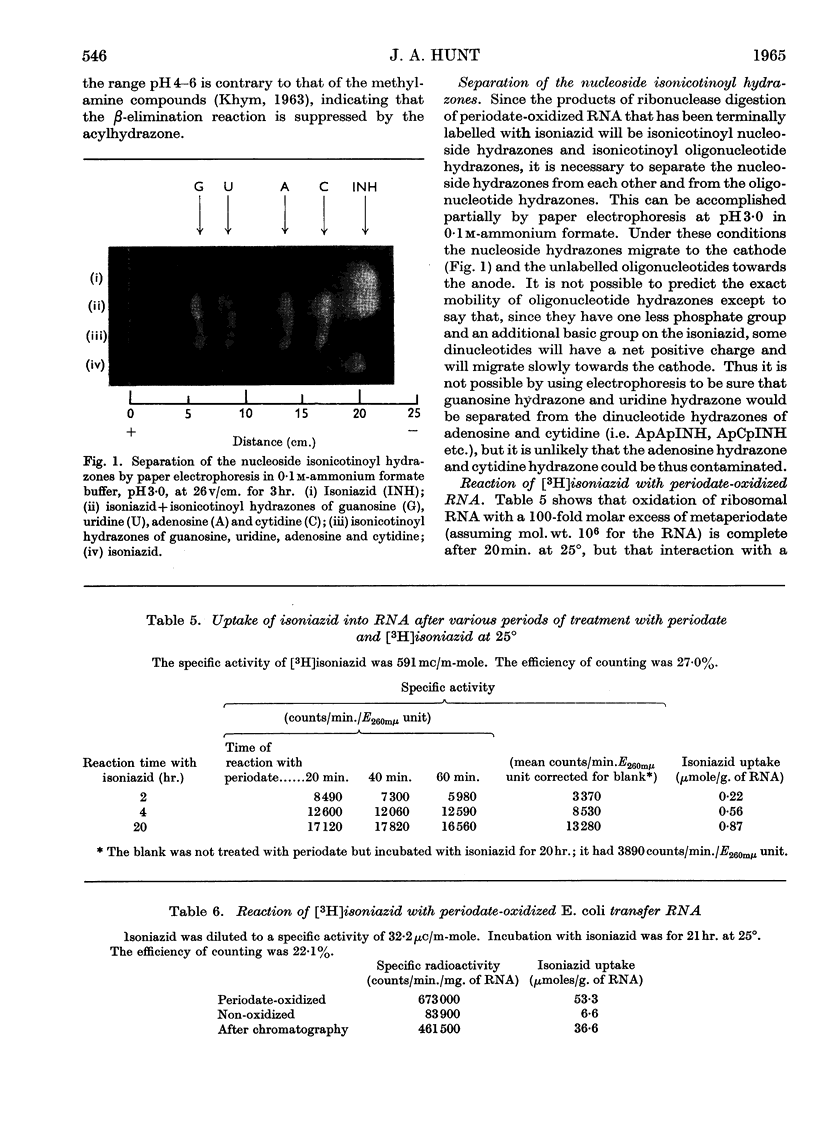
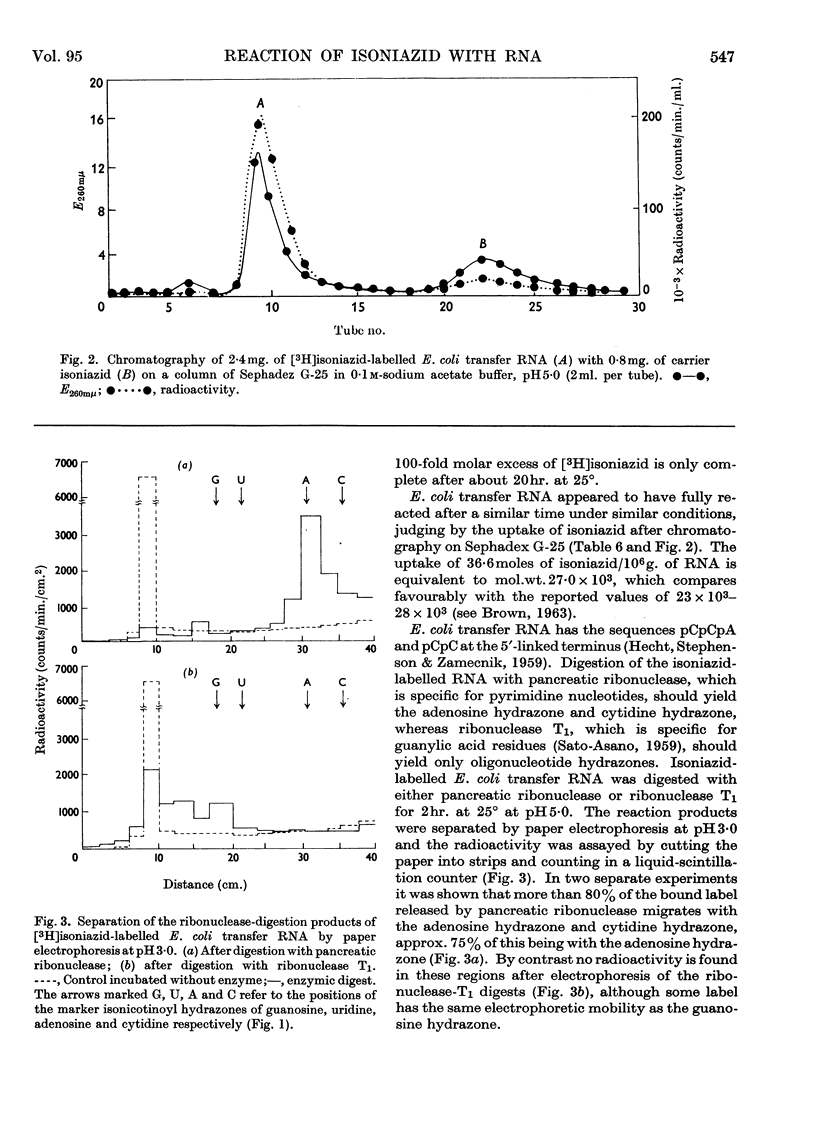
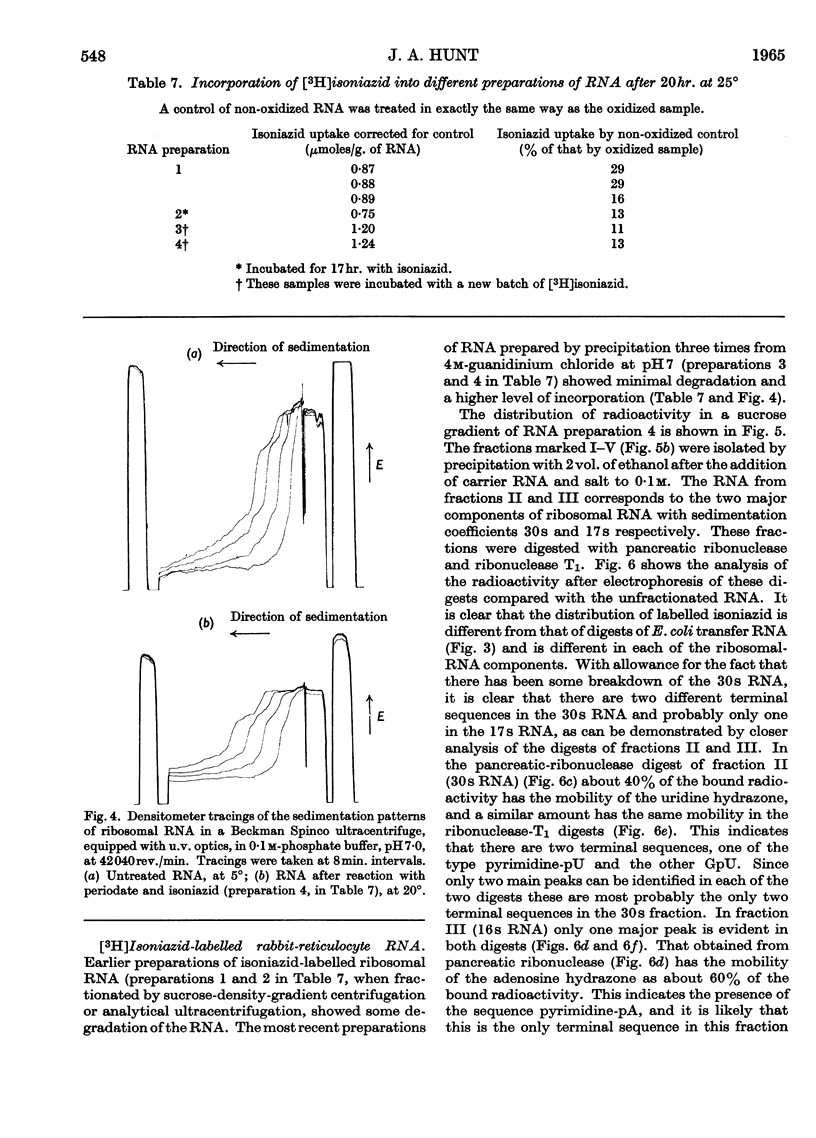
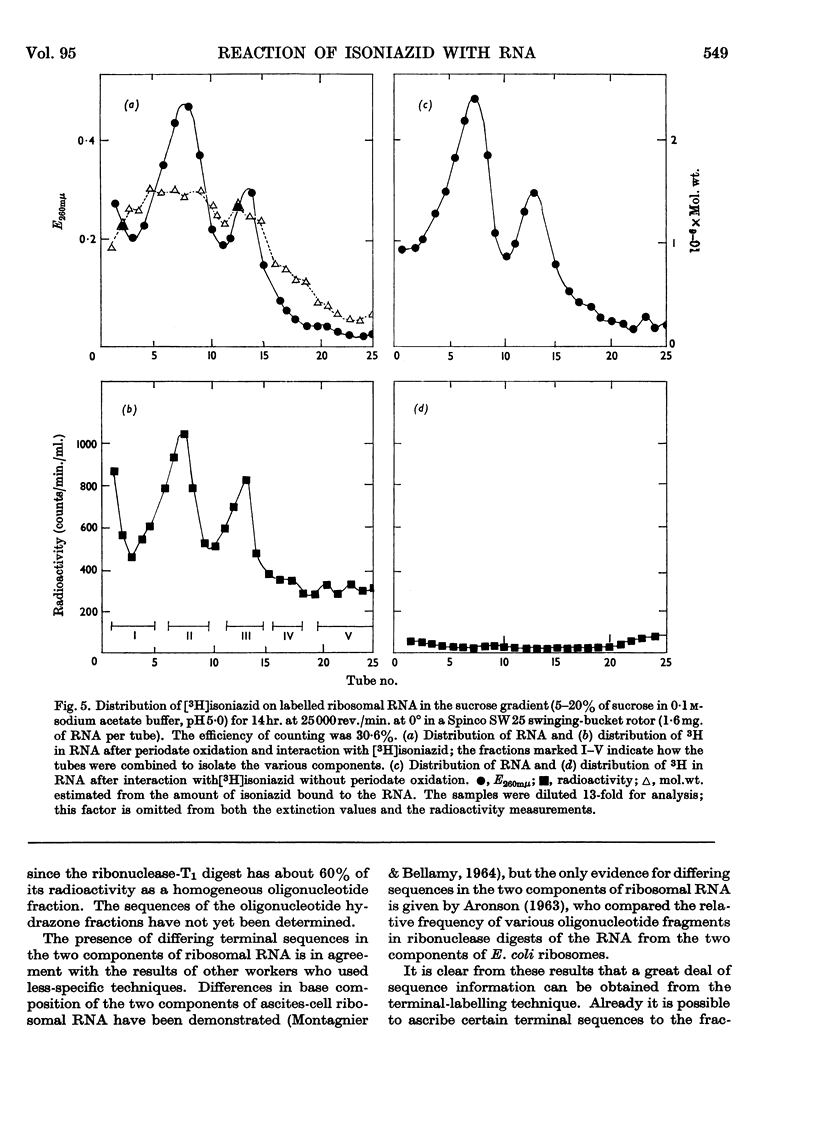
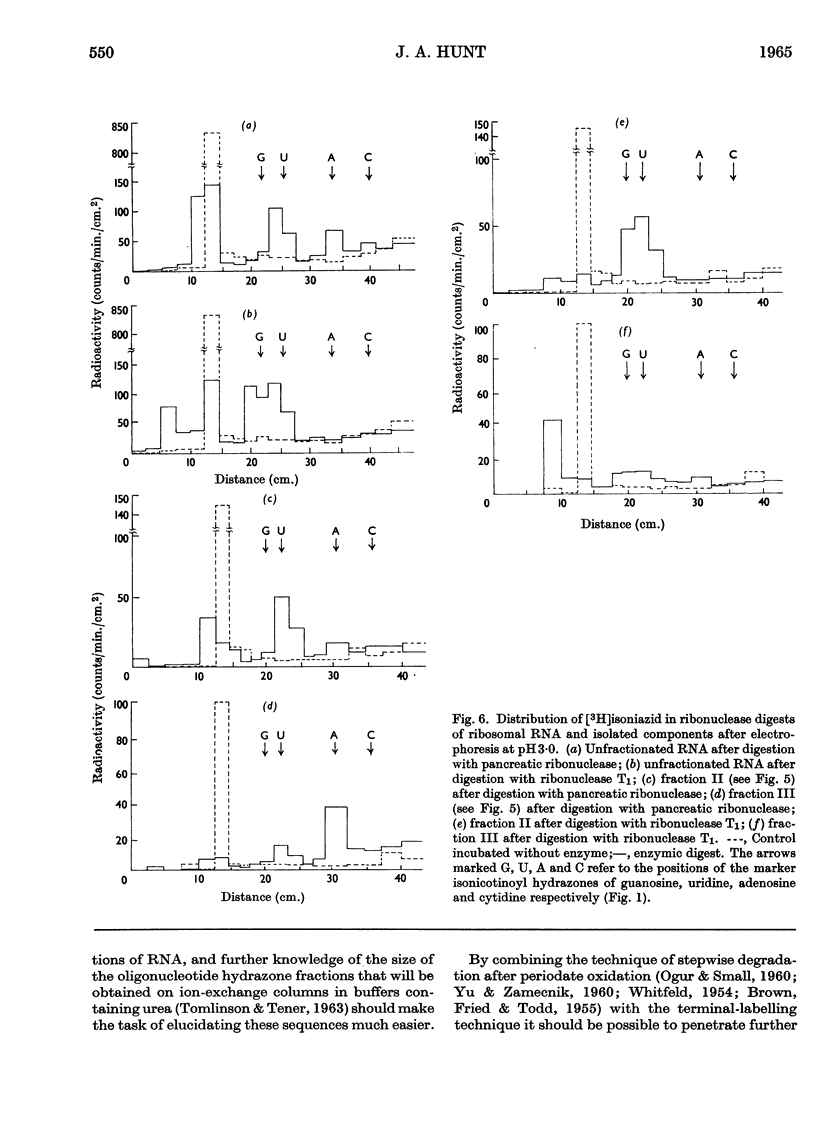
1. The reaction products of isoniazid with periodate-oxidized ribonucleosides and 5′-ribonucleotides have been characterized as the monohydrazones. 2. The stability, chromatographic and electrophoretic properties of the hydrazones are described. 3. 3H-labelled isoniazid was shown to react with the 5′-linked terminal adenosine and cytidine groups of periodate-oxidized Escherichia coli transfer RNA. One mole of isoniazid reacts with 27×103g. of the transfer RNA. 4. One mole of 3H-labelled isoniazid reacts with approx. 106g. of rabbit-reticulocyte ribosomal RNA. After fractionation of the RNA into its two components and treating the fractionated material with pancreatic ribonuclease and ribonuclease T1 evidence is presented for the existence of two 5′-linked terminal sequences in the 30s fraction and only one sequence in the 17s fraction. 5. The application of this method to determining terminal sequences of high-molecular-weight RNA is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRY J. M., BARTLEY W., LINZELL J. L., ROBINSON D. S. THE UPTAKE FROM THE BLOOD OF TRIGLYCERIDE FATTY ACIDS OF CHYLOMICRA AND LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS BY THE MAMMARY GLAND OF THE GOAT. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:6–11. doi: 10.1042/bj0890006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A., ARNSTEIN H. R. THE ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM RABBIT-RETICULOCYTE RIBOSOMES. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:574–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0890574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., SMITH J. D. The detection of terminal nucleoside residues in polyribonucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 8;39:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht L. I., Stephenson M. L., Zamecnik P. C. BINDING OF AMINO ACIDS TO THE END GROUP OF A SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Apr;45(4):505–518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHYM J. X. The reaction of methylamine with periodate-oxidized adenosine 5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:344–350. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE B. G., DIEMER J., BLASHKO C. A. END GROUP AND SEDIMENTATION DATA ON FRAGMENTED HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT RIBONUCLEATES. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 Sep;41:1927–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHIZKY G. W., SOBER H. A. Characterization of the major compounds in ribonuclease TI digests of ribonucleic acid. I. Mono-, di-, and trinucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:834–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIYAMA T., FRAENKEL-CONRAT H. The end-groups of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. II. Nature of the 3'-linked chain end in TMV and of both ends in four strains. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:332–334. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON R. V., TENER G. M. THE EFFECT OF UREA, FORMAMIDE, AND GLYCOLS ON THE SECONDARY BINDING FORCES IN THE ION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF POLYNUCLEOTIDES OF DEAE-CELLULOSE. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:697–702. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFELD P. R. A method for the determination of nucleotide sequence in polyribonucleotides. Biochem J. 1954 Nov;58(3):390–396. doi: 10.1042/bj0580390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFELD P. R. Identification of end groups in tobacco mosaic virus ribonucleic acid by enzymatic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2865–2868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YU C. T., ZAMECNIK P. C. A hydrolytic procedure for ribonucleosides and its possible application to the sequential degradation of RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:148–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]