Full text
PDF

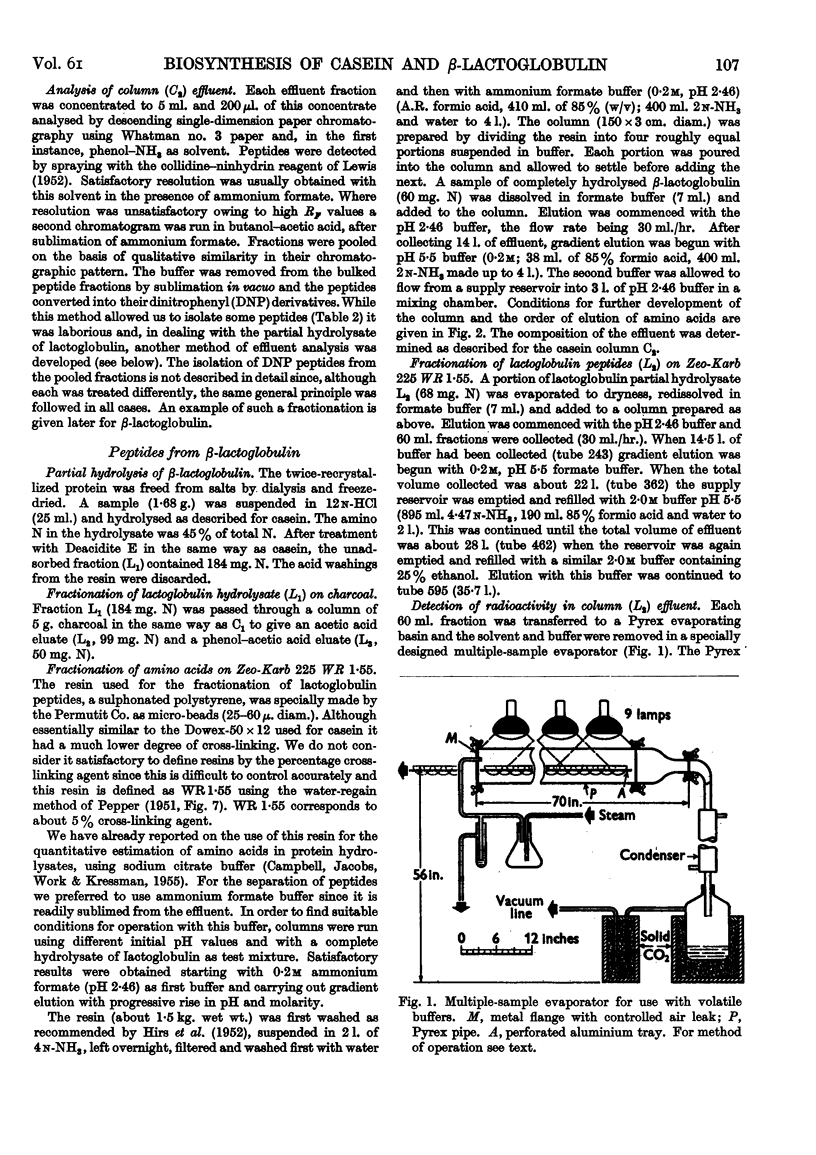


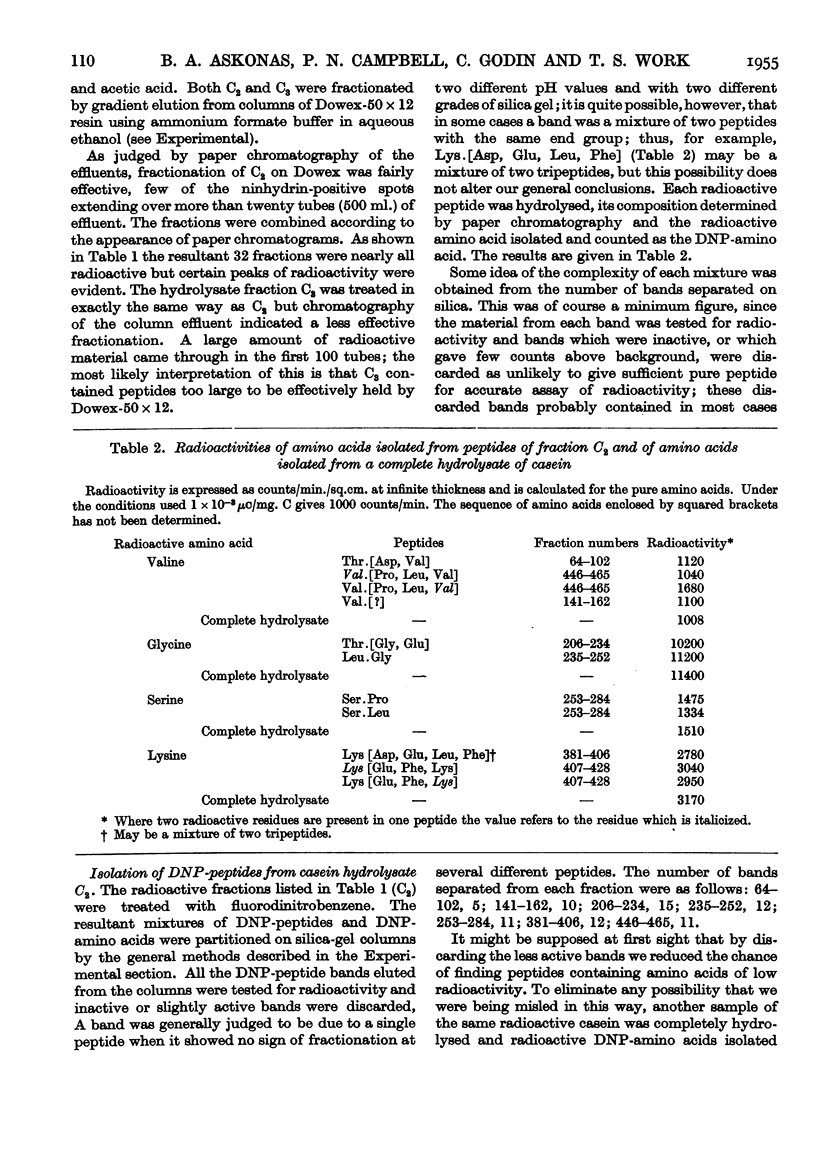
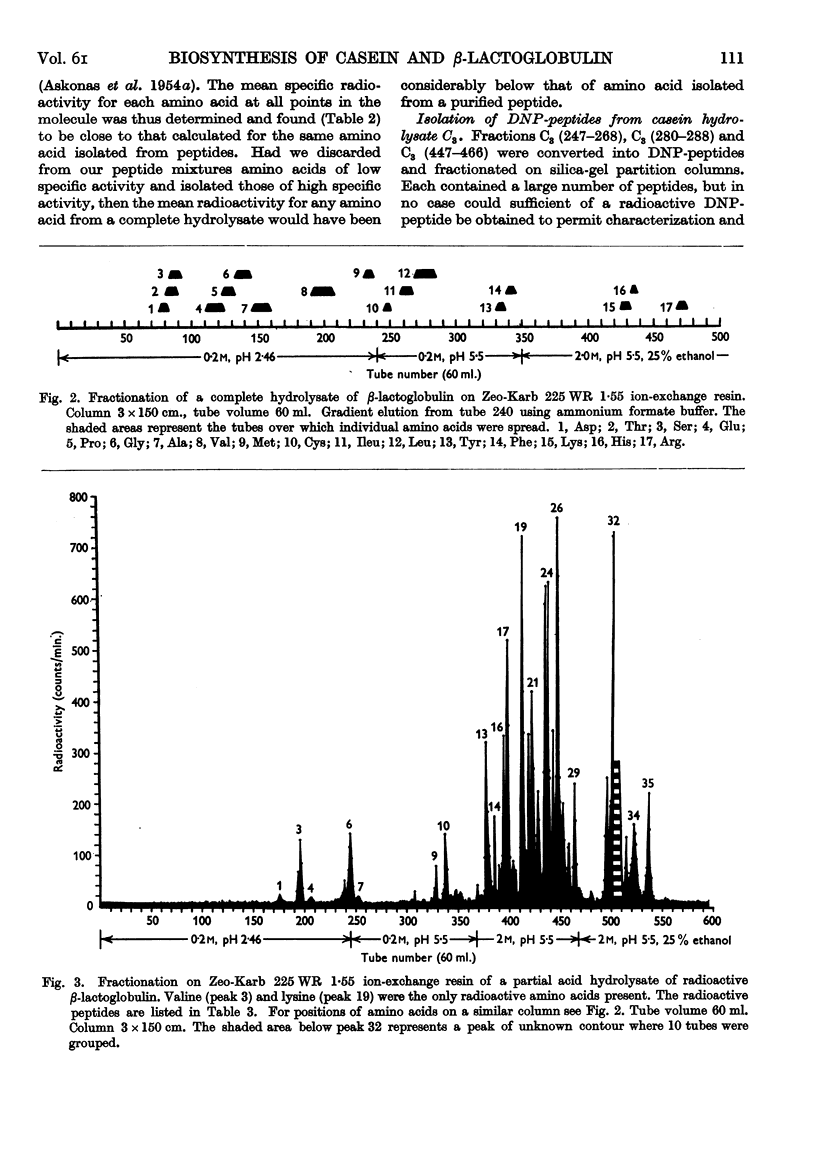




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A., CAMPBELL P. N., HUMPHREY J. H., WORK T. S. The source of antibody globulin in rabbit milk and goat colostrum. Biochem J. 1954 Apr;56(4):597–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKONAS B. A., CAMPBELL P. N., WORK T. S. The biosynthesis of proteins. II. Synthesis of milk proteins by the goat. Biochem J. 1954 Oct;58(2):326–331. doi: 10.1042/bj0580326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKONAS B. A., CAMPBELL P. N., WORK T. S. The distribution of radioactivity in goat casein after injection of radioactive amino acids and its bearing on theories of protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1953 Oct 17;56(322ND):iv–iv. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKONAS B. A. Crystallization of goat beta-lactoglobulin. Biochem J. 1954 Oct;58(2):332–336. doi: 10.1042/bj0580332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY J. M. The source of lysine, tyrosine, and phosphorus for casein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1952 Apr;195(2):795–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKBURN S., LOWTHER A. G. The separation of N-2:4-dinitrophenly amino-acids on paper chromatograms. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bj0480126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKBURN S. The use of buffered columns in the chromatographic separation of 2:4-dinitrophenyl amino acids. Biochem J. 1949;45(5):579–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0450579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL P. N., WORK T. S. The Biosynthesis of Protein. I. Uptake of glycine, serine, valine and lysine by the mammary gland of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj0520217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN H. N., RIGGS T. R. Amino acids and peptides in the oviduct of the laying hen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Aug-Sep;83(4):697–698. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWMONT Y. P., FRUTON J. S. Chromatography of peptides as applied to transamidation reactions. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):271–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCIS M. D., WINNICK T. Studies on the pathway of protein synthesis in tissue culture. J Biol Chem. 1953 May;202(1):273–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRUTON J. S. The role of proteolytic enzymes in the biosynthesis of peptide bonds. Yale J Biol Med. 1950 Jan;22(3):263–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino acids by bacteria. 18. The incorporation of glutamic acid into the protein fraction of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Dec;55(5):721–729. doi: 10.1042/bj0550721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., HIRD F. J. R., ISHERWOOD F. A. Enzymic transpeptidation reactions involving gamma-glutamyl peptides and alpha-amino-acyl peptides. Biochem J. 1952 Apr;51(1):25–35. doi: 10.1042/bj0510025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMBERG M., VELICK S. F. The synthesis of aldolase and phosphorylase in rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):725–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. W., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Isolation of amino acids by chromatography on ion exchange columns; use of volatile buffers. J Biol Chem. 1952 Apr;195(2):669–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., McFARLANE A. S. Rate of elimination of homologous globulins (including antibody) from the circulation. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):186–191. doi: 10.1042/bj0570186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROL S. The quantitative estimation of glycine in small samples of proteins. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):227–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R. The free amino-acids of invertebrate nerve. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):330–338. doi: 10.1042/bj0520330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):663–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Procedures for the chromatographic determination of amino acids on four per cent cross-linked sulfonated polystyrene resins. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):893–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIR H. M., NEUBERGER A., PERRONE J. C. Further isotopic studies on haemoglobin formation in the rat and rabbit. Biochem J. 1952 Sep;52(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj0520087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOVITZ M., OISON M. E., GREENBERG D. M. Independent antagonism of amino acid incorporation into protein. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):837–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., FOLLEY S. J. Synthetic activity of a single epithelial cell of the lactating goat udder. Nature. 1954 Oct 30;174(4435):828–829. doi: 10.1038/174828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., THOMPSON E. O. P. The amino-acid sequence in the glycyl chain of insulin. I. The identification of lower peptides from partial hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):353–366. doi: 10.1042/bj0530353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON M. V., VELICK S. F. The synthesis of aldolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in the rabbit. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG D., ANFINSEN C. B. Evidence for intermediates in ovalbumin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1952 Nov;199(1):25–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN M., ANFINSEN C. B. Non-uniform labeling of insulin and ribonuclease synthesized in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUILE C. L., LAMSON B. G., MILLER L. L., WHIPPLE G. H. Conversion of plasma protein to tissue protein without evidence of protein breakdown; results of giving plasma protein labeled with carbon 14 parenterally to dogs. J Exp Med. 1951 Jun;93(6):539–557. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.6.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


