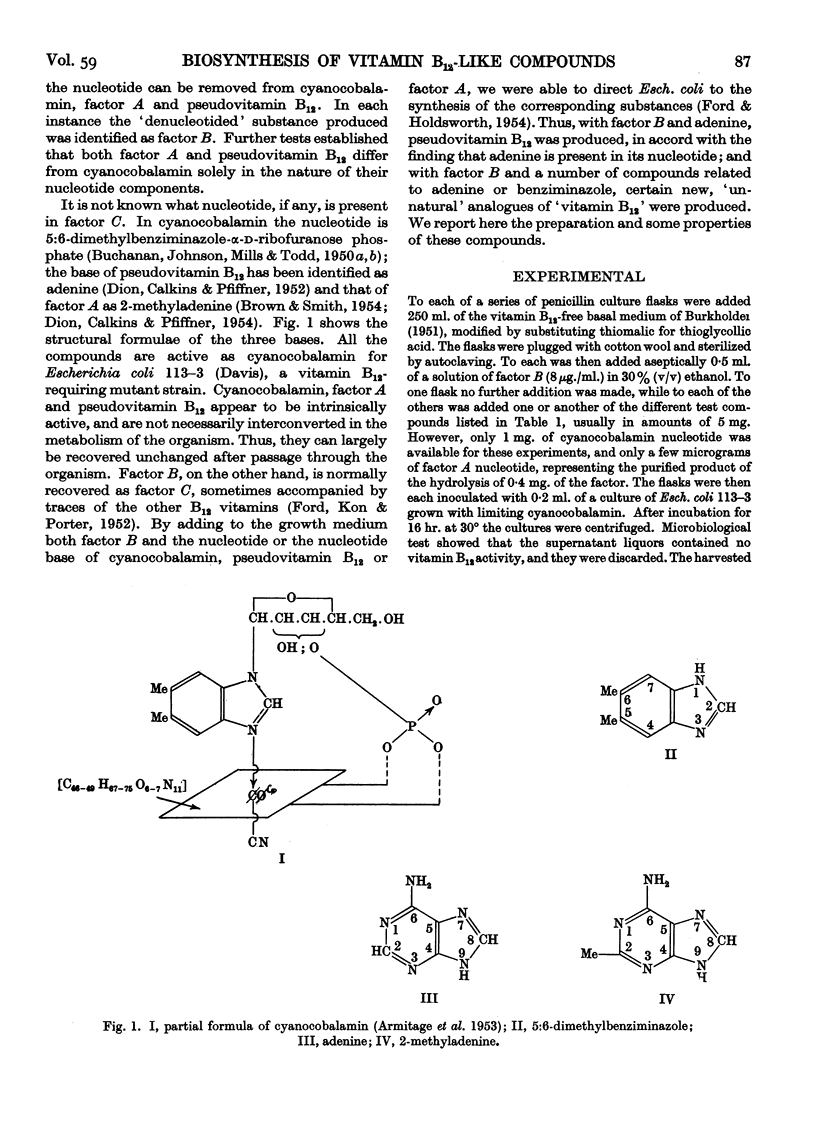
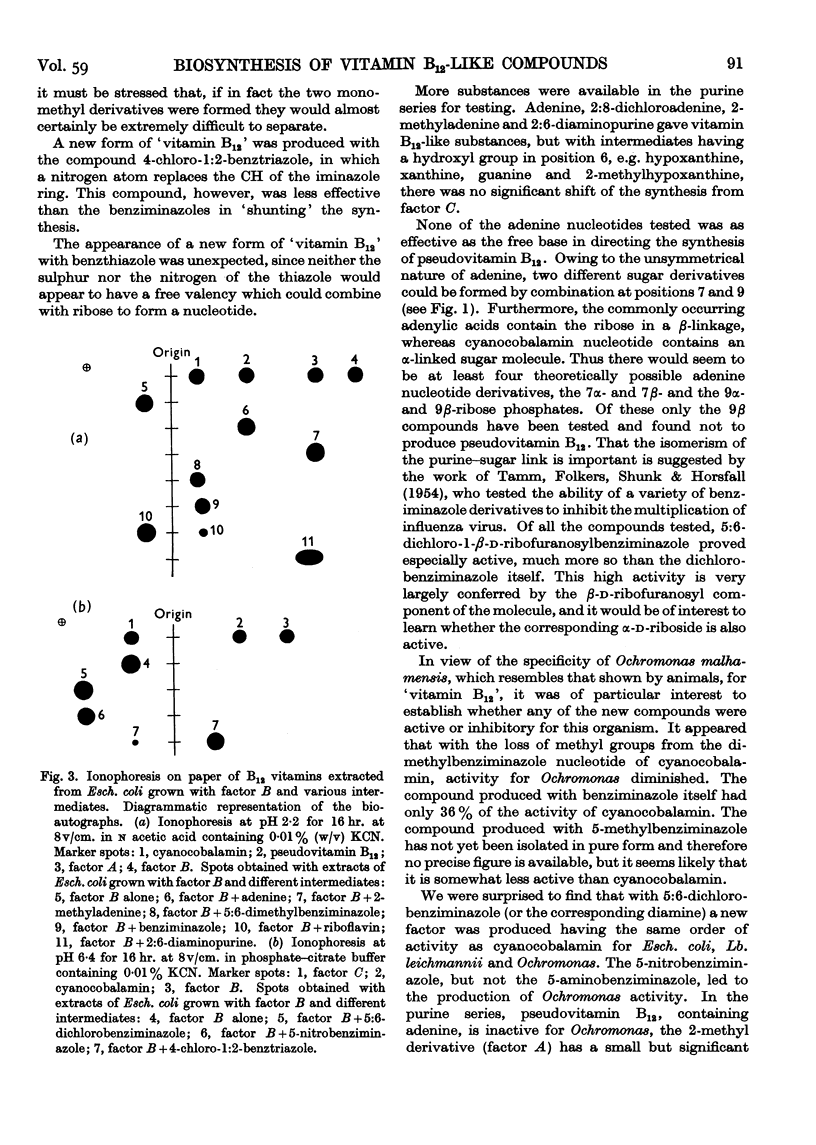
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAVEN G. R., HOLIDAY E. R. The chemistry of anti-pernicious anaemia factors; 5:6-disubstituted benziminazoles as products of acid hydrolysis of vitamin B12. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1949 Dec;1(12):957–970. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1949.tb12514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F. B., SMITH E. L. New purines in B12 vitamins. Biochem J. 1954 Jan 16;56(325TH):xxxiv–xxxv. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKHOLDER P. R. Determination of vitamin B12 with a mutant strain of Escherichia coli. Science. 1951 Nov 2;114(2966):459–460. doi: 10.1126/science.114.2966.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPERMAN J. M., TABENKIN B., DRUCKER R. Growth response and vitamin B12 tissue levels in vitamin B12-deficient rats and chicks fed riboflavin, 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole and related compounds. J Nutr. 1952 Apr;46(4):467–478. doi: 10.1093/jn/46.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANTES K. H., O'CALLAGHAN C. H. The biosynthesis of a new vitamin B12 analogue. Biochem J. 1954 Jul 16;58(331ST):xxi–xxi. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E. Differentiation of vitamin B12 active compounds by ionophoresis and microbiological assay; microbiological tests. Nature. 1953 Jan 24;171(4343):149–150. doi: 10.1038/171149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E., HOLDSWORTH E. S., KON S. K. Biosynthesis of vitamin B12-like compounds. Biochem J. 1954 Jul 16;58(331ST):xxiv–xxiv. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E., KON S. K., PORTER J. W. G. Some properties of vitamin B12-like factors from calf faeces. III. Further biological properties and interrelationships. Biochem J. 1952 Sep;52(1):viii–viii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E. The microbiological assay of vitamin B12; the specificity of the requirement of Ochromonas malhamensis for cyanocobalamin. Br J Nutr. 1953;7(4):299–306. doi: 10.1079/bjn19530039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANT D. E., SMITH E. L., PARKER L. F. Removal of nucleotide from B12 vitamins. Biochem J. 1954 Jan 16;56(325TH):xxxiv–xxxiv. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMAN A. M., DRYDEN L. P., CARY C. A. The effect of riboflavin on the bacterial synthesis of vitamin B12-active material in the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Dec;34(2):324–338. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH E. S. Differentiation of vitamin B12 active compounds by ionophoresis and microbiological assay; ionophoresis. Nature. 1953 Jan 24;171(4343):146–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., FOLKERS K., SHUNK C. H., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Inhibition of influenza virus multiplication by N-glycosides of benzimidazoles-N. J Exp Med. 1954 Mar;99(3):227–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEY D. W. Inhibition of synthesis of vitamin B12 and of riboflavin by 1,2-dichloro-4,5-diaminobenzene in bacterial cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Dec;75(3):745–746. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEY D. W., SINGER E. A., SMITH N. Selective toxicity of 1,2-dichloro-4,5-diaminobenzene: its relation to requirements for riboflavin and vitamin B12. J Exp Med. 1951 Jan;93(1):13–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



