Abstract
Risk factors for systemic embolisation in patients with ventricular thrombi caused by an acute myocardial infarction were studied in 150 consecutive patients with an infarction of the anterior wall. Serial echocardiograms were performed 2-10 days after the acute event and patients were followed up for three months. Anticoagulation treatment was started only after the detection of thrombi. Of the 55 patients in whom a thrombus developed, 15 (27%) had peripheral emboli between 6-62 days; but only two (2%) of 95 patients without thrombus had emboli. Among 15 variables, the best single predictors of embolisation were age greater than 68 years (80% sensitive, 85% specific), pendulous thrombus (60%, 93%), and independent thrombus mobility (60%, 85%). Logistic regression analysis showed that a formula that included patient age, thrombus area, and the length of thrombus in the ventricular lumen predicted embolisation (sensitivity 87%, specificity 88%). There was no correlation between age and the thrombus variables. The risk of embolisation from left ventricular thrombi in acute anterior myocardial infarction can be accurately assessed from patient age and echocardiographic features. The risk of peripheral emboli is high in patients with left ventricular thrombi and those aged greater than 68.
Full text
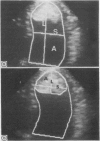
PDF
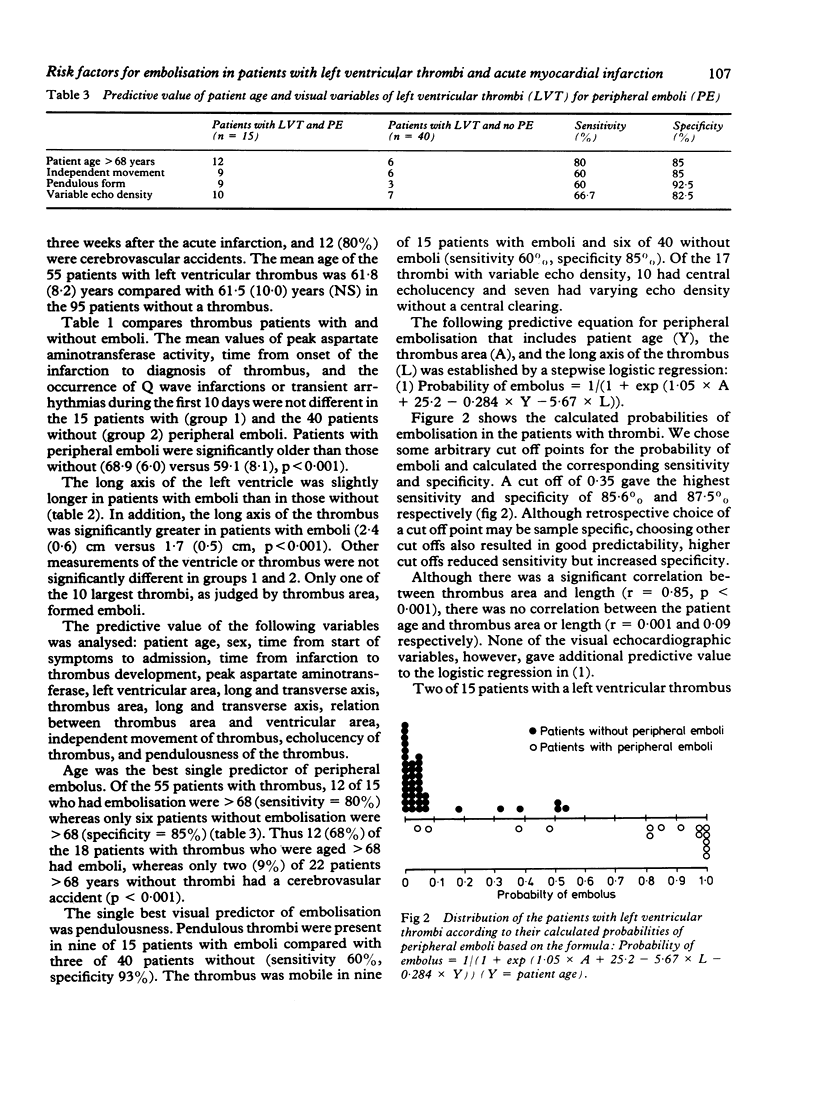
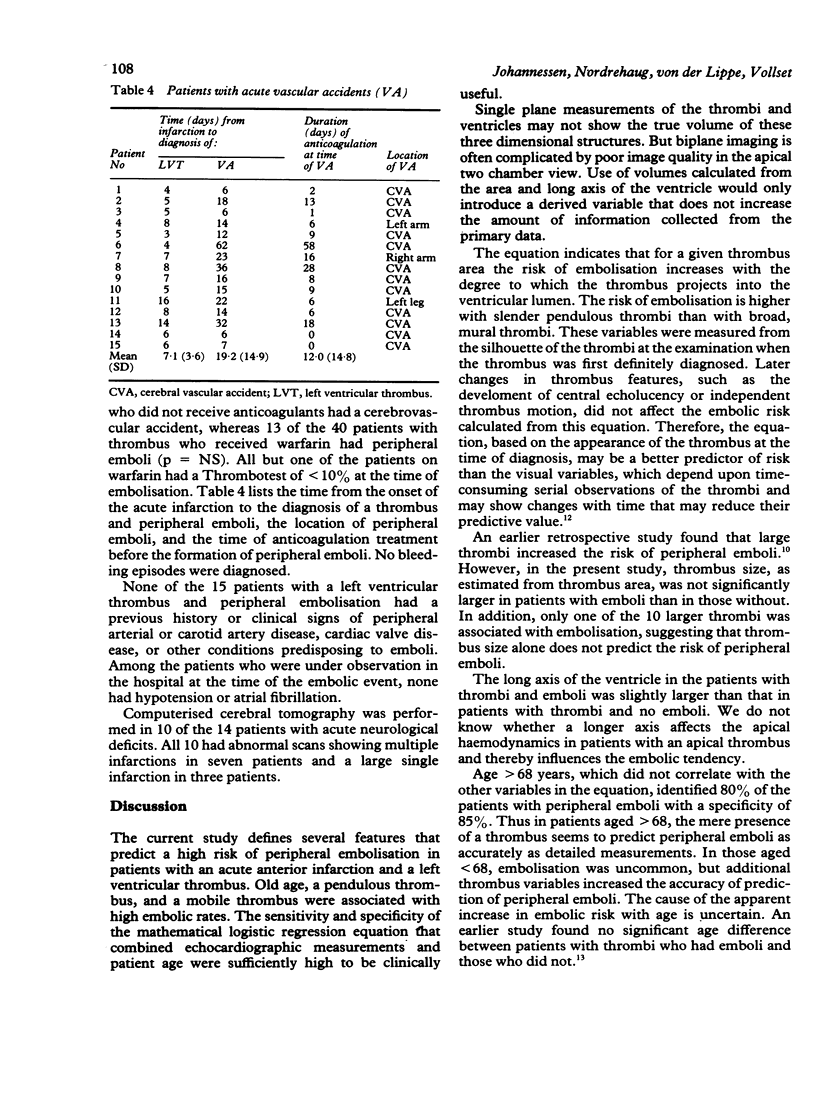


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvan S. Persistent intracardiac thrombi and systemic embolization despite anticoagulant therapy. Am Heart J. 1985 Jan;109(1):178–181. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90439-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvan S., Plehn J. Embolization of a left ventricular mural thrombus: verification by two-dimensional echocardiography. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Oct;142(10):1952–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asinger R. W., Mikell F. L., Elsperger J., Hodges M. Incidence of left-ventricular thrombosis after acute transmural myocardial infarction. Serial evaluation by two-dimensional echocardiography. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 6;305(6):297–302. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108063050601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénichou M., Aubry J., Larbi M. B., Romani A., Chiche G., Egré A., Djiane P., Bory M., Serradimigni A. Détection des caillots intra-ventriculaires gauches à la phase aiguë de l'infarctus du myocarde par l'échocardiographie bidimensionnelle. A propos de 103 cas. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1983 Sep;76(9):1012–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenicucci S., Bellotti P., Chiarella F., Lupi G., Vecchio C. Spontaneous morphologic changes in left ventricular thrombi: a prospective two-dimensional echocardiographic study. Circulation. 1987 Apr;75(4):737–743. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.4.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland J. M., Asinger R. W., Mikell F. L., Elsperger J., Hodges M. Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombi detected by two-dimensional echocardiography. Circulation. 1984 Oct;70(4):588–598. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.4.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen K. A., Nordrehaug J. E., von der Lippe G. Increased occurrence of left ventricular thrombi during early treatment with timolol in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1987 Jan;75(1):151–155. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen K. A., Nordrehaug J. E., von der Lippe G. Left ventricular thrombosis and cerebrovascular accident in acute myocardial infarction. Br Heart J. 1984 May;51(5):553–556. doi: 10.1136/hrt.51.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen K. A. Peripheral emboli from left ventricular thrombi of different echocardiographic appearance in acute myocardial infarction. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Apr;147(4):641–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating E. C., Gross S. A., Schlamowitz R. A., Glassman J., Mazur J. H., Pitt W. A., Miller D. Mural thrombi in myocardial infarctions. Prospective evaluation by two-dimensional echocardiography. Am J Med. 1983 Jun;74(6):989–995. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90798-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer R. S., Visser C. A., Kan G., Roelandt J. Two-dimensional echocardiographic appearance of left ventricular thrombi with systemic emboli after myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Jun 1;53(11):1511–1513. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90569-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordrehaug J. E., Johannessen K. A., von der Lippe G. Usefulness of high-dose anticoagulants in preventing left ventricular thrombus in acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1985 Jun 1;55(13 Pt 1):1491–1493. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(85)90959-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWREN P. A. Control of anticoagulant therapy. The use of new tests. Arch Intern Med. 1963 Feb;111:248–258. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1963.03620260108019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson B. B., Pulis J. L. Standardization of prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin time reagents and controls. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;65(2):213–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/65.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton J. R., Resnick A. D. Increased embolic risk in patients with left ventricular thrombi. Circulation. 1987 May;75(5):1004–1011. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.5.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser C. A., Kan G., Lie K. I., Durrer D. Left ventricular thrombus following acute myocardial infarction: a prospective serial echocardiographic study of 96 patients. Eur Heart J. 1983 May;4(5):333–337. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser C. A., Kan G., Meltzer R. S., Dunning A. J., Roelandt J. Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombus after myocardial infarction: a two-dimensional echocardiographic study of 119 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1276–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. J., Burke J. F., Pauletto F. J. Left ventricular mural thrombi complicating acute myocardial infarction. Long-term follow-up with serial echocardiography. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100(6):789–794. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-6-789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]