Abstract
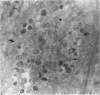
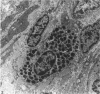
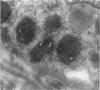
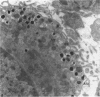
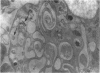
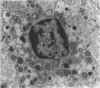
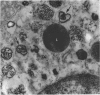
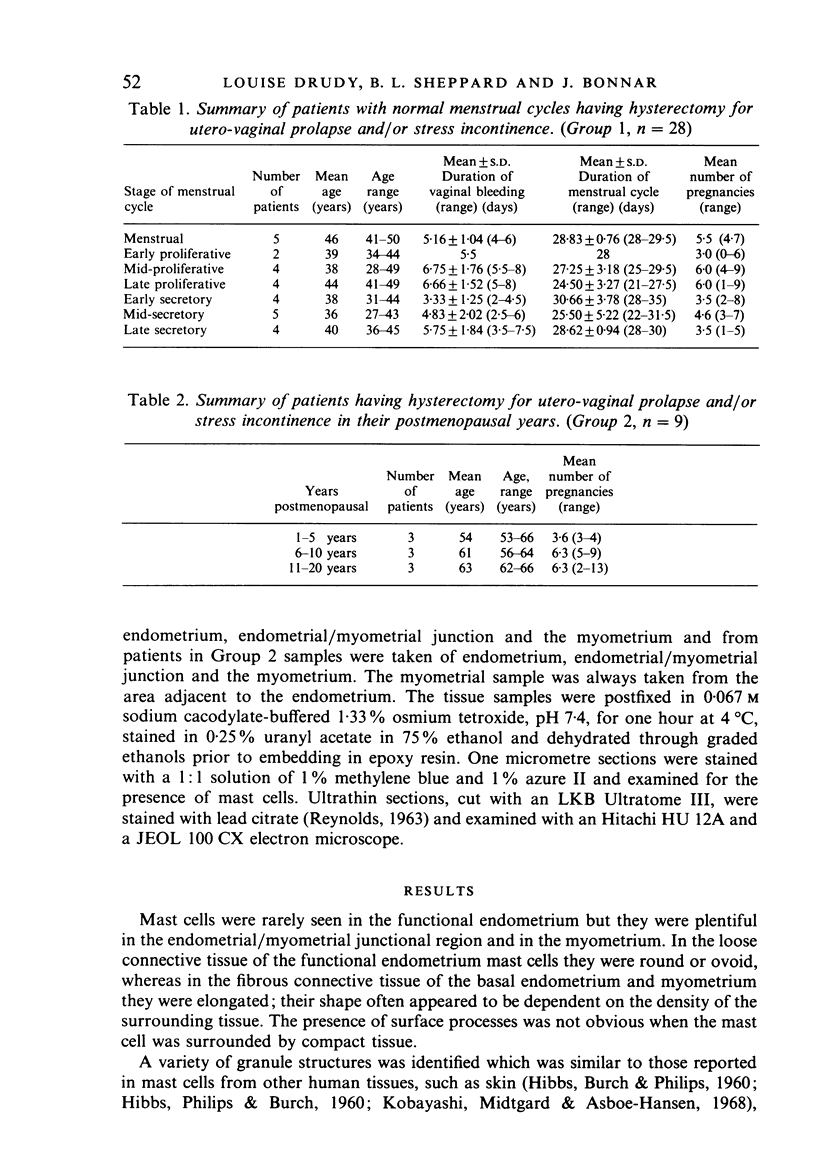
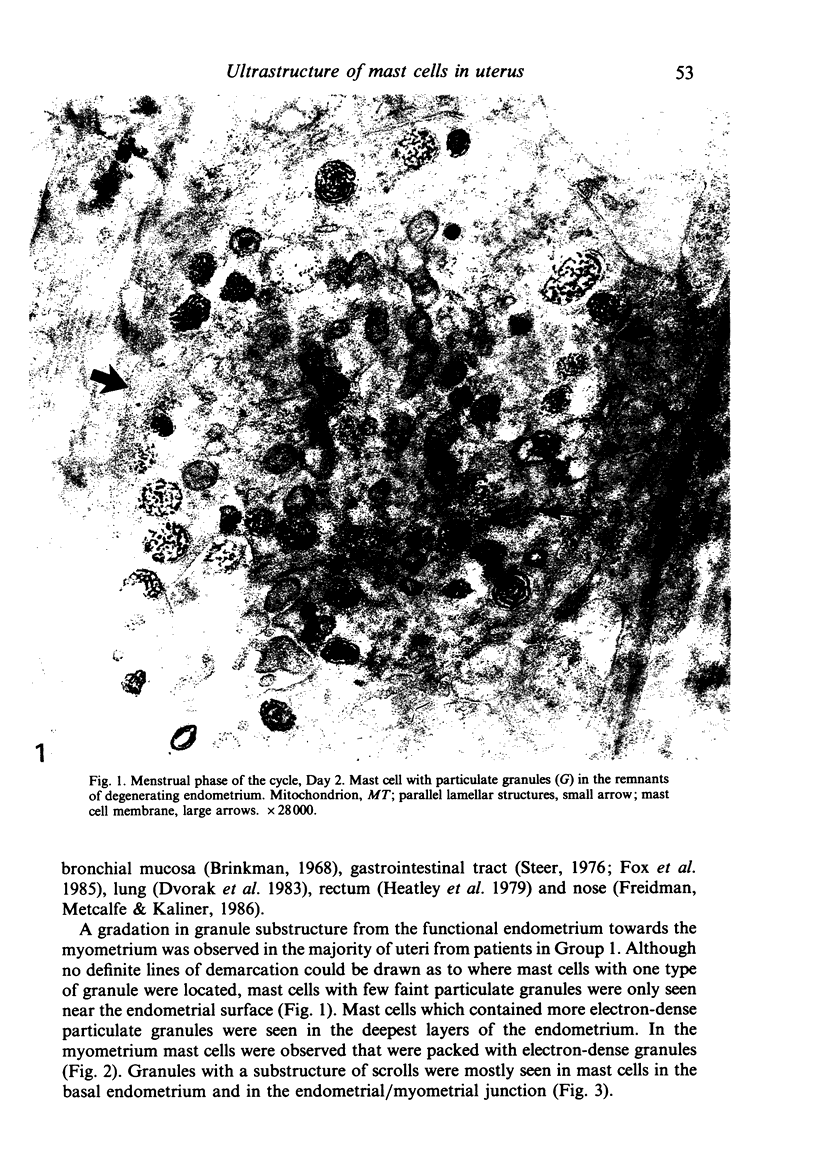
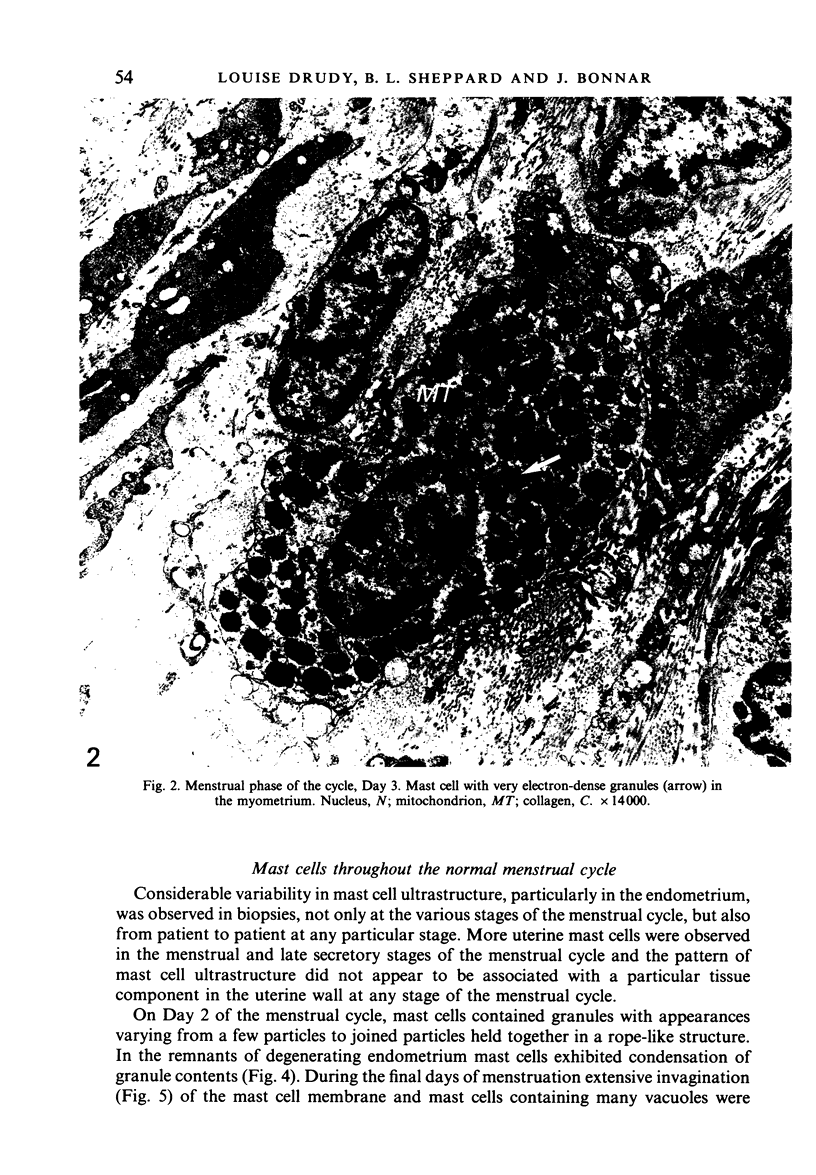
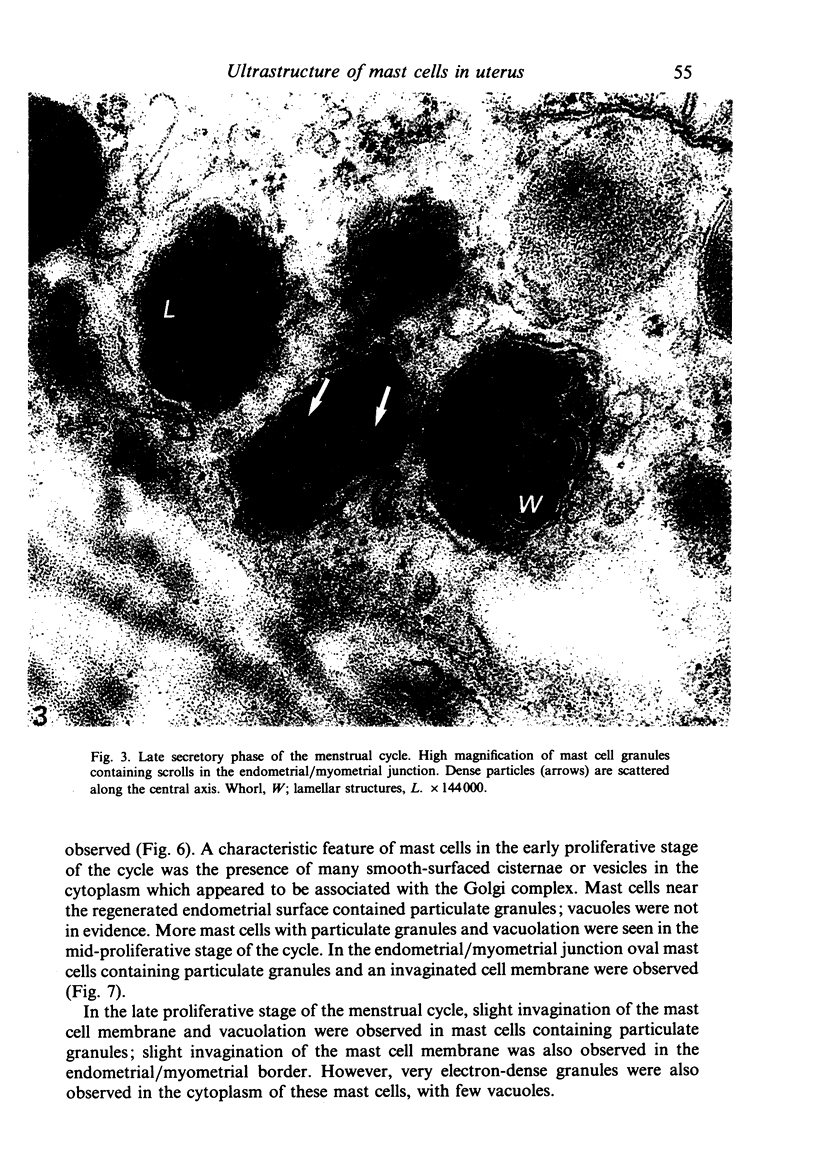
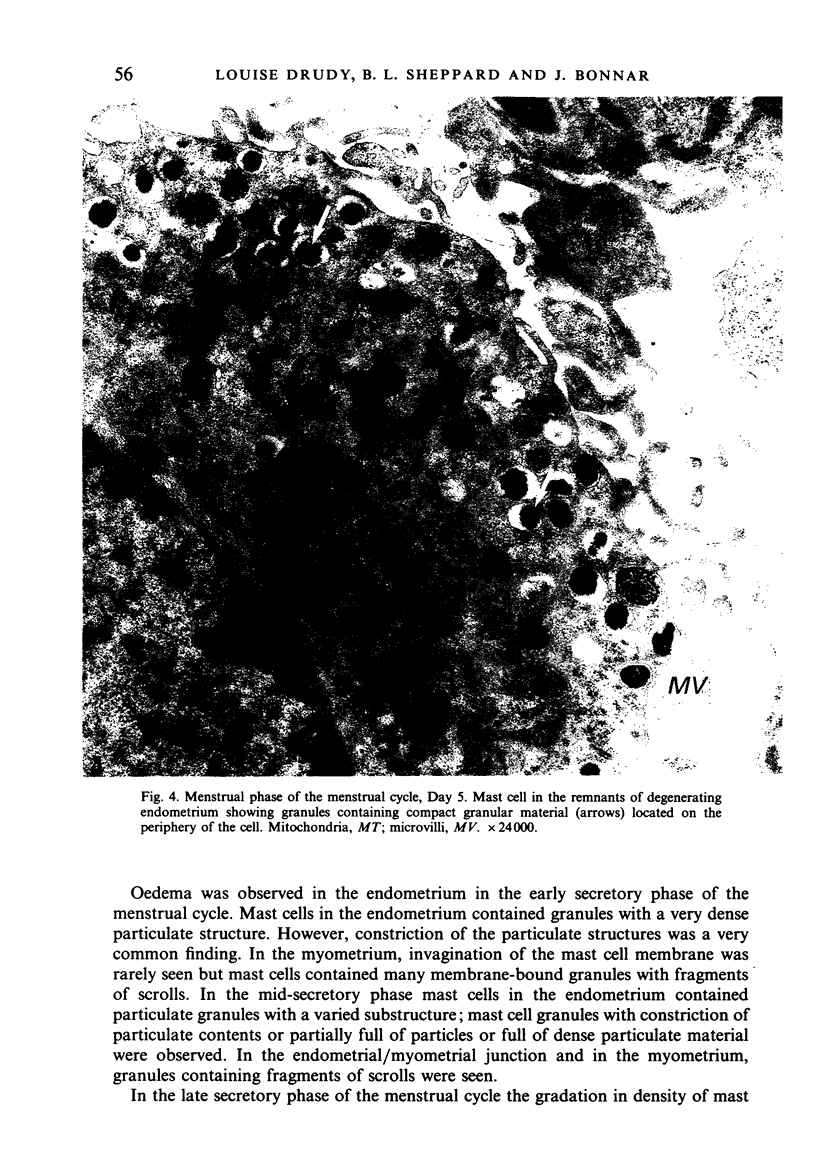
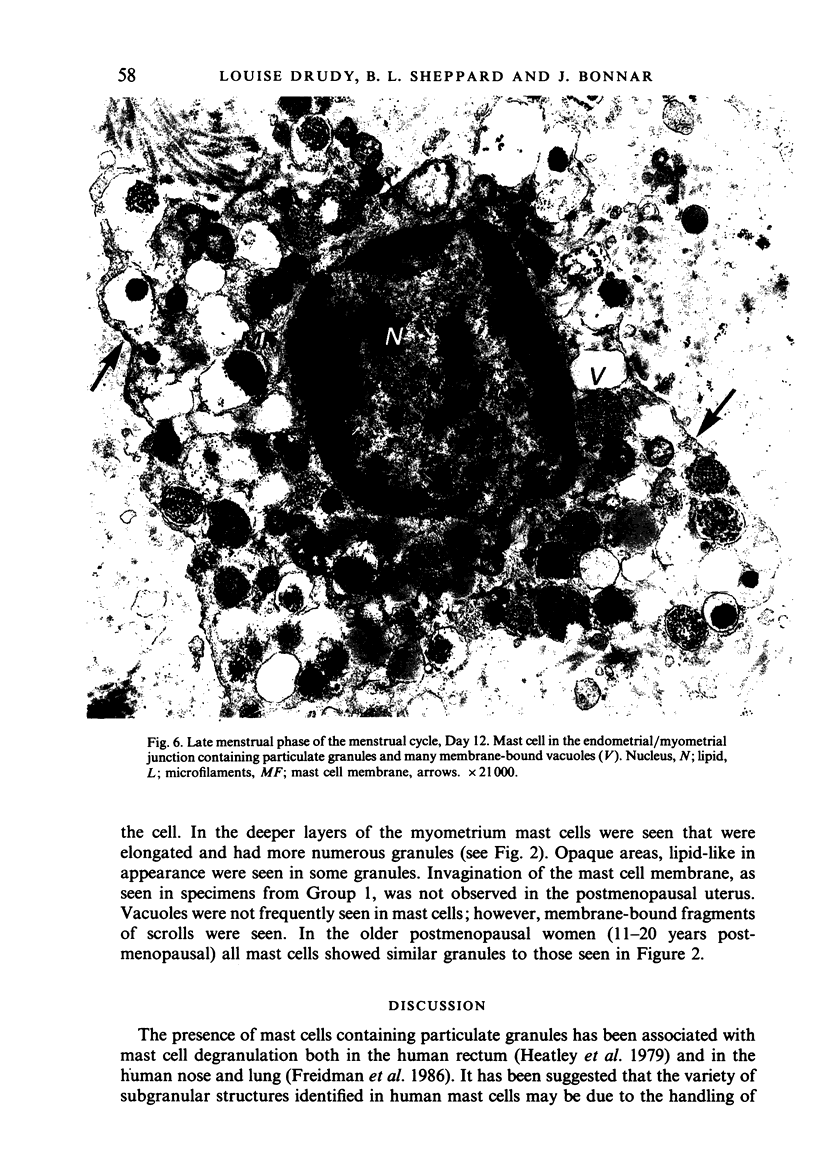
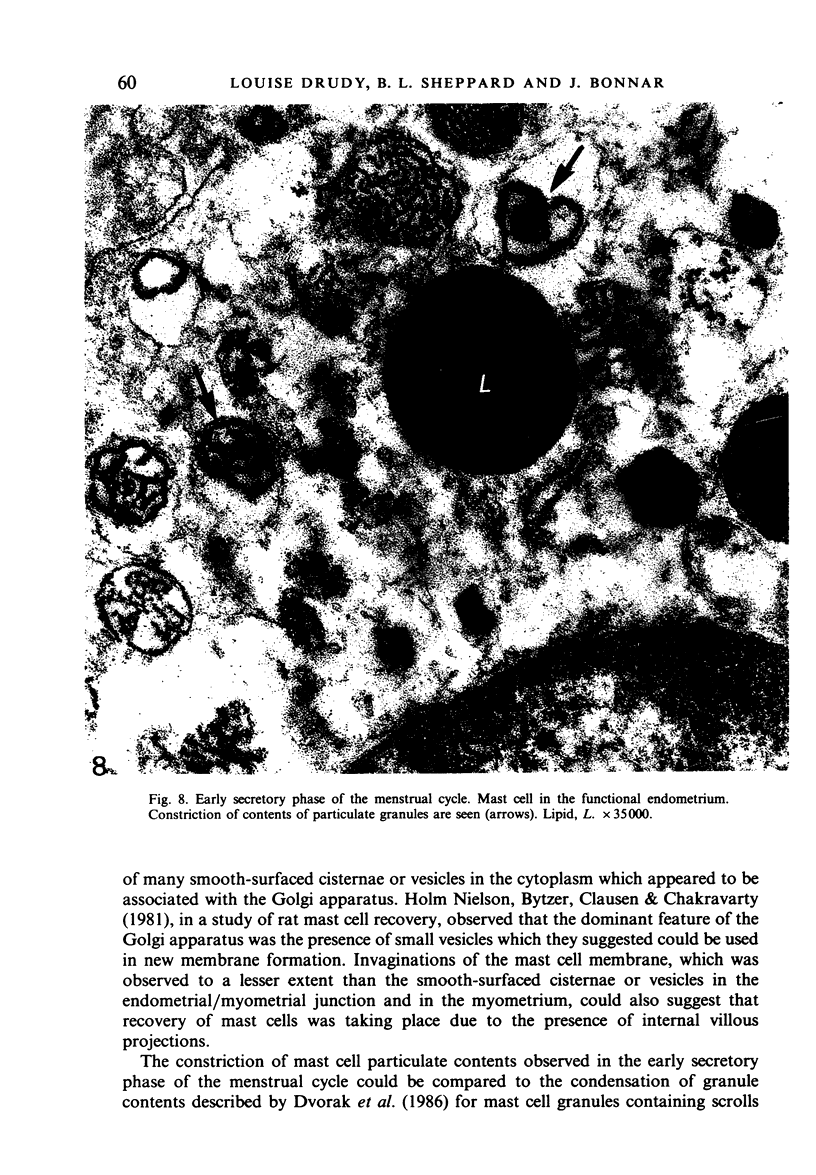
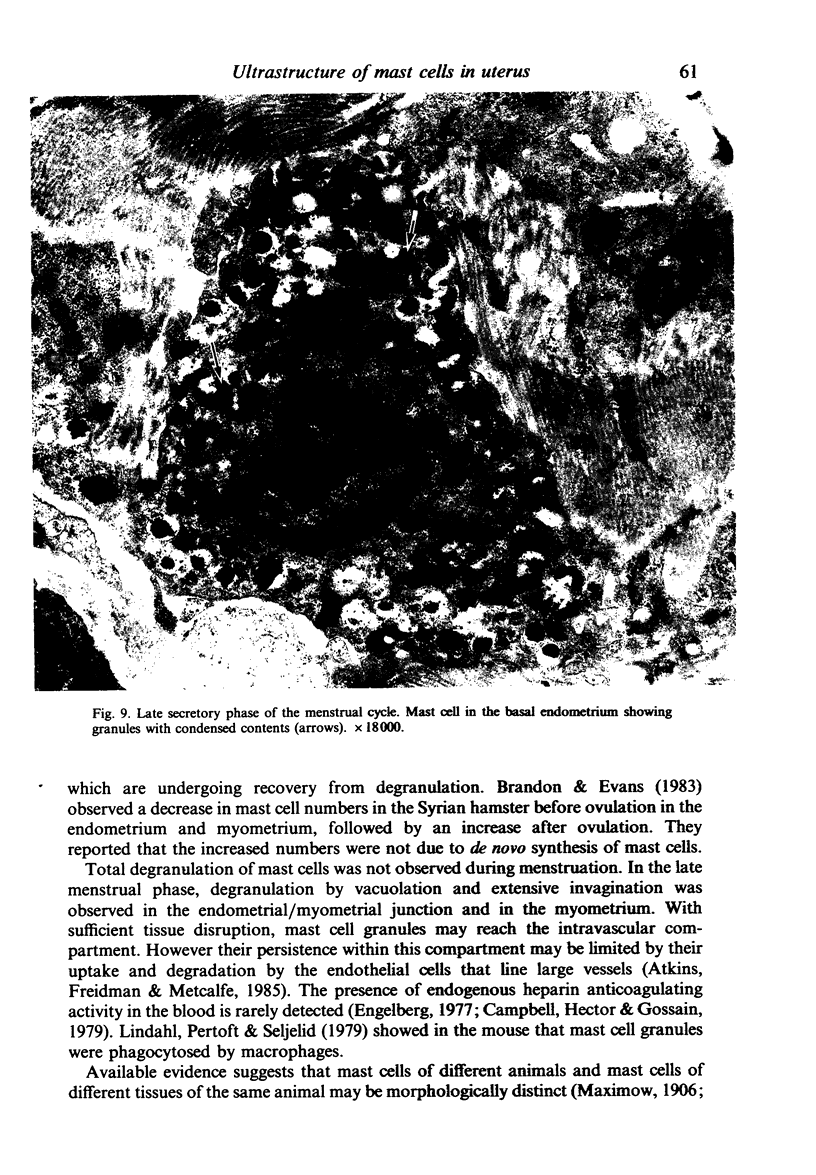
During the menstrual cycle a gradation in mast cell granule ultrastructure was observed from the functional endometrium towards the myometrium of the uterus. Mast cells with particulate granules were present in the functional endometrium and those with granules containing identifiable scrolls in the basal layer of the endometrium and in the myometrium; mast cells containing very electron-dense granules were present in the deeper layers of the myometrium. The secretory activity of mast cells throughout the menstrual cycle is described. Mast cell secretion was observed to a lesser extent in the postmenopausal uterus. Mast cells with particulate granules were absent in the postmenopausal uterus and many very electron-dense granules were observed in mast cells in the myometrium.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins F. M., Friedman M. M., Metcalfe D. D. Biochemical and microscopic evidence for the internalization and degradation of heparin-containing mast cell granules by bovine endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1985 Mar;52(3):278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhan R. G., Azizkhan J. C., Zetter B. R., Folkman J. Mast cell heparin stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):931–944. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandon J. M., Evans J. E. Changes in uterine mast cells during the estrous cycle in the Syrian hamster. Am J Anat. 1983 Jun;167(2):241–247. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001670209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman G. L. The mast cell in normal human bronchus and lung. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Apr;23(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. W., Jr, Hector D., Gossain V. Heparin activity in systemic mastocytosis. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jun;90(6):940–941. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-6-940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Lewis R. A., Hein A., Austen K. F. Secretion in dissociated human pulmonary mast cells. Evidence for solubilization of granule contents before discharge. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collan Y. Characteristics of nonepithelial cells in the epithelium of normal rat ileum. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1972;18:1–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Schulman E. S., Lichtenstein L. M., Dvorak H. F. Basophil and mast cell degranulation: ultrastructural analysis of mechanisms of mediator release. Fed Proc. 1983 May 15;42(8):2510–2515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Schleimer R. P., Schulman E. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Human mast cells use conservation and condensation mechanisms during recovery from degranulation. In vitro studies with mast cells purified from human lungs. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):663–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Schulman E. S., Peters S. P., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Newball H. H., Schleimer R. P., Lichtenstein L. M. Immunoglobulin E-mediated degranulation of isolated human lung mast cells. Lab Invest. 1985 Jul;53(1):45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L., Lundin P. M. Ultrastructure of mucosal mast cells in normal and compound 48-80-treated rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Jul 3;150(1):95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00220383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 2. Dye-binding and metachromatic properties. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):303–312. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 3. Reactivity towards compound 48/80. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):313–322. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. I. Effects of fixation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):289–302. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg H. Probable physiologic functions of heparin. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):70–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. C., Dvorak A. M., Peters S. P., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Isolation and characterization of human intestinal mucosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIBBS R. G., BURCH G. E., PHILLIPS J. H. Electron-microscopic observations on the human mast cell. Am Heart J. 1960 Jul;60:121–127. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(60)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIBBS R. G., PHILLIPS J. H., BURCH G. E. Electron microscopy of human tissue mast cells. JAMA. 1960 Oct 1;174:508–510. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.63030050006012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayasi T., Midtgård K., Asboe-Hansen G. Ultrastructure of human mast-cell granules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Apr;23(1):153–165. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Pertoft H., Seljelid R. Uptake and degradation of mast-cell granules by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):189–193. doi: 10.1042/bj1820189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen E. H., Bytzer P., Clausen J., Chakravarty N. Electron microscopic study of the regeneration in vitro of rat peritoneal mast cells after histamine secretion. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;216(3):635–645. doi: 10.1007/BF00238658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby K., Enerbäck L., Franzén L. Mast cell activation and tissue cell proliferation. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jul 30;170(3):289–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00219412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY J. F. Functional significance of histamine and heparin in tissue mast cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 26;103:151–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer H. W. Mast cells of the human stomach. J Anat. 1976 Apr;121(Pt 2):385–397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Miller H. R., Ferguson A. Human intestinal mucosal mast cells: evaluation of fixation and staining techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Aug;34(8):851–858. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.8.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]