Abstract
1. Experiments were performed in forty-one cats anaesthetized with chloralose.
2. The aim of the study was to investigate whether activity in stretch-sensitive muscle receptors may cause reflex effects in fusimotor neurones.
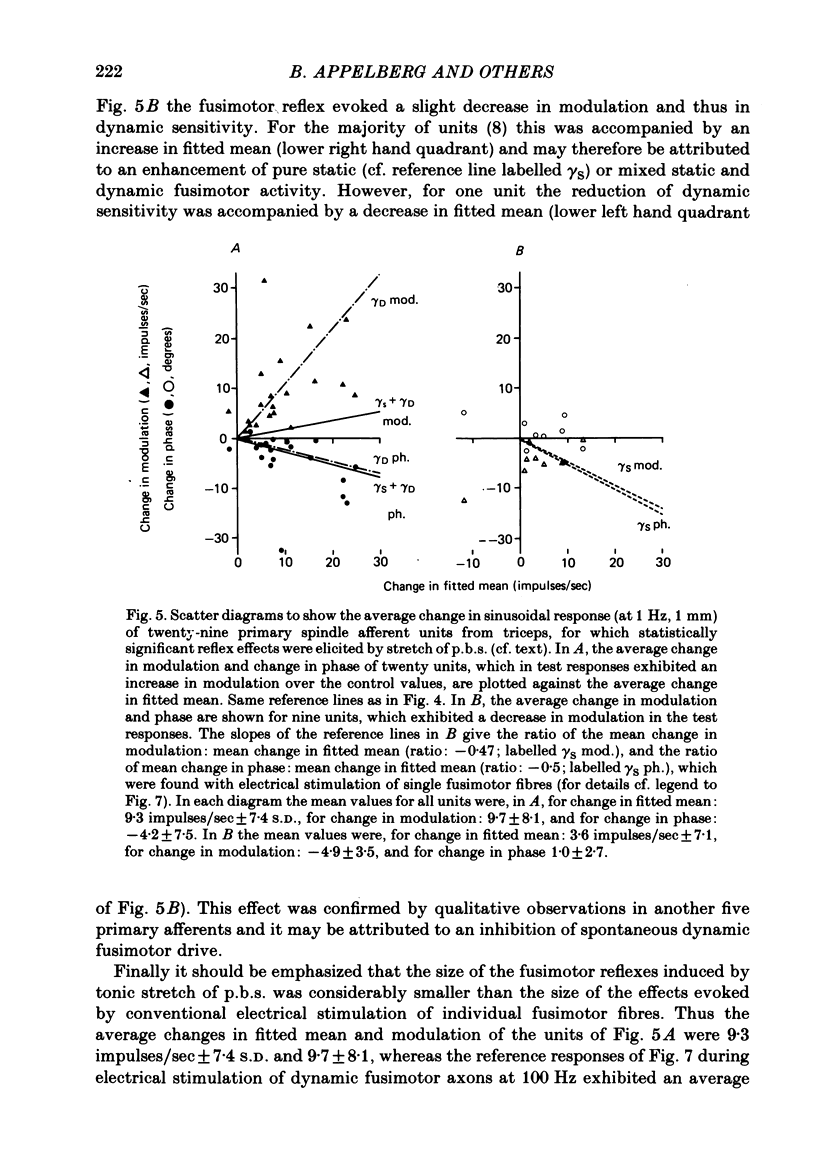
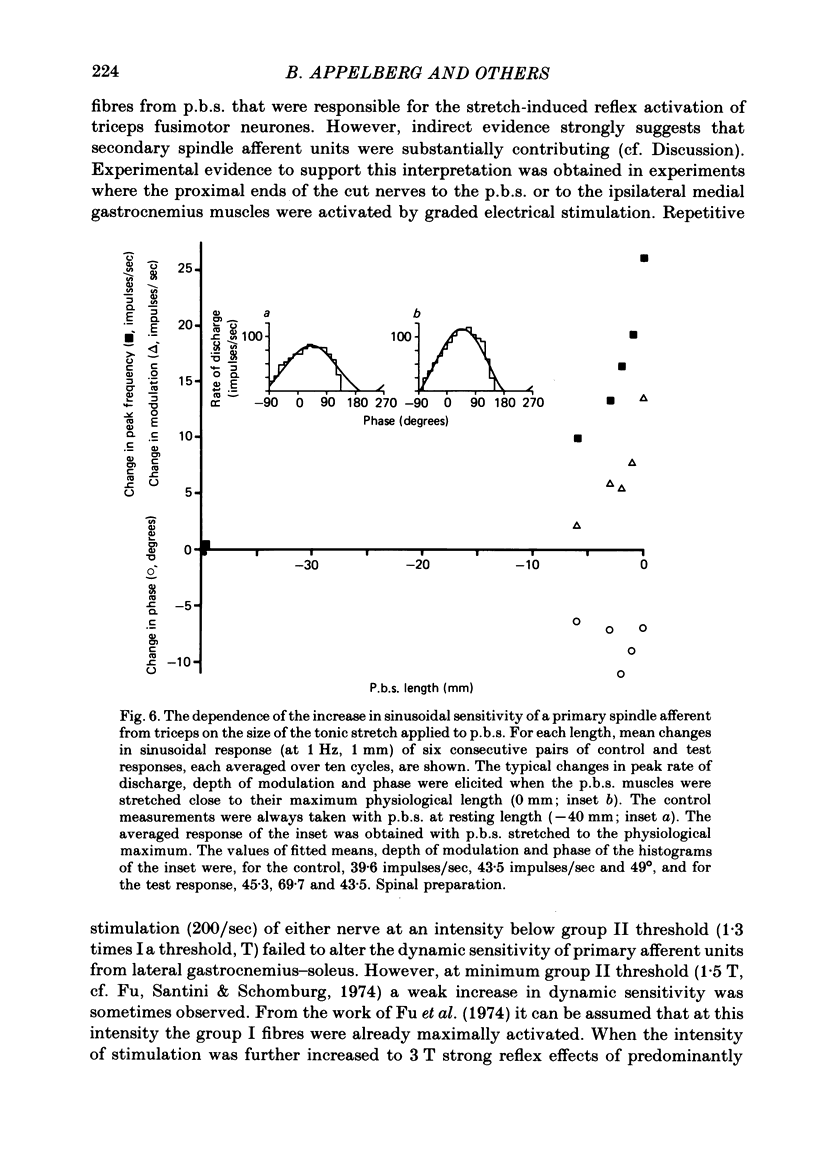
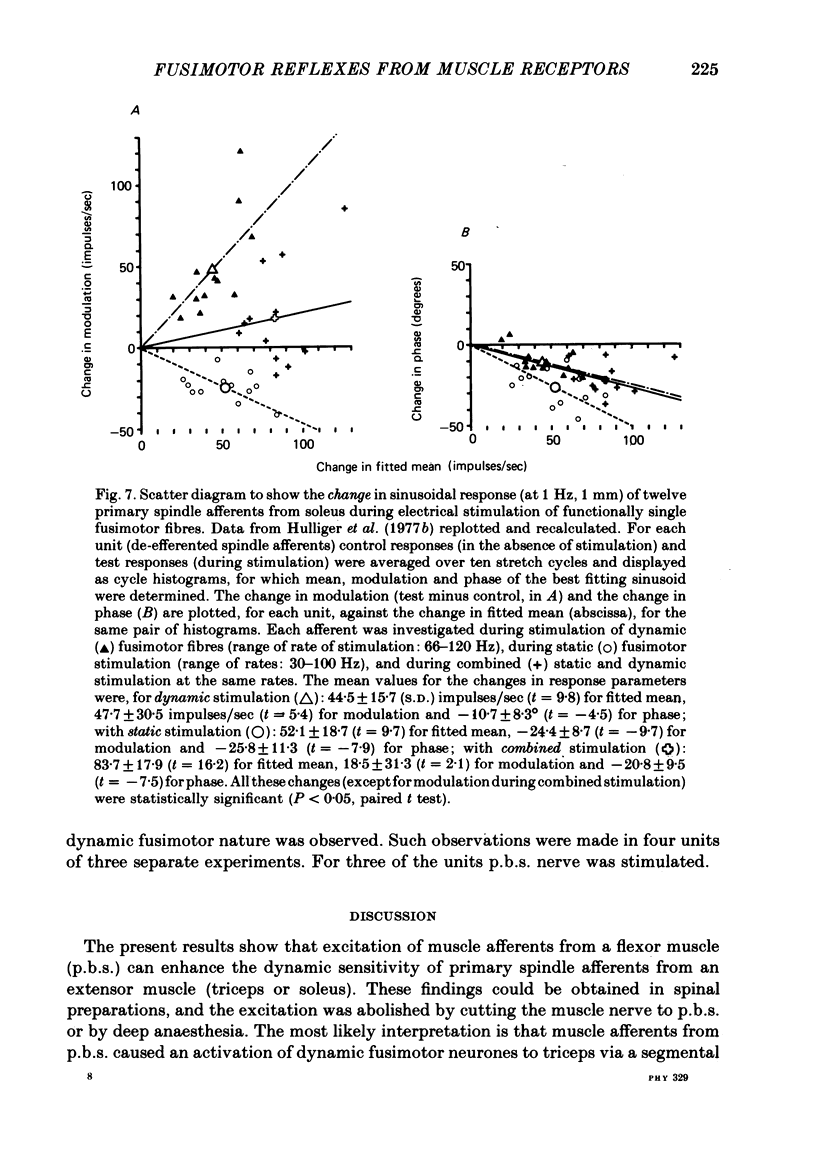
3. Activity in fusimotor neurones was studied indirectly by recording from primary and secondary muscle spindle afferents of the triceps surae muscle. The mean rate of firing of the afferents as well as either dynamic index (during ramp extension) or modulation (during sinusoidal extension) was determined. This was done under control conditions, with the posterior biceps—semitendinosus muscles relaxed, and under test conditions, with the same muscles extended.
4. All together, seventy-one primary afferents were studied quantitatively. Pure or predominantly dynamic effects were observed in twenty-two, pure or predominantly static effects in nine and no statistically significant effects in forty of the units. Amongst seven secondary afferents studied, two showed weak fusimotor activation, the other five were not influenced.
5. Electrical stimulation of the posterior biceps—semitendinosus or medial gastrocnemius nerves at group II strength was observed to cause dynamic fusimotor reflexes on a number of occasions.
6. The reflex effects observed were, on many occasions, recorded in spinalized preparations.
7. The reflex effects were not accompanied by any detectable e.m.g. activity in triceps, as judged from surface e.m.g. recordings. The reflex effects observed are therefore tentatively ascribed to activation of γ-motoneurones, yet a contribution from β-motoneurones cannot wholly be excluded.
8. On the basis of available evidence concerning reflex connexions to γ-motoneurones from various muscle afferents, it is suggested that the effects observed were caused by activation of muscle spindle secondary endings.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALNAES E., JANSEN J. K., RUDJORD T. FUSIMOTOR ACTIVITY IN THE SPINAL CAT. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Mar;63:197–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Bessou P., Laporte Y. Action of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres on secondary endings of cat's spindles. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):160–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. Excitation of dynamic fusimotor neurones of the cat triceps surae by contralateral joint afferents. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 19;160(3):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Hulliger M., Johansson H., Sojka P. The action of joint and secondary muscle-spindle afferents on dynamic gamma-motoneurones of the cat triceps surae muscle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:176P–177P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Jeneskog T., Johansson H. Rubrospinal control of static and dynamic fusimotor neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Dec;95(4):431–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb10071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Johansson H., Kalistratov G. The influence of group II muscle afferents and low threshold skin afferents on dynamic fusimotor neurones to the triceps surae of the cat. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 19;132(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90713-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans J., Grillner S. Reciprocal control of spontaneous activity and reflex effects in static and dynamic flexor gamma-motoneurones revealed by an injection of DOPA. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Sep-Oct;77(1):106–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Lawrence D. G., Matthews P. B. Static fusimotor fibres and the position sensitivity of muscle spindle receptors. Brain Res. 1969 Jun;14(1):173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. FURTHER STUDIES OF STATIC AND DYNAMIC FUSIMOTOR FIBRES. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:132–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. THE EFFECTS OF STIMULATION OF STATIC AND DYNAMIC FUSIMOTOR FIBRES ON THE RESPONSE TO STRETCHING OF THE PRIMARY ENDINGS OF MUSCLE SPINDLES. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:109–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N. The response to stretch of human intercostal muscle spindles studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):561–579. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murphy P. R., Trott J. R. Inhibition of gamma motoneurone discharge by contraction of the homonymous muscle in the decerebrated cat. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:425–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H. Recurrent inhibition of fusimotor neurones exhibiting background discharges in the decerebrate and the spinal cat. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):419–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Trott J. R. Autogenetic reflex action on to gamma motoneurones by stretch of triceps surae in the decerebrated cat. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:49–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Matthews P. B., Petit J. On the subdivision of static and dynamic fusimotor actions on the primary ending of the cat muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):827–861. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Proportion of muscles spindles supplied by skeletofusimotor axons (beta-axons) in peroneus brevis muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1390–1394. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm C., Noth J. Reflex responses of gamma motoneurones to vibration of the muscle they innervate. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):117–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. C., Santini M., Schomburg E. D. Characteristics and distribution of spinal focal synaptic potentials generated by group II muscle afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jul;91(3):298–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goslow G. E., Jr, Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. The cat step cycle: hind limb joint angles and muscle lengths during unrestrained locomotion. J Morphol. 1973 Sep;141(1):1–41. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051410102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S. Supraspinal and segmental control of static and dynamic gamma-motoneurones in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;327:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. J., MATTHEWS P. B. Some effects of stimulation of the muscle nerve on afferent endings of muscle spindles, and the classification of their responses into types A1 and A2. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:470–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulliger M., Matthews P. B., Noth J. Effects of combining static and dynamic fusimotor stimulation on the response of the muscle spindle primary ending to sinusoidal stretching. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;267(3):839–856. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulliger M., Matthews P. B., Noth J. Static and dynamic fusimotor action on the response of Ia fibres to low frequency sinusoidal stretching of widely ranging amplitude. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;267(3):811–838. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulliger M. The responses of primary spindle afferents to fusimotor stimulation at constant and abruptly changing rates. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:461–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniffki K. D., Mense S., Schmidt R. F. Responses of group IV afferent units from skeletal muscle to stretch, contraction and chemical stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Apr 14;31(4):511–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00239809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennerstrand G. Position and velocity sensitivity of muscle spindles in the cat. I. Primary and secondary endings deprived of fusimotor activation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Jul;73(3):281–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B. THE RESPONSE OF DE-EFFERENTED MUSCLE SPINDLE RECEPTORS TO STRETCHING AT DIFFERENT VELOCITIES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:660–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noth J., Thilmann A. Autogenetic excitation of extensor gamma-motoneurones by group II muscle afferents in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Apr;17(1-2):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. Functional analysis of group III afferent fibres of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:250–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trott J. R. The effect of low amplitude muscle vibration on the discharge of fusimotor neurones in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):635–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


