Abstract
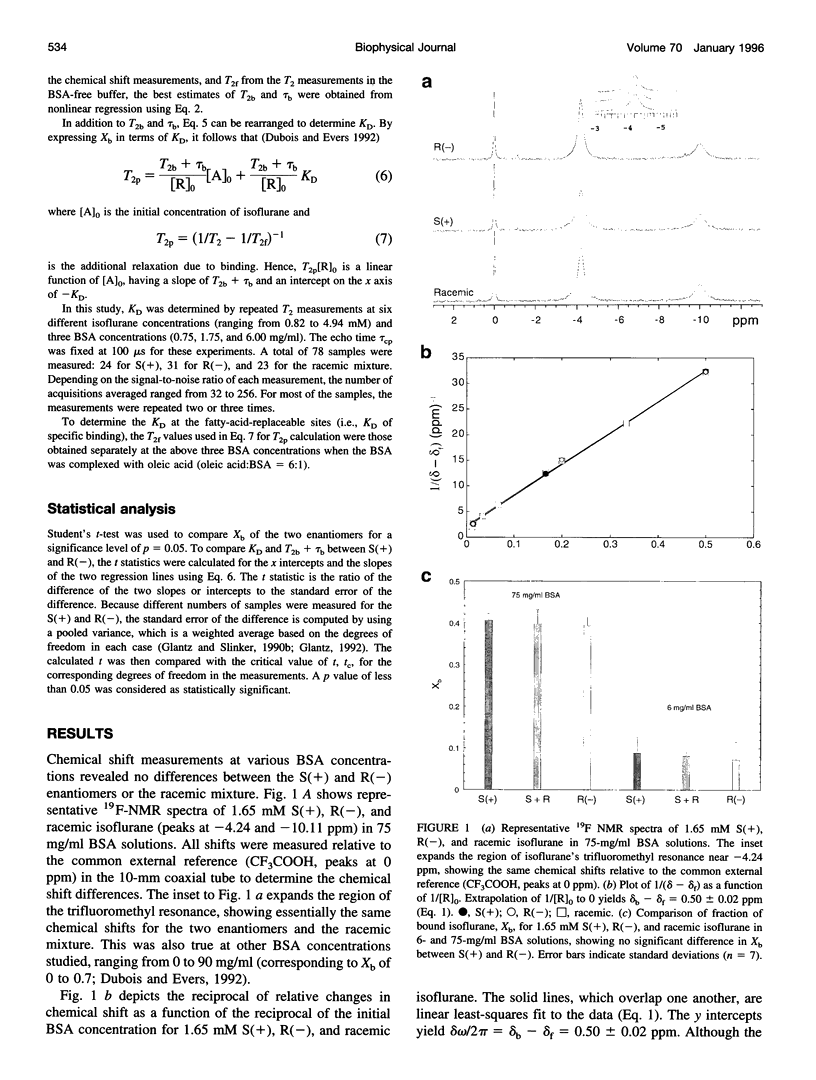
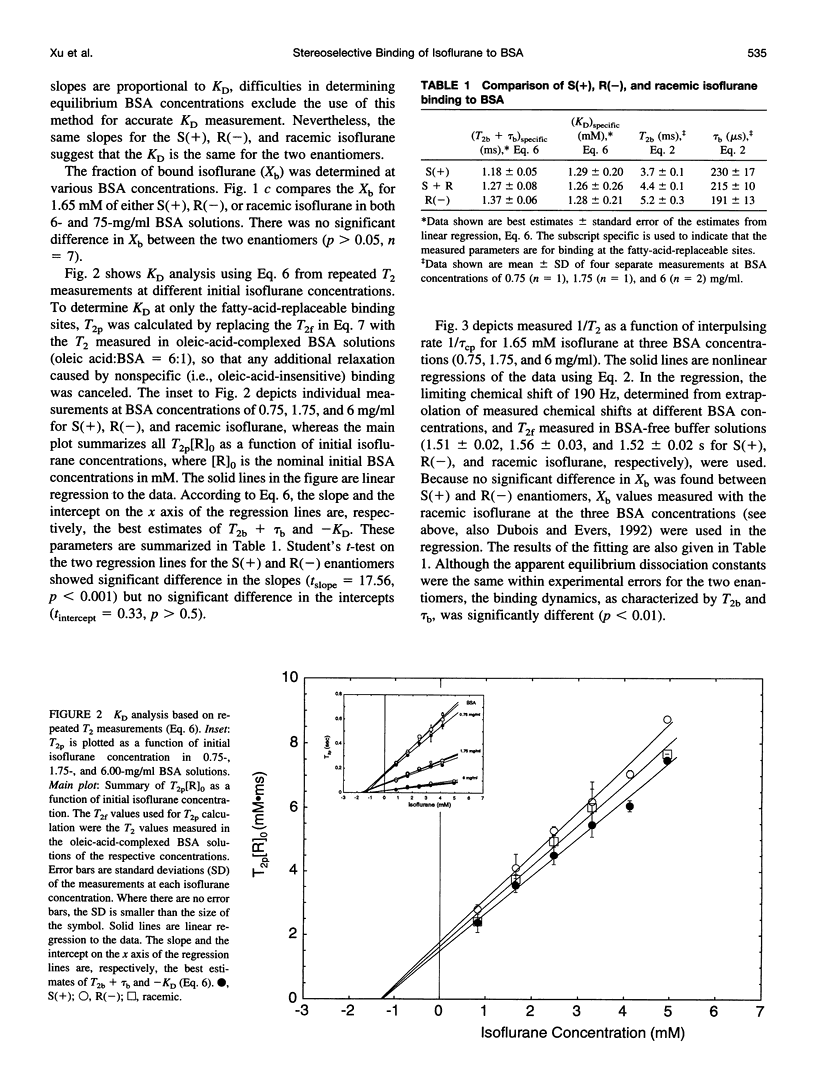
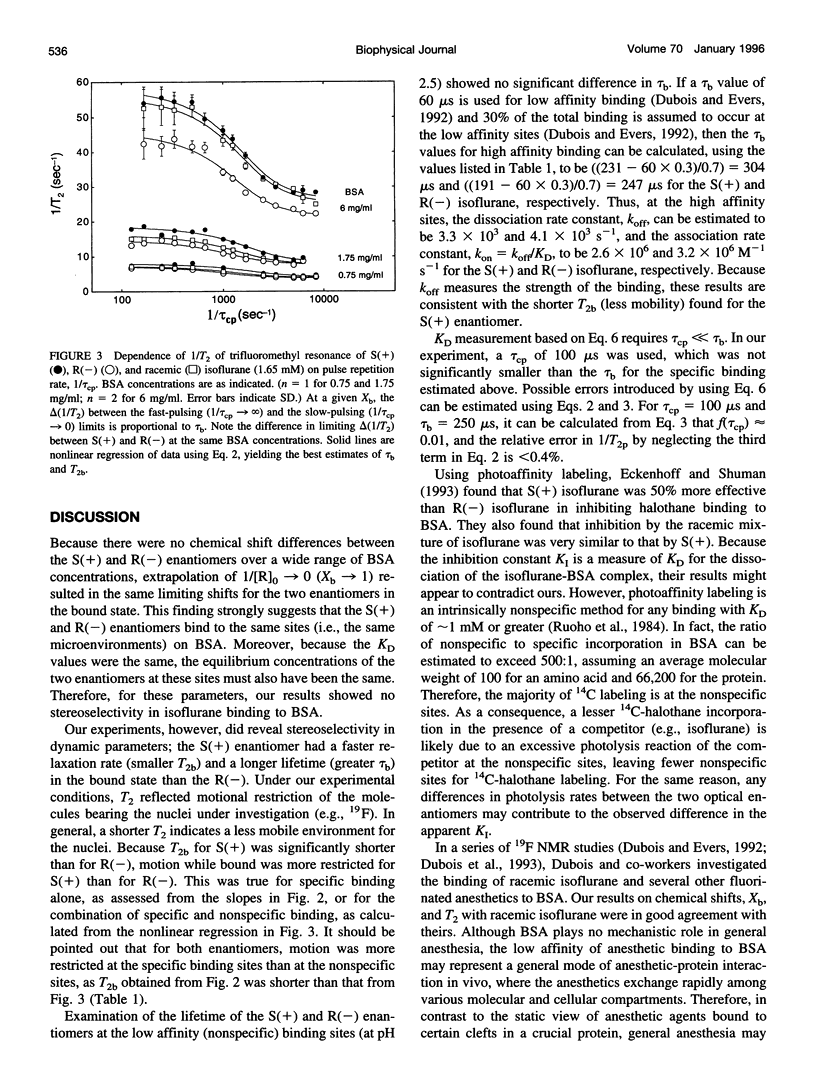
Whether proteins or lipids are the primary target sites for general anesthetic action has engendered considerable debate. Recent in vivo studies have shown that the S(+) and R(-) enantiomers of isoflurane are not equipotent, implying involvement of proteins. Bovine serum albumin (BSA), a soluble protein devoid of lipid, contains specific binding sites for isoflurane and other anesthetics. We therefore conducted 19F nuclear magnetic resonance measurements to determine whether binding of isoflurane to BSA was stereoselective. Isoflurane chemical shifts were measured as a function of BSA concentration to determine the chemical shift differences between the free and bound isoflurane. KD was determined by measuring the 19F transverse relaxation times (T2) as a function of isoflurane concentration. The binding duration was determined by assessing increases in 1/T2 as a result of isoflurane exchanging between the free and bound states. The S(+) and R(-) enantiomers exhibited no stereoselectivity in chemical shifts and KD values (KD = 1.3 +/- 0.2 mM, mean +/- SE, for S(+), R(-), and the racemic mixture). Nonetheless, stereoselectivity was observed in dynamic binding parameters; the S(+) enantiomer bound with slower association and dissociation rates than the R(-).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLERHAND A., GUTOWSKY H. S. SPIN-ECHO STUDIES OF CHEMICAL EXCHANGE. II. CLOSED FORMULAS FOR TWO SITES. J Chem Phys. 1965 Mar 1;42:1587–1599. doi: 10.1063/1.1696165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abadji V. C., Raines D. E., Watts A., Miller K. W. The effect of general anesthetics on the dynamics of phosphatidylcholine-acetylcholine receptor interactions in reconstituted vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 8;1147(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90325-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson R., Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Thermodynamics of anesthetic/protein interactions. Temperature studies on firefly luciferase. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1264–1271. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81491-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Brett R. S. Actions of volatile anesthetics and alcohols on cholinergic receptor channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:616–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Brett R. S., Lesko L. A. Effects of isoflurane on acetylcholine receptor channels. 1. Single-channel currents. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):127–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Brett R. S., Mody H. I. The effects of isoflurane on acetylcholine receptor channels.: 2. Currents elicited by rapid perfusion of acetylcholine. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;44(5):1056–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Liu Y. Desensitization of acetylcholine receptors in BC3H-1 cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Apr;420(5-6):479–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00374622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Vidal A. M., Mody H. I., Liu Y. Evidence for direct actions of general anesthetics on an ion channel protein. A new look at a unified mechanism of action. Anesthesiology. 1994 Aug;81(2):431–442. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199408000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois B. W., Cherian S. F., Evers A. S. Volatile anesthetics compete for common binding sites on bovine serum albumin: a 19F-NMR study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6478–6482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois B. W., Evers A. S. 19F-NMR spin-spin relaxation (T2) method for characterizing volatile anesthetic binding to proteins. Analysis of isoflurane binding to serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7069–7076. doi: 10.1021/bi00146a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenhoff R. G., Shuman H. Halothane binding to soluble proteins determined by photoaffinity labeling. Anesthesiology. 1993 Jul;79(1):96–106. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199307000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone L. L., Alifimoff J. K., Miller K. W. Does general anesthetic-induced desensitization of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor correlate with lipid disordering? Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):508–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone L. L., Sauter J. F., Braswell L. M., Miller K. W. Actions of general anesthetics on acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo californica. Anesthesiology. 1986 Jun;64(6):694–702. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198606000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel Y., Navon G., Aronheim A., Gershoni J. M. Direct measurement of agonist binding to genetically engineered peptides of the acetylcholine receptor by selective T1 NMR relaxation. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2617–2622. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Do general anaesthetics act by competitive binding to specific receptors? Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):599–601. doi: 10.1038/310599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):607–614. doi: 10.1038/367607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Stereospecific effects of inhalational general anesthetic optical isomers on nerve ion channels. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):427–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1925602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. M., Louro S. R., Horváath L. I., Miller K. W., Watts A. A study of the effect of general anesthetics on lipid-protein interactions in acetylcholine receptor enriched membranes from Torpedo nobiliana using nitroxide spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2664–2669. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. C., Lieb W. R., Franks N. P. Stereoselective and non-stereoselective actions of isoflurane on the GABAA receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):906–910. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris B. D., Moody E. J., Basile A. S., Skolnick P. Volatile anesthetics bidirectionally and stereospecifically modulate ligand binding to GABA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 May 17;267(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris B., Moody E., Skolnick P. Isoflurane anesthesia is stereoselective. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):215–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90875-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Kugler J. L., Jones M. V., Greenblatt E. P., Pritchett D. B. Positive modulation of human gamma-aminobutyric acid type A and glycine receptors by the inhalation anesthetic isoflurane. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;44(3):628–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. V., Brooks P. A., Harrison N. L. Enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid-activated Cl- currents in cultured rat hippocampal neurones by three volatile anaesthetics. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:279–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. V., Harrison N. L. Effects of volatile anesthetics on the kinetics of inhibitory postsynaptic currents in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Oct;70(4):1339–1349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.4.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. H., Chen L. L., Zirrolli J. A., Harris R. A. General anesthetics potentiate gamma-aminobutyric acid actions on gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors expressed by Xenopus oocytes: lack of involvement of intracellular calcium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Nov;263(2):569–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. H., Leonard S., Harris R. A. Enflurane inhibits the function of mouse and human brain phosphatidylinositol-linked acetylcholine and serotonin receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;43(6):941–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. H., Whiting P., Harris R. A. Molecular determinants of general anesthetic action: role of GABAA receptor structure. J Neurochem. 1993 Apr;60(4):1548–1553. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko G. S., Robinson J. L., Casto R., Ferrone R. A. The stereospecific effects of isoflurane isomers in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 22;263(1-2):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody E. J., Harris B. D., Skolnick P. Stereospecific actions of the inhalation anesthetic isoflurane at the GABAA receptor complex. Brain Res. 1993 Jun 25;615(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91119-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody E. J., Harris B. D., Skolnick P. The potential for safer anaesthesia using stereoselective anaesthetics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Oct;15(10):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahiro M., Yeh J. Z., Brunner E., Narahashi T. General anesthetics modulate GABA receptor channel complex in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1850–1854. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A. Structure and lipid binding properties of serum albumin. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:320–339. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudell J. R., Hubbell W. L. Localization of molecular halothane in phospholipid bilayer model nerve membranes. Anesthesiology. 1976 Mar;44(3):202–205. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197603000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamori M., Ikemoto Y., Akaike N. Effects of two volatile anesthetics and a volatile convulsant on the excitatory and inhibitory amino acid responses in dissociated CNS neurons of the rat. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Dec;66(6):2014–2021. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.6.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. A., Jones M. V., Harrison N. L. Potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor Cl- current correlates with in vivo anesthetic potency. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Sep;270(3):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]