Abstract
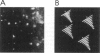
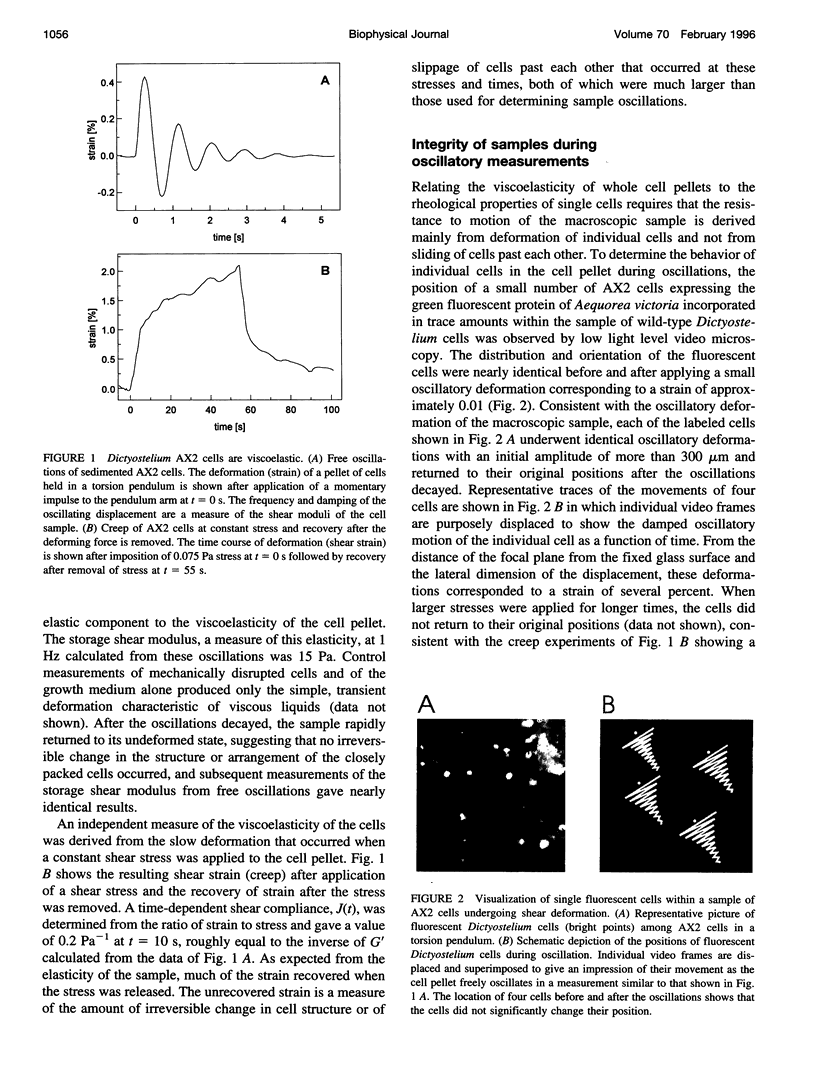
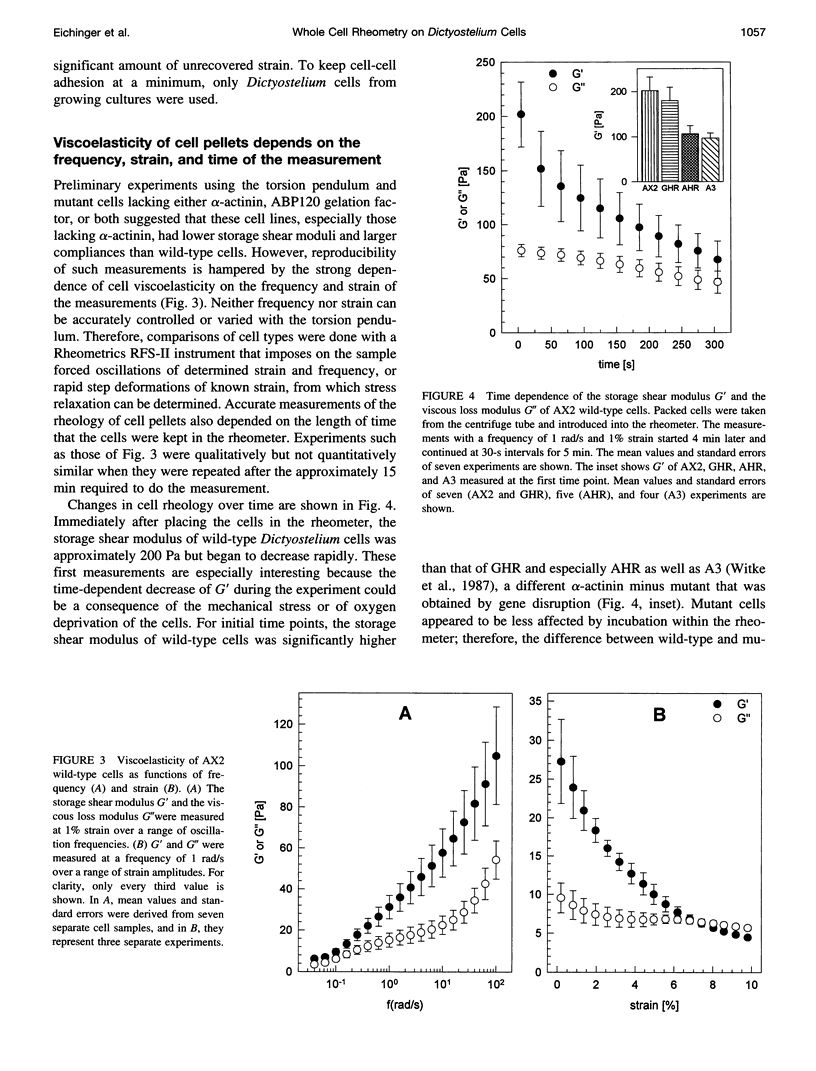
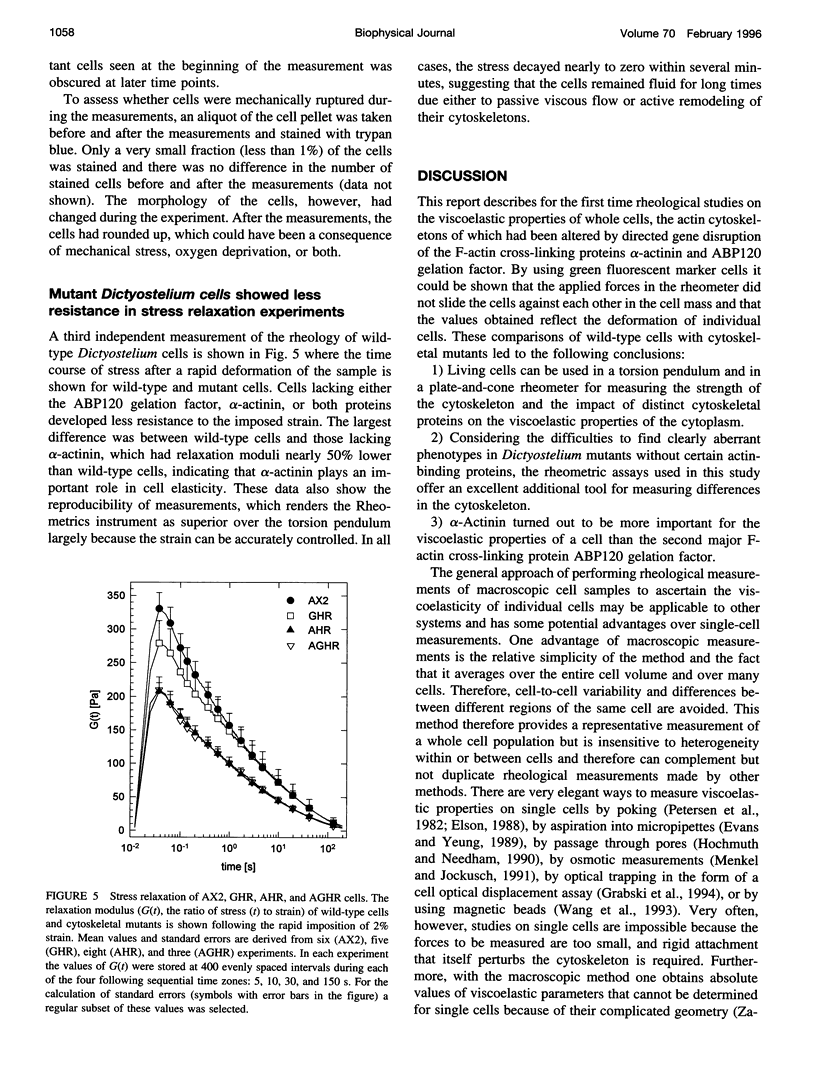
To determine the specific contribution of cytoskeletal proteins to cellular viscoelasticity we performed rheological experiments with Dictyostelium discoideum wild-type cells (AX2) and mutant cells altered by homologous recombination to lack alpha-actinin (AHR), the ABP120 gelation factor (GHR), or both of these F-actin cross-linking proteins (AGHR). Oscillatory and steady flow measurements of Dictyostelium wild-type cells in a torsion pendulum showed that there is a large elastic component to the viscoelasticity of the cell pellet. Quantitative rheological measurements were performed with an electronic plate-and-cone rheometer, which allowed determination of G', the storage shear modulus, and G", the viscous loss modulus, as a function of time, frequency, and strain, respectively. Whole cell viscoelasticity depends strongly on all three parameters, and comparison of wild-type and mutant strains under identical conditions generally produced significant differences. Especially stress relaxation experiments consistently revealed a clear difference between cells that lacked alpha-actinin as compared with wild-type cells or transformants without ABP120 gelation factor, indicating that alpha-actinin plays an important role in cell elasticity. Direct observation of cells undergoing shear deformation was done by incorporating a small number of AX2 cells expressing the green fluorescent protein of Aequorea victoria and visualizing the strained cell pellet by fluorescence and phase contrast microscopy. These observations confirmed that the shear strain imposed by the rheometer does not injure the cells and that the viscoelastic response of the cell pellet is due to deformation of individual cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André E., Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A., Schleicher M., Segall J. E., Wallraff E. A Dictyostelium mutant deficient in severin, an F-actin fragmenting protein, shows normal motility and chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):985–995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Vasiliev J. Cell motility. Networks from mutants. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):203–204. doi: 10.1038/338203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A. A., Segall J. E., Wallraff E., Schleicher M. A Dictyostelium mutant lacking an F-actin cross-linking protein, the 120-kD gelation factor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1477–1489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Tu Y., Euskirchen G., Ward W. W., Prasher D. C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):802–805. doi: 10.1126/science.8303295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claviez M., Pagh K., Maruta H., Baltes W., Fisher P., Gerisch G. Electron microscopic mapping of monoclonal antibodies on the tail region of Dictyostelium myosin. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):1017–1022. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J. Life at the leading edge: the formation of cell protrusions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:411–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Condeelis J., Wessels D., Soll D., Kern H., Knecht D. A. Targeted disruption of the ABP-120 gene leads to cells with altered motility. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):943–955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Ridsdale J. A., Condeelis J., Hartwig J. Genetic deletion of ABP-120 alters the three-dimensional organization of actin filaments in Dictyostelium pseudopods. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):819–835. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. C., Gorlin J. B., Kwiatkowski D. J., Hartwig J. H., Janmey P. A., Byers H. R., Stossel T. P. Actin-binding protein requirement for cortical stability and efficient locomotion. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):325–327. doi: 10.1126/science.1549777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L. Cellular mechanics as an indicator of cytoskeletal structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:397–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Yeung A. Apparent viscosity and cortical tension of blood granulocytes determined by micropipet aspiration. Biophys J. 1989 Jul;56(1):151–160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82660-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabski S., Xie X. G., Holland J. F., Schindler M. Lipids trigger changes in the elasticity of the cytoskeleton in plant cells: a cell optical displacement assay for live cell measurements. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):713–726. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugwitz M., Noegel A. A., Karakesisoglou J., Schleicher M. Dictyostelium amoebae that lack G-actin-sequestering profilins show defects in F-actin content, cytokinesis, and development. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Needham D. The viscosity of neutrophils and their transit times through small pores. Biorheology. 1990;27(6):817–828. doi: 10.3233/bir-1990-27603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A. A torsion pendulum for measurement of the viscoelasticity of biopolymers and its application to actin networks. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1991 Jan;22(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(91)90080-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Hvidt S., Lamb J., Stossel T. P. Resemblance of actin-binding protein/actin gels to covalently crosslinked networks. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):89–92. doi: 10.1038/345089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiting B., Noegel A. A. The ble gene of Streptoalloteichus hindustanus as a new selectable marker for Dictyostelium discoideum confers resistance to phleomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1403–1407. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manstein D. J., Titus M. A., De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Gene replacement in Dictyostelium: generation of myosin null mutants. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):923–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menke A., Jockusch H. Decreased osmotic stability of dystrophin-less muscle cells from the mdx mouse. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):69–71. doi: 10.1038/349069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., Aebi U. Bundling of actin filaments by alpha-actinin depends on its molecular length. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2013–2024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Rapp S., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M., Stewart M. The Dictyostelium gelation factor shares a putative actin binding site with alpha-actinins and dystrophin and also has a rod domain containing six 100-residue motifs that appear to have a cross-beta conformation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):607–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Witke W. Inactivation of the alpha-actinin gene in Dictyostelium. Dev Genet. 1988;9(4-5):531–538. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020090429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Witke W., Schleicher M. Calcium-sensitive non-muscle alpha-actinin contains EF-hand structures and highly conserved regions. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80962-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak C., Wong S., Elson E. L. Mechanical function of dystrophin in muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(3):355–361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O., McConnaughey W. B., Elson E. L. Dependence of locally measured cellular deformability on position on the cell, temperature, and cytochalasin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5327–5331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Schwarz W. H., Pollard T. D. Dependence of the mechanical properties of actin/alpha-actinin gels on deformation rate. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):828–830. doi: 10.1038/325828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher M., André B., Andréoli C., Eichinger L., Haugwitz M., Hofmann A., Karakesisoglou J., Stöckelhuber M., Noegel A. A. Structure/function studies on cytoskeletal proteins in Dictyostelium amoebae as a paradigm. FEBS Lett. 1995 Aug 1;369(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. Dynamics of the Dictyostelium cytoskeleton during chemotaxis. New Biol. 1992 May;4(5):461–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher M., Noegel A., Schwarz T., Wallraff E., Brink M., Faix J., Gerisch G., Isenberg G. A Dictyostelium mutant with severe defects in alpha-actinin: its characterization using cDNA probes and monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1988 May;90(Pt 1):59–71. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. On the crawling of animal cells. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1086–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.8493552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsstock D. H., Schwartz W. H., Pollard T. D. Affinity of alpha-actinin for actin determines the structure and mechanical properties of actin filament gels. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81059-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallraff E., Schleicher M., Modersitzki M., Rieger D., Isenberg G., Gerisch G. Selection of Dictyostelium mutants defective in cytoskeletal proteins: use of an antibody that binds to the ends of alpha-actinin rods. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Butler J. P., Ingber D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1124–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.7684161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilczynska Z., Fisher P. R. Analysis of a complex plasmid insertion in a phototaxis-deficient transformant of Dictyostelium discoideum selected on a Micrococcus luteus lawn. Plasmid. 1994 Sep;32(2):182–194. doi: 10.1006/plas.1994.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Nellen W., Noegel A. Homologous recombination in the Dictyostelium alpha-actinin gene leads to an altered mRNA and lack of the protein. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4143–4148. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. Redundancy in the microfilament system: abnormal development of Dictyostelium cells lacking two F-actin cross-linking proteins. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90205-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahalak G. I., McConnaughey W. B., Elson E. L. Determination of cellular mechanical properties by cell poking, with an application to leukocytes. J Biomech Eng. 1990 Aug;112(3):283–294. doi: 10.1115/1.2891186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahalak G. I. On the ambiguity of viscoelastic-fluid representations of cytoplasm subjected to large deformations. Biorheology. 1993 Sep-Dec;30(5-6):471–472. doi: 10.3233/bir-1993-305-617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]