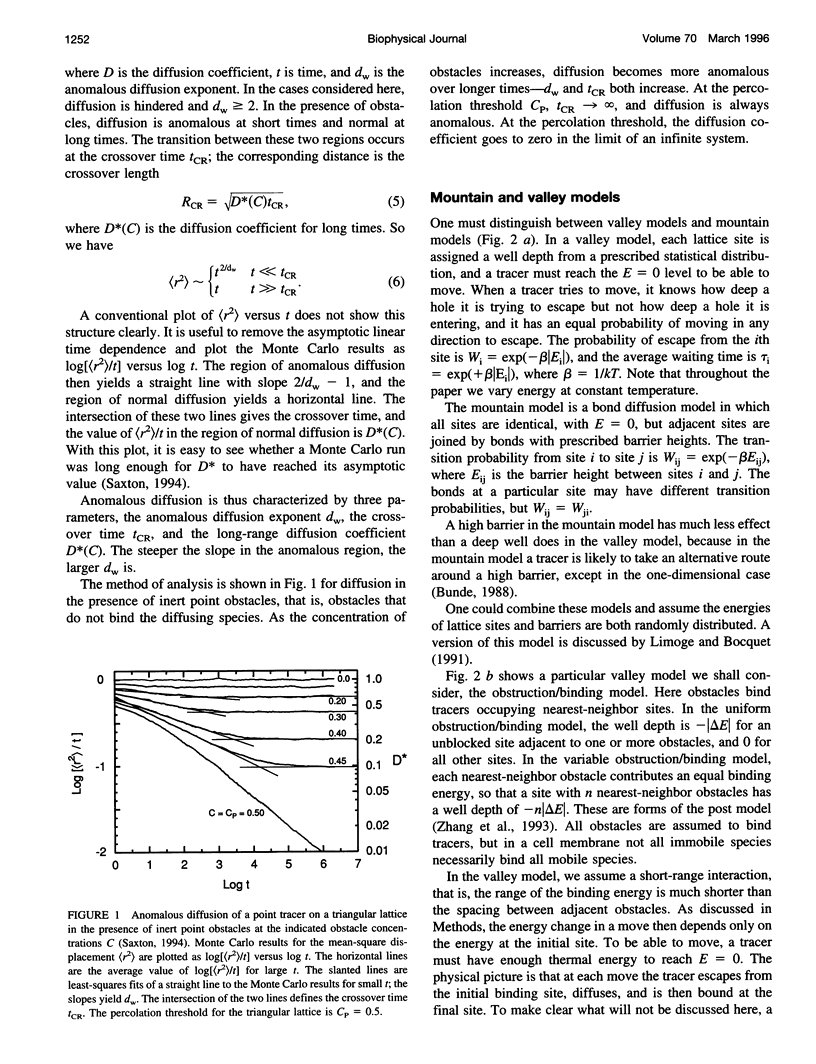
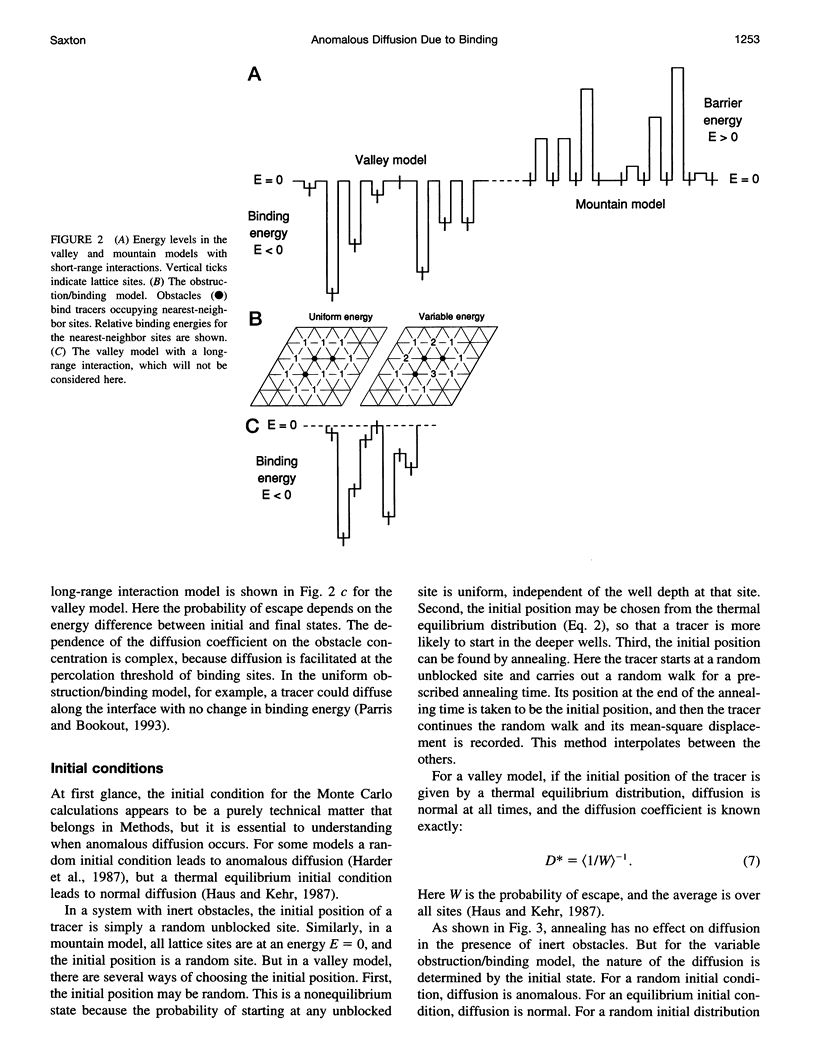
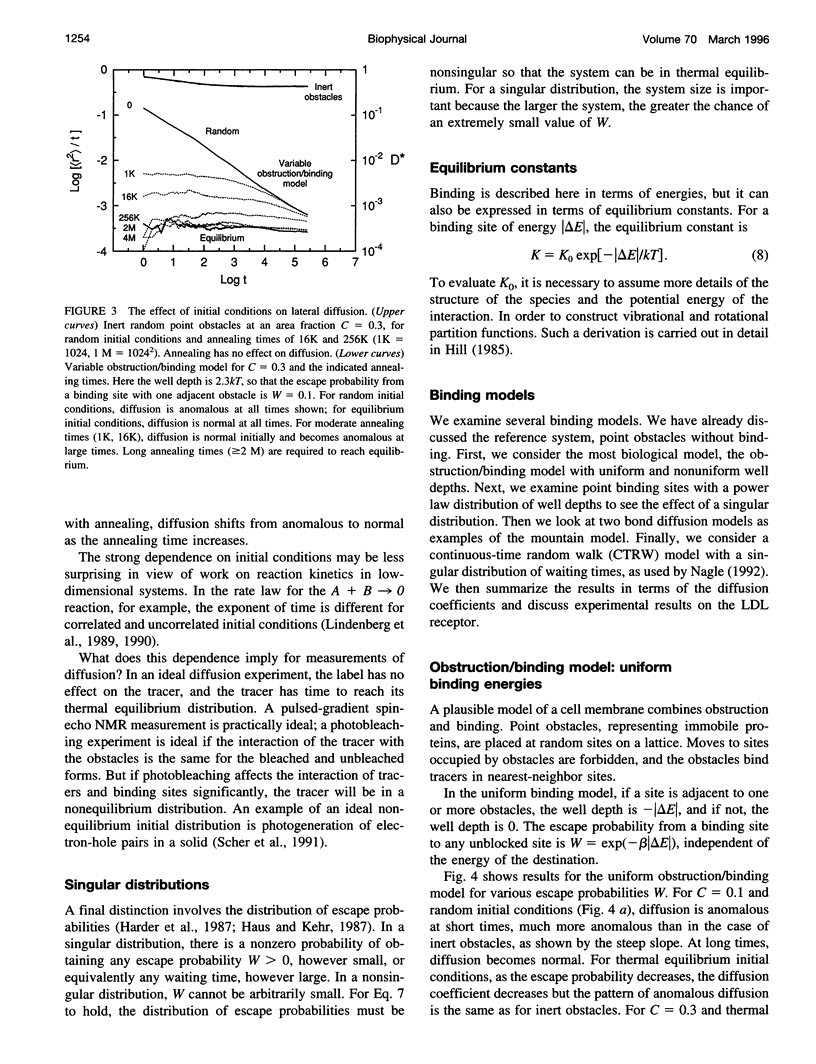
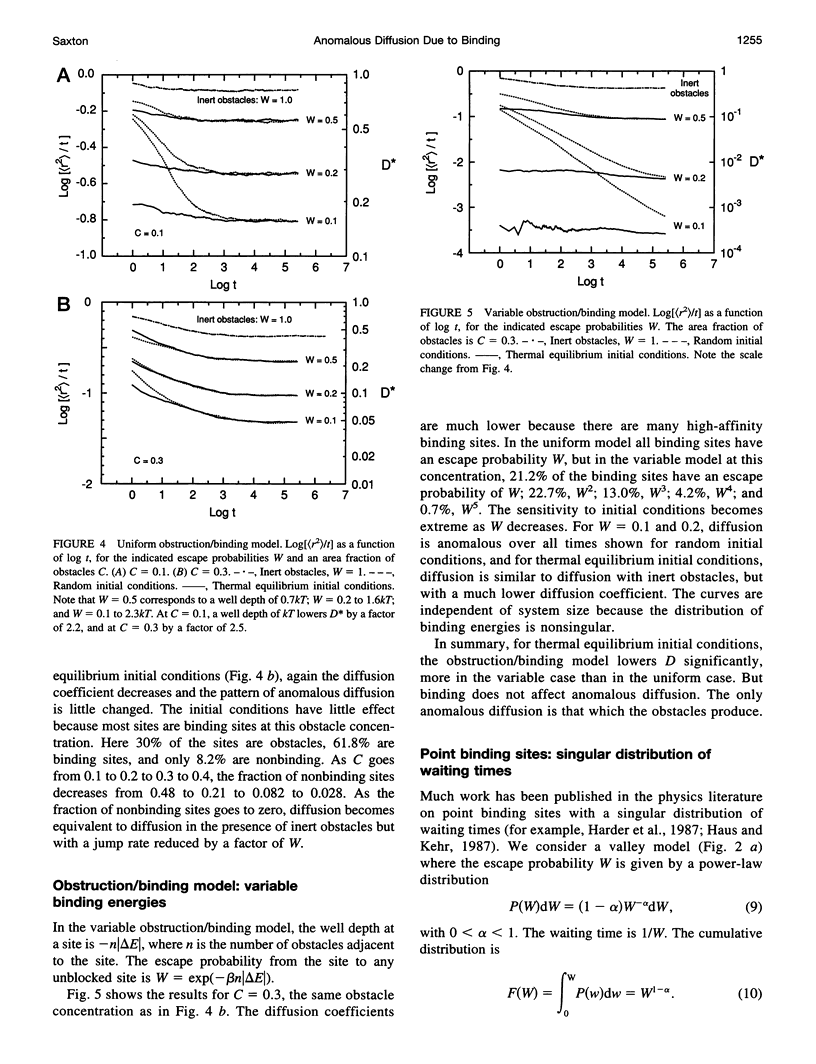
Abstract
In classical diffusion, the mean-square displacement increases linearly with time. But in the presence of obstacles or binding sites, anomalous diffusion may occur, in which the mean-square displacement is proportional to a nonintegral power of time for some or all times. Anomalous diffusion is discussed for various models of binding, including an obstruction/binding model in which immobile membrane proteins are represented by obstacles that bind diffusing particles in nearest-neighbor sites. The classification of binding models is considered, including the distinction between valley and mountain models and the distinction between singular and nonsingular distributions of binding energies. Anomalous diffusion is sensitive to the initial conditions of the measurement. In valley models, diffusion is anomalous if the diffusing particles start at random positions but normal if the particles start at thermal equilibrium positions. Thermal equilibration leads to normal diffusion, or to diffusion as normal as the obstacles allow.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambaye H, Kehr KW. Asymptotic diffusion coefficient of particles in a random medium. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1995 May;51(5):5101–5102. doi: 10.1103/physreve.51.5101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. M., Georgiou G. N., Morrison I. E., Stevenson G. V., Cherry R. J. Tracking of cell surface receptors by fluorescence digital imaging microscopy using a charge-coupled device camera. Low-density lipoprotein and influenza virus receptor mobility at 4 degrees C. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):415–425. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argyrakis P, Milchev A, Pereyra V, V, Kehr KW. Dependence of the diffusion coefficient on the energy distribution of random barriers. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1995 Oct;52(4):3623–3631. doi: 10.1103/physreve.52.3623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Webb W. W. Diffusion of low density lipoprotein-receptor complex on human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):846–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussell S. J., Koch D. L., Hammer D. A. Effect of hydrodynamic interactions on the diffusion of integral membrane proteins: diffusion in plasma membranes. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1836–1849. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80360-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M., Stroynowski I. Differences between the lateral organization of conventional and inositol phospholipid-anchored membrane proteins. A further definition of micrometer scale membrane domains. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1143–1150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M., Zúiga M. C., Sheetz M. P. Truncation mutants define and locate cytoplasmic barriers to lateral mobility of membrane glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3378–3382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh R. N., Webb W. W. Automated detection and tracking of individual and clustered cell surface low density lipoprotein receptor molecules. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1301–1318. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80939-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder H, Havlin S, Bunde A. Diffusion on fractals with singular waiting-time distribution. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1987 Sep 1;36(7):3874–3879. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.36.3874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenberg K, West BJ, Kopelman R. Diffusion-limited A+B-->0 reaction: Correlated initial condition. Phys Rev A. 1990 Jul 15;42(2):890–894. doi: 10.1103/physreva.42.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Long tail kinetics in biophysics? Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81602-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris PE, Bookout BD. Trapping-to-percolation transition in the hopping diffusion of substitutionally disordered solids with a binary energy distribution. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1993 Jan 1;47(1):562–565. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.47.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Myers J., Holowka D., Baird B., Webb W. W. Molecular crowding on the cell surface. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):61–64. doi: 10.1126/science.2962287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Anomalous diffusion due to obstacles: a Monte Carlo study. Biophys J. 1994 Feb;66(2 Pt 1):394–401. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80789-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion and aggregation. A Monte Carlo study. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81821-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. Dependence on tracer size. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81471-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. Single-particle diffusion. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1766–1780. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81548-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. The effect of mobile obstacles. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):989–997. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83291-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schram V., Tocanne J. F., Lopez A. Influence of obstacles on lipid lateral diffusion: computer simulation of FRAP experiments and application to proteoliposomes and biomembranes. Eur Biophys J. 1994;23(5):337–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00188657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Schindler M., Koppel D. E. Lateral mobility of integral membrane proteins is increased in spherocytic erythrocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):510–511. doi: 10.1038/285510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simson R., Sheets E. D., Jacobson K. Detection of temporary lateral confinement of membrane proteins using single-particle tracking analysis. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):989–993. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79972-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yechiel E., Edidin M. Micrometer-scale domains in fibroblast plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):755–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Lee G. M., Jacobson K. Protein lateral mobility as a reflection of membrane microstructure. Bioessays. 1993 Sep;15(9):579–588. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


