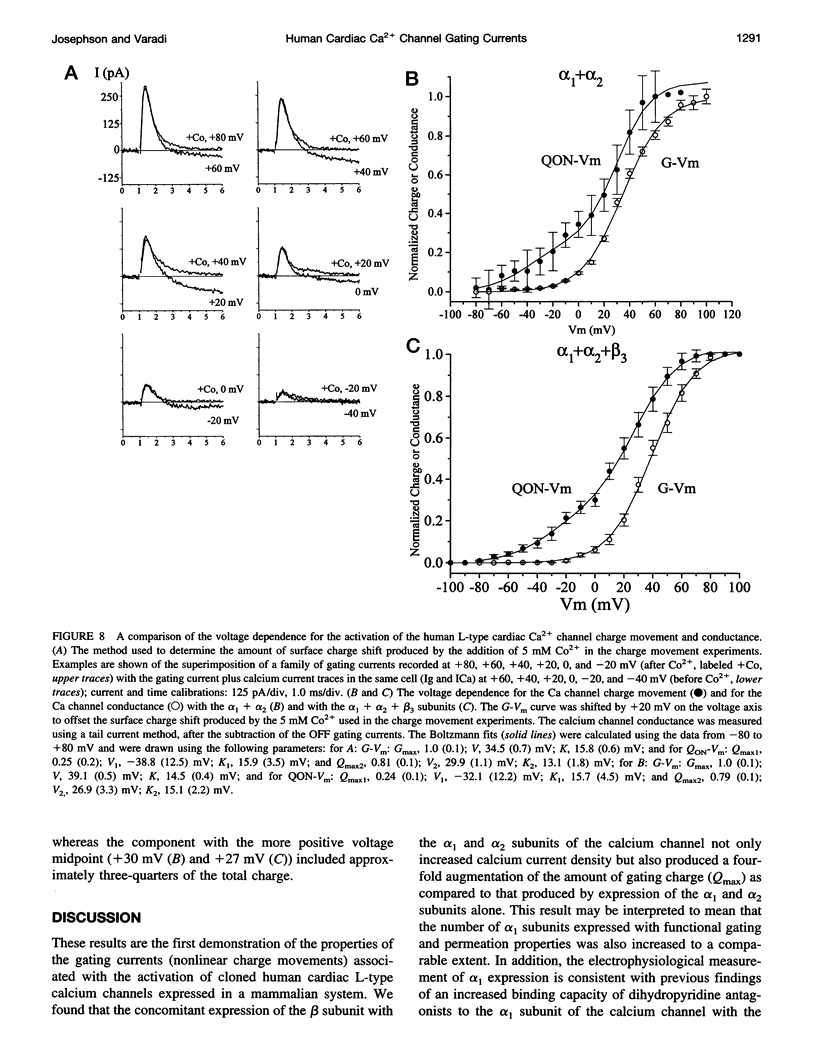
Abstract
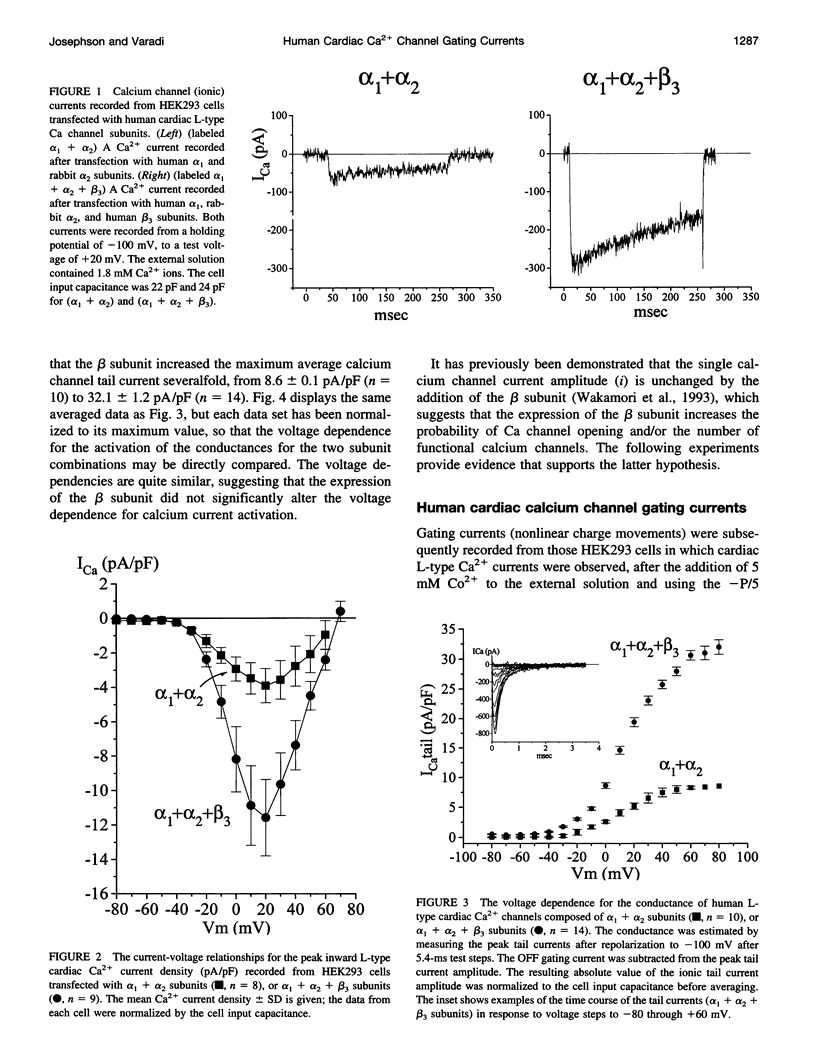
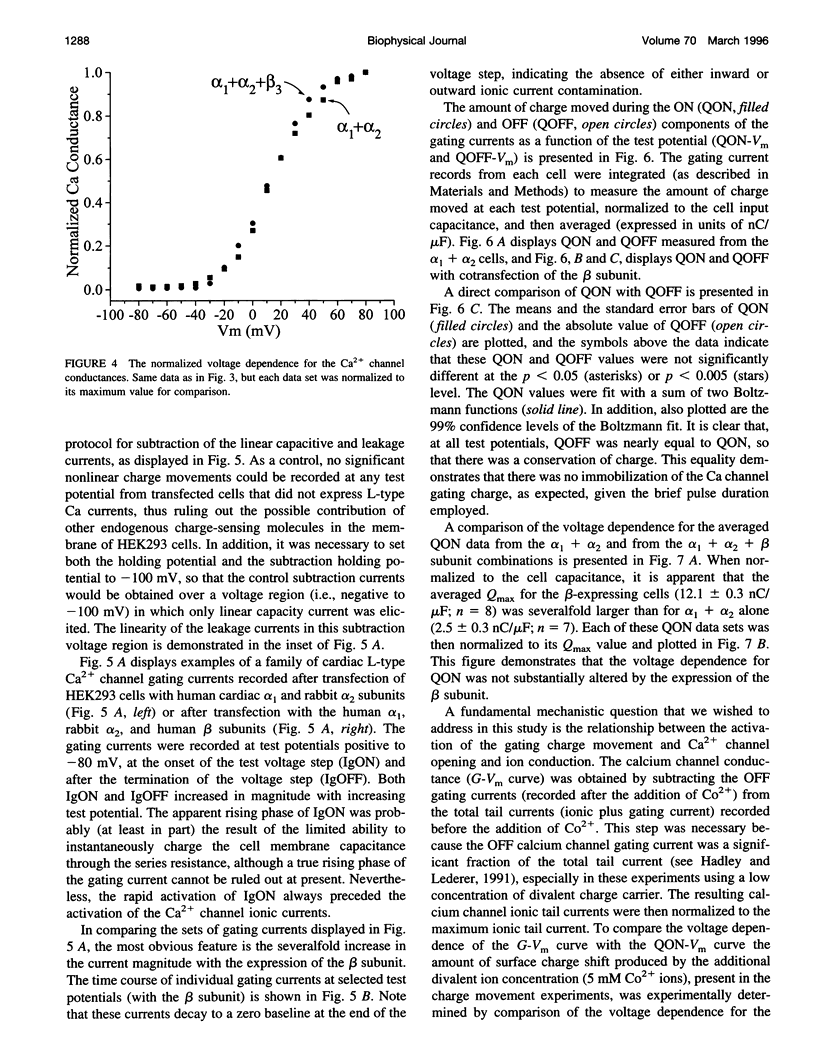
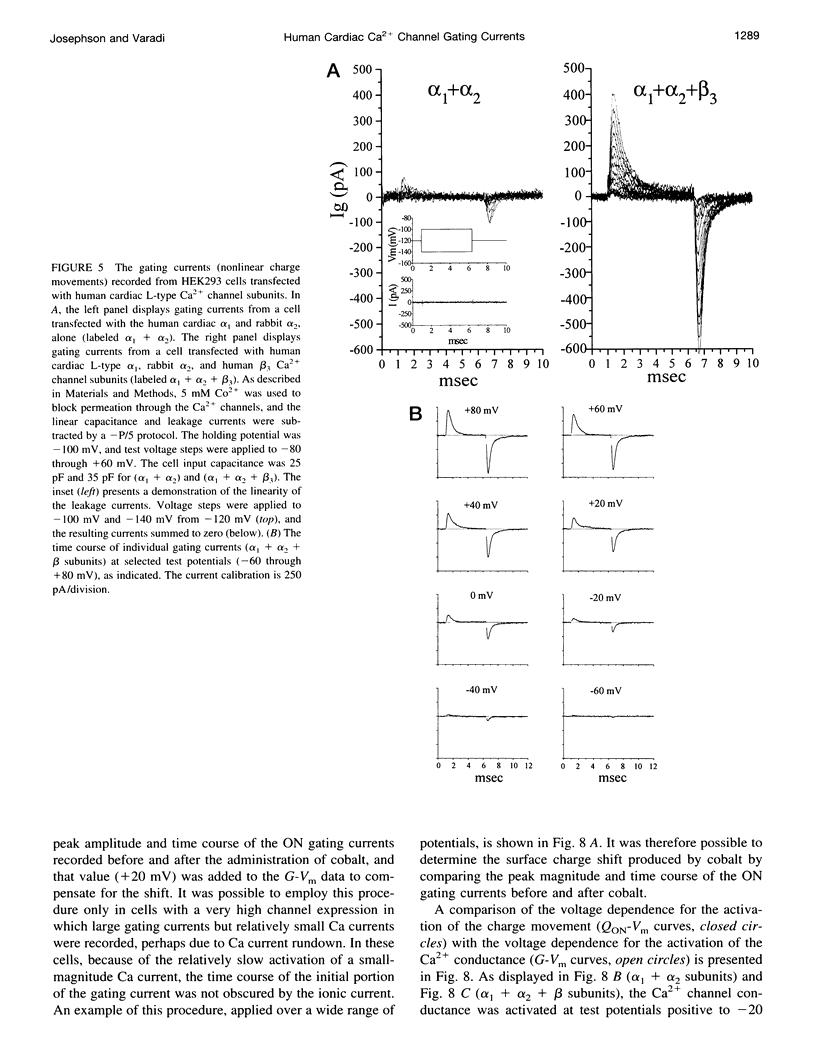
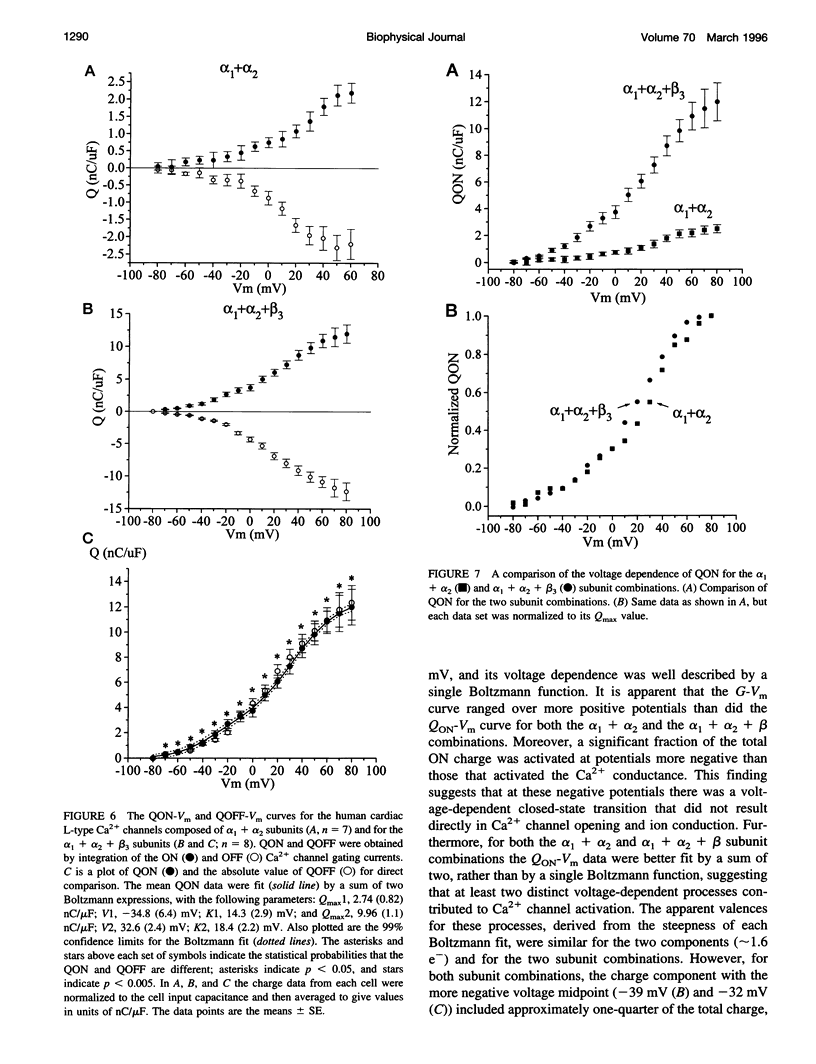
The properties of the gating currents (nonlinear charge movements) of human cardiac L-type Ca2- channels and their relationship to the activation of the Ca2+ channel (ionic) currents were studied using a mammalian expression system. Cloned human cardiac alpha1 + rabbit alpha 2 subunits or human cardiac alpha 1 + rabbit alpha 2 + human beta 3 subunits were transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. The maximum Ca2+ current density increased from -3.9 +/- 0.9 pA/pF for the alpha 1 + alpha 2 subunits to -11.6 +/- 2.2 pA/pF for alpha 1 + alpha 2 + beta 3 subunits. Calcium channel gating currents were recorded after the addition of 5 mM Co2+, using a -P/5 protocol. The maximum nonlinear charge movement (Qmax) increased from 2.5 +/- 0.3 nC/muF for alpha 1 + alpha 2 subunit to 12.1 +/- 0.3 nC/muF for alpha 1 + alpha 2 + beta 3 subunit expression. The QON was equal to the QOFF for both subunit combinations. The QON-Vm data were fit by a sum of two Boltzmann expressions and ranged over more negative potentials, as compared with the voltage dependence for activation of the Ca2+ conductance. We conclude that 1) the beta subunit increases the number of functional alpha 1 subunits expressed in the plasma membrane of these cells and 2) the voltage-dependent activation of the human cardiac L-type calcium channel involves the movements of at least two nonidentical and functionally distinct gating structures.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P., Rios E. Nonlinear charge movement in mammalian cardiac ventricular cells. Components from Na and Ca channel gating. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):65–93. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collin T., Lory P., Taviaux S., Courtieu C., Guilbault P., Berta P., Nargeot J. Cloning, chromosomal location and functional expression of the human voltage-dependent calcium-channel beta 3 subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 15;220(1):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waard M., Pragnell M., Campbell K. P. Ca2+ channel regulation by a conserved beta subunit domain. Neuron. 1994 Aug;13(2):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90363-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. B., Williams M. E., Ways N. R., Brenner R., Sharp A. H., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P., McKenna E., Koch W. J., Hui A. Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the alpha 1 and alpha 2 subunits of a DHP-sensitive calcium channel. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2458626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley R. W., Lederer W. J. Intramembrane charge movement in guinea-pig and rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:601–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley R. W., Lederer W. J. Properties of L-type calcium channel gating current in isolated guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Aug;98(2):265–285. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Biel M., Flockerzi V. Molecular basis for Ca2+ channel diversity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:399–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Catterall W. A. Auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson I. R., Cui Y. Cardiac channel gating charge movements: recovery from inactivation. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Sep;430(5):682–689. doi: 10.1007/BF00386162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson I. R., Cui Y. Voltage- and concentration-dependent effects of lidocaine on cardiac Na channel gating charge movements. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(5-6):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00374569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson I. R., Sperelakis N. Kinetic and steady-state properties of Na+ channel and Ca2+ channel charge movements in ventricular myocytes of embryonic chick heart. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Aug;100(2):195–216. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöckner U., Mikala G., Varadi M., Varadi G., Schwartz A. Involvement of the carboxyl-terminal region of the alpha 1 subunit in voltage-dependent inactivation of cardiac calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17306–17310. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuniyasu A., Oka K., Ide-Yamada T., Hatanaka Y., Abe T., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y. Structural characterization of the dihydropyridine receptor-linked calcium channel from porcine heart. J Biochem. 1992 Aug;112(2):235–242. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory P., Varadi G., Slish D. F., Varadi M., Schwartz A. Characterization of beta subunit modulation of a rabbit cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit as expressed in mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 4;315(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81156-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitterdorfer J., Froschmayr M., Grabner M., Striessnig J., Glossmann H. Calcium channels: the beta-subunit increases the affinity of dihydropyridine and Ca2+ binding sites of the alpha 1-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 26;352(2):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00938-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Takaki S., Araki K., Tashiro F., Tominaga A., Takatsu K., Yamamura K. Expression vector system based on the chicken beta-actin promoter directs efficient production of interleukin-5. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely A., Wei X., Olcese R., Birnbaumer L., Stefani E. Potentiation by the beta subunit of the ratio of the ionic current to the charge movement in the cardiac calcium channel. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):575–578. doi: 10.1126/science.8211185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., De Waard M., Mori Y., Tanabe T., Snutch T. P., Campbell K. P. Calcium channel beta-subunit binds to a conserved motif in the I-II cytoplasmic linker of the alpha 1-subunit. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):67–70. doi: 10.1038/368067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-García M. T., Kamp T. J., Marbán E. Functional properties of cardiac L-type calcium channels transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. Roles of alpha 1 and beta subunits. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Feb;105(2):289–305. doi: 10.1085/jgp.105.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D., Mikala G., Yatani A., Engle D. B., Iles D. E., Segers B., Sinke R. J., Weghuis D. O., Klöckner U., Wakamori M. Cloning, chromosomal localization, and functional expression of the alpha 1 subunit of the L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel from normal human heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6228–6232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadi G., Lory P., Schultz D., Varadi M., Schwartz A. Acceleration of activation and inactivation by the beta subunit of the skeletal muscle calcium channel. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):159–162. doi: 10.1038/352159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadi G., Mori Y., Mikala G., Schwartz A. Molecular determinants of Ca2+ channel function and drug action. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Feb;16(2):43–49. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)88977-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamori M., Mikala G., Schwartz A., Yatani A. Single-channel analysis of a cloned human heart L-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit and the effects of a cardiac beta subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 15;196(3):1170–1176. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling A., Bosse E., Cavalié A., Bottlender R., Ludwig A., Nastainczyk W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Stable co-expression of calcium channel alpha 1, beta and alpha 2/delta subunits in a somatic cell line. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:749–765. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


