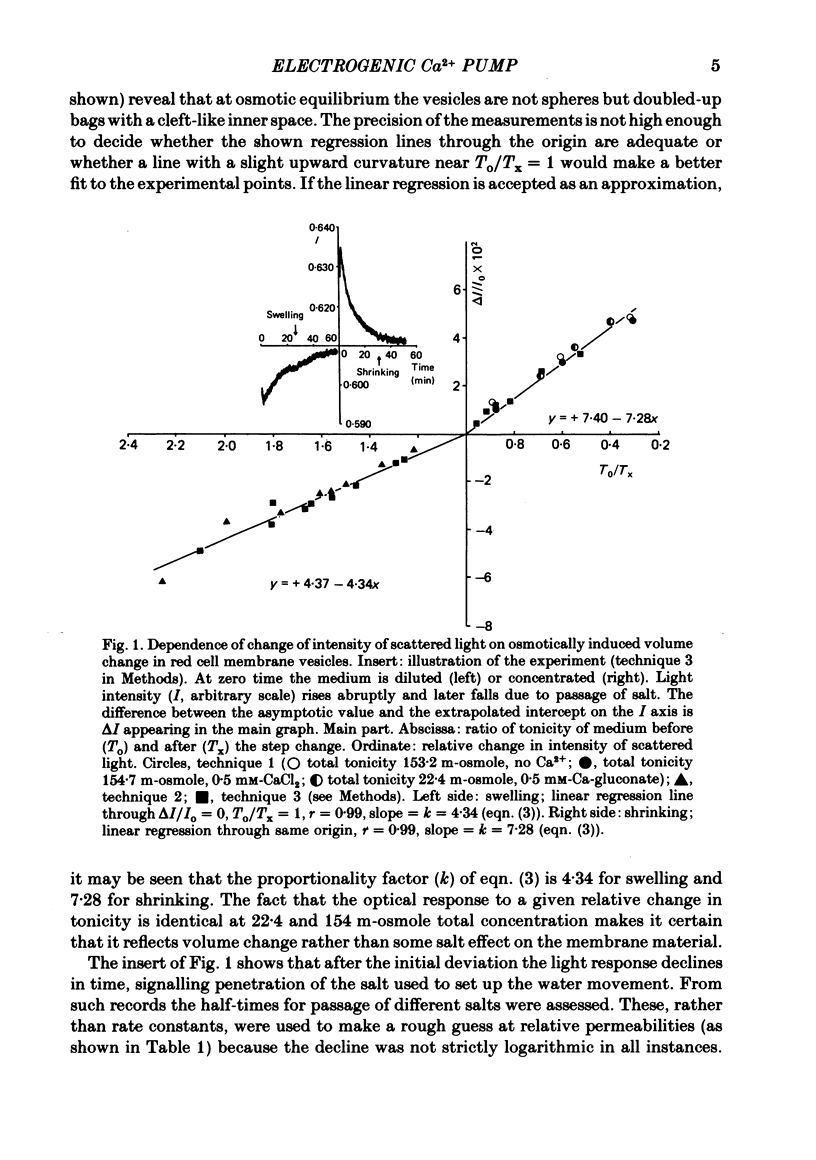
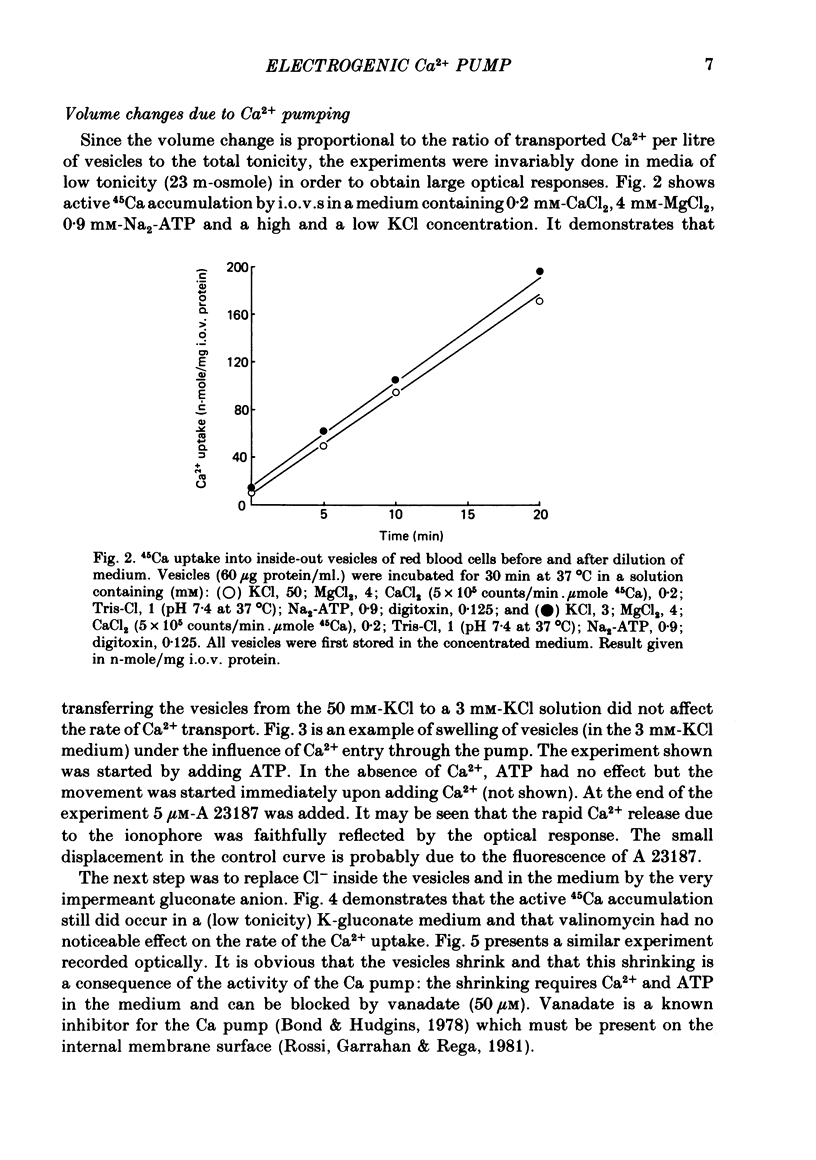
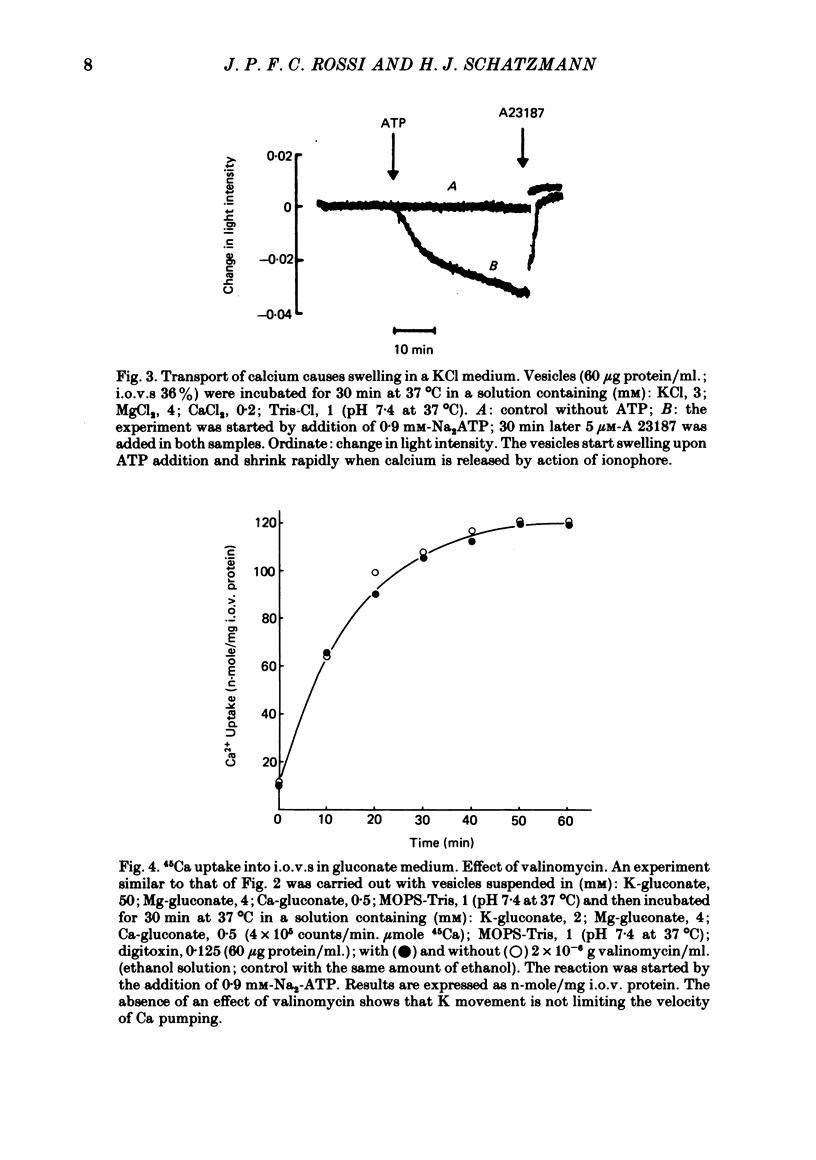
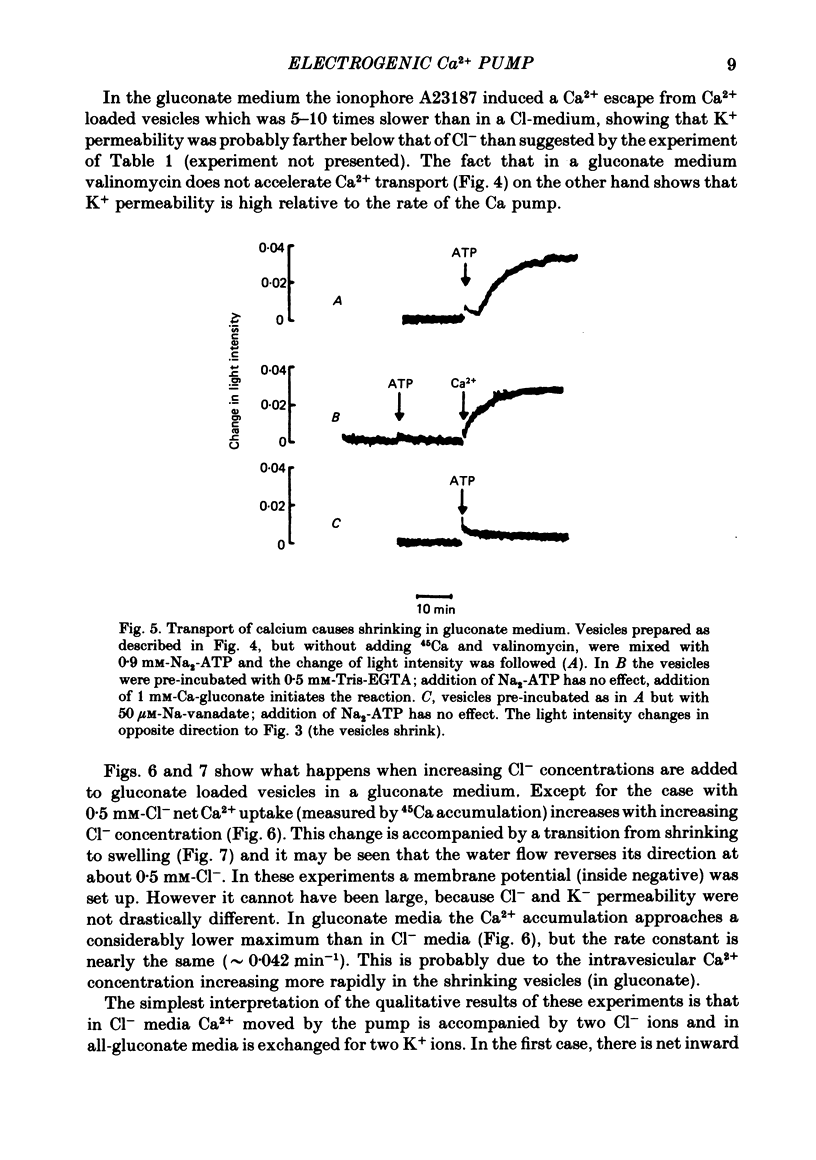
Abstract
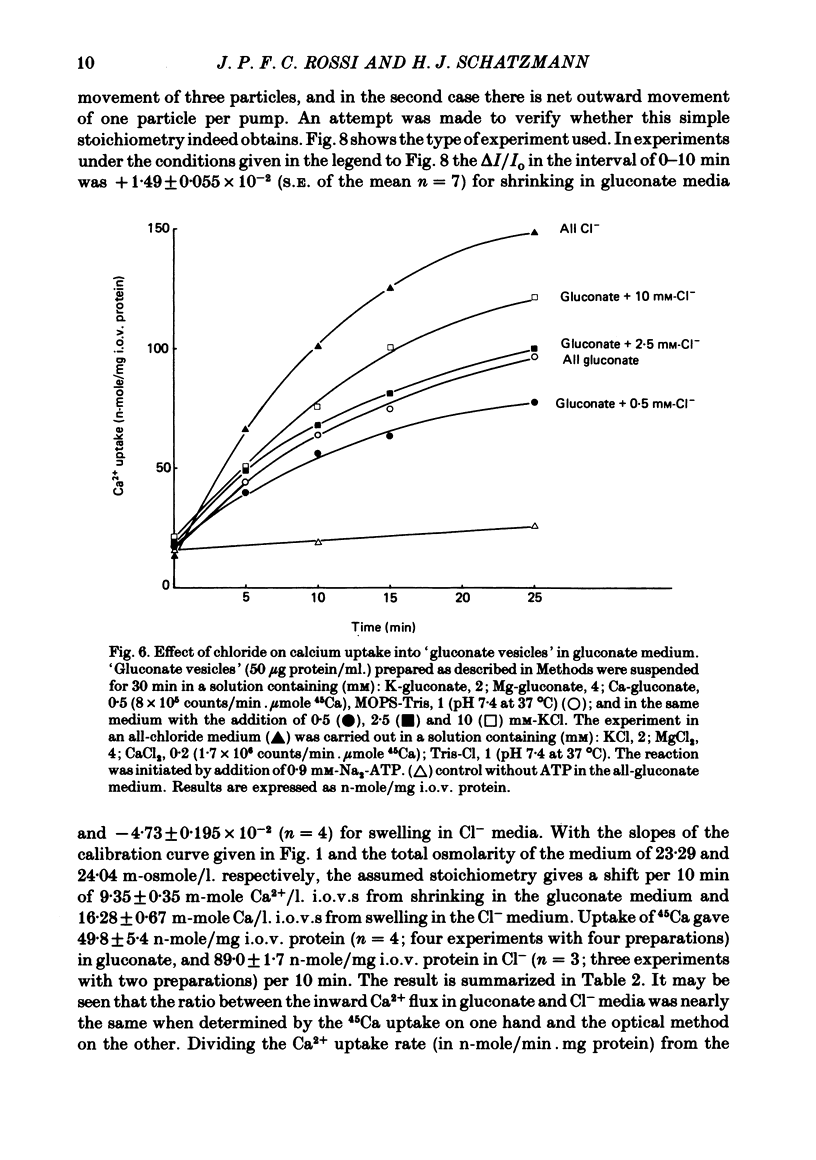
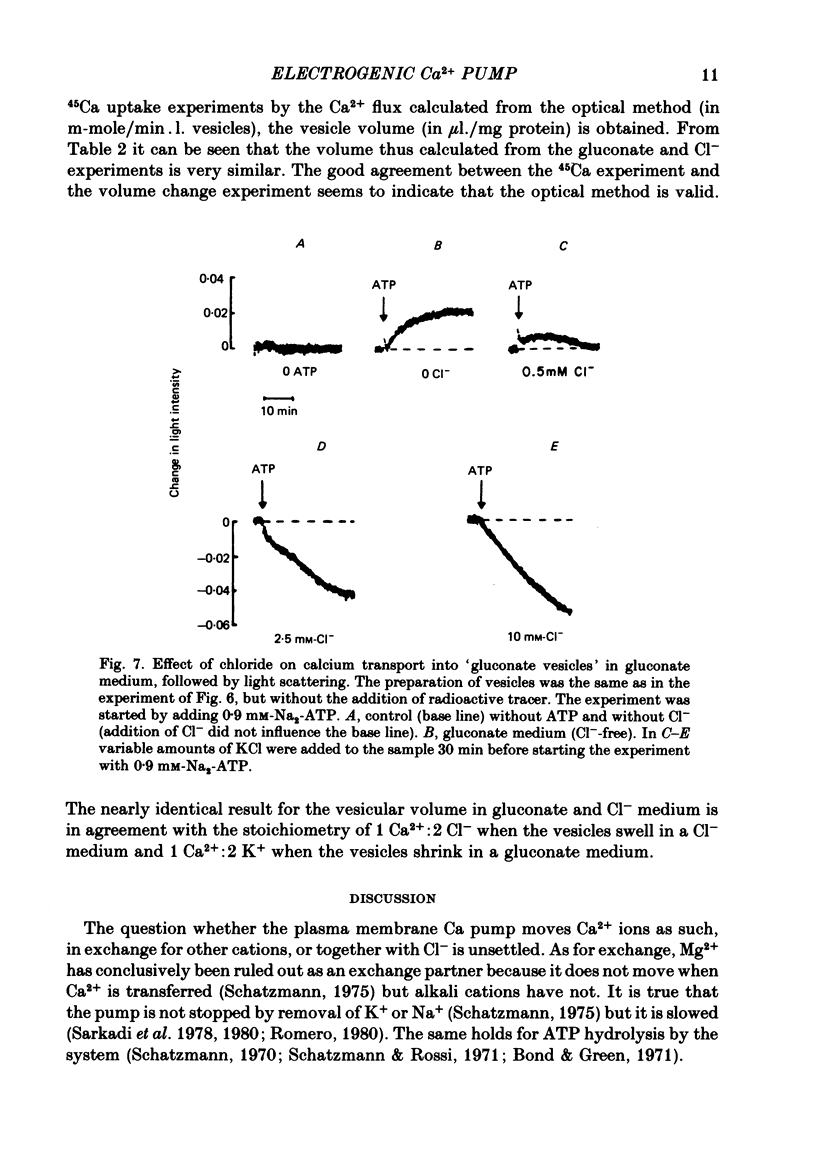
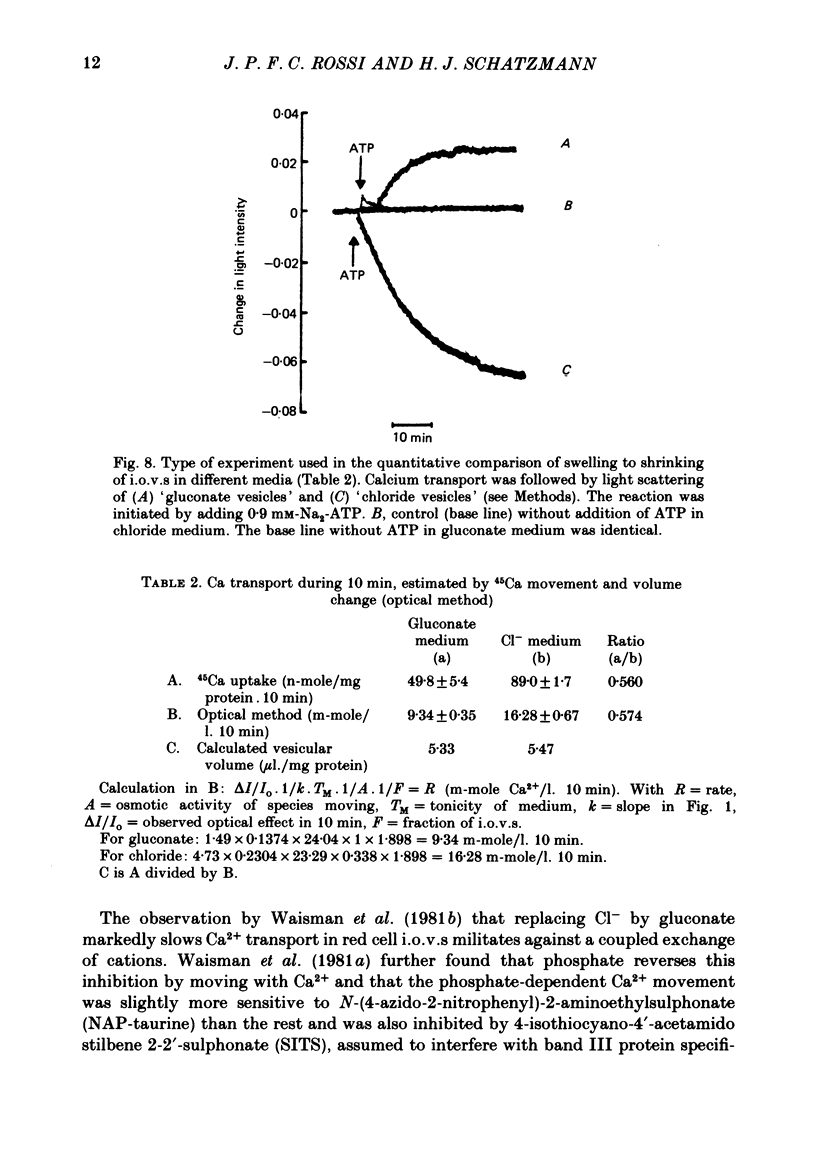
1. In inside-out vesicles of high potassium permeability, prepared from human red cell membranes, volume changes accompanying the action of the Ca2+ pump were measured by recording the intensity of light scattered by a suspension of these vesicles. Replacing Cl- by the impermeant gluconate anion changed swelling into shrinking. 2. Assuming that in Cl- media two Cl- ions accompany one Ca+ ion moved by the pump and in gluconate media two K+ ions are exchanged for one Ca2+ ion resulted in a good agreement between relative Ca2+ transport rate obtained from the volume change and from direct measurement of 45Ca uptake in the two media. 3. The fact that it is possible to change co-transport of Ca with Cl- into counter-transport of Ca2+ for K+ rules out that within the pump there is an obligatory coupling of Ca2+ movement with movement of another ion species (including the proton). The conclusion, therefore, is that the Ca2+ pump must be electrogenic. 4. The combination of measurement of volume change with direct measurement of 45Ca movement yielded 5-6 microliter/mg protein for the volume of the vesicles.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berenblum I., Chain E. Studies on the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):286–294. doi: 10.1042/bj0320286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond G. H., Green J. W. Effects of monovalent cations on the (Mg 2+ + Ca 2+ )-dependent ATPase of the red cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDOS G. The function of calcium in the potassium permeability of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Dec;30(3):653–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kometani T., Kasai M. Ion movement accompanied by calcium uptake of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles studied through the osmotic volume change by the light scattering method. J Membr Biol. 1980 Sep 30;56(2):159–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01875967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kometani T., Kasai M. Ionic permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles measured by light scattering method. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jul 18;41(4):295–308. doi: 10.1007/BF01871994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. P., Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. Vanadate inhibition of active Ca2+ transport across human red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 6;648(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Macintyre J. D., Gárdos G. Kinetics of active calcium transport in inside-out red cell membrane vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80526-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Szász I., Gárdos G. Characteristics and regulation of active calcium transport in inside-out red cell membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):326–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. Dependence on calcium concentration and stoichiometry of the calcium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):551–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. Role of magnesium in the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-stimulated membrane ATPase of human red blood cells. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):149–158. doi: 10.1007/BF01869946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Rossi G. L. (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )-activated membrane ATPases in human red cells and their possible relations to cation transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Gimble J. M., Goodman D. B., Rasmussen H. Studies of the Ca2+ transport mechanism of human erythrocyte inside-out plasma membrane vesicles. II. Stimulation of the Ca2+ pump by phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):415–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Gimble J. M., Goodman D. B., Rasmussen H. Studies of the Ca2+ transport mechanism of human erythrocyte inside-out plasma membrane vesicles. III. Stimulation of the Ca2+ pump by anions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):420–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. L., Lee K. S. Active calcium ion uptake by inside-out and right side-out vesicles of red blood cell membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):462–475. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


