Abstract
1. The circadian rhythms of urinary excretion of water, sodium, chloride, potassium, urate, calcium and phosphate have been studied in several groups of volunteers. 2. These rhythms have been measured: under nychthemeral and constant routine regimens; while subjects were in an Isolation Unit or allowed free egress into society; with spontaneous changes in dietary intake; or after potassium-loading. 3. A direct relationship between 24 h mean rate of excretion and range of excretion was found in all circumstances and for all variables; this relationship was found also when the mesor and amplitude of the cosine curve best describing each 24 h of data were considered. 4. These relationships derive from the observation that, with increases in 24 h mean rates of excretion, nocturnal rates increased less than diurnal rates. 5. This differential sensitivity as between the night and day times has both endogenous and exogenous components. 6. It is suggested that circadian rhythms of urinary excretion result at least partially from this differential sensitivity of the kidney to homeostatic control mechanisms.
Full text
PDF

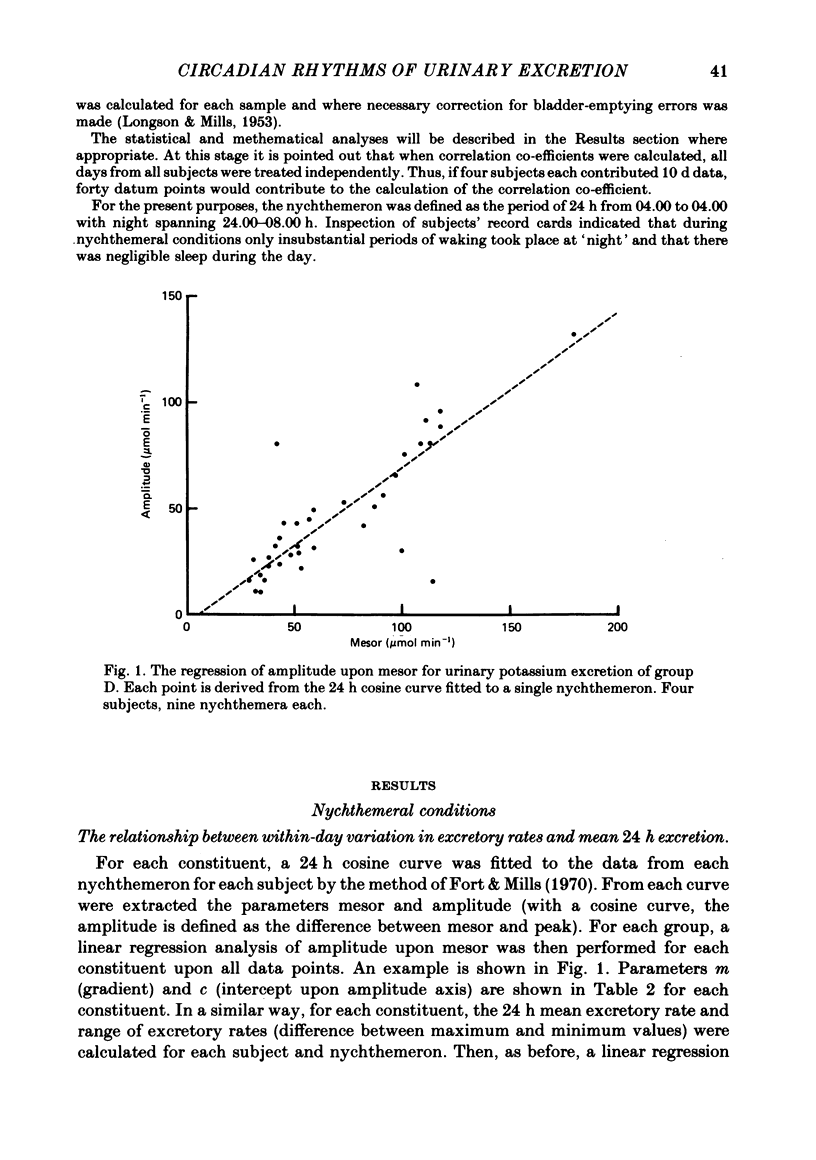
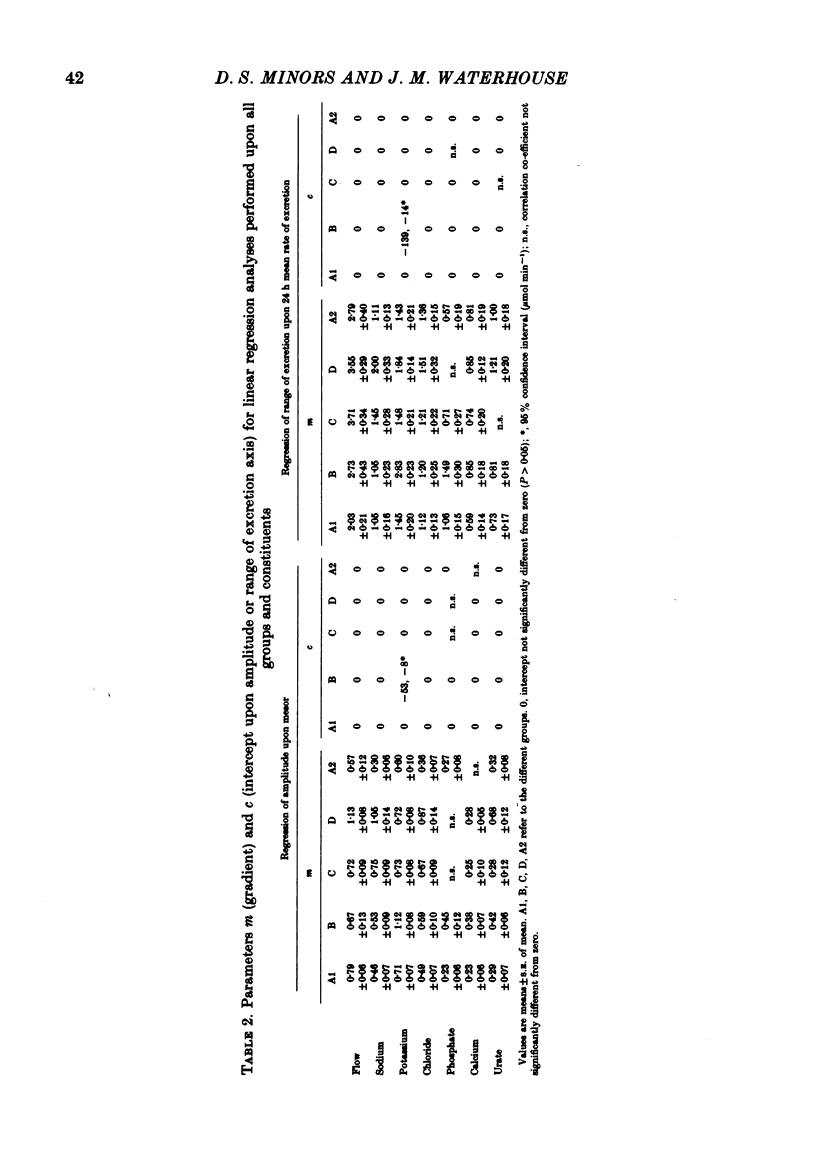

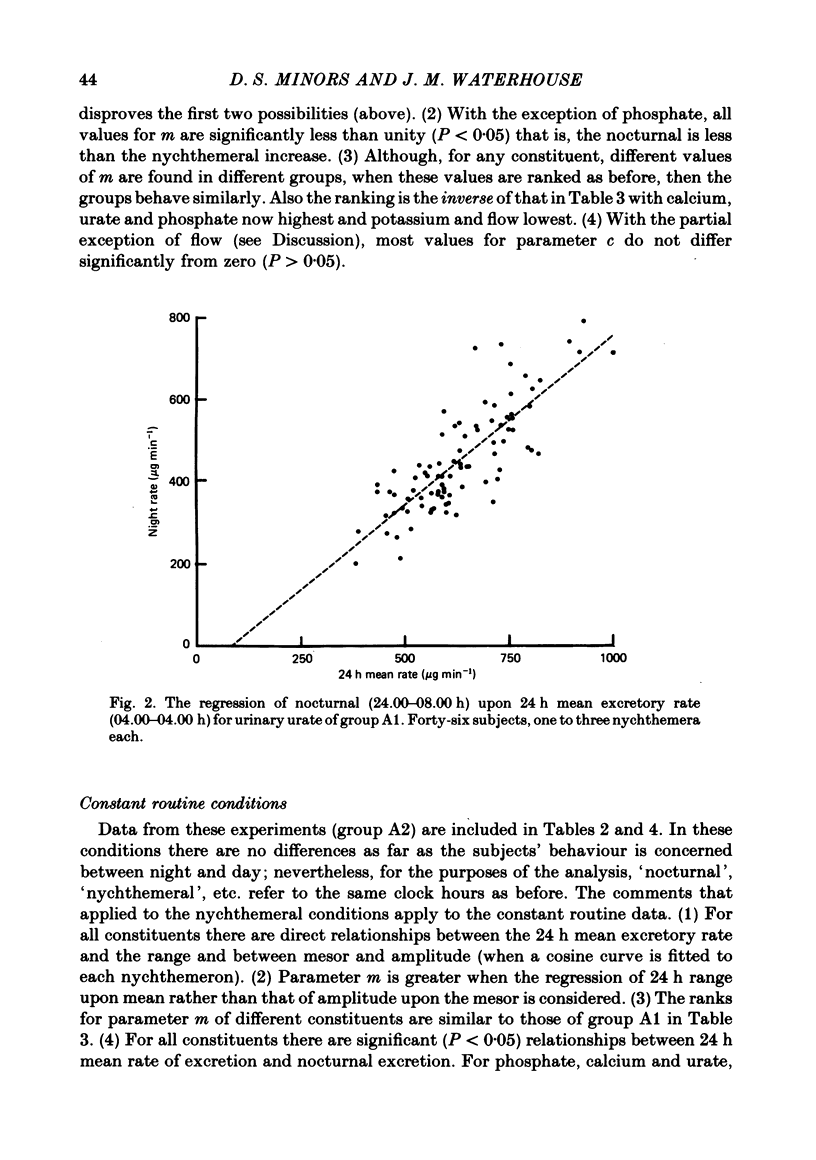
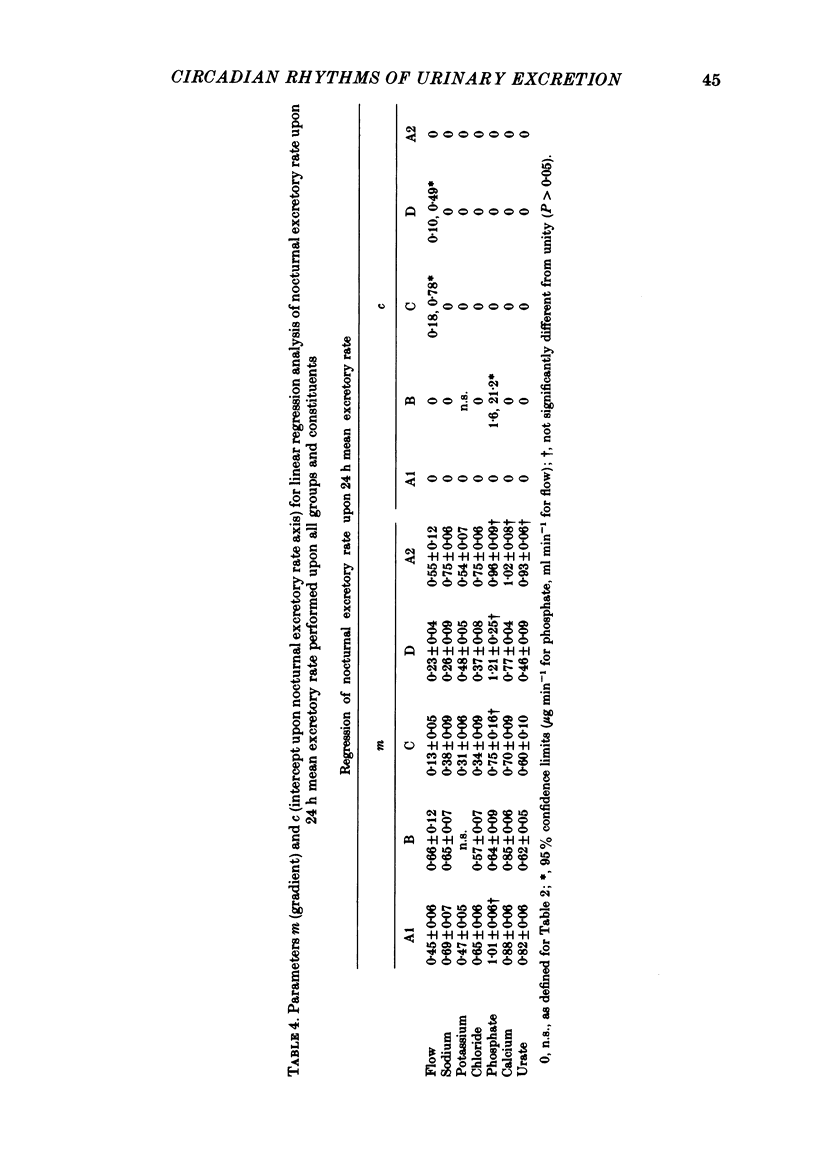





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aschoff J. Features of circadian rhythms relevant for the design of shift schedules. Ergonomics. 1978 Oct;21(10):739–754. doi: 10.1080/00140137808931777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aschoff J., Hoffmann K., Pohl H., Wever R. Re-entrainment of circadian rhythms after phase-shifts of the Zeitgeber. Chronobiologia. 1975 Jan-Mar;2(1):23–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aschoff J., von Saint Paul U. Circadian rhythms of brain temperature in the chicken, measured at different levels of constant illumination. Jpn J Physiol. 1973 Feb;23(1):69–80. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.23.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslanian N. L., Assatrian D. G., Bagdassarian R. A., Kurginian A. G., Shukhian V. M. Circadian rhythms of electrolyte excretion in hypertensive patients and healthy subjects. Chronobiologia. 1978 Jul-Sep;5(3):251–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULOW K. Respiration and wakefulness in man. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1963;209:1–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A. L., Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. The effect of real and simulated time-zone shifts upon the circadian rhythms of body temperature, plasma 11-hydroxycorticosteroids, and renal excretion in human subjects. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):227–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort A., Mills J. N. Fitting sine curves to 24 h urinary data. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):657–658. doi: 10.1038/226657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith R. S., Siemsen A. W., Mason A. D., Jr, Forland M. Primary role of plasma hydrocortisone concentration in the regulation of the normal forenoon pattern of urinary phosphate excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Dec;25(12):1649–1659. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-12-1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halberg F., Reinhardt J., Bartter F. C., Delea C., Gordon R., Reinberg A., Ghata J., Halhuber M., Hofmann H., Günther R. Agreement in endpoints from circadian rhythmometry on healthy humans beings living on different continents. Experientia. 1969 Jan 15;25(1):107–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01903927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier P., Knapp M. S., Cove-Smith R. Circadian variations in urine excretion in chronic renal failure. Q J Med. 1980 Autumn;49(196):461–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass D. A., Sulzman F. M., Fuller C. A., Moore-Ede M. C. Renal responses to central vascular expansion are suppressed at night in conscious primates. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):F343–F351. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.4.F343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R., LOBBAN M. C. Dissociation of diurnal rhythms in human subjects living on abnormal time routines. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1957 Oct;42(4):371–386. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1957.sp001281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R., LOBBAN M. C. Patterns of electrolyte excretion in human subjects during a prolonged period of life on a 22-hour day. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):670–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGSON D., MILLS J. N. The failure of the kidney to respond to respiratory acidosis. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):81–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann H. Circadian control of sodium and potassium balance: the relationship between mean and range of oscillation of 24-hour rhythms of renal excretion of sodium and potassium. Pflugers Arch. 1972;332(Suppl):R28–R28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann H., Rutenfranz J., Wever R. Untersuchungen zur Tagesperiodik der Reaktionszeit bei Nachtarbeit. II. Beziehungen zwischen Gleichwert und Schwingungsbreite. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1972;29(3):175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann H., Stiller S., Korz R. Biological balance of sodium and potassium: a control system with oscillating correcting variable. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 30;362(2):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00583639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N. Human circadian rhythms. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jan;46(1):128–171. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. Adaptation to abrupt time shifts of the oscillator(s) controlling human circadian rhythms. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:455–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. The effect of sleep upon human circadian rhythms. Chronobiologia. 1978 Jan-Mar;5(1):14–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Minors D. S., Waterhouse J. M. The physiological rhythms of subjects living on a day of abnormal length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):803–826. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N., Waterhouse J. M. Circadian rhythms over the course of a year in a man living alone. Int J Chronobiol. 1973;1(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minors D. S., Mills J. N., Waterhouse J. M. The circadian variations of the rates of excretion of urinary electrolytes and of deep body temperature. Int J Chronobiol. 1976;4(1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore Ede M. C., Brennan M. F., Ball M. R. Circadian variation of intercompartmental potassium fluxes in man. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):163–170. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLLBERGER A. Statistical aspects of diurnal biorhythm. Acta Anat (Basel) 1955;23(2):97–127. doi: 10.1159/000140988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagnucci A. H., Shapiro A. P., McDonald R. H., Jr Effects of upright posture on renal electrolyte cycles. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Jun;26(6):720–731. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.6.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSON L. G., Jr ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION IN RELATION TO DIURNAL CYCLES OF RENAL FUNCTION. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Sep;43:547–592. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196409000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesson L. G. Diurnal circadian rhythms of electrolyte excretion and filtration rate in end-stage renal disease. Nephron. 1980;26(5):211–214. doi: 10.1159/000181986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesson L. G. Diurnal circadian rhythms of renal function and electrolyte excretion in heart failure. Int J Chronobiol. 1979;6(2):109–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


