Abstract
1. Extracellular recordings of the responses of single caudal trigeminal nucleus neurones to non-noxious and noxious facial stimuli and to ionophoretically applied L-glutamate, L-aspartate and acetylcholine were made in urethane anaesthetized rats. 2. Neurones excited by non-noxious mechanical stimuli were located primarily in the magnocellular part of nucleus caudalis, whereas neurones excited by both noxious and non-noxious stimuli were located either ventromedially to the magnocellular part of nucleus caudalis or superficially to the substantia gelatinosa. 3. Both L-aspartate and L-glutamate were found to excite all neurones tested in nucleus caudalis. In contrast, however, acetylcholine was found to excite only 31% of the neurones tested. 4. Responses of nucleus caudalis neurones to non-noxious sensory stimulation were not antagonized by the excitatory amino acid antagonist D-alpha-aminoadipate, but were antagonized by cis-2, 3-piperidine dicarboxylate and gamma-D-glutamylglycine, two excitatory amino acid antagonists with a broader spectrum of action. 5. It is concluded that the chemical synaptic transmitter of non-nociceptive mechanoreceptive primary afferent fibres to nucleus caudalis may be a ligand for an excitatory amino acid receptor other than a D-alpha-aminoadipate-sensitive receptor. The synaptic receptor may thus be of the kainate or quisqualate type, and the transmitter possibly L-glutamate, L-aspartate or an as yet unidentified substance.
Full text
PDF

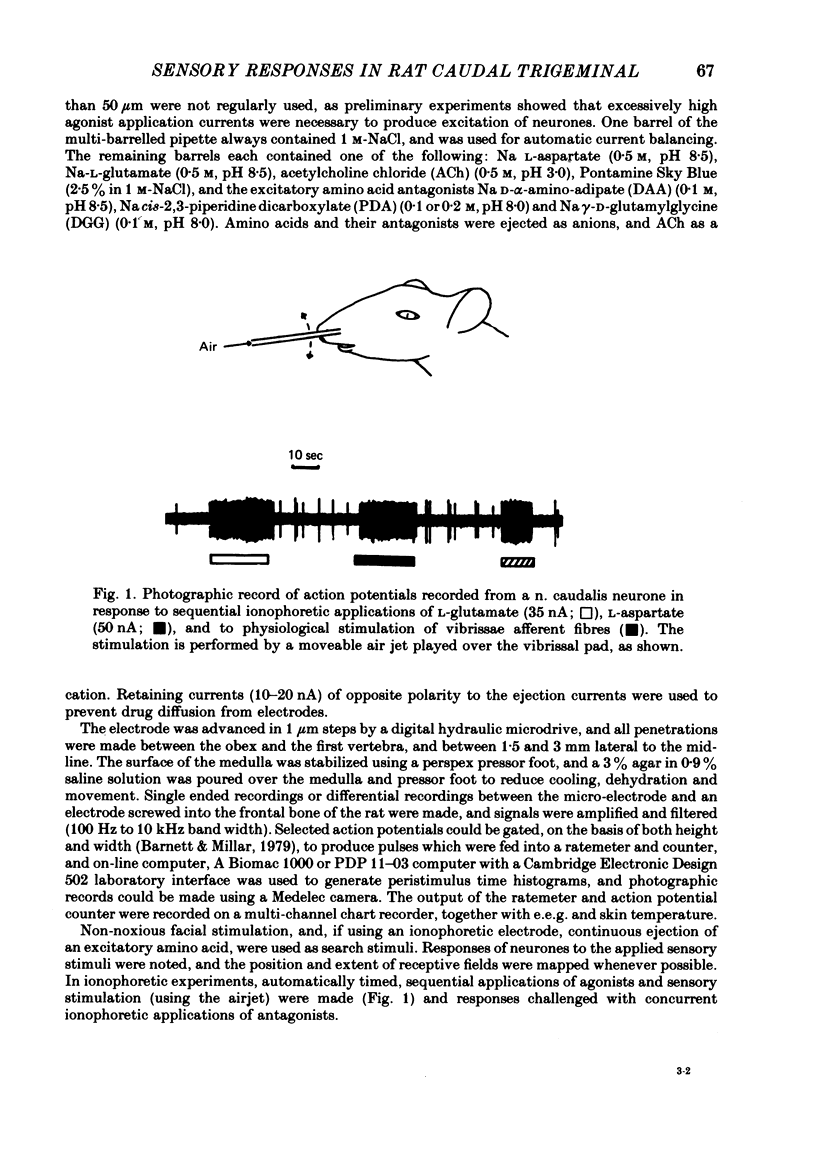

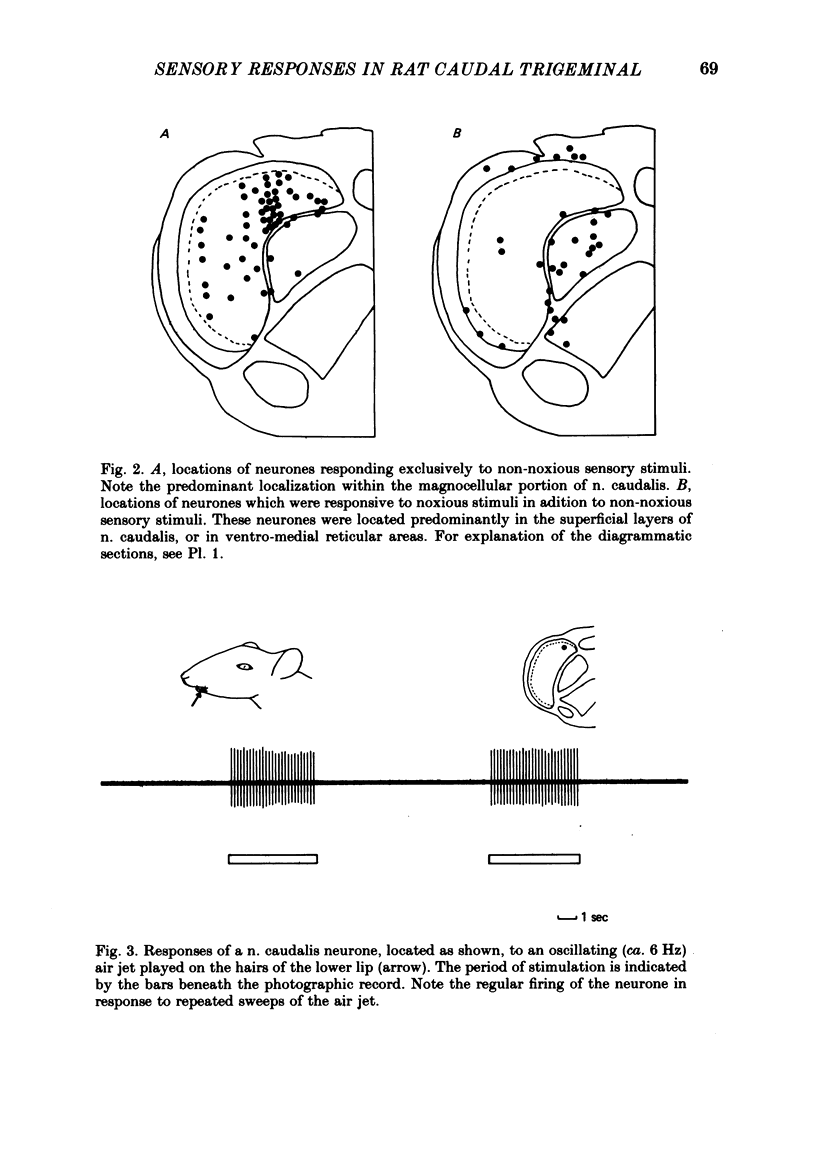
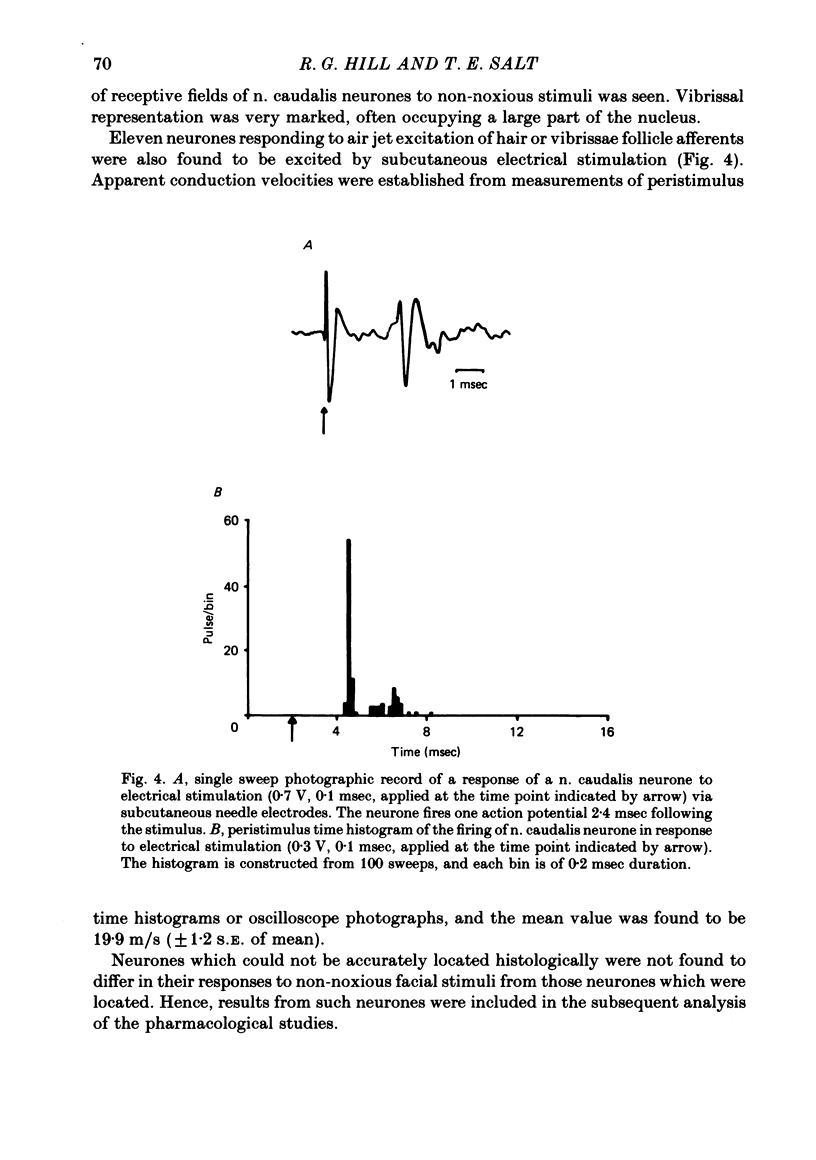
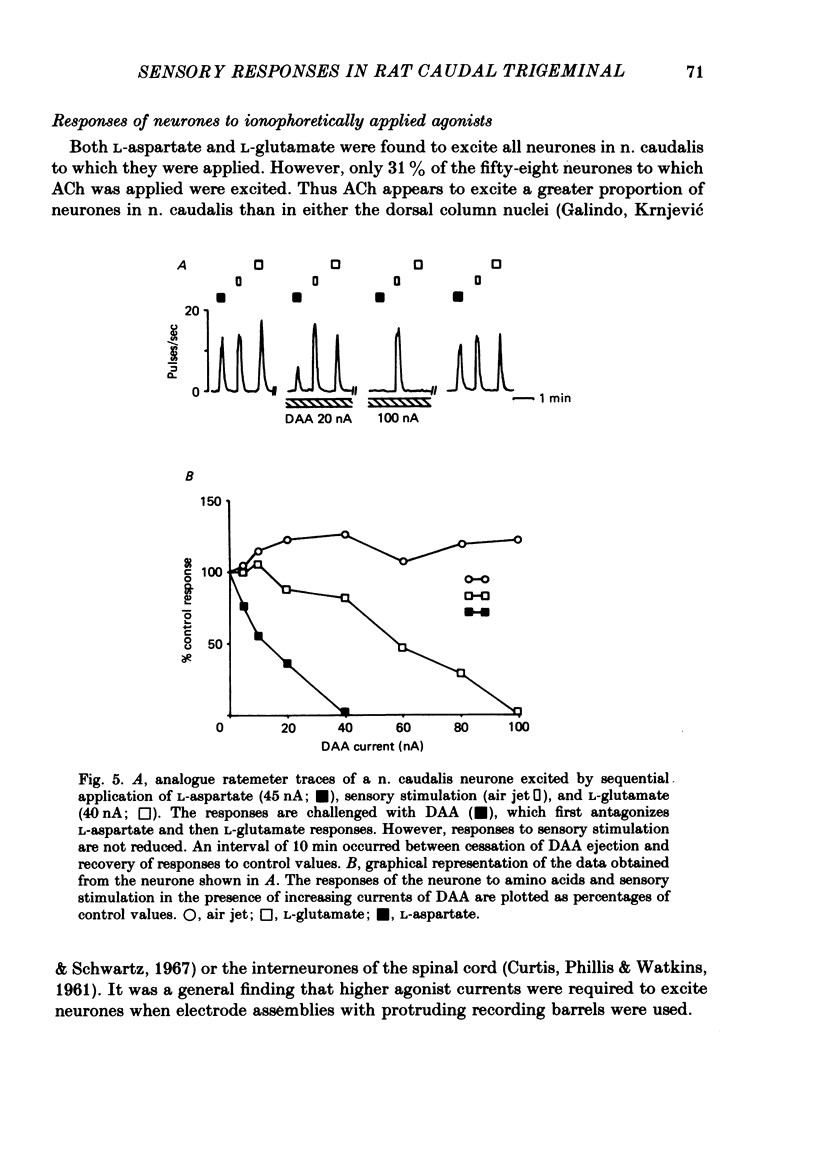
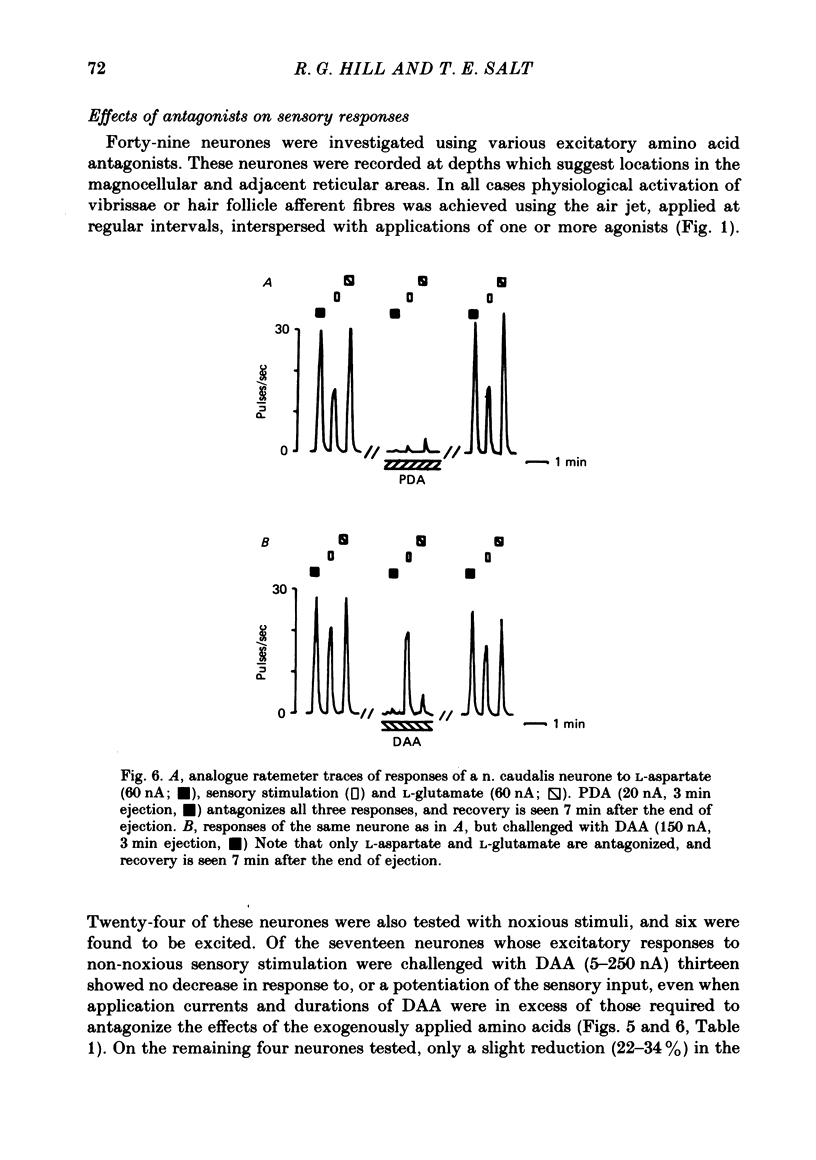
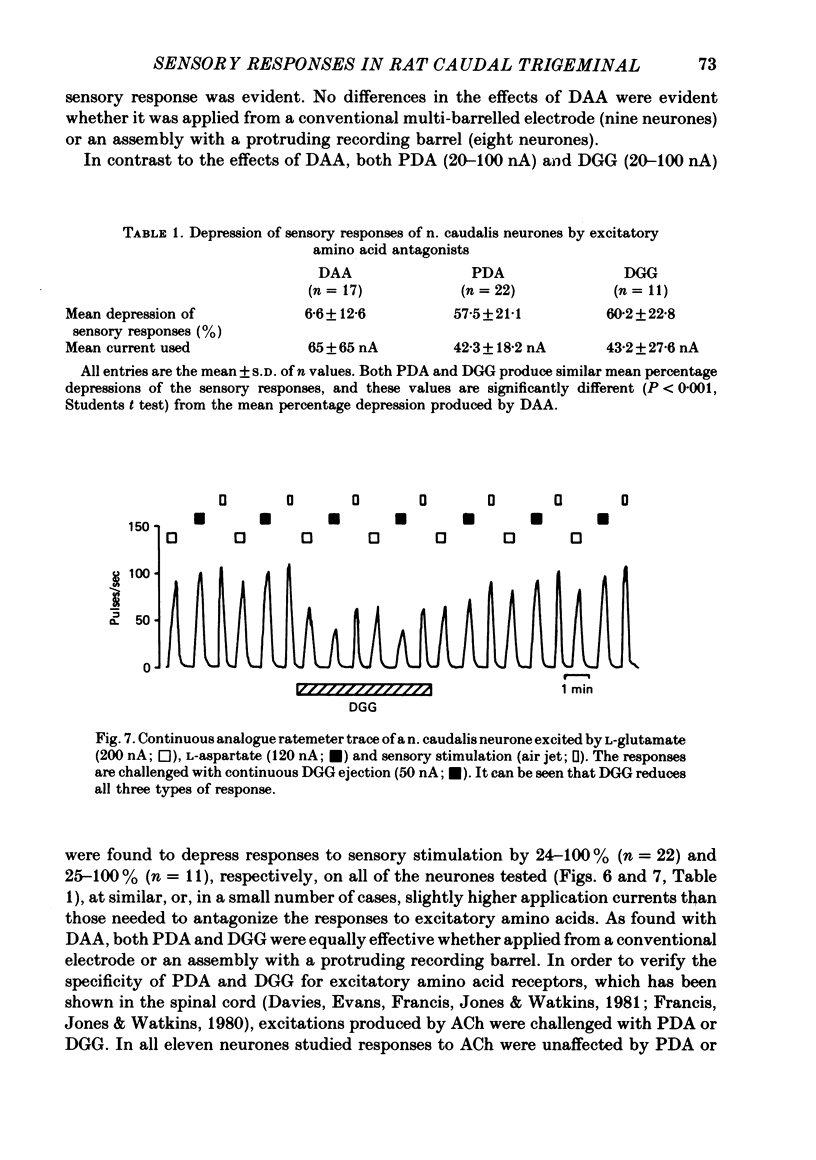




Images in this article
Selected References
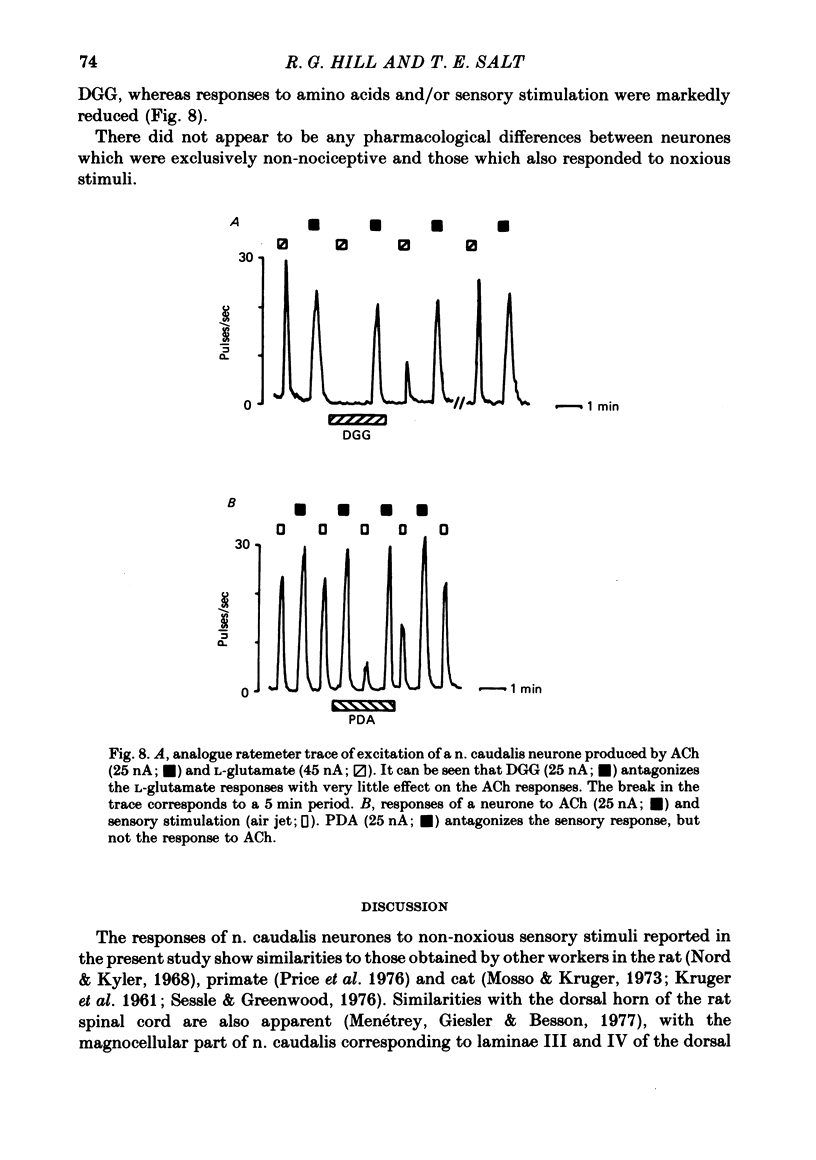
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayliffe S. J., Hill R. G. Responses of cells in the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis of the rat to noxious stimuli [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:18P–19P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T. G., Millar J. A simple 'wave form window' for nerve spikes [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:15P–16P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Noble R. Relationships between hair follicle afferent fibres and spinocervical tract neurones in the cat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:38P–39P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic transmission in the mammalian spinal cord. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:296–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G. Two types of extrajunctional L-glutamate receptors in locust muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):449–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Effects of D-alpha-aminoadipate on physiologically evoked responses of cat dorsal horn neurones. Experientia. 1979 Mar 15;35(3):353–354. doi: 10.1007/BF01964348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. Antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation of spinal neurones by cis-2,3-piperidine dicarboxylate. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):1305–1307. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. Dipeptide antagonists of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the frog spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1980 Dec;35(6):1458–1460. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo A., Krnjević K., Schwartz S. Micro-iontophoretic studies on neurones in the cuneate nucleus. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):359–377. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Aprison M. H. The distribution of glutamic acid, a transmitter candidate, and other amino acids in the dorsal sensory neuron of the cat. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 1;24(2):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUGER L., SIMINOFF R., WITKOVSKY P. Single neuron analysis of dorsal column nuclei and spinal nucleus of trigeminal in cat. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Jul;24:333–349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr F. W., Kruger L., Schwassmann H. O., Stern R. Somatotopic organization of mechanoreceptor units in the trigeminal nuclear complex of the macaque. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Oct;134(2):127–144. doi: 10.1002/cne.901340202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisney S. J. Some anatomical and electrophysiological properties of tooth-pulp afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:19–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menétrey D., Giesler G. J., Jr, Besson J. M. An analysis of response properties of spinal cord dorsal horn neurones to nonnoxious and noxious stimuli in the spinal rat. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Jan 18;27(1):15–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00234822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosso J. A., Kruger L. Receptor categories represented in spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis. J Neurophysiol. 1973 May;36(3):472–488. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Noise analysis of drug induced voltage clamp currents in denervated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):705–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord S. G., Kyler H. J. A single unit analysis of trigeminal projections to bulbar reticular nuclei of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Dec;134(4):485–494. doi: 10.1002/cne.901340407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord S. G. Somatotopic organization in the spinal trigeminal nucleus, the dorsal column nuclei and related structures in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1967 Aug;130(4):343–356. doi: 10.1002/cne.901300406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Fuller T. A., de Gubareff T. Kainate-like neurotoxicity of folates. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):165–167. doi: 10.1038/292165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Jacobowitz D. M. Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. II. Hindbrain (mesencephalon, rhombencephalon). J Comp Neurol. 1974 Sep 1;157(1):29–42. doi: 10.1002/cne.901570104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. D., Dubner R., Hu J. W. Trigeminothalamic neurons in nucleus caudalis responsive to tactile, thermal, and nociceptive stimulation of monkey's face. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Sep;39(5):936–953. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.5.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts F., Hill R. G. The effect of dorsal column lesions on amino acid levels and glutamate uptake in rat dorsal column nuclei. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1549–1551. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J., Foster G. A., Thomas E. M. Neurotoxic action of methyltetrahydrofolate in rat cerebellum unrelated to direct activation of kainate receptors. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):654–655. doi: 10.1038/293654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J., Keen P. Effect of dorsal root section on amino acids of rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1974 Jul 12;74(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90587-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J. The release of amino acids with proposed neurotransmitter function from the cuneate and gracile nuclei of the rat in vivo. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 8;67(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruck A., Kramer S., Metz J., Brennan M. J. Methyltetrahydrofolate is a potent and selective agonist for kainic acid receptors. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):852–853. doi: 10.1038/287852a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt T. E., Hill R. G. Excitatory amino acids as transmitter candidates of vibrissae afferent fibres to the rat trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Mar 10;22(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessle B. J., Greenwood L. F. Inputs to trigeminal brain stem neurones from facial, oral, tooth pulp and pharyngolaryngeal tissues: I. Responses to innocuous and noxious stimuli. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 26;117(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90731-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley M. T. Response characteristics of single units in the rat's trigeminal nuclei to vibrissa displacements. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Jan;37(1):73–90. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D., TAUB A. Four aspects of trigeminal nucleus and a paradox. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jan;25:110–126. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Nishikawa N. Reappraisal of somatotopic tactile representation within trigeminal subnucleus caudalis. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Mar;43(3):700–712. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.3.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



