Abstract
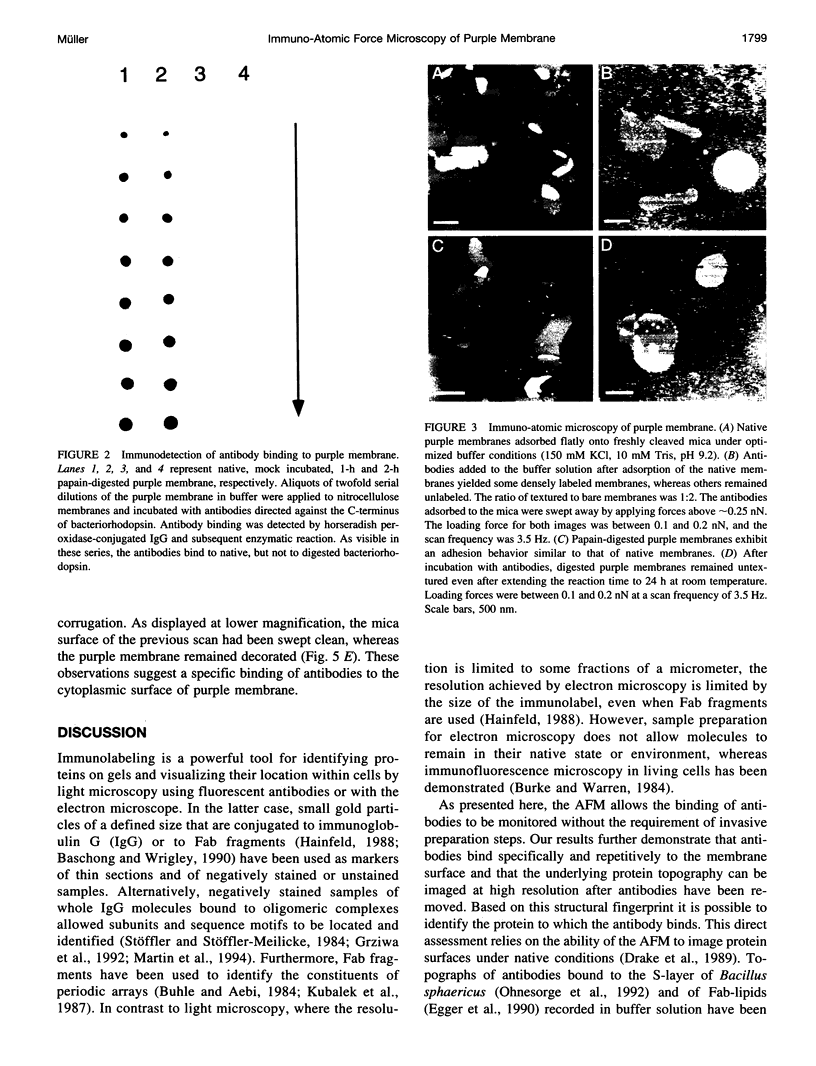
The atomic force microscope is a useful tool for imaging native biological structures at high resolution. In analogy to conventional immunolabeling techniques, we have used antibodies directed against the C-terminus of bacteriorhodopsin to distinguish the cytoplasmic and extracellular surface of purple membrane while imaging in buffer solution. At forces > or = 0.8 nN the antibodies were removed by the scanning stylus and the molecular topography of the cytoplasmic purple membrane surface was revealed. When the stylus was retracted, the scanned membrane area was relabeled with antibodies within 10 min. The extracellular surface of purple membrane was imaged at 0.7 nm resolution, exhibiting a major and a minor protrusion per bacteriorhodopsin monomer. As confirmed by immuno-dot blot analysis and sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis, labeling of the purple membrane was not observed if the C-terminus of bacteriorhodopsin was cleaved off by papain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdulaev N. G., Feigina M. Y., Kiselev A. V., Ovchinnikov Y. A., Drachev L. A., Kaulen A. D., Khitrina L. V., Skulachev V. P. Products of limited proteolysis of bacteriorhodopsin generate a membrane potential. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baschong W., Wrigley N. G. Small colloidal gold conjugated to Fab fragments or to immunoglobulin G as high-resolution labels for electron microscopy: a technical overview. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1990 Apr;14(4):313–323. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060140405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhle E. L., Jr, Aebi U. Specific labeling of protein domains with antibody fragments. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Nov;89(2):165–178. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Warren G. Microinjection of mRNA coding for an anti-Golgi antibody inhibits intracellular transport of a viral membrane protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):847–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90034-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Downing K. H., Hansma P. K. Imaging the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82492-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fimmel S., Choli T., Dencher N. A., Büldt G., Wittmann-Liebold B. Topography of surface-exposed amino acids in the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin determined by proteolysis and micro-sequencing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 30;978(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin E. L., Moy V. T., Gaub H. E. Adhesion forces between individual ligand-receptor pairs. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.8153628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grziwa A., Dahlmann B., Cejka Z., Santarius U., Baumeister W. Localization of a sequence motif complementary to the nuclear localization signal in proteasomes from Thermoplasma acidophilum by immunoelectron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Sep-Oct;109(2):168–175. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainfeld J. F. Gold cluster-labelled antibodies. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):281–282. doi: 10.1038/333281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han W., Mou J., Sheng J., Yang J., Shao Z. Cryo atomic force microscopy: a new approach for biological imaging at high resolution. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 4;34(26):8215–8220. doi: 10.1021/bi00026a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Sosinsky G. E., Revel J. P., Hansma P. K. Structure of the extracellular surface of the gap junction by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81074-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungblut H., Campbell S. A., Giersig M., Müller D. J., Lewerenz H. J. Scanning tunnelling microscopy observations of biomolecules on layered materials. Faraday Discuss. 1992;(94):183–197. doi: 10.1039/fd9929400183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrasch S., Dolder M., Schabert F., Ramsden J., Engel A. Covalent binding of biological samples to solid supports for scanning probe microscopy in buffer solution. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2437–2446. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81327-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrasch S., Hegerl R., Hoh J. H., Baumeister W., Engel A. Atomic force microscopy produces faithful high-resolution images of protein surfaces in an aqueous environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):836–838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubalek E., Ralston S., Lindstrom J., Unwin N. Location of subunits within the acetylcholine receptor by electron image analysis of tubular crystals from Torpedo marmorata. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):9–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao M. J., Khorana H. G. Removal of the carboxyl-terminal peptide does not affect refolding or function of bacteriorhodopsin as a light-dependent proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4194–4199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Goldie K. N., Engel A., Hartl F. U. Topology of the morphological domains of the chaperonin GroEL visualized by immuno-electron microscopy. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994 Sep;375(9):635–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D. J., Büldt G., Engel A. Force-induced conformational change of bacteriorhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 2;249(2):239–243. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D. J., Schabert F. A., Büldt G., Engel A. Imaging purple membranes in aqueous solutions at sub-nanometer resolution by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1681–1686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80345-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnesorge F., Heckl W. M., Häberle W., Pum D., Sara M., Schindler H., Schilcher K., Kiener A., Smith D. P., Sleytr U. B. Scanning force microscopy studies of the S-layers from Bacillus coagulans E38-66, Bacillus sphaericus CCM2177 and of an antibody binding process. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1236–1242. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90429-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehorek M., Heyn M. P. Binding of all-trans-retinal to the purple membrane. Evidence for cooperativity and determination of the extinction coefficient. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4977–4983. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. O., Baumeister W. The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein. J Microsc. 1982 Aug;127(Pt 2):127–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schabert F. A., Henn C., Engel A. Native Escherichia coli OmpF porin surfaces probed by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1995 Apr 7;268(5207):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.7701347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao Z., Yang J. Progress in high resolution atomic force microscopy in biology. Q Rev Biophys. 1995 May;28(2):195–251. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Stöffler-Meilicke M. Immunoelectron microscopy of ribosomes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:303–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
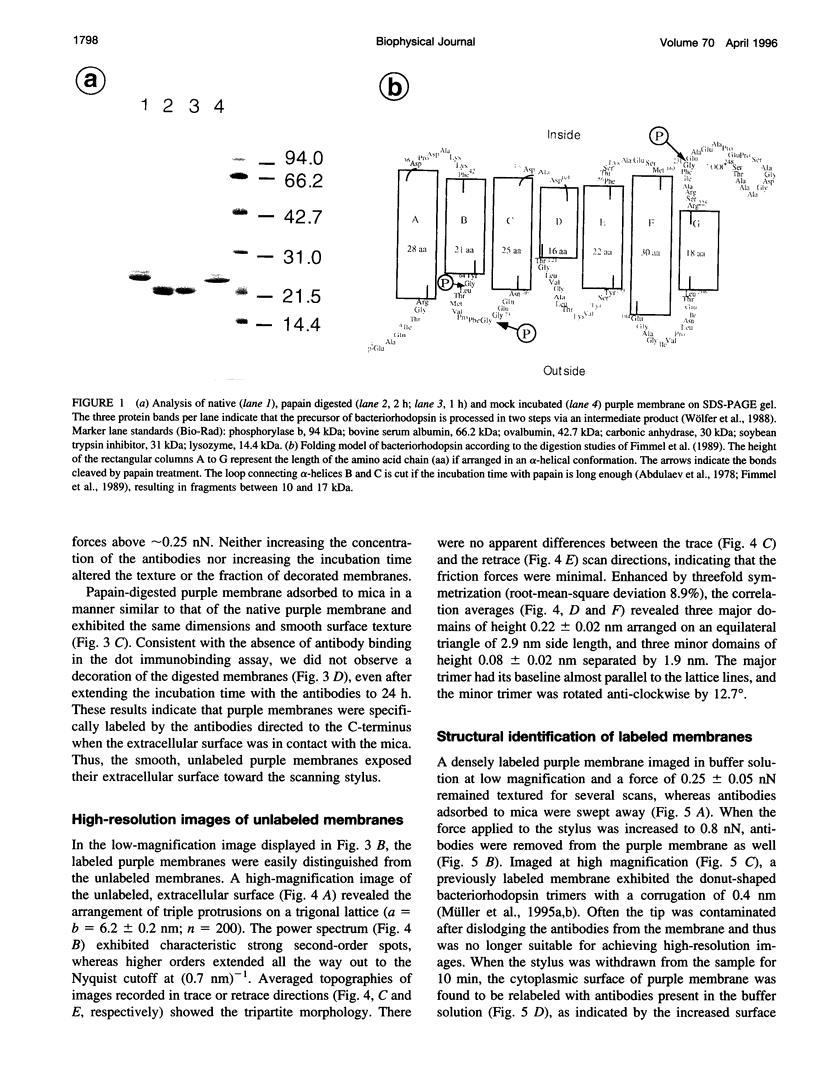
- Wölfer U., Dencher N. A., Büldt G., Wrede P. Bacteriorhodopsin precursor is processed in two steps. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 16;174(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Mou J., Shao Z. Molecular resolution atomic force microscopy of soluble proteins in solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 2;1199(2):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(94)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Tamm L. K., Tillack T. W., Shao Z. New approach for atomic force microscopy of membrane proteins. The imaging of cholera toxin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):286–290. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]