Full text
PDF
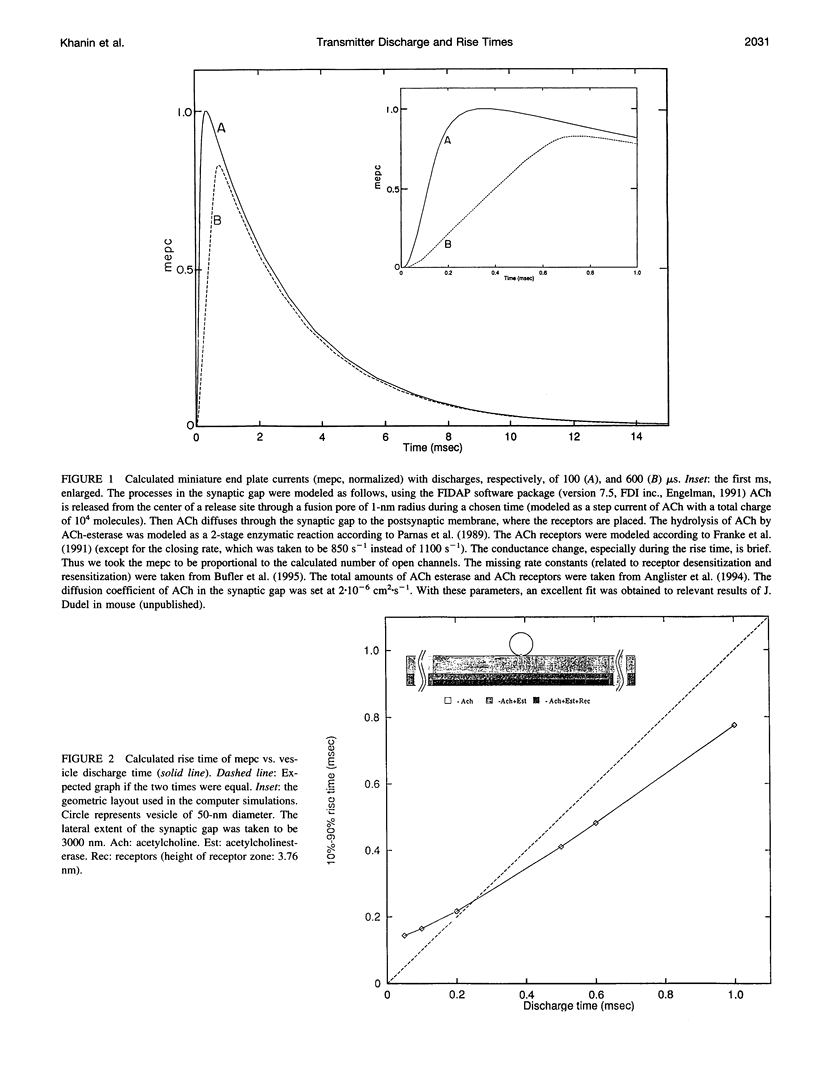

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anglister L., Stiles J. R., Salpeter M. M. Acetylcholinesterase density and turnover number at frog neuromuscular junctions, with modeling of their role in synaptic function. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):783–794. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H., Parnas H., Dudel J. Kinetic constants of the acetylcholine (ACh) receptor reaction deduced from the rise in open probability after steps in ACh concentration. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1008–1016. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82138-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Spontaneous and evoked activity of motor nerve endings in calcium Ringer. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):689–706. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanin R., Parnas H., Segel L. Diffusion cannot govern the discharge of neurotransmitter in fast synapses. Biophys J. 1994 Sep;67(3):966–972. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80562-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Flashner M., Spira M. E. Sequential model to describe the nicotinic synaptic current. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):875–884. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82886-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kloot W. The rise times of miniature endplate currents suggest that acetylcholine may be released over a period of time. Biophys J. 1995 Jul;69(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79884-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]