Abstract
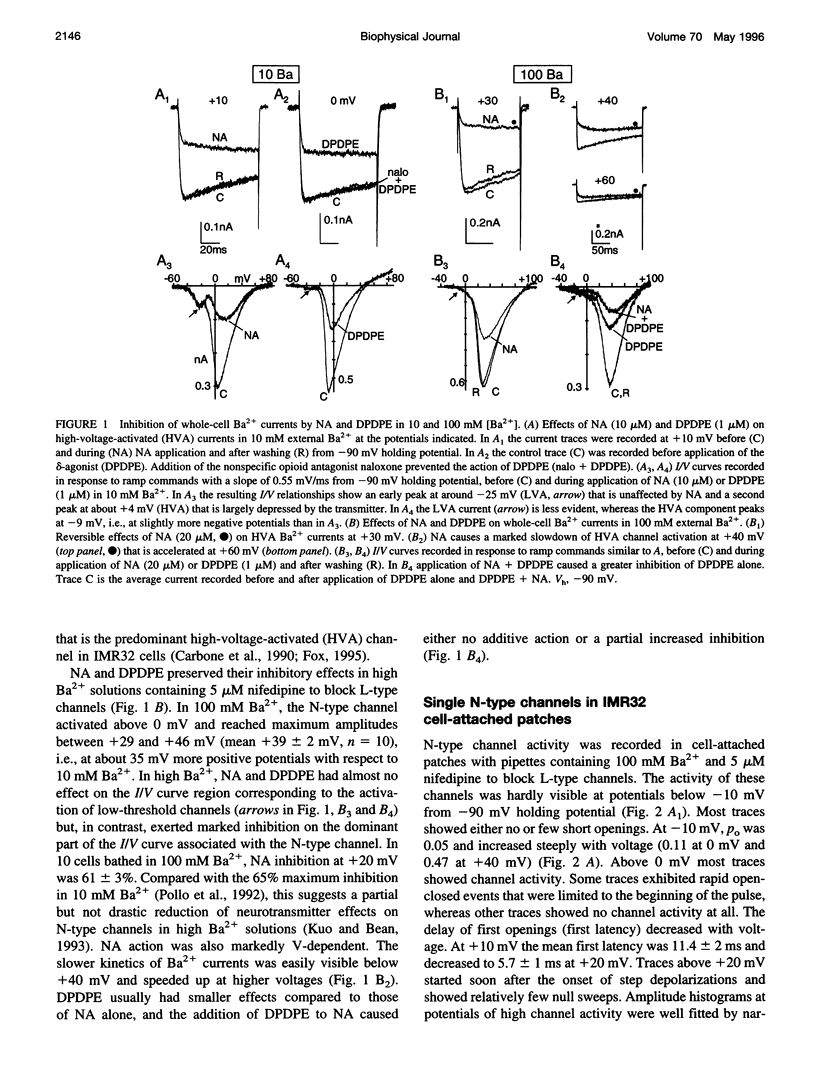
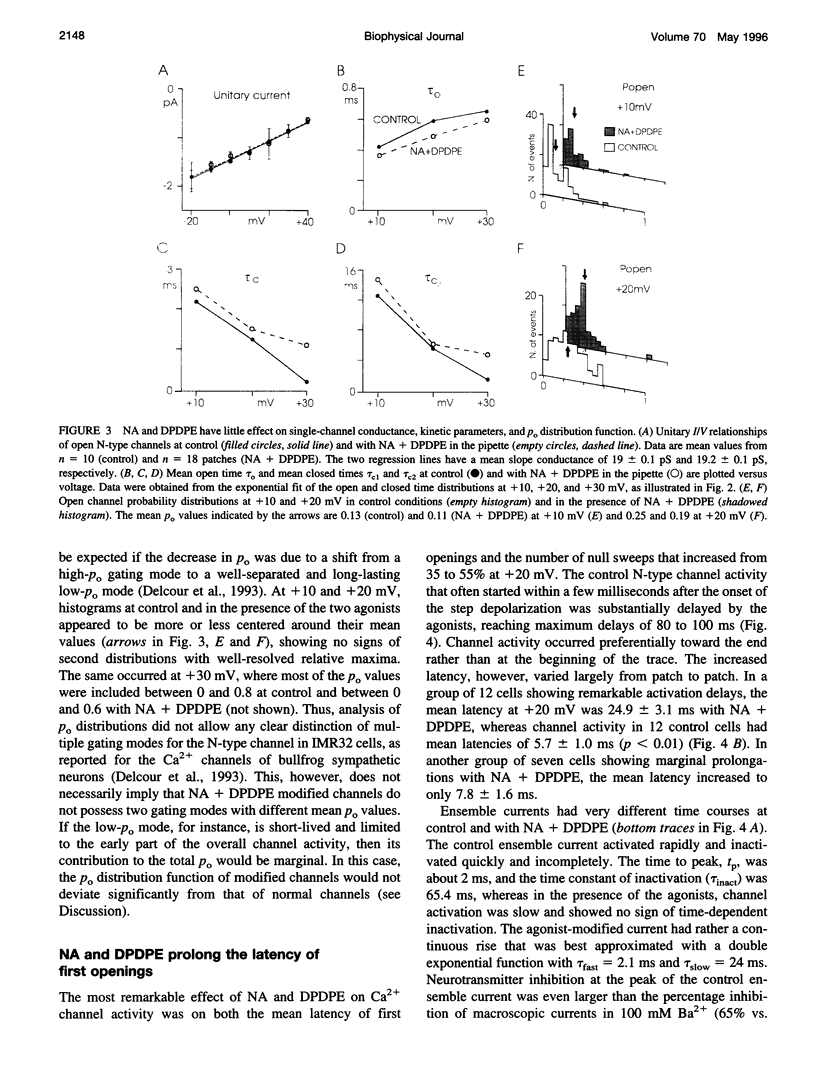
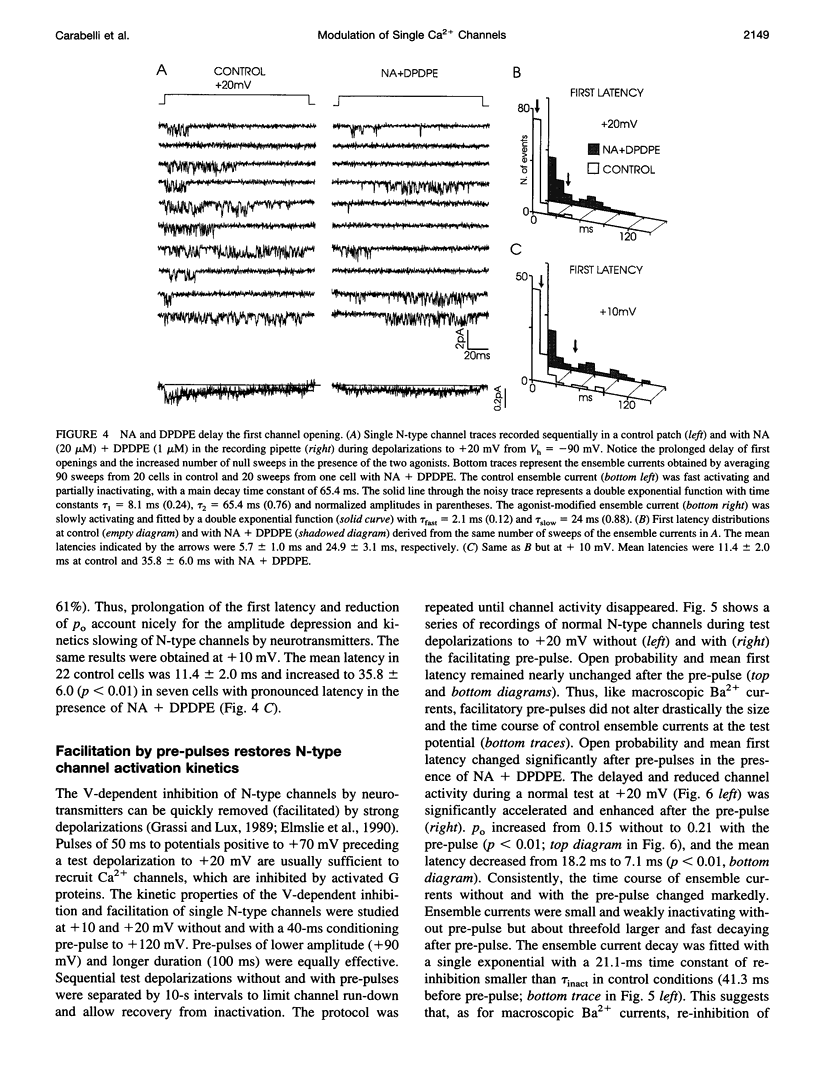
The voltage-dependent inhibition of single N-type Ca(2+) channels by noradrenaline (NA) and the delta-opioid agonist D-Pen(2)-D-Pen (5)-enkephalin (DPDPE) was investigated in cell-attached patches of human neuroblastoma IMR32 cells with 100 mM Ba(2+) and 5 microM nifedipine to block L-type channels. In 70% of patches, addition of 20 microM NA + 1 microM DPDPE delayed markedly the first channel openings, causing a four- to fivefold increase of the first latency at +20 mV. The two agonists or NA alone decreased also by 35% the open probability (P(o)), prolonged partially the mean closed time, and increased the number of null sweeps. In contrast, NA + DPDPE had little action on the single-channel conductance (19 versus 19.2 pS) and minor effects on the mean open time. Similarly to macroscopic Ba(2+) currents, the ensemble currents were fast activating at control but slowly activating and depressed with the two agonists. Inhibition of single N-type channels was effectively removed (facilitated) by short and large depolarizations. Facilitatory pre-pulses increased P(o) significantly and decreased fourfold the first latency. Ensemble currents were small and slowly activating before pre-pulses and became threefold larger and fast decaying after facilitation. Our data suggest that slowdown of Ca(2+) channel activation by transmitters is mostly due to delayed transitions from a modified to a normal (facilitated) gating mode. This single-channel gating modulation could be well simulated by a Monte Carlo method using previously proposed kinetic models predicting marked prolongation of first channel openings.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland L. M., Bean B. P. Modulation of N-type calcium channels in bullfrog sympathetic neurons by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone: kinetics and voltage dependence. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):516–533. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00516.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Lux H. D., Wilson D. L. Activation and inactivation of single calcium channels in snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1984 May;83(5):751–769. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Single low-voltage-activated calcium channels in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:571–601. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Sher E., Clementi F. Ca currents in human neuroblastoma IMR32 cells: kinetics, permeability and pharmacology. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):170–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00370239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Lipscombe D., Tsien R. W. Multiple modes of N-type calcium channel activity distinguished by differences in gating kinetics. J Neurosci. 1993 Jan;13(1):181–194. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-01-00181.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Tsien R. W. Altered prevalence of gating modes in neurotransmitter inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):980–984. doi: 10.1126/science.8094902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diversé-Pierluissi M., Goldsmith P. K., Dunlap K. Transmitter-mediated inhibition of N-type calcium channels in sensory neurons involves multiple GTP-binding proteins and subunits. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. Regulation of calcium channel activity by GTP binding proteins and second messengers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 10;1091(1):68–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90224-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Kammermeier P. J., Jones S. W. Reevaluation of Ca2+ channel types and their modulation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Zhou W., Jones S. W. LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90035-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formenti A., Arrigoni E., Mancia M. Two distinct modulatory effects on calcium channels in adult rat sensory neurons. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1029–1037. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81468-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A. Irreversible and reversible blockade of IMR32 calcium channel currents by synthetic MVIIA and iodinated MVIIC omega-conopeptides. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Apr;429(6):873–875. doi: 10.1007/BF00374813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golard A., Siegelbaum S. A. Kinetic basis for the voltage-dependent inhibition of N-type calcium current by somatostatin and norepinephrine in chick sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3884–3894. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03884.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi F., Lux H. D. Voltage-dependent GABA-induced modulation of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Modulation of ion-channel function by G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H. Voltage- and time-dependent inhibition of neuronal calcium channels by a GTP-binding protein in a mammalian cell line. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:189–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Bean B. P. G-protein modulation of ion permeation through N-type calcium channels. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):258–262. doi: 10.1038/365258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Hess P. Characterization of the high-affinity Ca2+ binding sites in the L-type Ca2+ channel pore in rat phaeochromocytoma cells. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:657–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Kongsamut S., Tsien R. W. Alpha-adrenergic inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmitter release mediated by modulation of N-type calcium-channel gating. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):639–642. doi: 10.1038/340639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez H. S., Brown A. M. Correlation between G protein activation and reblocking kinetics of Ca2+ channel currents in rat sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):1061–1068. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luebke J. I., Dunlap K. Sensory neuron N-type calcium currents are inhibited by both voltage-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(5-6):499–507. doi: 10.1007/BF00374571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnelli V., Avaltroni A., Carbone E. A single non-L-, non-N-type Ca2+ channel in rat insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Jan;431(3):341–352. doi: 10.1007/BF02207271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti C., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Effects of dopamine and noradrenaline on Ca channels of cultured sensory and sympathetic neurons of chick. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00586670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meriney S. D., Gray D. B., Pilar G. R. Somatostatin-induced inhibition of neuronal Ca2+ current modulated by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):336–339. doi: 10.1038/369336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollo A., Lovallo M., Sher E., Carbone E. Voltage-dependent noradrenergic modulation of omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca2+ channels in human neuroblastoma IMR32 cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Oct;422(1):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00381516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., Surprenant A. Noradrenaline, somatostatin and opioids inhibit activity of single HVA/N-type calcium channels in excised neuronal membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Jul;418(6):614–616. doi: 10.1007/BF00370580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Do calcium channel classifications account for neuronal calcium channel diversity? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90018-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toselli M., Taglietti V. Muscarinic inhibition of high-voltage-activated calcium channels in excised membranes of rat hippocampal neurons. Eur Biophys J. 1994;22(6):391–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00180160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A. Molecular diversity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90595-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





