Abstract
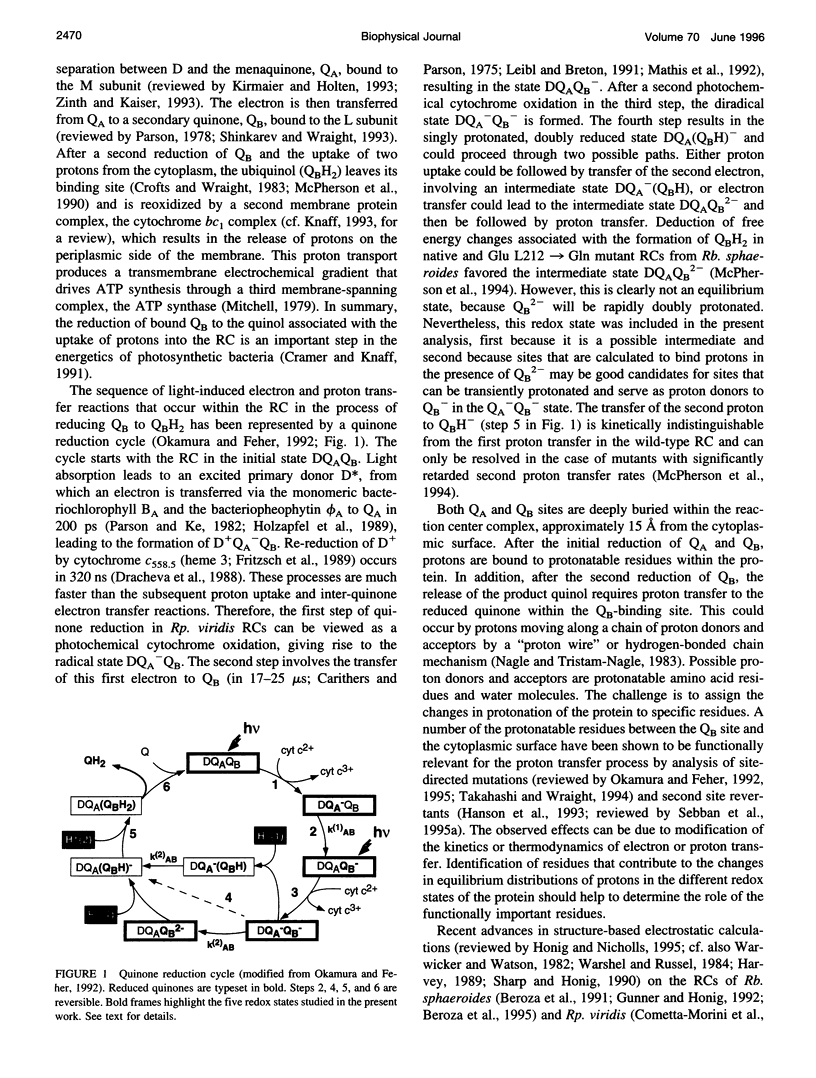
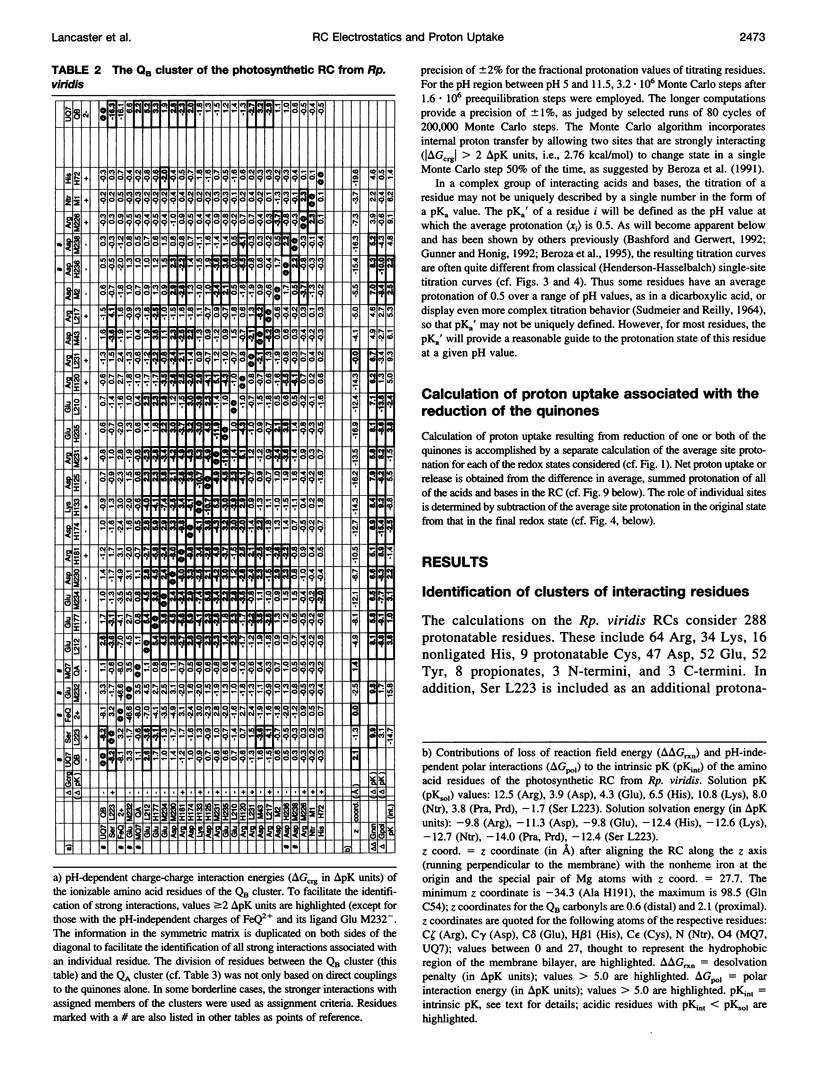
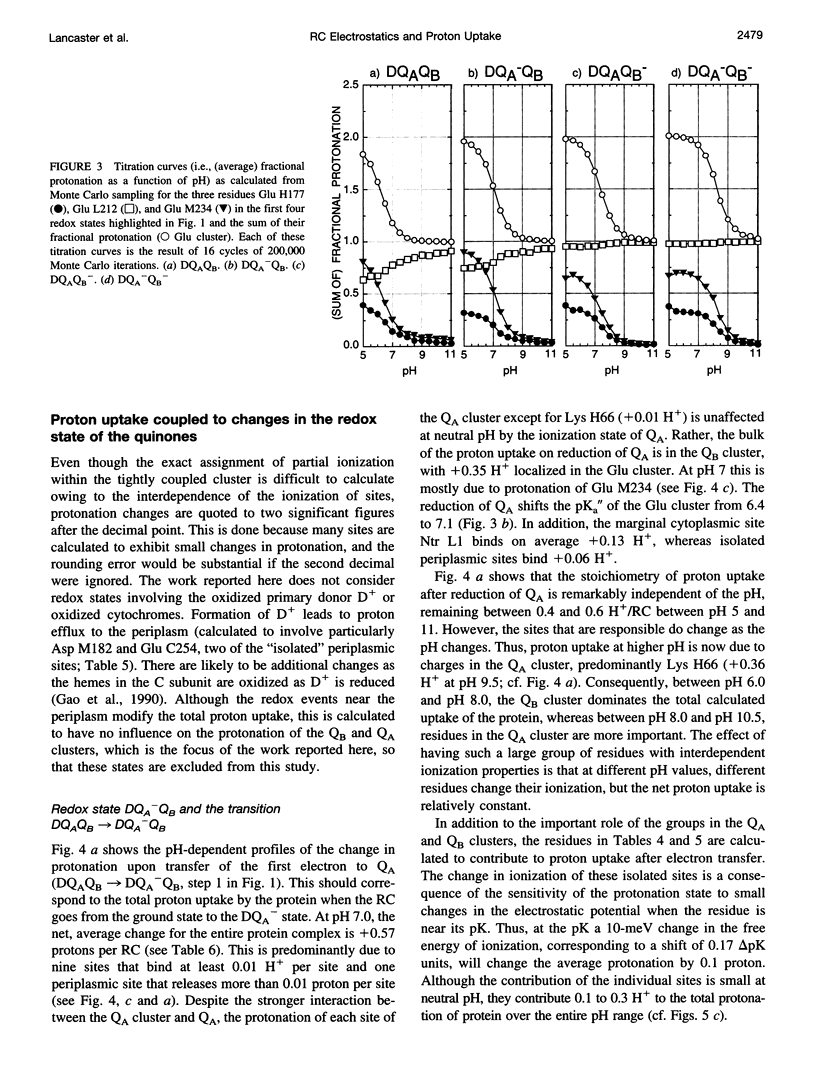
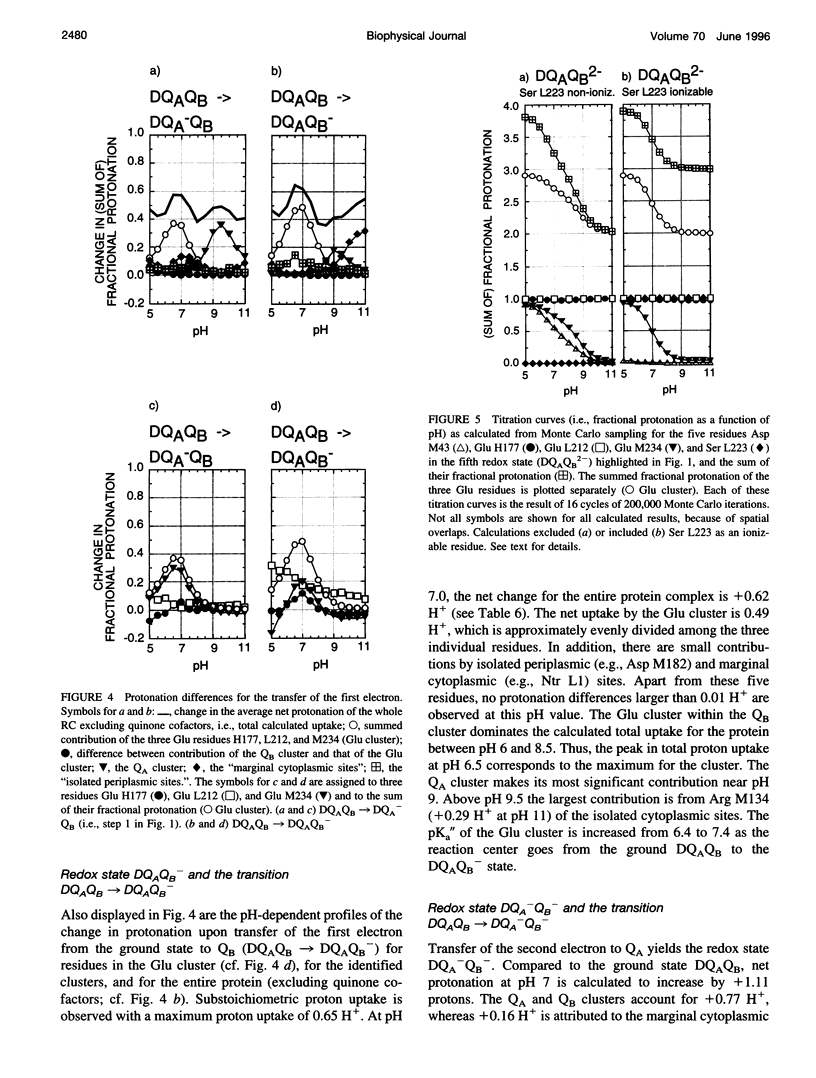
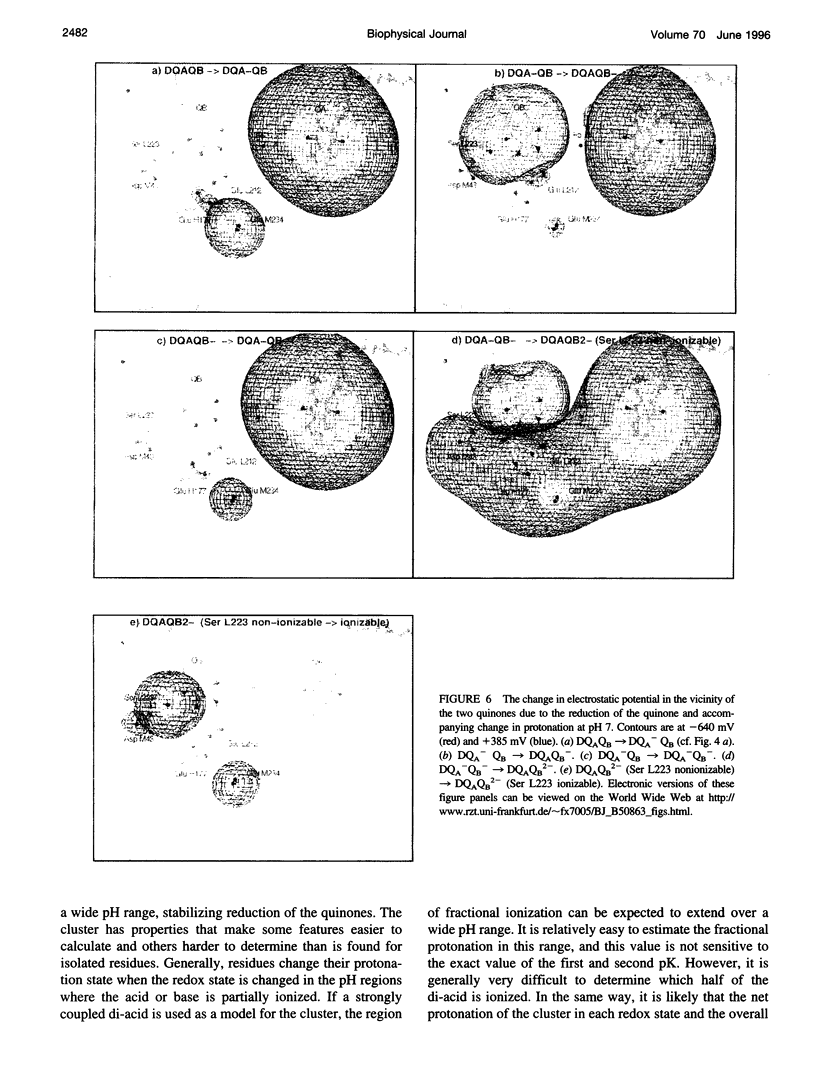
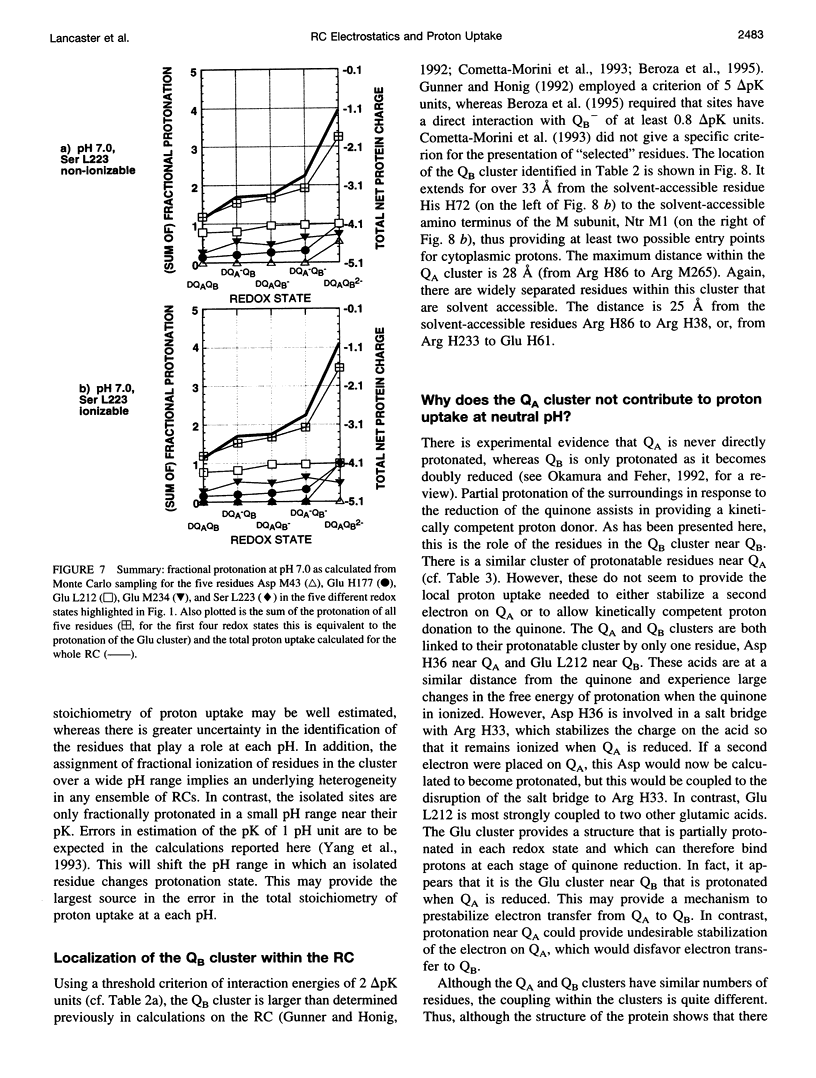
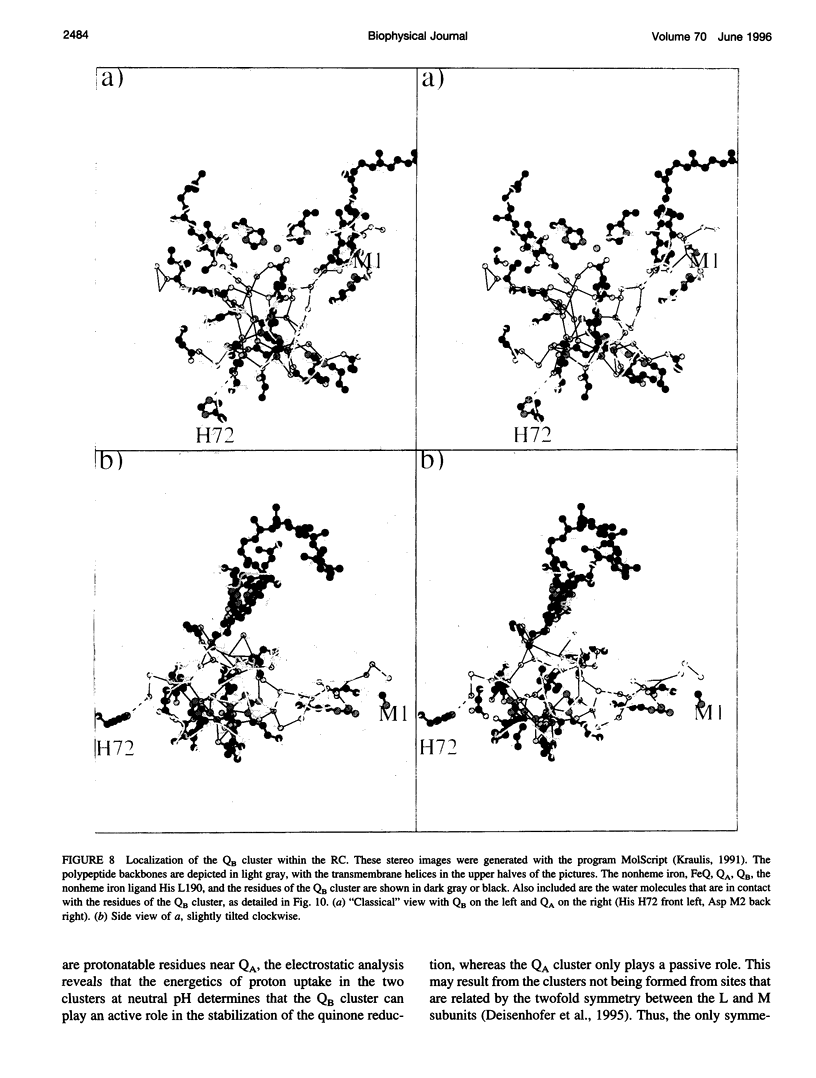
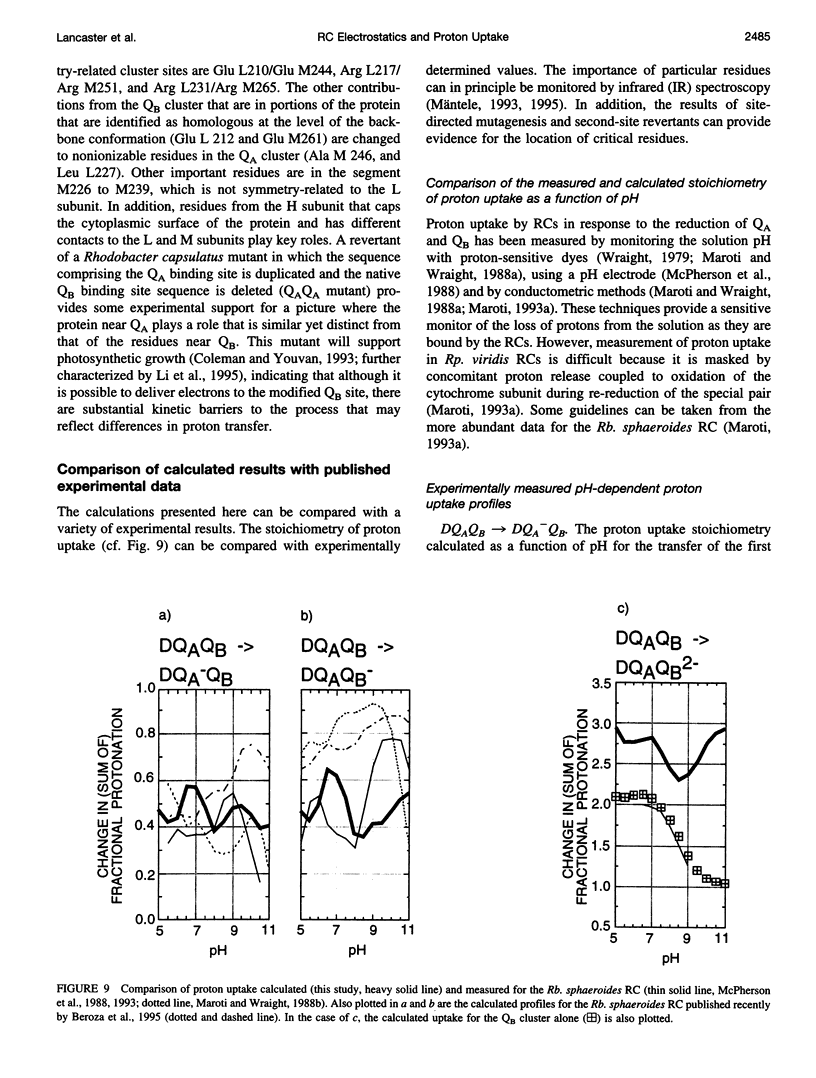
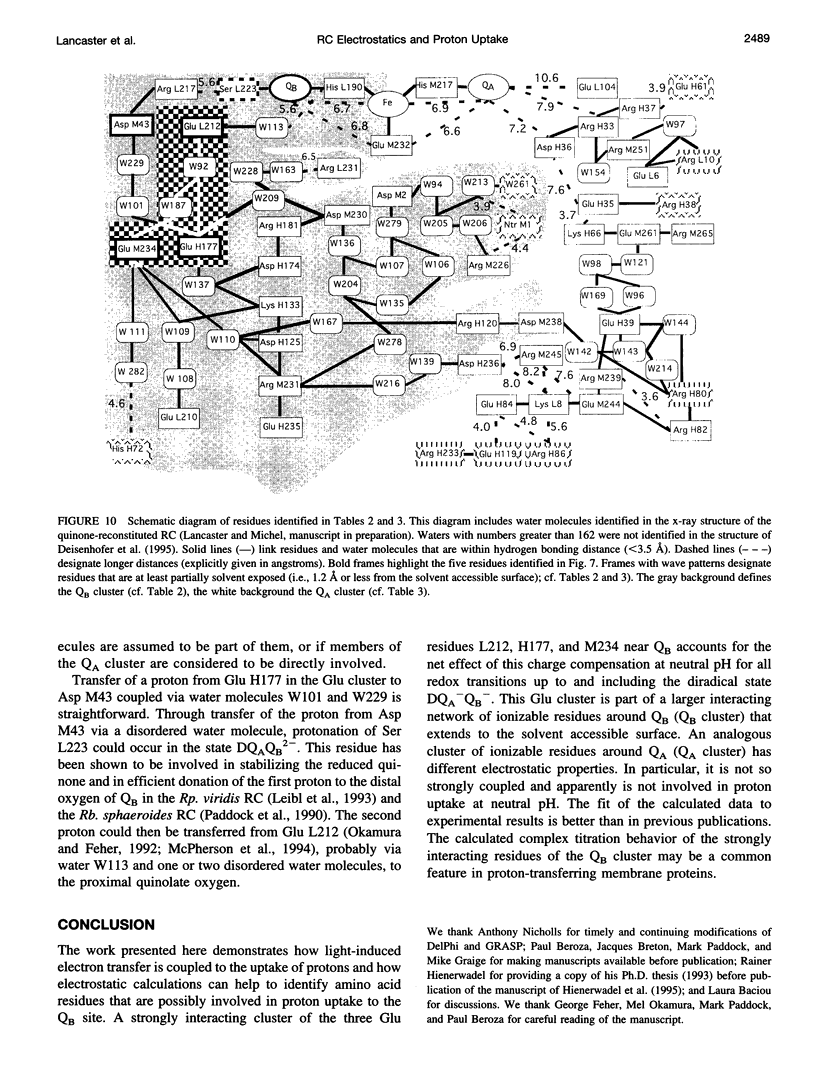
Based on new Rhodopseudomonas (Rp.) viridis reaction center (RC) coordinates with a reliable structure of the secondary acceptor quinone (QB) site, a continuum dielectric model and finite difference technique have been used to identify clusters of electrostatically interacting ionizable residues. Twenty-three residues within a distance of 25 A from QB (QB cluster) have been shown to be strongly electrostatically coupled to QB, either directly or indirectly. An analogous cluster of 24 residues is found to interact with QA (QA cluster). Both clusters extend to the cytoplasmic surface in at least two directions. However, the QB cluster differs from the QA cluster in that it has a surplus of acidic residues, more strong electrostatic interactions, is less solvated, and experiences a strong positive electrostatic field arising from the polypeptide backbone. Consequently, upon reduction of QA or QB, it is the QB cluster, and not the QA cluster, which is responsible for substoichiometric proton uptake at neutral pH. The bulk of the changes in the QB cluster are calculated to be due to the protonation of a tightly coupled cluster of the three Glu residues (L212, H177, and M234) within the QB cluster. If the lifetime of the doubly reduced state QB2- is long enough, Asp M43 and Ser L223 are predicted to also become protonated. The calculated complex titration behavior of the strongly interacting residues of the QB cluster and the resulting electrostatic response to electron transfer may be a common feature in proton-transferring membrane protein complexes.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antosiewicz J., McCammon J. A., Gilson M. K. Prediction of pH-dependent properties of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 6;238(3):415–436. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Gerwert K. Electrostatic calculations of the pKa values of ionizable groups in bacteriorhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91009-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Karplus M. pKa's of ionizable groups in proteins: atomic detail from a continuum electrostatic model. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10219–10225. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beroza P., Fredkin D. R., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Electrostatic calculations of amino acid titration and electron transfer, Q-AQB-->QAQ-B, in the reaction center. Biophys J. 1995 Jun;68(6):2233–2250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80406-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beroza P., Fredkin D. R., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Protonation of interacting residues in a protein by a Monte Carlo method: application to lysozyme and the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5804–5808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton J., Berthomieu C., Thibodeau D. L., Nabedryk E. Probing the secondary quinone (QB) environment in photosynthetic bacterial reaction centers by light-induced FTIR difference spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81014-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton J., Boullais C., Berger G., Mioskowski C., Nabedryk E. Binding sites of quinones in photosynthetic bacterial reaction centers investigated by light-induced FTIR difference spectroscopy: symmetry of the carbonyl interactions and close equivalence of the QB vibrations in Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Rhodopseudomonas viridis probed by isotope labeling. Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 12;34(36):11606–11616. doi: 10.1021/bi00036a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Parson W. W. Delayed fluorescence from Rhodopseudomonas viridis following single flashes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 15;387(2):194–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman W. J., Youvan D. C. Atavistic reaction centre. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):517–518. doi: 10.1038/366517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Epp O., Sinning I., Michel H. Crystallographic refinement at 2.3 A resolution and refined model of the photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. J Mol Biol. 1995 Feb 24;246(3):429–457. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Michel H. Nobel lecture. The photosynthetic reaction centre from the purple bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2149–2170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracheva S. M., Drachev L. A., Konstantinov A. A., Semenov AYu, Skulachev V. P., Arutjunjan A. M., Shuvalov V. A., Zaberezhnaya S. M. Electrogenic steps in the redox reactions catalyzed by photosynthetic reaction-centre complex from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):253–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermler U., Fritzsch G., Buchanan S. K., Michel H. Structure of the photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodobacter sphaeroides at 2.65 A resolution: cofactors and protein-cofactor interactions. Structure. 1994 Oct 15;2(10):925–936. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. H. The dielectric constant of a folded protein. Biopolymers. 1986 Nov;25(11):2097–2119. doi: 10.1002/bip.360251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunner M. R., Honig B. Electrostatic control of midpoint potentials in the cytochrome subunit of the Rhodopseudomonas viridis reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9151–9155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson D. K., Tiede D. M., Nance S. L., Chang C. H., Schiffer M. Site-specific and compensatory mutations imply unexpected pathways for proton delivery to the QB binding site of the photosynthetic reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8929–8933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C. Treatment of electrostatic effects in macromolecular modeling. Proteins. 1989;5(1):78–92. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hienerwadel R., Grzybek S., Fogel C., Kreutz W., Okamura M. Y., Paddock M. L., Breton J., Nabedryk E., Mäntele W. Protonation of Glu L212 following QB- formation in the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides: evidence from time-resolved infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1995 Mar 7;34(9):2832–2843. doi: 10.1021/bi00009a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Nicholls A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science. 1995 May 26;268(5214):1144–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.7761829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibl W., Breton J. Kinetic properties of the acceptor quinone complex in Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9634–9642. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibl W., Sinning I., Ewald G., Michel H., Breton J. Evidence that serine L223 is involved in the proton transfer pathway to QB in the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1958–1964. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maróti P., Hanson D. K., Baciou L., Schiffer M., Sebban P. Proton conduction within the reaction centers of Rhodobacter capsulatus: the electrostatic role of the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5617–5621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maróti P., Hanson D. K., Schiffer M., Sebban P. Long-range electrostatic interaction in the bacterial photosynthetic reaction centre. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Dec;2(12):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/nsb1295-1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P. H., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Light-induced proton uptake by photosynthetic reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26.1. II. Protonation of the state DQAQB2-. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 4;1144(3):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90116-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P. H., Schönfeld M., Paddock M. L., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Protonation and free energy changes associated with formation of QBH2 in native and Glu-L212-->Gln mutant reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 8;33(5):1181–1193. doi: 10.1021/bi00171a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Keilin's respiratory chain concept and its chemiosmotic consequences. Science. 1979 Dec 7;206(4423):1148–1159. doi: 10.1126/science.388618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Proton transfer in reaction centers from photosynthetic bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:861–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock M. L., McPherson P. H., Feher G., Okamura M. Y. Pathway of proton transfer in bacterial reaction centers: replacement of serine-L223 by alanine inhibits electron and proton transfers associated with reduction of quinone to dihydroquinone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6803–6807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rongey S. H., Paddock M. L., Feher G., Okamura M. Y. Pathway of proton transfer in bacterial reaction centers: second-site mutation Asn-M44-->Asp restores electron and proton transfer in reaction centers from the photosynthetically deficient Asp-L213-->Asn mutant of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1325–1329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampogna R. V., Honig B. Environmental effects on the protonation states of active site residues in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1341–1352. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80925-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebban P., Maróti P., Hanson D. K. Electron and proton transfer to the quinones in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers: insight from combined approaches of molecular genetics and biophysics. Biochimie. 1995;77(7-8):677–694. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(96)88183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebban P., Maróti P., Schiffer M., Hanson D. K. Electrostatic dominoes: long distance propagation of mutational effects in photosynthetic reaction centers of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 4;34(26):8390–8397. doi: 10.1021/bi00026a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Honig B. Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules: theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:301–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treutlein H., Schulten K., Brünger A. T., Karplus M., Deisenhofer J., Michel H. Chromophore-protein interactions and the function of the photosynthetic reaction center: a molecular dynamics study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):75–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Russell S. T. Calculations of electrostatic interactions in biological systems and in solutions. Q Rev Biophys. 1984 Aug;17(3):283–422. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J., Watson H. C. Calculation of the electric potential in the active site cleft due to alpha-helix dipoles. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraight C. A. Electron acceptors of bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. II. H+ binding coupled to secondary electron transfer in the quinone acceptor complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 8;548(2):309–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Gunner M. R., Sampogna R., Sharp K., Honig B. On the calculation of pKas in proteins. Proteins. 1993 Mar;15(3):252–265. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Chirino A., Rees D. C., Allen J. P., Feher G. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 and 2.4.1: protein-cofactor (bacteriochlorophyll, bacteriopheophytin, and carotenoid) interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7993–7997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]