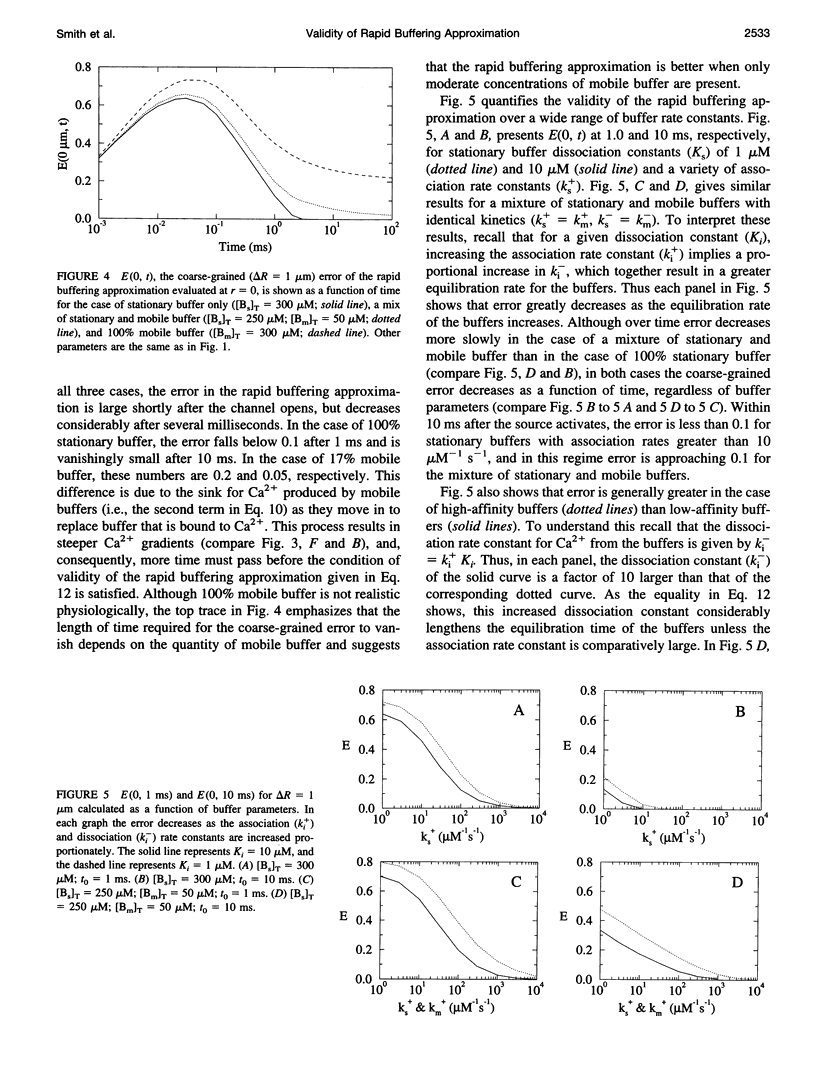
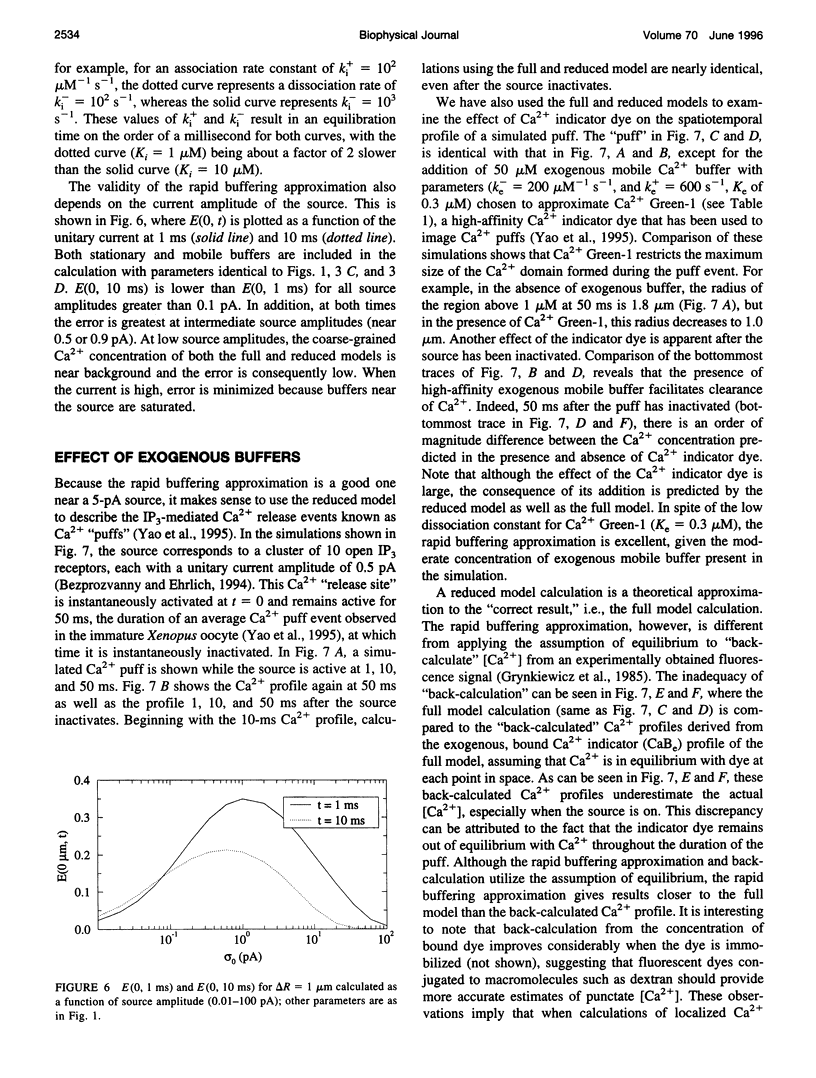
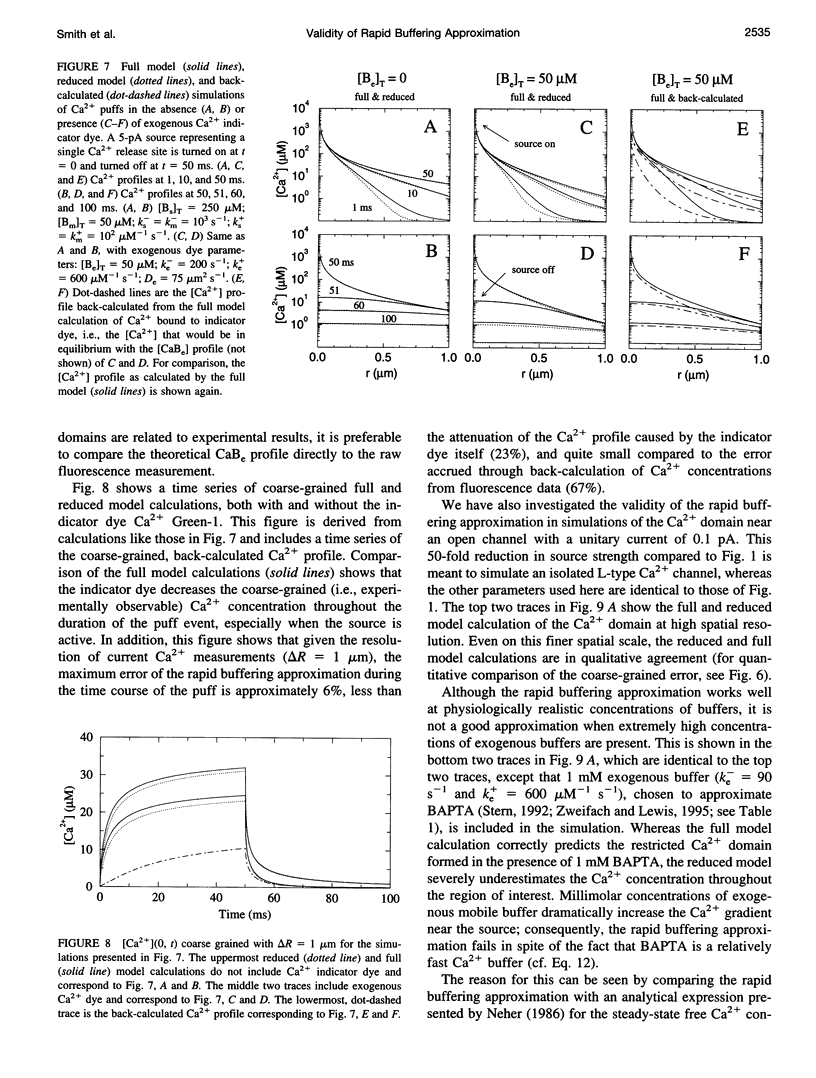
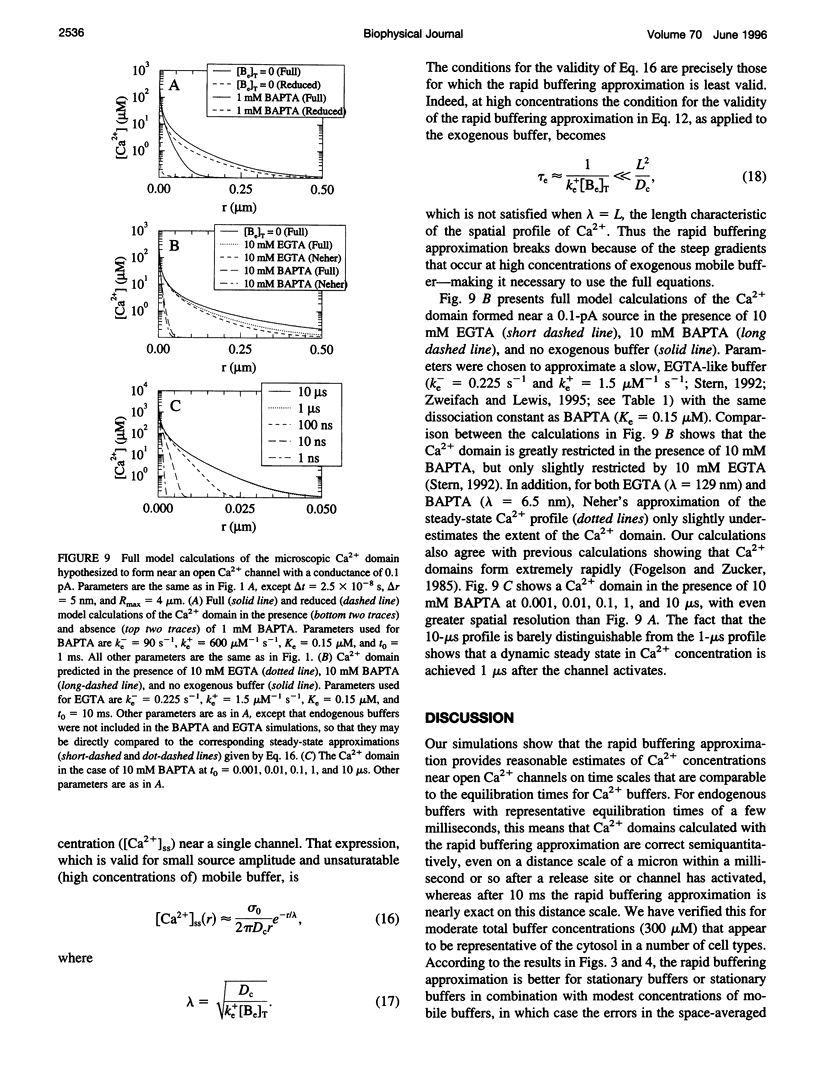
Abstract
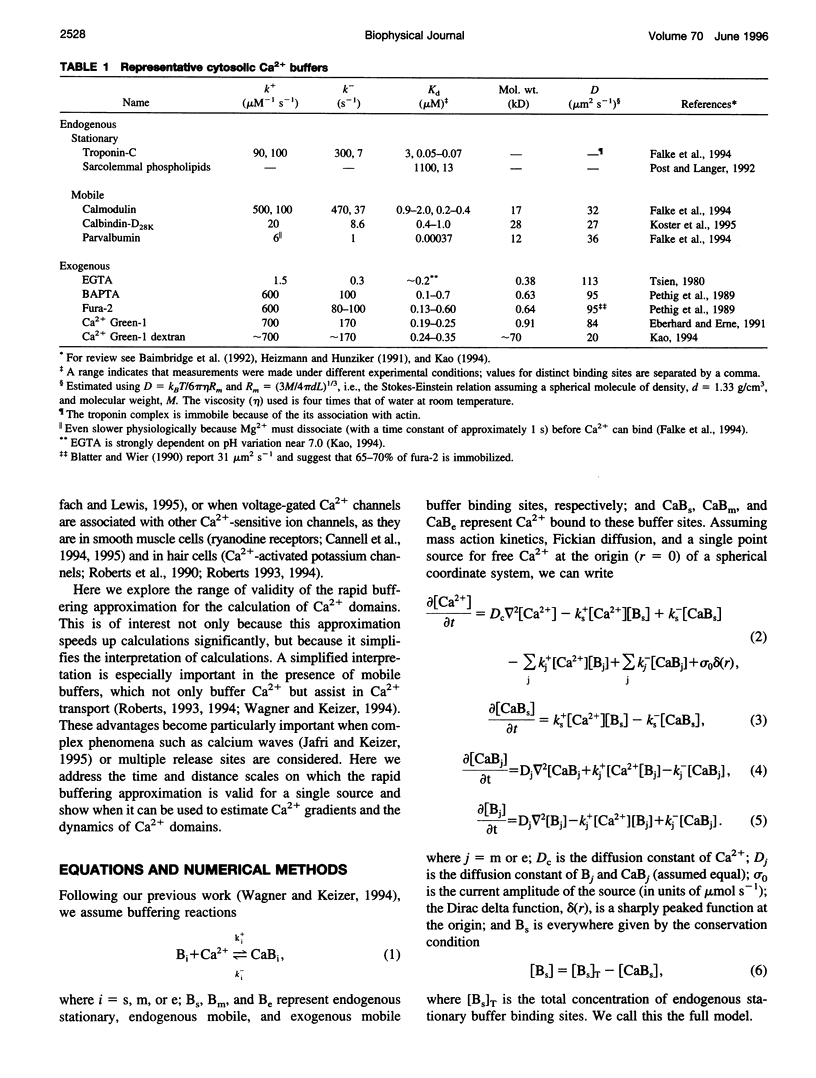
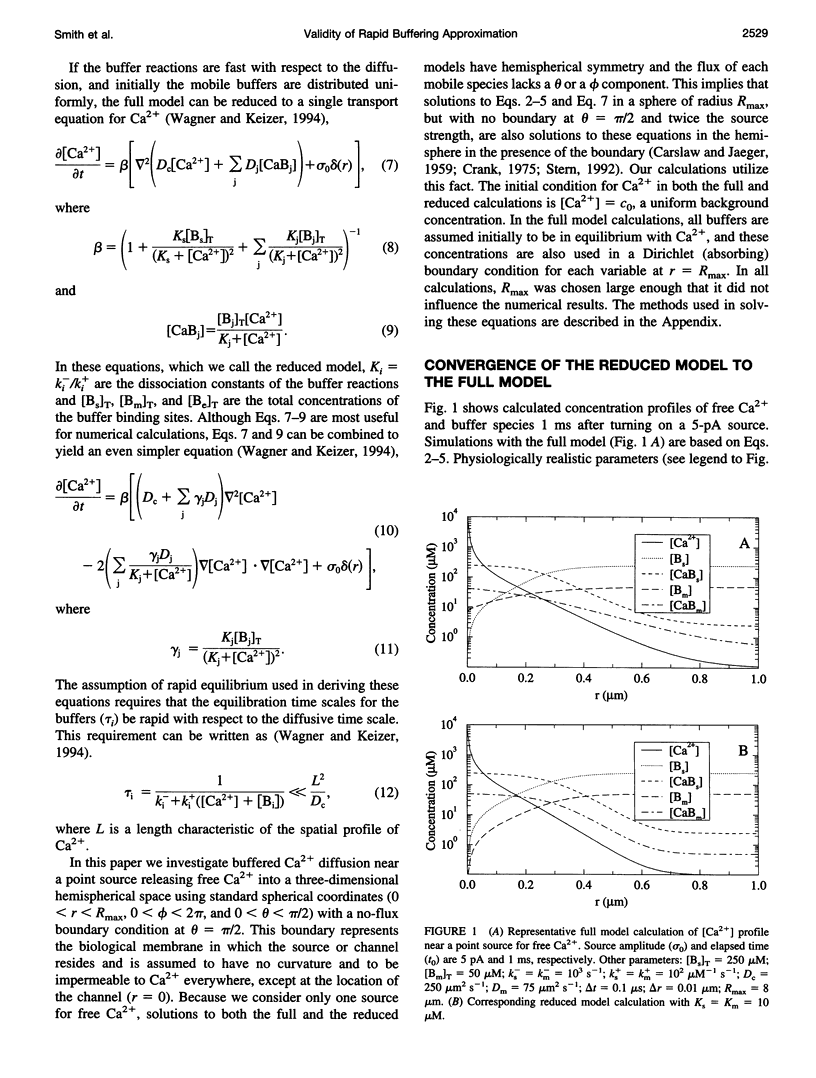
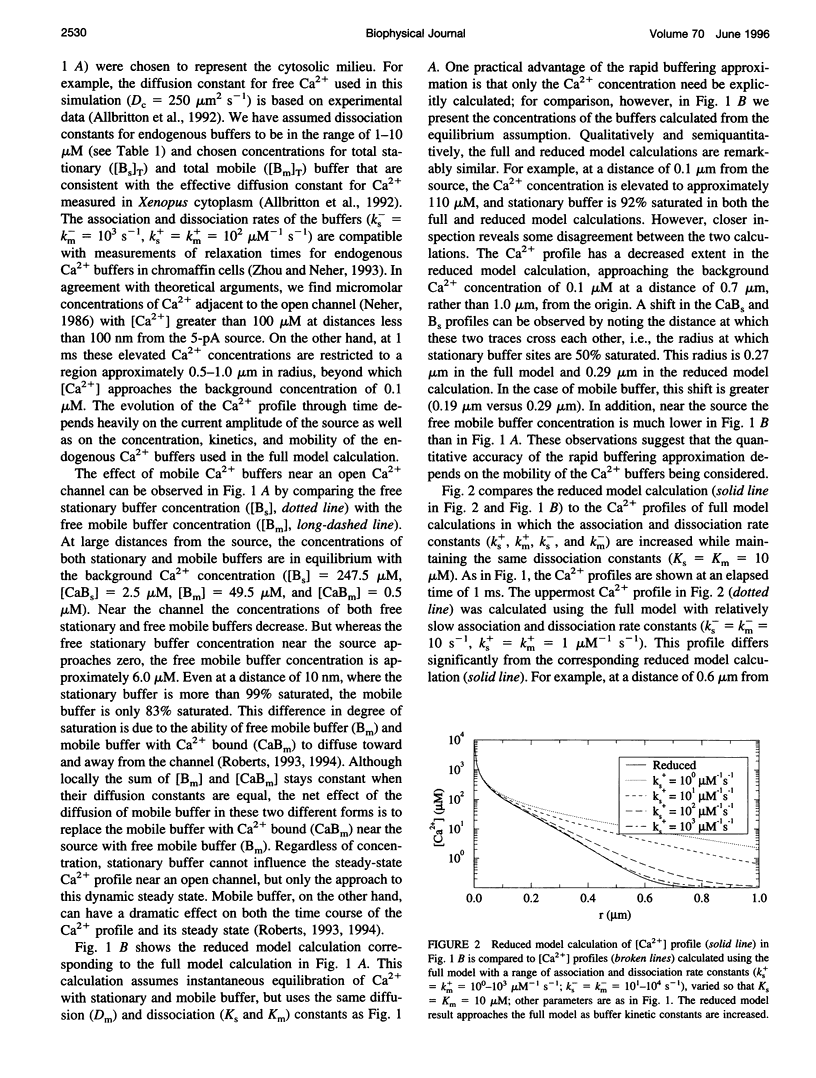
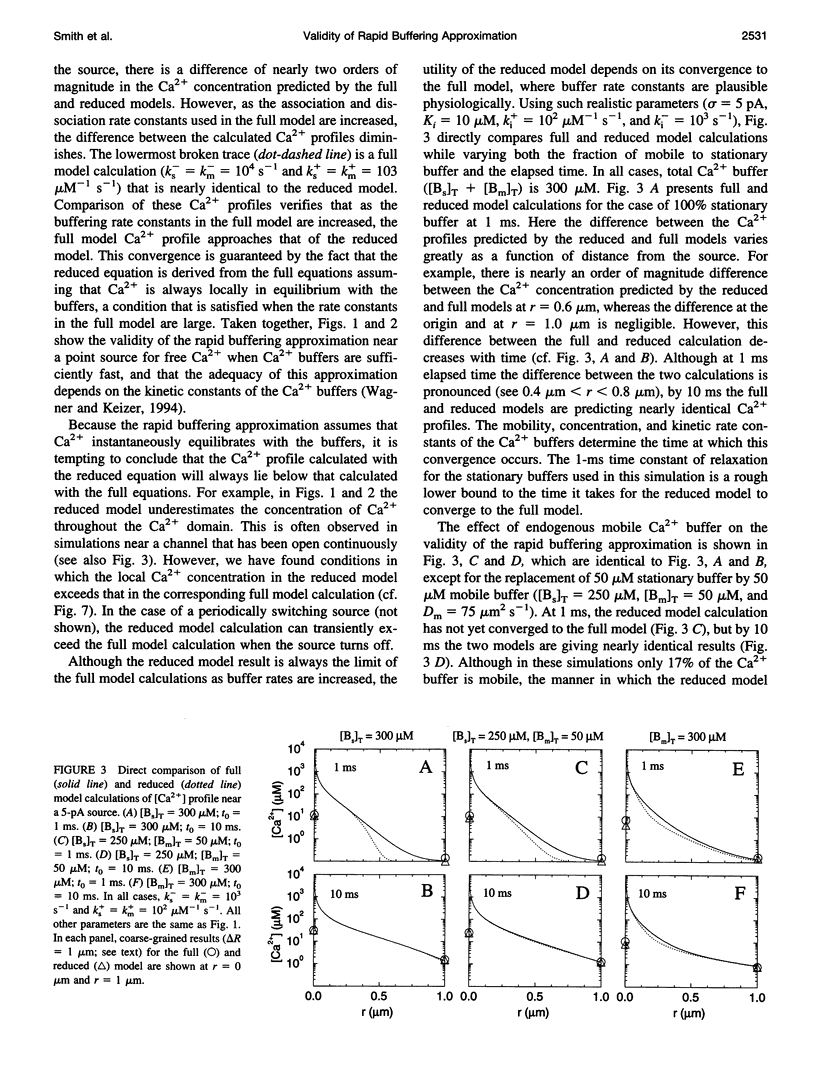
In the presence of rapid buffers the full reaction-diffusion equations describing Ca2+ transport can be reduced using the rapid buffering approximation to a single transport equation for [Ca2+]. Here we simulate the full and reduced equations, exploring the conditions necessary for the validity of the rapid buffering approximation for an isolated Ca2+ channel or a cluster of channels. Using a point source and performing numerical simulations of different durations, we quantify the error of the rapid buffering approximation as a function of buffer and source parameters as well as the time and spatial scale set by the resolution of confocal microscopic measurements. We carry out simulations of Ca2+ "sparks" and "puffs," both with and without the indicator dye Ca2+ Green-1, and find that the rapid buffering approximation is excellent. These calculations also show that the traditional calculation of [Ca2+] from a fluorescence signal may grossly underestimate the true value of [Ca2+] near a source. Finally, we use the full model to simulate the transient Ca2+ domain near the pore of an open Ca2+ channel in a cell dialyzed with millimolar concentrations of 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N,N-tetraacetic acid or EGTA. In this regime, where the rapid buffering approximation is poor. Neher's equation for the steady-state Ca2+ profile is shown to be a reliable approximation adjacent to the pore.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allbritton N. L., Meyer T., Stryer L. Range of messenger action of calcium ion and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1812–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.1465619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baimbridge K. G., Celio M. R., Rogers J. H. Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Aug;15(8):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90081-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Bassani J. W., Bers D. M. Intrinsic cytosolic calcium buffering properties of single rat cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1775–1787. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80652-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. Inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate (InsP3)-gated Ca channels from cerebellum: conduction properties for divalent cations and regulation by intraluminal calcium. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Nov;104(5):821–856. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.5.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Intracellular diffusion, binding, and compartmentalization of the fluorescent calcium indicators indo-1 and fura-2. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82494-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld H., Zablow L., Sabatini B. Evaluation of cellular mechanisms for modulation of calcium transients using a mathematical model of fura-2 Ca2+ imaging in Aplysia sensory neurons. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):1146–1164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81670-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Cheng H., Lederer W. J. Spatial non-uniformities in [Ca2+]i during excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1942–1956. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80677-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Cheng H., Lederer W. J. The control of calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1045–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.7754384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Lederer W. J., Cannell M. B. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):740–744. doi: 10.1126/science.8235594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard M., Erne P. Calcium binding to fluorescent calcium indicators: calcium green, calcium orange and calcium crimson. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):209–215. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Drake S. K., Hazard A. L., Peersen O. B. Molecular tuning of ion binding to calcium signaling proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 Aug;27(3):219–290. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelson A. L., Zucker R. S. Presynaptic calcium diffusion from various arrays of single channels. Implications for transmitter release and synaptic facilitation. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):1003–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83863-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann C., Chow R. H., Neher E., Zucker R. S. Kinetics of the secretory response in bovine chromaffin cells following flash photolysis of caged Ca2+. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2546–2557. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80744-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann C. W., Hunziker W. Intracellular calcium-binding proteins: more sites than insights. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90041-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jafri M. S., Keizer J. On the roles of Ca2+ diffusion, Ca2+ buffers, and the endoplasmic reticulum in IP3-induced Ca2+ waves. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):2139–2153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80088-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P. Practical aspects of measuring [Ca2+] with fluorescent indicators. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;40:155–181. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster H. P., Hartog A., Van Os C. H., Bindels R. J. Calbindin-D28K facilitates cytosolic calcium diffusion without interfering with calcium signaling. Cell Calcium. 1995 Sep;18(3):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(95)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Pinter M. J. Time courses of calcium and calcium-bound buffers following calcium influx in a model cell. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81342-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Yao Y. Regenerative release of calcium from functionally discrete subcellular stores by inositol trisphosphate. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Dec 23;246(1317):269–274. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pethig R., Kuhn M., Payne R., Adler E., Chen T. H., Jaffe L. F. On the dissociation constants of BAPTA-type calcium buffers. Cell Calcium. 1989 Oct;10(7):491–498. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post J. A., Langer G. A. Sarcolemmal calcium binding sites in heart: I. Molecular origin in "gas-dissected" sarcolemma. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jul;129(1):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00232054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M., Jacobs R. A., Hudspeth A. J. Colocalization of ion channels involved in frequency selectivity and synaptic transmission at presynaptic active zones of hair cells. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3664–3684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03664.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M. Localization of calcium signals by a mobile calcium buffer in frog saccular hair cells. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3246–3262. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03246.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M. Spatial calcium buffering in saccular hair cells. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):74–76. doi: 10.1038/363074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman A., Keizer J., Rinzel J. Domain model for Ca2(+)-inactivation of Ca2+ channels at low channel density. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):985–995. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82443-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Buffering of calcium in the vicinity of a channel pore. Cell Calcium. 1992 Mar;13(3):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90046-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A., Tse F. W., Hille B. Calcium homeostasis in identified rat gonadotrophs. J Physiol. 1994 Jun 15;477(Pt 3):511–525. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugorka A., Ríos E., Blatter L. A. Imaging elementary events of calcium release in skeletal muscle cells. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.7569901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J., Keizer J. Effects of rapid buffers on Ca2+ diffusion and Ca2+ oscillations. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):447–456. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80500-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Choi J., Parker I. Quantal puffs of intracellular Ca2+ evoked by inositol trisphosphate in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1995 Feb 1;482(Pt 3):533–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Mobile and immobile calcium buffers in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:245–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweifach A., Lewis R. S. Rapid inactivation of depletion-activated calcium current (ICRAC) due to local calcium feedback. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Feb;105(2):209–226. doi: 10.1085/jgp.105.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Leon M., Wang Y., Jones L., Perez-Reyes E., Wei X., Soong T. W., Snutch T. P., Yue D. T. Essential Ca(2+)-binding motif for Ca(2+)-sensitive inactivation of L-type Ca2+ channels. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1502–1506. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


