Abstract
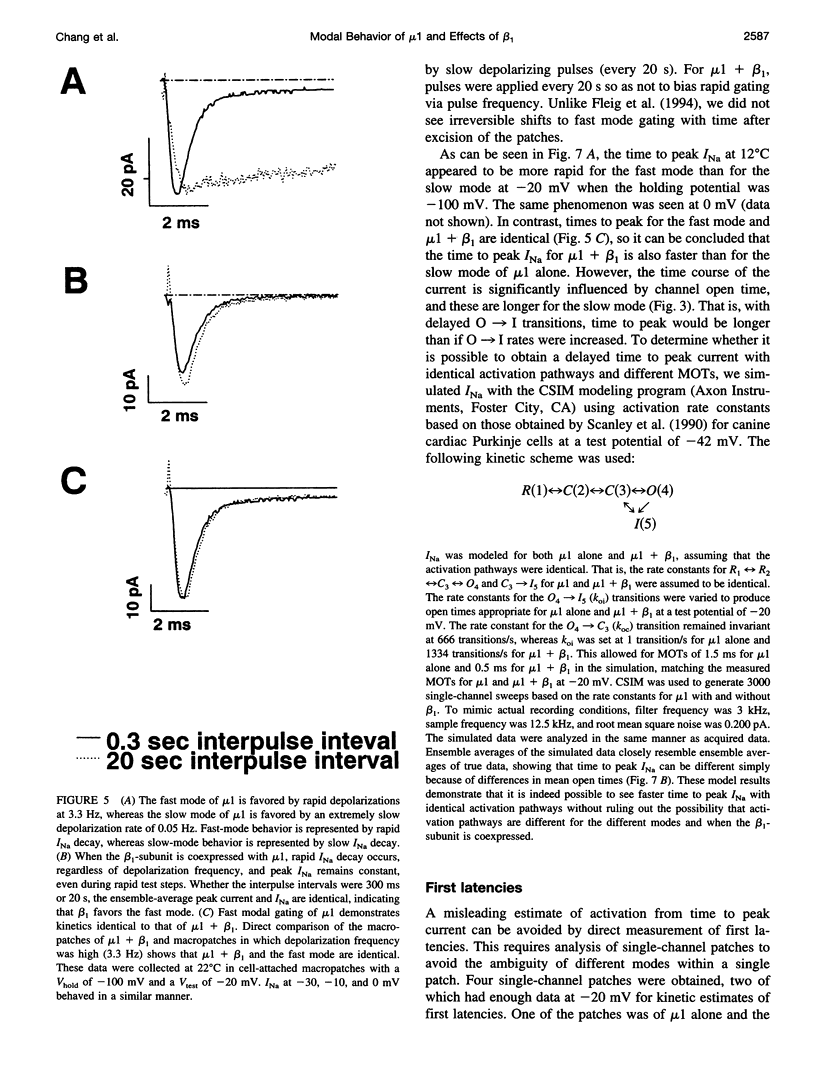
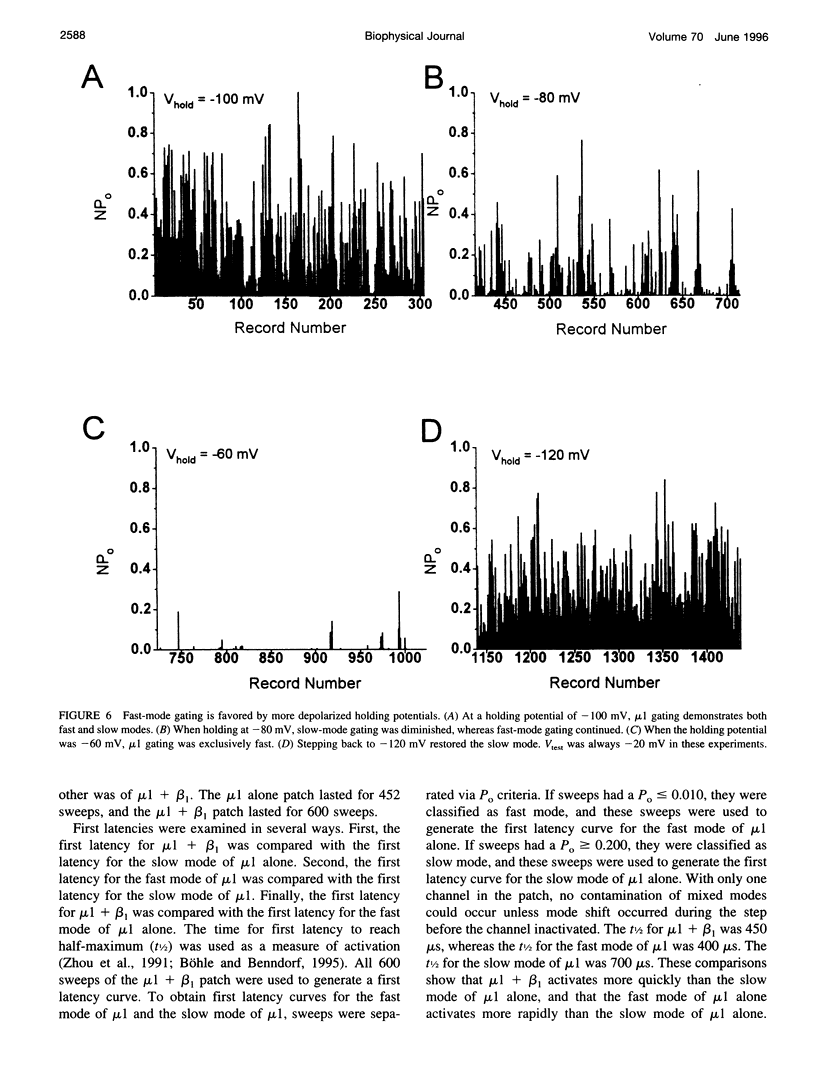
The adult rat skeletal muscle Na+ channel alpha-subunit (mu 1) appears to gate modally with two kinetic schemes when the channel is expressed in Xenopus oocytes. In the fast mode mu 1 single channels open only once or twice per depolarizing pulse, but in the slow mode the channels demonstrate bursting behavior. Slow-mode gating was favored by hyperpolarized holding potentials and slow depolarizing rates, whereas fast-mode gating was favored by depolarized holding potentials and rapid depolarizations. Single-channel studies showed that coexpression of beta 1 reduces slow-mode gating, so that channels gate almost exclusively in the fast mode. Analysis of open-time histograms showed that mu 1 and mu 1 + beta 1 both have two open-time populations with the same mean open times (MOTs). The difference lies in the relative sizes of the long and short MOT components. When beta 1 was coexpressed with mu 1 in oocytes, the long MOT fraction was greatly reduced. It appears that although mu 1 and mu 1 + beta 1 share the same two open states, the beta 1-subunit favors the mode with the shorter open state. Examination of first latencies showed that it is likely that the rate of activation is increased upon coexpression with beta 1. Experiments also showed that the rate of activation for the fast mode of mu 1 is identical to that for mu 1 + beta 1 and is thus more rapid than the rate of activation for the slow mode. It can be concluded that beta 1 restores native-like kinetics in mu 1 by favoring the fast-gating mode.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alzheimer C., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Modal gating of Na+ channels as a mechanism of persistent Na+ current in pyramidal neurons from rat and cat sensorimotor cortex. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):660–673. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00660.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhle T., Benndorf K. Multimodal action of single Na+ channels in myocardial mouse cells. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80166-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., McClatchey A. I., Gusella J. F. Modification of the Na+ current conducted by the rat skeletal muscle alpha subunit by coexpression with a human brain beta subunit. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):155–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00374974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., Strittmatter S. M. Functional expression of sodium channel mutations identified in families with periodic paralysis. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90321-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Lipscombe D., Tsien R. W. Multiple modes of N-type calcium channel activity distinguished by differences in gating kinetics. J Neurosci. 1993 Jan;13(1):181–194. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-01-00181.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Tsien R. W. Altered prevalence of gating modes in neurotransmitter inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):980–984. doi: 10.1126/science.8094902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleig A., Ruben P. C., Rayner M. D. Kinetic mode switch of rat brain IIA Na channels in Xenopus oocytes excised macropatches. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Jul;427(5-6):399–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00374253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Snutch T., Lübbert H., Dowsett A., Marshall J., Auld V., Downey W., Fritz L. C., Lester H. A., Dunn R. Messenger RNA coding for only the alpha subunit of the rat brain Na channel is sufficient for expression of functional channels in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7503–7507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji S., Sun W., George A. L., Jr, Horn R., Barchi R. L. Voltage-dependent regulation of modal gating in the rat SkM1 sodium channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Oct;104(4):625–643. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Kinetic states and modes of single large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:79–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Evidence for two voltage-dependent Ca2+ binding reactions. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):511–542. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., VanDongen A. M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Fast and slow gating of sodium channels encoded by a single mRNA. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo D., Brehm P. Modal shifts in acetylcholine receptor channel gating confer subunit-dependent desensitization. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1811–1814. doi: 10.1126/science.8511590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B. Modal gating behavior of cardiac sodium channels in cell-free membrane patches. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):857–862. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83166-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Gration K. A., Usherwood P. N. Single glutamate-activated channels in locust muscle. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):643–645. doi: 10.1038/278643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M. Slow currents through single sodium channels of the adult rat heart. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):89–104. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M. Two modes of gating during late Na+ channel currents in frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Feb;87(2):305–326. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B. Sodium channel subconductance levels measured with a new variance-mean analysis. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. E., Isom L. L., Catterall W. A., Goldin A. L. The adult rat brain beta 1 subunit modifies activation and inactivation gating of multiple sodium channel alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17649–17655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Hess P. Reversible uncoupling of inactivation in N-type calcium channels. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):657–659. doi: 10.1038/351657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W. A Fourier method for the analysis of exponential decay curves. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85660-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Rogart R. B., Fozzard H. A. The cloned cardiac Na channel alpha-subunit expressed in Xenopus oocytes show gating and blocking properties of native channels. J Membr Biol. 1992 Oct;130(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00233735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanley B. E., Hanck D. A., Chay T., Fozzard H. A. Kinetic analysis of single sodium channels from canine cardiac Purkinje cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):411–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibmayer W., Wallner M., Lotan I. Mechanism of modulation of single sodium channels from skeletal muscle by the beta 1-subunit from rat brain. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Feb;426(3-4):360–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00374796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Neher E. Single Na+ channel currents observed in cultured rat muscle cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):447–449. doi: 10.1038/287447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., Sigworth F. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukomadu C., Zhou J., Sigworth F. J., Agnew W. S. muI Na+ channels expressed transiently in human embryonic kidney cells: biochemical and biophysical properties. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):663–676. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90088-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner M., Weigl L., Meera P., Lotan I. Modulation of the skeletal muscle sodium channel alpha-subunit by the beta 1-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):535–539. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80871-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. E., Horn R. Functional differences between two classes of sodium channels in developing rat skeletal muscle. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):361–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2425432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. S., Bennett P. B., Makita N., George A. L., Barchi R. L. Expression of the sodium channel beta 1 subunit in rat skeletal muscle is selectively associated with the tetrodotoxin-sensitive alpha subunit isoform. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):915–922. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J. Y., Potts J. F., Trimmer J. S., Agnew W. S., Sigworth F. J. Multiple gating modes and the effect of modulating factors on the microI sodium channel. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90280-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



