Abstract
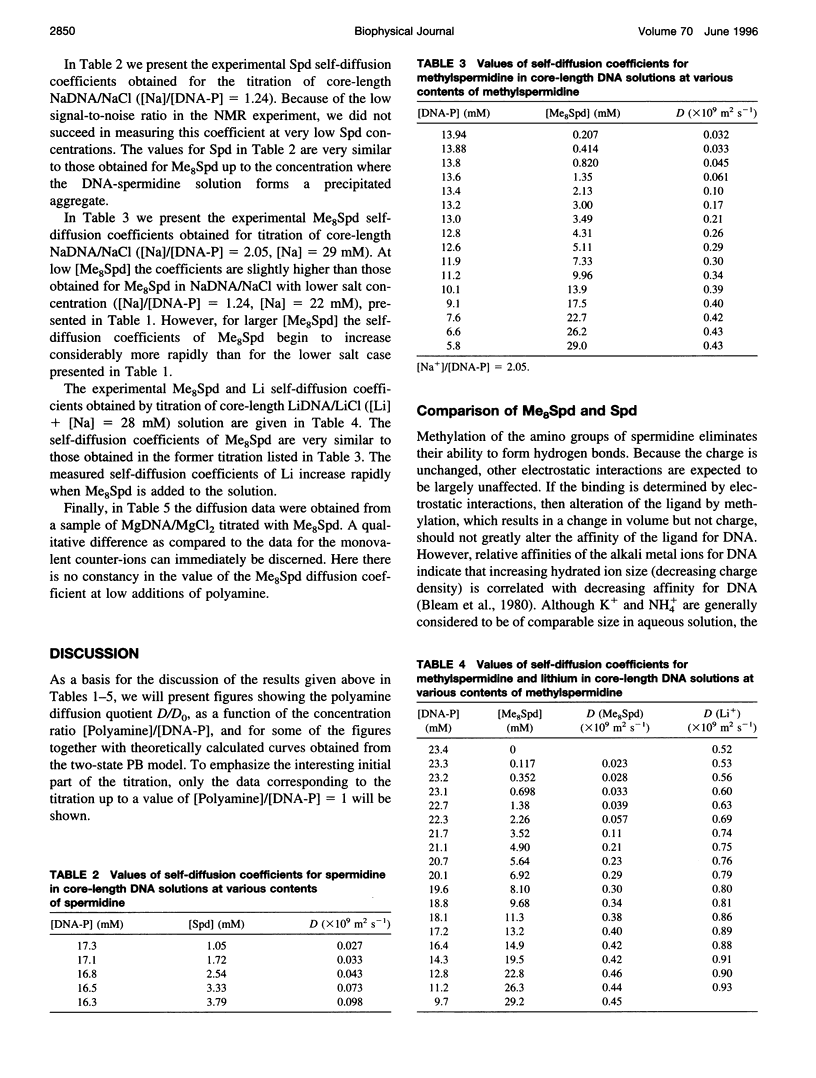
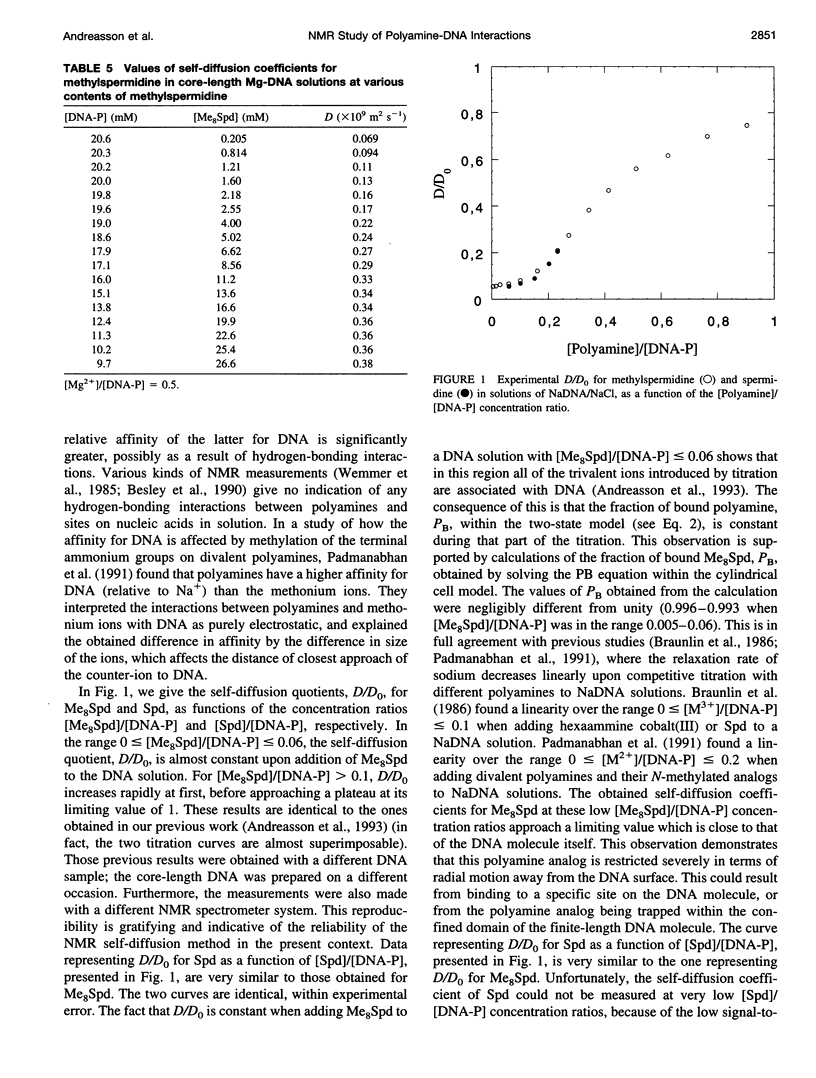
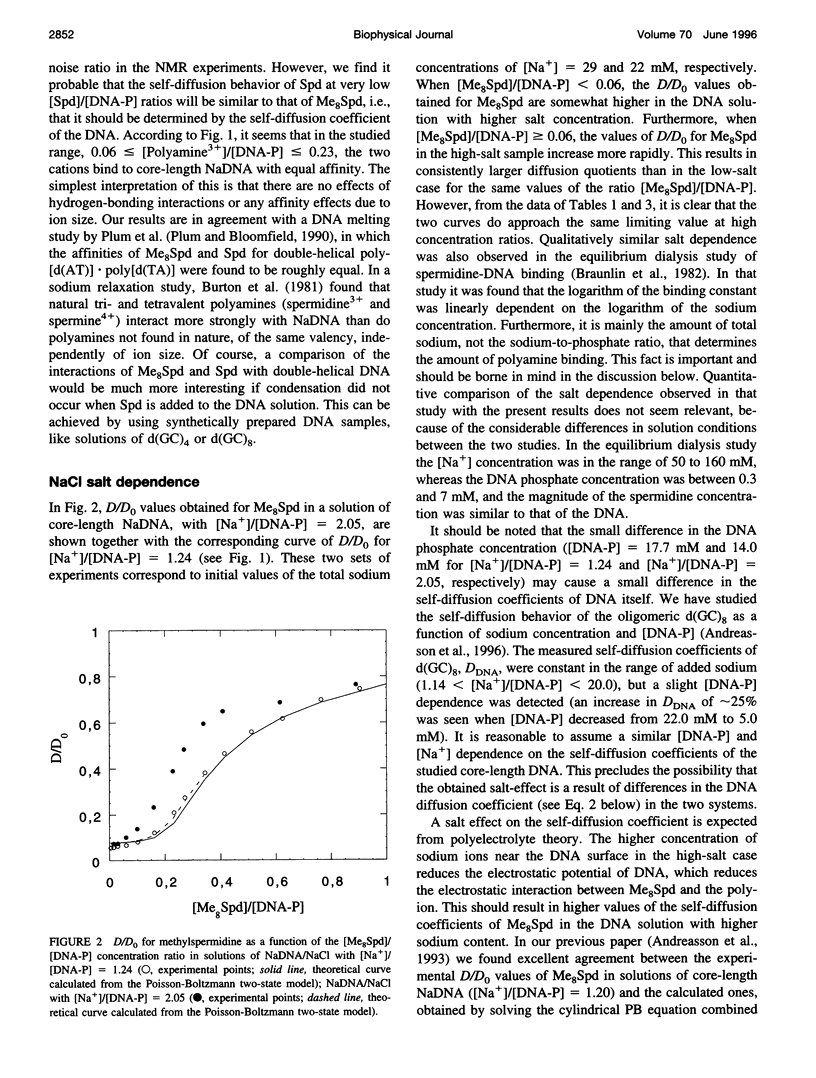
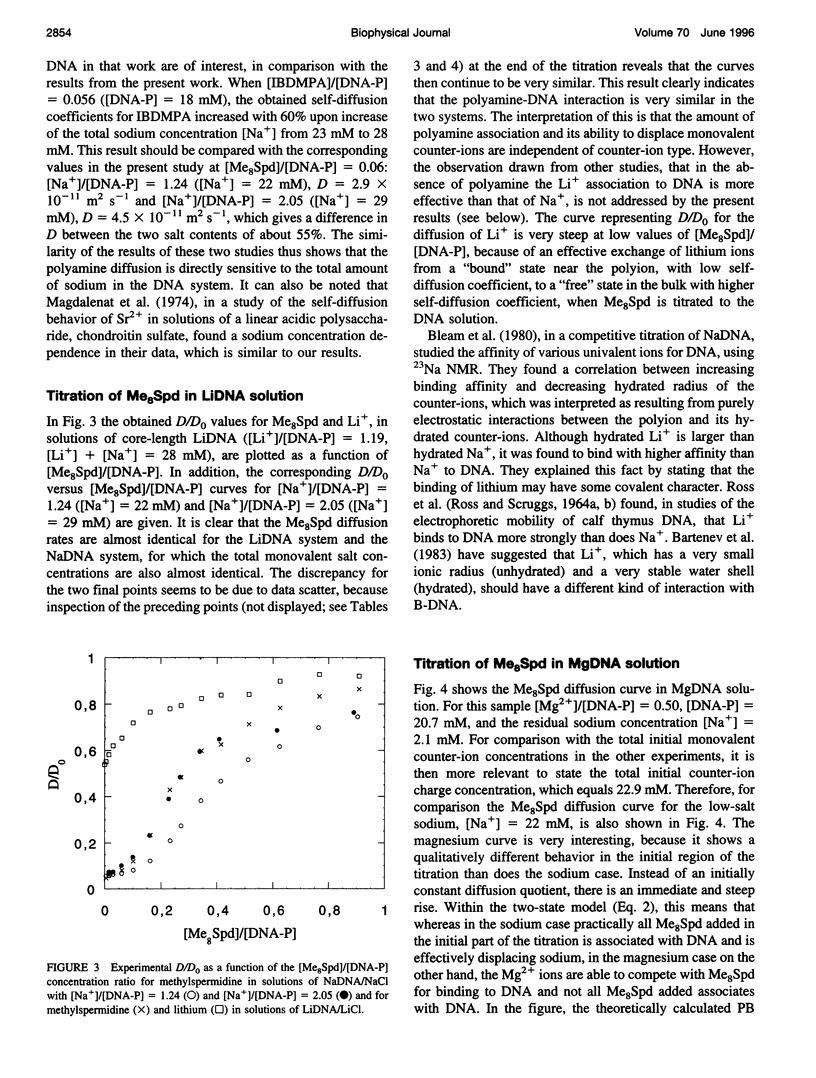
The NMR pulsed field gradient self-diffusion method has been used to study the self-diffusion of the polyamine spermidine and the polyamine analog methylspermidine (completely N-methylated spermidine). The self-diffusion coefficient, D, was measured in solutions of calf thymus DNA prepared from nucleosome core particles (with an average length of 120 base pairs) as a function of the concentration ratio of polyamine to DNA phosphate. A study of the self-diffusion quotient, D/Do (where Do is the diffusion coefficient for free polyamine, not associated with DNA), in additions of spermidine and methyl-spermidine to solutions of NaDNA/NaCl, gave almost identical results with complete association of polyamine to DNA in the initial part of the titrations, indicating similar affinities for DNA. A large influence on the measured self-diffusion coefficients was detected for methylspermidine in NaDNA solutions with different concentrations of NaCl, which shows a considerable salt effect on the polyamine-DNA association. No notable differences in D/Do for methylspermidine were observed in competitive titrations of solutions of Li- and NaDNA, indicating that sodium and lithium ions behave similarly in their interactions with DNA. In titration experiments of methylspermidine into MgDNA solution, the results showed that the polyamine association is less effective than in the case of NaDNA, because of competition from magnesium binding to DNA. Comparisons with calculations based on the electrostatic Poisson-Boltzmann cell model were performed. It is suggested that the interaction is primarily of electrostatic nature, with no binding to specific sites on the DNA molecule.
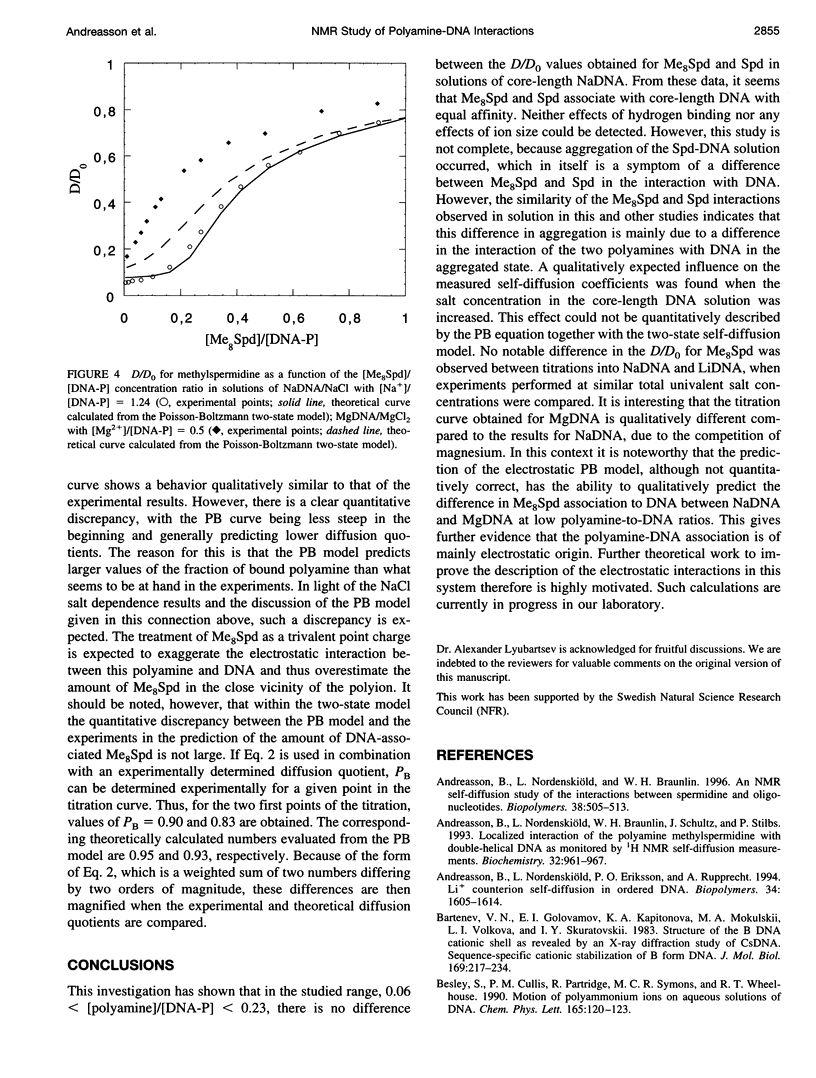
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasson B., Nordenskiöld L., Braunlin W. H. An NMR self-diffusion study of the interactions between spermidine and oligonucleotides. Biopolymers. 1996 Apr;38(4):505–513. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(199604)38:4%3C505::AID-BIP6%3E3.0.CO;2-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasson B., Nordenskiöld L., Braunlin W. H., Schultz J., Stilbs P. Localized interaction of the polyamine methylspermidine with double-helical DNA as monitored by 1H NMR self-diffusion measurements. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):961–967. doi: 10.1021/bi00054a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenev V. N., Golovamov EuI, Kapitonova K. A., Mokulskii M. A., Volkova L. I., Skuratovskii IYa Structure of the B DNA cationic shell as revealed by an X-ray diffraction study of CsDNA. Sequence-specific cationic stabilization of B form DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):217–234. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleam M. L., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. Relative binding affinities of monovalent cations for double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. 23Na-NMR investigations of counterion exchange reactions of helical DNA. Biopolymers. 1986 Jan;25(1):205–214. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Drakenberg T., Nordenskiöld L. A 43Ca-NMR study of Ca(II)-DNA interactions. Biopolymers. 1987 Jul;26(7):1047–1062. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Strick T. J., Record M. T., Jr Equilibrium dialysis studies of polyamine binding to DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Jul;21(7):1301–1314. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Forsén S., Reimarsson P. The interaction of polyamines with DNA: a 23Na NMR study. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1219–1228. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Gosule L. C., Schellman A. DNA condensation with polyamines. II. Electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. III. Geometry of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):535–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosule L. C., Schellman J. A. DNA condensation with polyamines I. Spectroscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S., Zon G., Sundaralingam M. Base only binding of spermine in the deep groove of the A-DNA octamer d(GTGTACAC). Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2360–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Fratini A. V., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Ordered water structure around a B-DNA dodecamer. A quantitative study. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):129–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm G., Wong L., Pack G. R. Monte Carlo and Poisson-Boltzmann calculations of the fraction of counterions bound to DNA. Biopolymers. 1994 Feb;34(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/bip.360340209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdelenat H., Turq P., Chemla M. Study of the self-diffusion coefficients of cations in the presence of an acidic polysaccharide. Biopolymers. 1974;13(8):1535–1548. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenskiöld L., Chang D. K., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr 23Na NMR relaxation study of the effects of conformation and base composition on the interactions of counterions with double-helical DNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4309–4317. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan S., Brushaber V. M., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Relative affinities of divalent polyamines and of their N-methylated analogues for helical DNA determined by 23Na NMR. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7550–7559. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan S., Richey B., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Interaction of an N-methylated polyamine analogue, hexamethonium(2+), with NaDNA: quantitative 14N and 23Na NMR relaxation rate studies of the cation-exchange process. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4367–4376. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen M. D., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Counterion exchange reactions on DNA: Monte Carlo and Poisson-Boltzmann analysis. Biopolymers. 1988 Aug;27(8):1249–1265. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum G. E., Bloomfield V. A. Structural and electrostatic effects on binding of trivalent cations to double-stranded and single-stranded poly[d (AT)]. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):13–27. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Teeter M. M., Rich A. Structural analysis of spermine and magnesium ion binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Mazur S. J., Melançon P., Roe J. H., Shaner S. L., Unger L. Double helical DNA: conformations, physical properties, and interactions with ligands. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:997–1024. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rill R. L., Hilliard P. R., Jr, Levy G. C. Spontaneous ordering of DNA. Effects of intermolecular interactions on DNA motional dynamics monitored by 13C and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Nordenskiöld L., Rupprecht A. A study of the quadrupolar NMR splittings of 7Li+, 23Na+, and 133Cs+ counterions in macroscopically oriented DNA fibers. Biopolymers. 1992 Dec;32(12):1631–1642. doi: 10.1002/bip.360321206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemmer D. E., Srivenugopal K. S., Reid B. R., Morris D. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of polyamine binding to a defined DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):457–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


