Abstract
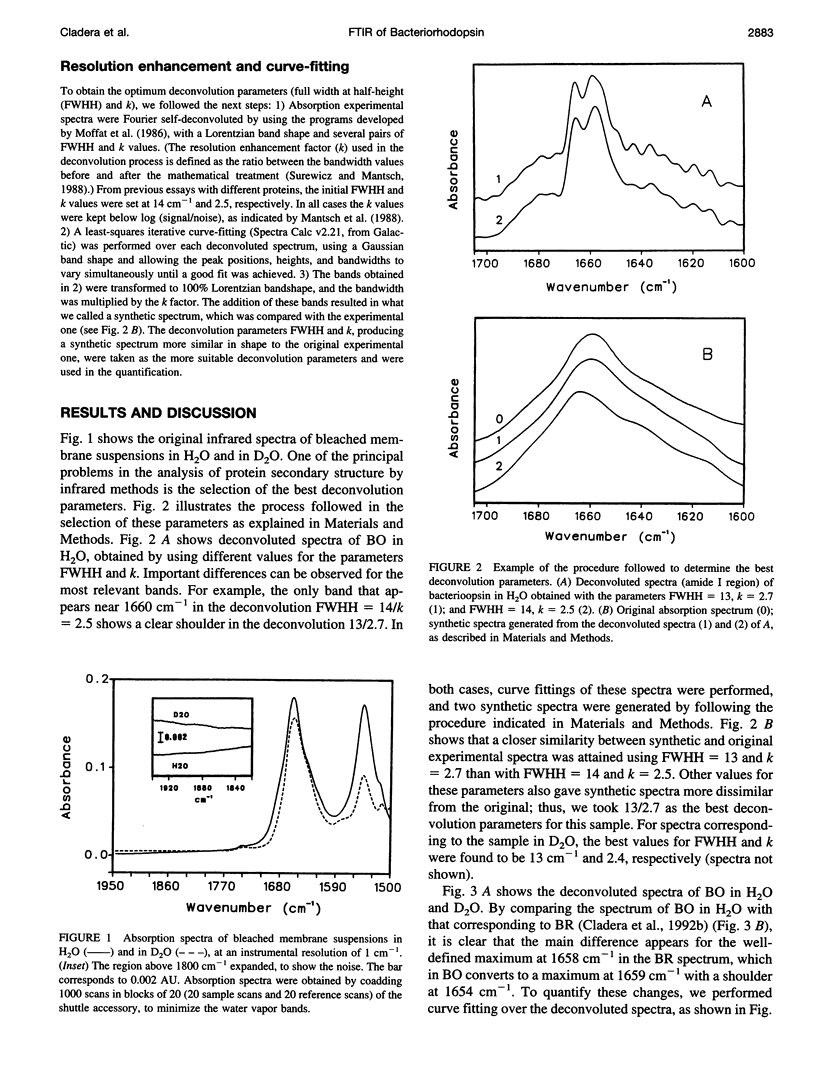
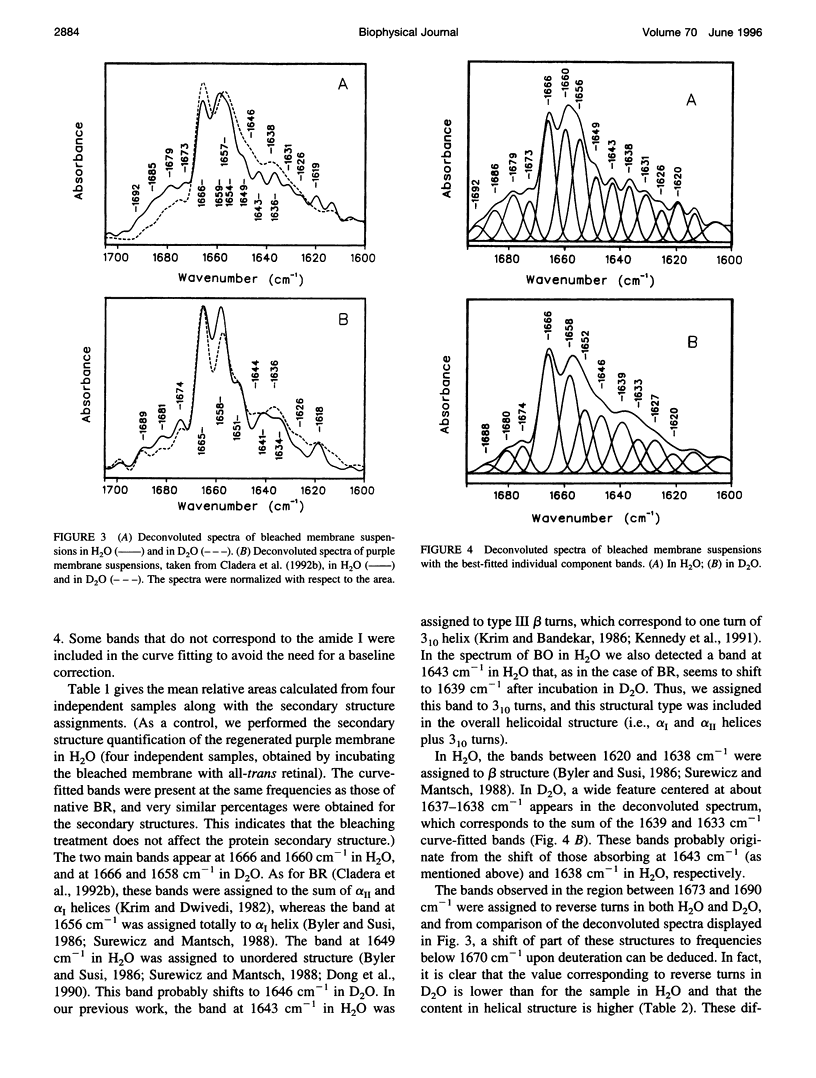
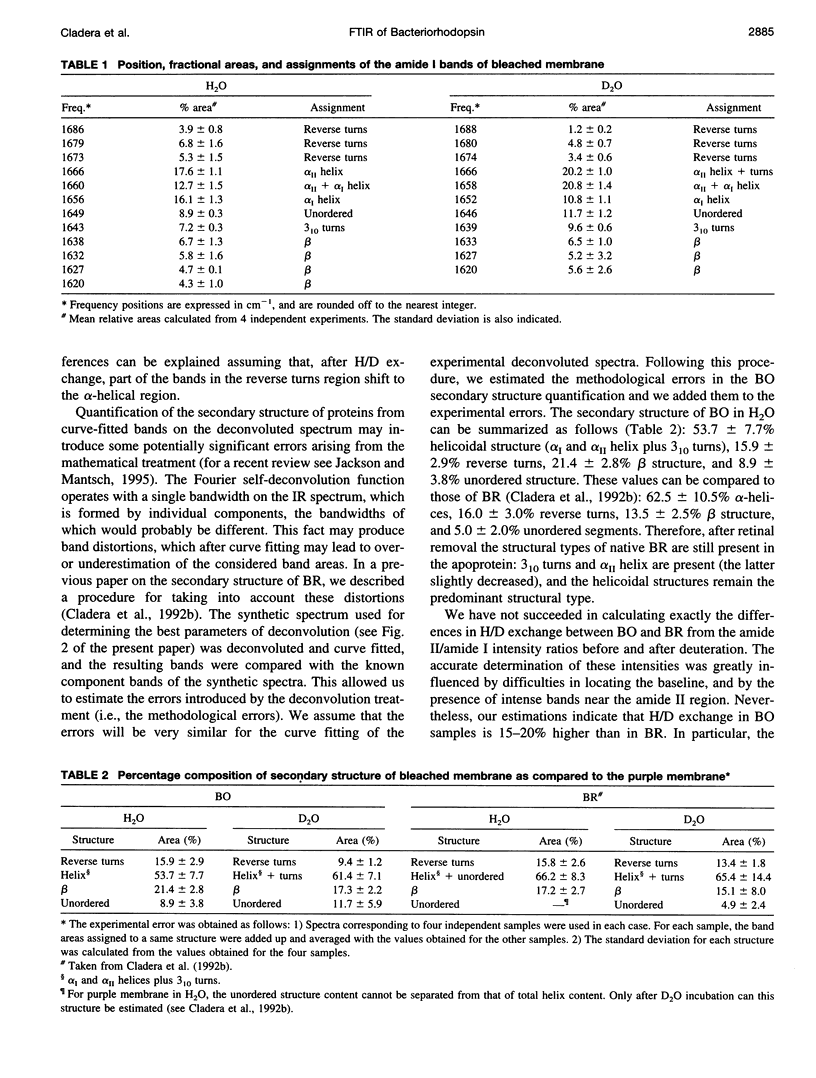
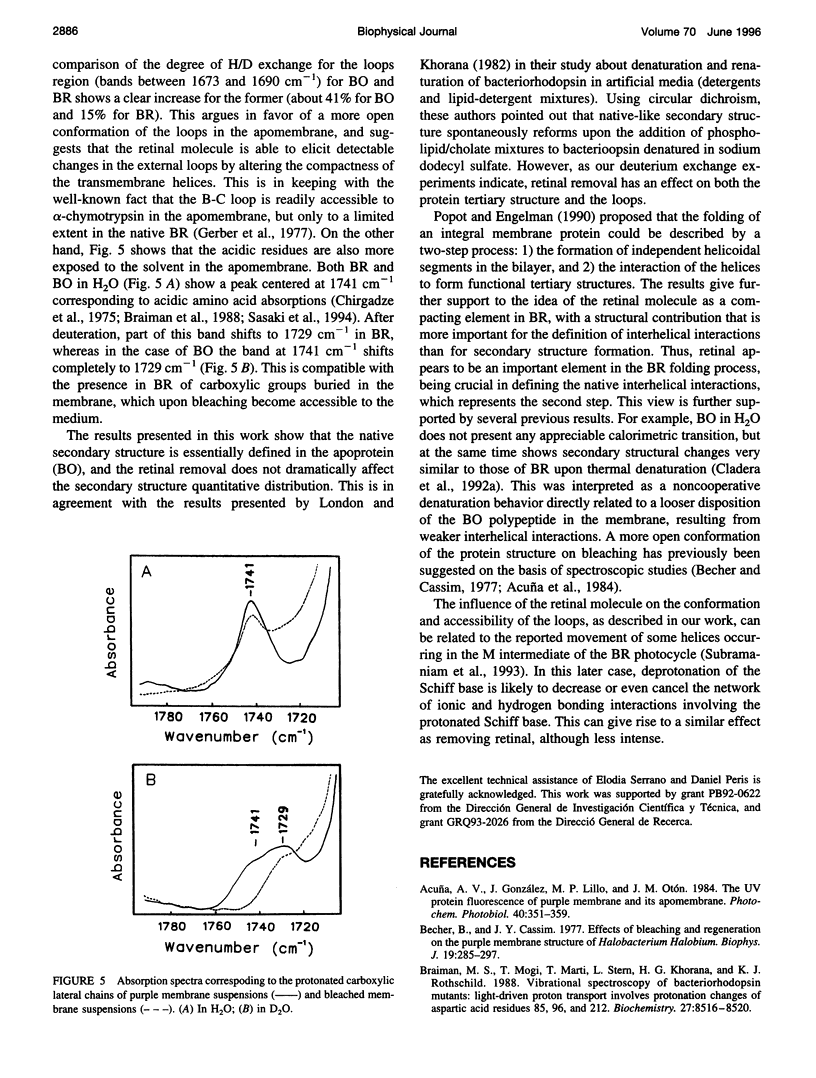
The conformation of bacterioopsin in the apomembrane has been studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Resolution enhancement techniques and curve-fitting procedures have been used to determine the secondary structural components from the amide I region. Bacterioopsin contains about 54% helicoidal structure (alpha I and alpha II helices + 3(10) turns), 21% sheets, 16% reverse turns, and 9% unordered structure. Thus, after retinal removal, all of the secondary structural types of bacteriorhodopsin remain present, and only slight quantitative differences appear. On the other hand, H/D exchange studies show that there is a higher degree of exchange for reverse turns and protonated carboxylic lateral chains in bacterioopsin as compared to bacteriorhodopsin. This gives further support to the idea of a more open tertiary structure of bacterioopsin, and to the consideration of the retinal molecule as an important element in complementing the interhelical interactions in bacteriorhodopsin folding.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becher B., Cassim J. Y. Effects of bleaching and regeneration on the purple membrane structure of Halobaterium halobium. Biophys J. 1977 Sep;19(3):285–297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(77)85588-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghaus P. A., Dencher N. A. The chromophore retinal hinders passive proton/hydroxide ion translocation through bacteriorhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Dec;275(2):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byler D. M., Susi H. Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers. 1986 Mar;25(3):469–487. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgadze Y. N., Fedorov O. V., Trushina N. P. Estimation of amino acid residue side-chain absorption in the infrared spectra of protein solutions in heavy water. Biopolymers. 1975 Apr;14(4):679–694. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladera J., Galisteo M. L., Sabés M., Mateo P. L., Padrós E. The role of retinal in the thermal stability of the purple membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):581–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladera J., Sabés M., Padrós E. Fourier transform infrared analysis of bacteriorhodopsin secondary structure. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12363–12368. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong A., Huang P., Caughey W. S. Protein secondary structures in water from second-derivative amide I infrared spectra. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3303–3308. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duñach M., Padrós E., Muga A., Arrondo J. L. Fourier-transform infrared studies on cation binding to native and modified purple membranes. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8940–8945. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duñach M., Seigneuret M., Rigaud J. L., Padrós E. The relationship between the chromophore moiety and the cation binding sites in bacteriorhodopsin. Biosci Rep. 1986 Nov;6(11):961–966. doi: 10.1007/BF01114972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Gray C. P., Wildenauer D., Khorana H. G. Orientation of bacteriorhodopsin in Halobacterium halobium as studied by selective proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5426–5430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M., Mantsch H. H. The use and misuse of FTIR spectroscopy in the determination of protein structure. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1995;30(2):95–120. doi: 10.3109/10409239509085140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. F., Crisma M., Toniolo C., Chapman D. Studies of peptides forming 3(10)- and alpha-helices and beta-bend ribbon structures in organic solution and in model biomembranes by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6541–6548. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin, a membrane protein that uses light to translocate protons. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimm S., Bandekar J. Vibrational spectroscopy and conformation of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:181–364. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimm S., Dwivedi A. M. Infrared spectrum of the purple membrane: clue to a proton conduction mechanism? Science. 1982 Apr 23;216(4544):407–408. doi: 10.1126/science.6280277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Proton translocation mechanism and energetics in the light-driven pump bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 7;1183(2):241–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London E., Khorana H. G. Denaturation and renaturation of bacteriorhodopsin in detergents and lipid-detergent mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7003–7011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Schuhmann L., Gruber H. Light-dependent reaction of bacteriorhodopsin with hydroxylamine in cell suspensions of Halobacterium halobium: demonstration of an apo-membrane. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Engelman D. M. Membrane protein folding and oligomerization: the two-stage model. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4031–4037. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J. FTIR difference spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin: toward a molecular model. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):147–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00762674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki J., Lanyi J. K., Needleman R., Yoshizawa T., Maeda A. Complete identification of C = O stretching vibrational bands of protonated aspartic acid residues in the difference infrared spectra of M and N intermediates versus bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 22;33(11):3178–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00177a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S., Gerstein M., Oesterhelt D., Henderson R. Electron diffraction analysis of structural changes in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05625.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surewicz W. K., Mantsch H. H. New insight into protein secondary structure from resolution-enhanced infrared spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 29;952(2):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Gärtner W. The secondary structure of bacteriorhodopsin determined by Raman and circular dichroism spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11464–11469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


