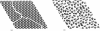Abstract
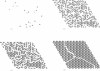
We simulated the structure of reversible protein aggregates as a function of protein surface characteristics, protein-protein interaction energies, and the entropic penalty accompanying the immobilization of protein in a solid phase. These simulations represent an extension of our previous work on kinetically irreversible protein aggregate structure and are based on an explicit accounting of the specific protein-protein interactions that occur within reversible aggregates and crystals. We considered protein monomers with a mixture of hydrophobic and hydrophilic surface regions suspended in a polar solvent; the energetic driving force for aggregation is provided by the burial of solvent-exposed hydrophobic surface area. We analyzed the physical properties of the generated aggregates, including density, protein-protein contact distributions, solvent accessible surface area, porosity, and order, and compared our results with the protein crystallization literature as well as with the kinetically irreversible case. The physical properties of reversible aggregates were consonant with those observed for the irreversible aggregates, although in general, reversible aggregates were more stable energetically and were more crystal-like in their order content than their irreversible counterparts. The reversible aggregates were less dense than the irreversible aggregates, indicating that the increased energetic stability is derived primarily from the optimality rather than the density of the packing in the solid phase. The extent of hydrophobic protein-protein contacts and solvent-exposed surface area within the aggregate phase depended on the aggregation pathway: reversible aggregates tended to have a greater proportion of hydrophobic-hydrophobic contacts and a smaller fraction of hydrophobic solvent-exposed surface area. Furthermore, the arrangement of hydrophobic patches on the protein surface played a major role in the distribution of protein contacts and solvent content. This was readily reflected in the order of the aggregates: the greater the contiguity of the hydrophobic patches on the monomer surface, the less ordered the aggregates became, despite the opportunities for rearrangement offered by a reversible pathway. These simulations have enhanced our understanding of the impact of protein structural motifs on aggregate properties and on the demarcation between aggregation and crystallization.
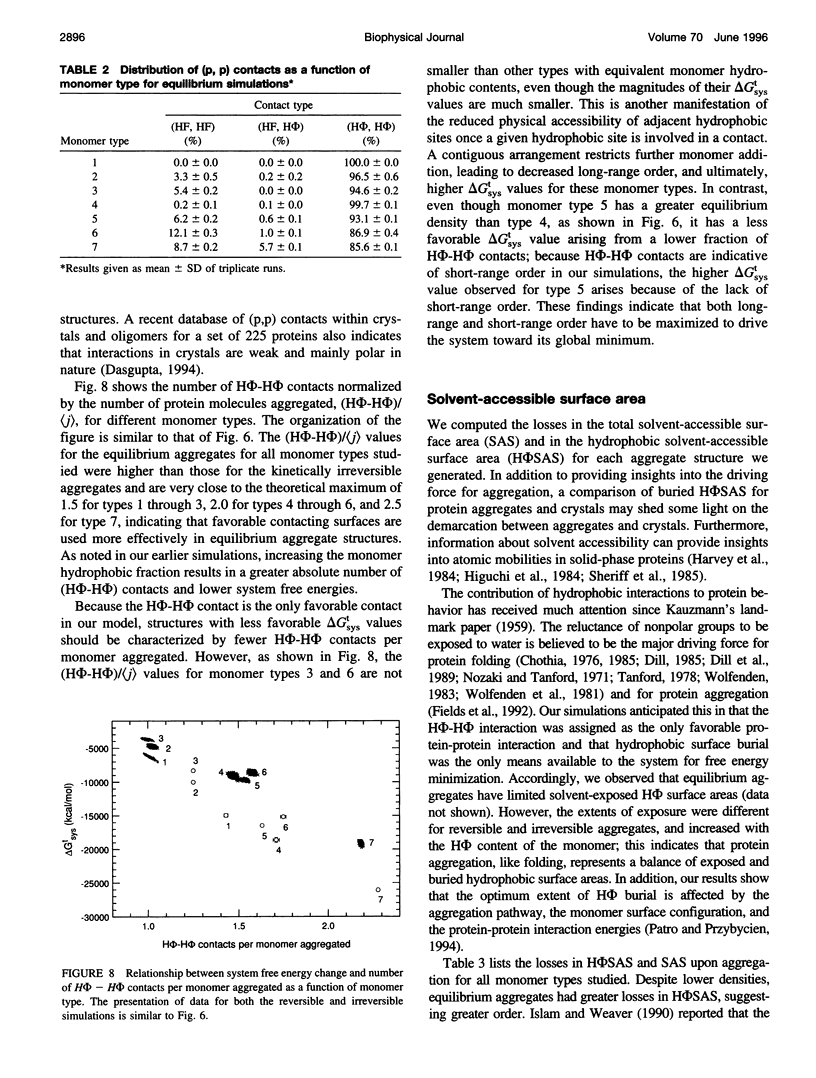
Full text
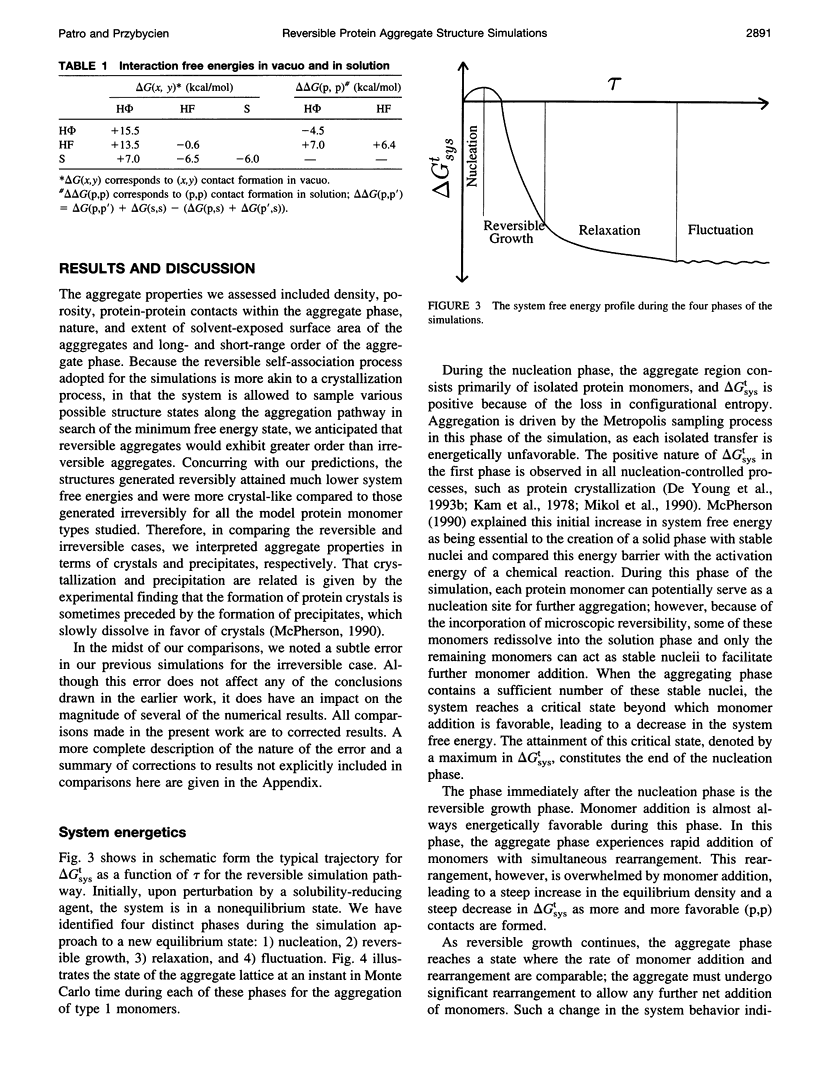
PDF






Images in this article
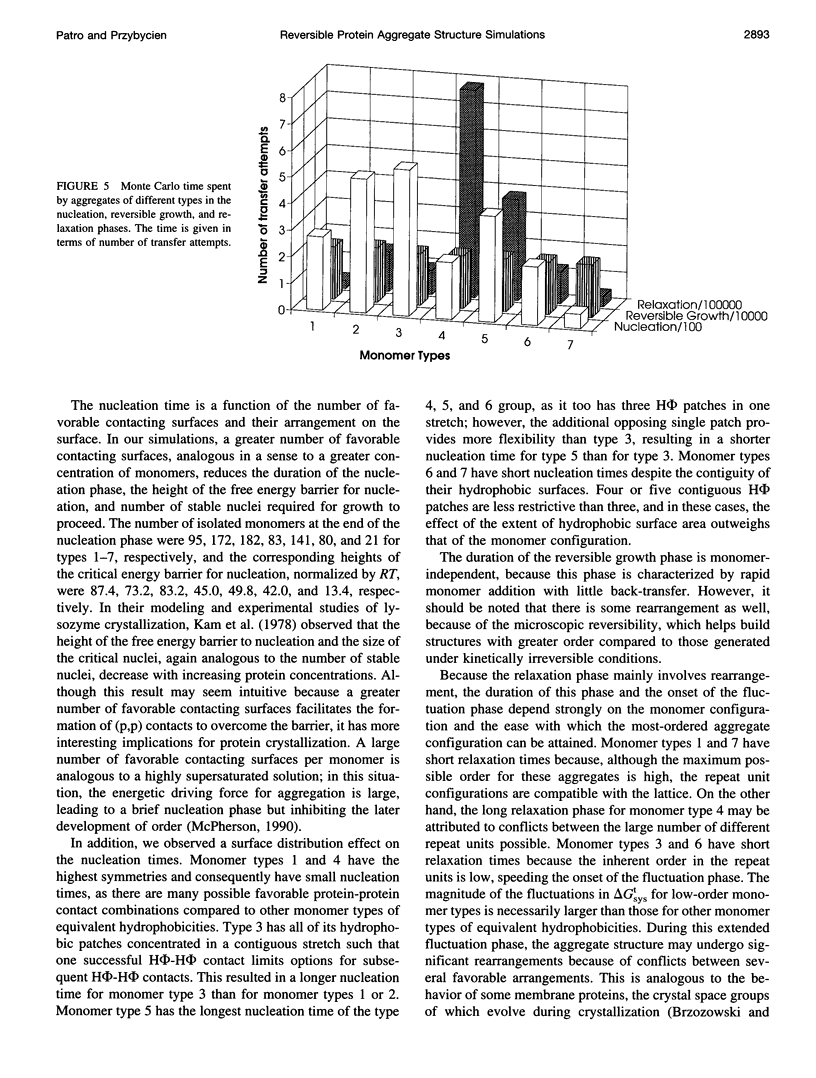
Selected References
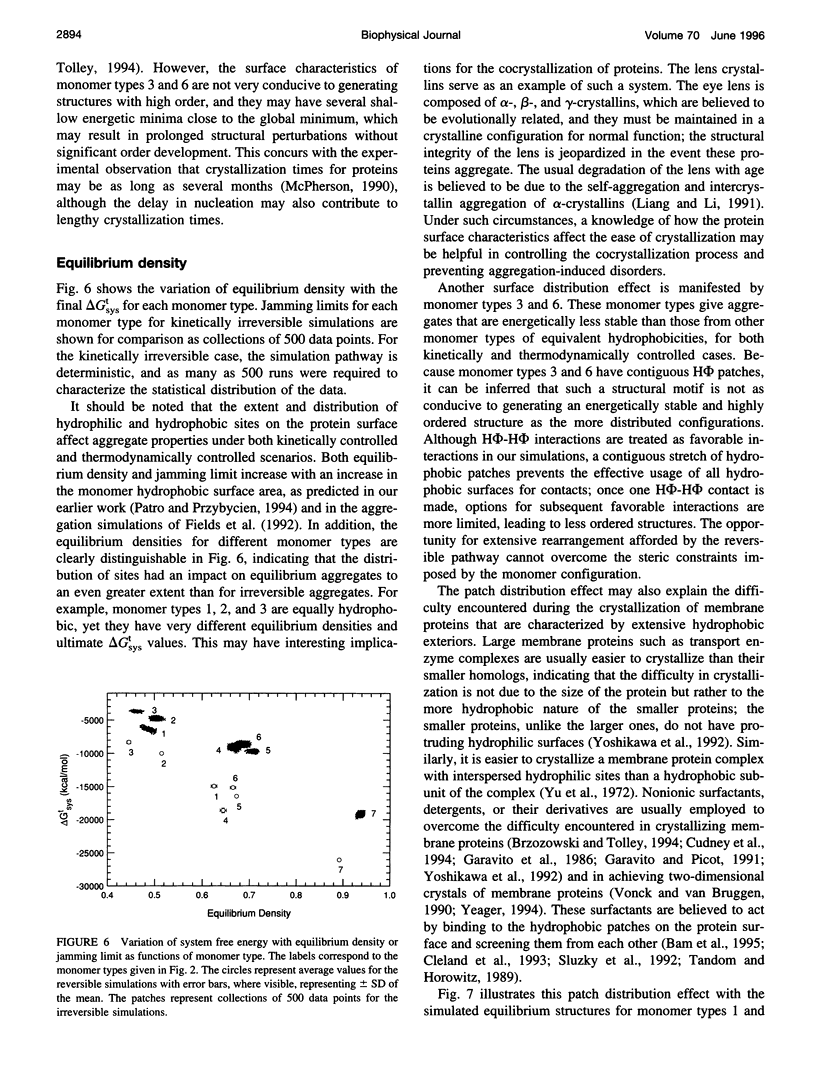
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bam N. B., Randolph T. W., Cleland J. L. Stability of protein formulations: investigation of surfactant effects by a novel EPR spectroscopic technique. Pharm Res. 1995 Jan;12(1):2–11. doi: 10.1023/a:1016286600229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker G. W., Bowsher R. R., Mackellar W. C., Poor M. L., Tackitt P. M., Riggin R. M. Chemical, physical, and biological characterization of a dimeric form of biosynthetic human growth hormone. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1987 Dec;9(6):478–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1470-8744.1987.tb00491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Nagel R. L., Ranney H. M. The effect of beta 73 Asn on the interactions of sickling hemoglobins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 17;221(2):373–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brems D. N., Alter L. A., Beckage M. J., Chance R. E., DiMarchi R. D., Green L. K., Long H. B., Pekar A. H., Shields J. E., Frank B. H. Altering the association properties of insulin by amino acid replacement. Protein Eng. 1992 Sep;5(6):527–533. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.6.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowski A. M., Tolley S. P. Poly(ethylene) glycol monomethyl ethers - an alternative to poly(ethylene) glycols in protein crystallization. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 Jul 1;50(Pt 4):466–468. doi: 10.1107/S090744499400199X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal H. L., Köhler U., Mantsch H. H. Structural and conformational changes of beta-lactoglobulin B: an infrared spectroscopic study of the effect of pH and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 2;957(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Principles that determine the structure of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:537–572. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. The nature of the accessible and buried surfaces in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland J. L., Powell M. F., Shire S. J. The development of stable protein formulations: a close look at protein aggregation, deamidation, and oxidation. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1993;10(4):307–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosio M. P., Janin J., Jullien M. Crystal packing in six crystal forms of pancreatic ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90503-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudney R., Patel S., Weisgraber K., Newhouse Y., McPherson A. Screening and optimization strategies for macromolecular crystal growth. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 Jul 1;50(Pt 4):414–423. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994002660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arcy A. Crystallizing proteins - a rational approach? Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 Jul 1;50(Pt 4):469–471. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993014362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young L. R., Dill K. A., Fink A. L. Aggregation and denaturation of apomyoglobin in aqueous urea solutions. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 20;32(15):3877–3886. doi: 10.1021/bi00066a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A., Alonso D. O., Hutchinson K. Thermal stabilities of globular proteins. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5439–5449. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A. Theory for the folding and stability of globular proteins. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1501–1509. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton W. A., Kashi Y., Furtak K., Horwich A. L. Residues in chaperonin GroEL required for polypeptide binding and release. Nature. 1994 Oct 13;371(6498):614–619. doi: 10.1038/371614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald R. D., Wright S. E. Maintenance of optical quality during crystalline lens growth. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):618–620. doi: 10.1038/301618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks F., Hatley R. H., Friedman H. L. The thermodynamics of protein stability. Cold destabilization as a general phenomenon. Biophys Chem. 1988 Sep;31(3):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)80037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. P., Smith D. H., King J. Genetic analysis of the folding pathway for the tail spike protein of phage P22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7060–7064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C., Prabhakaran M., Mao B., McCammon J. A. Phenylalanine transfer RNA: molecular dynamics simulation. Science. 1984 Mar 16;223(4641):1189–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.6560785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Carter D. C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):209–215. doi: 10.1038/358209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi Y., Kusunoki M., Matsuura Y., Yasuoka N., Kakudo M. Refined structure of cytochrome c3 at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 5;172(1):109–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM V. M. Abnormal human haemoglobins. III. The chemical difference between normal and sickle cell haemoglobins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Dec;36:402–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam S. A., Weaver D. L. Molecular interactions in protein crystals: solvent accessible surface and stability. Proteins. 1990;8(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadima W., McPherson A., Dunn M. F., Jurnak F. A. Characterization of precrystallization aggregation of canavalin by dynamic light scattering. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82513-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam Z., Shore H. B., Feher G. On the crystallization of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):539–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Cheever E. V., Seavey B. K. Aggregate-free human growth hormone. I. Isolation by ultrafiltration. Endocrinology. 1969 Feb;84(2):325–331. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Parker D. C., Okerlund M. D., Boyar R. M., Litteria M., Vanderlaan W. P. Aggregate-free human growth hormone. II. Physicochemical and biological properties. Endocrinology. 1969 Feb;84(2):332–339. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J. N., Li X. Y. Interaction and aggregation of lens crystallins. Exp Eye Res. 1991 Jul;53(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson A. Current approaches to macromolecular crystallization. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 20;189(1):1–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikol V., Hirsch E., Giegé R. Diagnostic of precipitant for biomacromolecule crystallization by quasi-elastic light-scattering. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):187–195. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S., Janin J., Lesk A. M., Chothia C. Interior and surface of monomeric proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):641–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitraki A., Fane B., Haase-Pettingell C., Sturtevant J., King J. Global suppression of protein folding defects and inclusion body formation. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):54–58. doi: 10.1126/science.1648264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. V., Leppert P. Role of aggregated human growth hormone (hGH) in development of antibodies to hGH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):691–697. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. Establishment of a hydrophobicity scale. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2211–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., ITANO H. A. Sickle cell anemia a molecular disease. Science. 1949 Nov 25;110(2865):543–548. doi: 10.1126/science.110.2865.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patro S. Y., Przybycien T. M. Simulations of kinetically irreversible protein aggregate structure. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1274–1289. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80922-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattou D., Maigret B., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Computational analysis of conformational behavior of cholecystokinin fragments. I-CCK4, CCK5, CCK6 and CCK7 molecules. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 May;37(5):440–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinas U., Tsai L. B., Lyons D., Fox G. M., Stearns G., Fieschko J., Fenton D., Bailey J. E. Cysteine to serine substitutions in basic fibroblast growth factor: effect on inclusion body formation and proteolytic susceptibility during in vitro refolding. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Apr;10(4):435–440. doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick B., Jurnak F. Extension of the diffraction resolution of crystals. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 Jul 1;50(Pt 4):563–568. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994001976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedzik J. DESIGN: a guide to protein crystallization experiments. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Feb 1;308(2):342–348. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedzik J., Kirschner D. A. Is myelin basic protein crystallizable? Neurochem Res. 1992 Feb;17(2):157–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00966794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev Y. V., Chirgadze Y. N., Mylvaganam S. E., Driessen H., Slingsby C., Blundell T. L. Surface interactions of gamma-crystallins in the crystal medium in relation to their association in the eye lens. Proteins. 1988;4(2):137–147. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff S., Hendrickson W. A., Stenkamp R. E., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Influence of solvent accessibility and intermolecular contacts on atomic mobilities in hemerythrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1104–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Chan H. S., Dill K. A. Modeling the effects of mutations on the denatured states of proteins. Protein Sci. 1992 Feb;1(2):201–215. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Endo S., Nagayama K. Stabilization of protein crystals by electrostatic interactions as revealed by a numerical approach. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 20;234(2):421–432. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon S., Horowitz P. M. Reversible folding of rhodanese. Presence of intermediate(s) at equilibrium. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9859–9866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. The hydrophobic effect and the organization of living matter. Science. 1978 Jun 2;200(4345):1012–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.653353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonck J., van Bruggen E. F. Electron microscopy and image analysis of two-dimensional crystals and single molecules of alcohol oxidase from Hansenula polymorpha. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 29;1038(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R., Perry L. J., Veilleux C. Mutations in human interferon gamma affecting inclusion body formation identified by a general immunochemical screen. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Aug;9(8):731–737. doi: 10.1038/nbt0891-731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. E., Driessen H. P., Slingsby C., Moss D. S., Lindley P. F. Packing interactions in the eye-lens. Structural analysis, internal symmetry and lattice interactions of bovine gamma IVa-crystallin. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):217–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90452-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R., Andersson L., Cullis P. M., Southgate C. C. Affinities of amino acid side chains for solvent water. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):849–855. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. Waterlogged molecules. Science. 1983 Dec 9;222(4628):1087–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.6359416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager M. In situ two-dimensional crystallization of a polytopic membrane protein: the cardiac gap junction channel. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 Jul 1;50(Pt 4):632–638. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993014313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Yu L., King T. E. Preparation and properties of cardiac cytochrome c 1 . J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1012–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue K., Dill K. A. Inverse protein folding problem: designing polymer sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4163–4167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]