Abstract
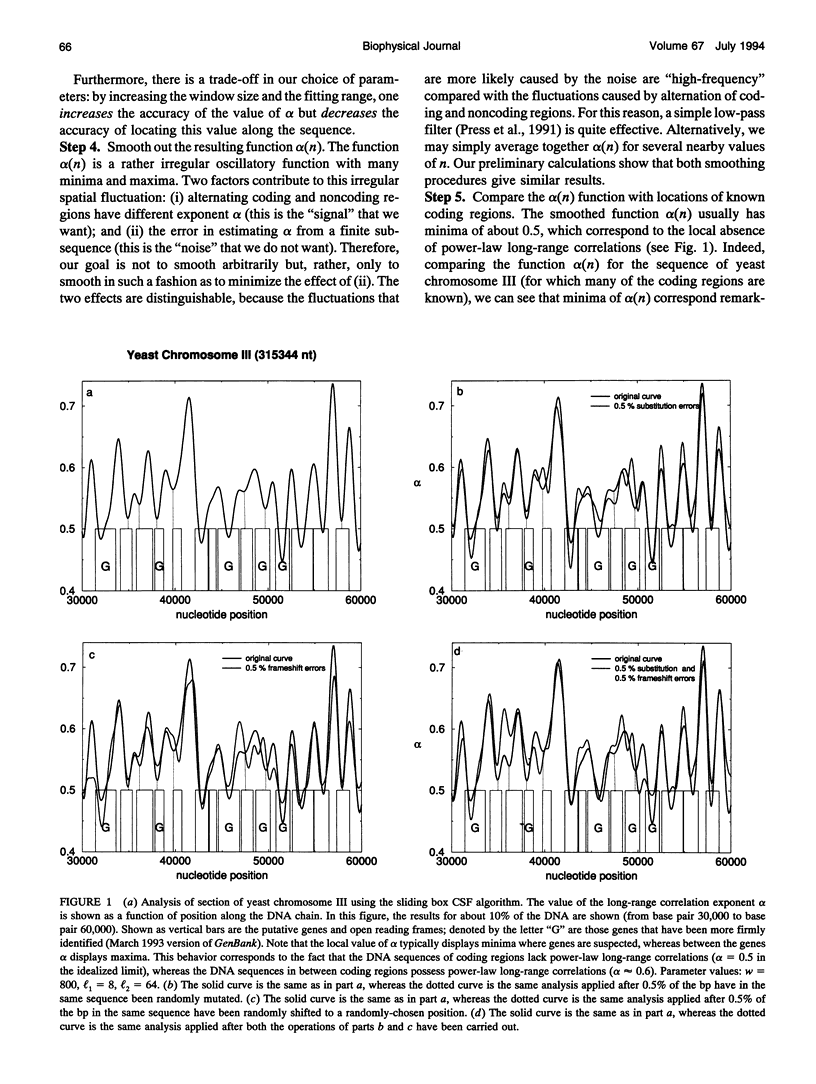
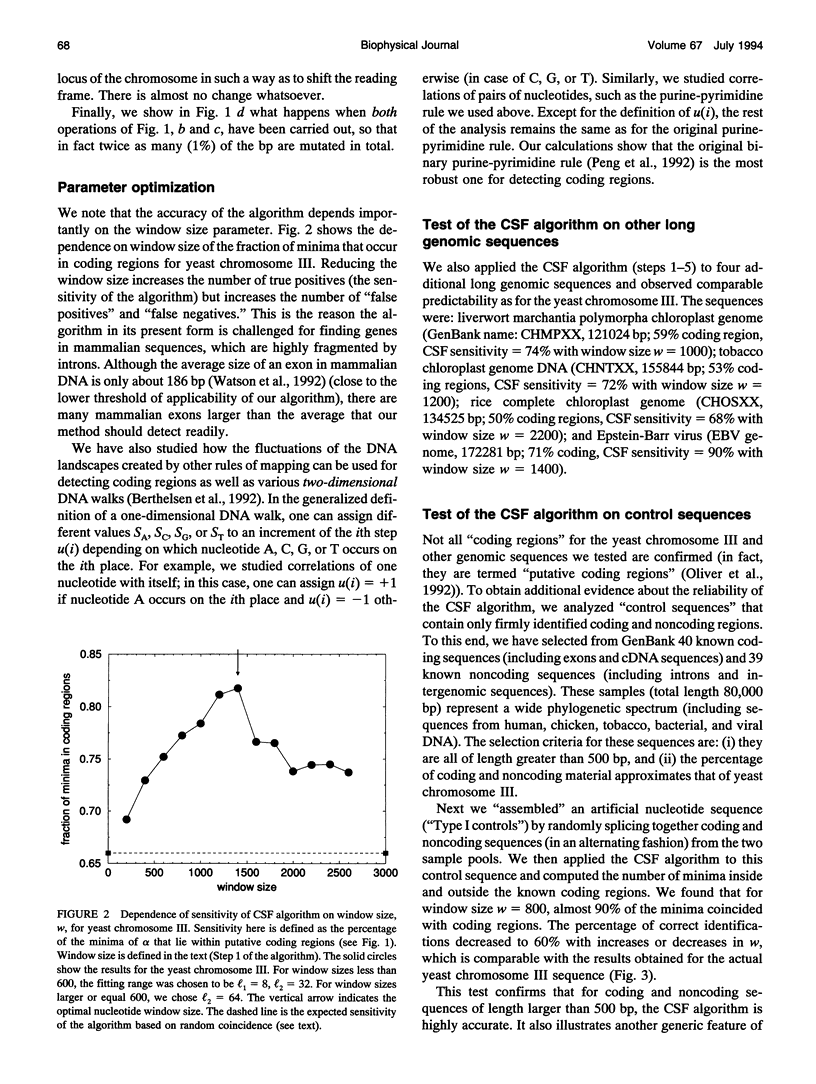
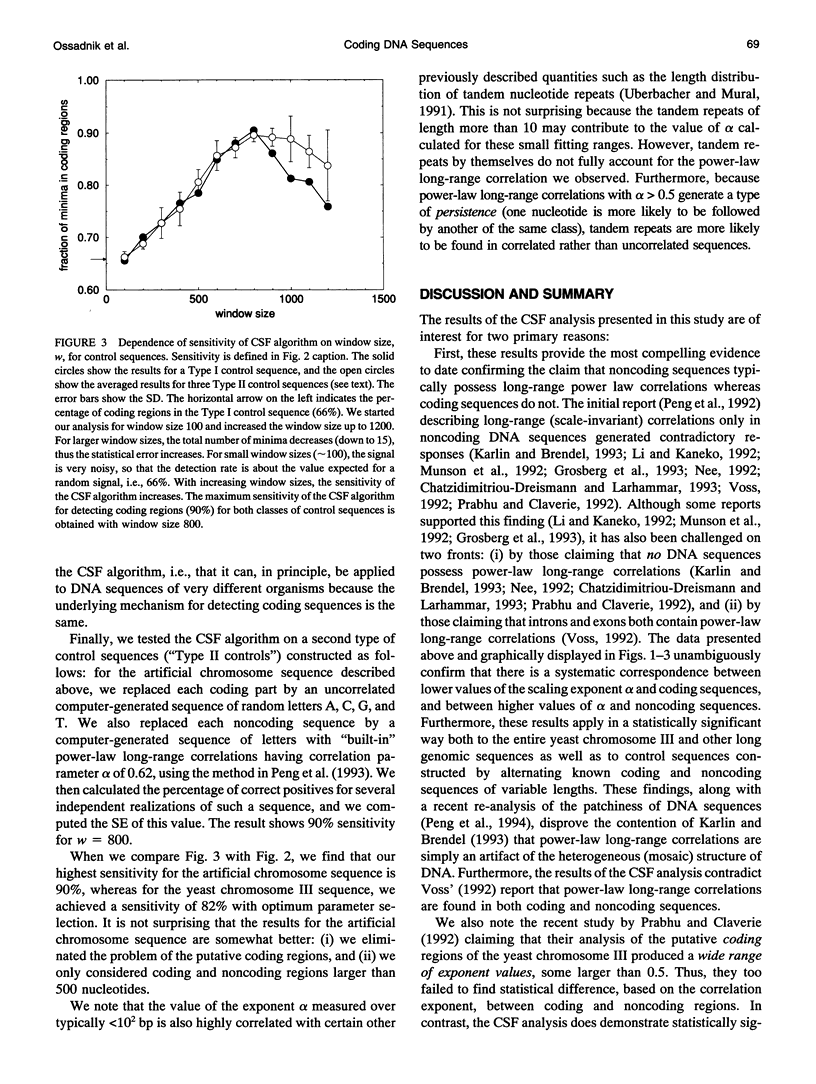
Recently, it was observed that noncoding regions of DNA sequences possess long-range power-law correlations, whereas coding regions typically display only short-range correlations. We develop an algorithm based on this finding that enables investigators to perform a statistical analysis on long DNA sequences to locate possible coding regions. The algorithm is particularly successful in predicting the location of lengthy coding regions. For example, for the complete genome of yeast chromosome III (315,344 nucleotides), at least 82% of the predictions correspond to putative coding regions; the algorithm correctly identified all coding regions larger than 3000 nucleotides, 92% of coding regions between 2000 and 3000 nucleotides long, and 79% of coding regions between 1000 and 2000 nucleotides. The predictive ability of this new algorithm supports the claim that there is a fundamental difference in the correlation property between coding and noncoding sequences. This algorithm, which is not species-dependent, can be implemented with other techniques for rapidly and accurately locating relatively long coding regions in genomic sequences.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelsen CL, Glazier JA, Skolnick MH. Global fractal dimension of human DNA sequences treated as pseudorandom walks. Phys Rev A. 1992 Jun 15;45(12):8902–8913. doi: 10.1103/physreva.45.8902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buldyrev S. V., Goldberger A. L., Havlin S., Peng C-K, Simons M., Stanley H. E. Generalized Lévy-walk model for DNA nucleotide sequences. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1993 Jun;47(6):4514–4523. doi: 10.1103/physreve.47.4514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buldyrev S. V., Goldberger A. L., Havlin S., Peng C. K., Stanley H. E., Stanley M. H., Simons M. Fractal landscapes and molecular evolution: modeling the myosin heavy chain gene family. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2673–2679. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81290-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatzidimitriou-Dreismann C. A., Larhammar D. Long-range correlations in DNA. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):212–213. doi: 10.1038/361212b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Brendel V. Patchiness and correlations in DNA sequences. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):677–680. doi: 10.1126/science.8430316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Taylor R. C., Michaels G. S. DNA correlations. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):636–636. doi: 10.1038/360636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nee S. Uncorrelated DNA walks. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):450–450. doi: 10.1038/357450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C-K, Buldyrev S. V., Goldberger A. L., Havlin S., Simons M., Stanley H. E. Finite-size effects on long-range correlations: implications for analyzing DNA sequences. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1993 May;47(5):3730–3733. doi: 10.1103/physreve.47.3730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C. K., Buldyrev S. V., Goldberger A. L., Havlin S., Sciortino F., Simons M., Stanley H. E. Long-range correlations in nucleotide sequences. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):168–170. doi: 10.1038/356168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C. K., Buldyrev S. V., Havlin S., Simons M., Stanley H. E., Goldberger A. L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1994 Feb;49(2):1685–1689. doi: 10.1103/physreve.49.1685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu V. V., Claverie J. M. Correlations in intronless DNA. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):782–782. doi: 10.1038/359782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakhnovich E. I., Gutin A. M. Implications of thermodynamics of protein folding for evolution of primary sequences. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):773–775. doi: 10.1038/346773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uberbacher E. C., Mural R. J. Locating protein-coding regions in human DNA sequences by a multiple sensor-neural network approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11261–11265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss RF. Evolution of long-range fractal correlations and 1/f noise in DNA base sequences. Phys Rev Lett. 1992 Jun 22;68(25):3805–3808. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


