Abstract
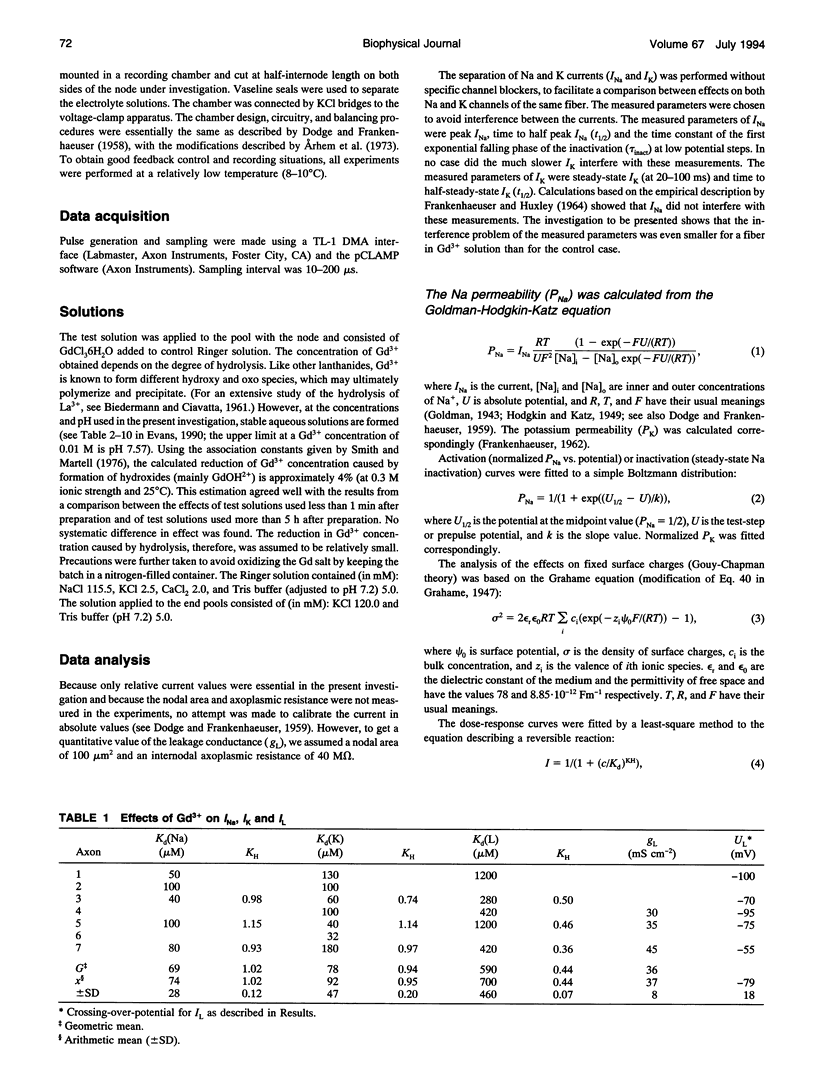
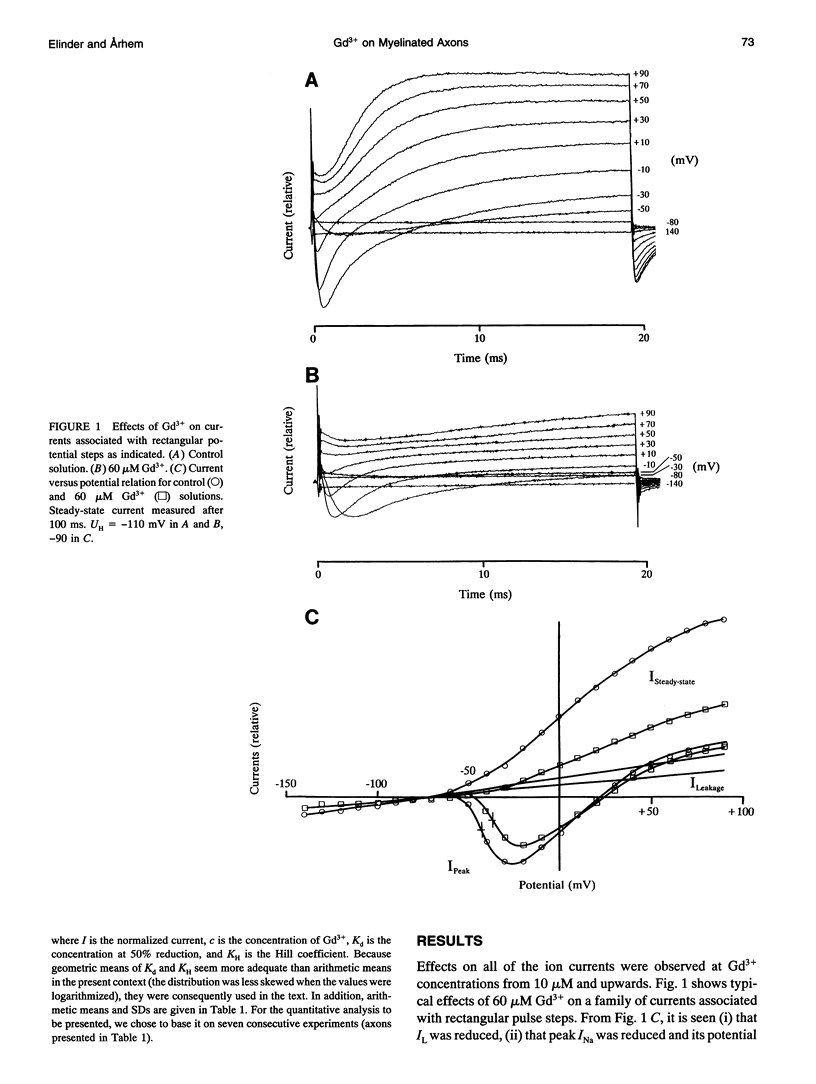
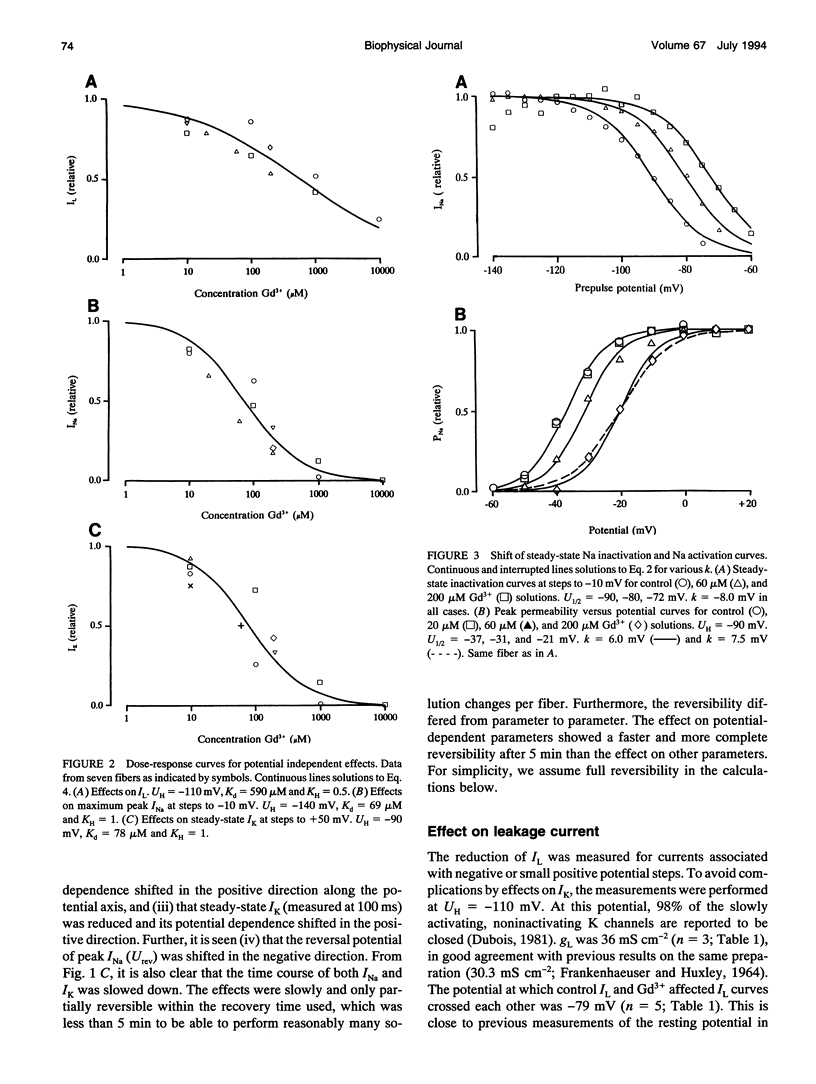
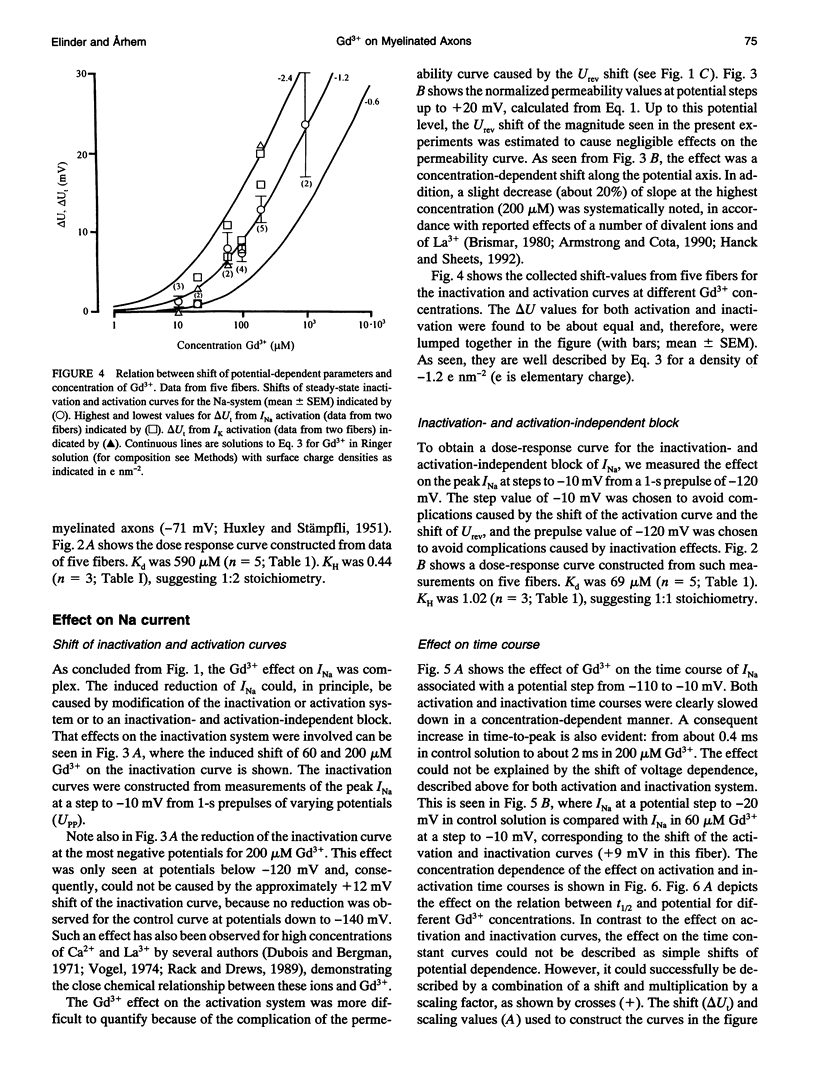
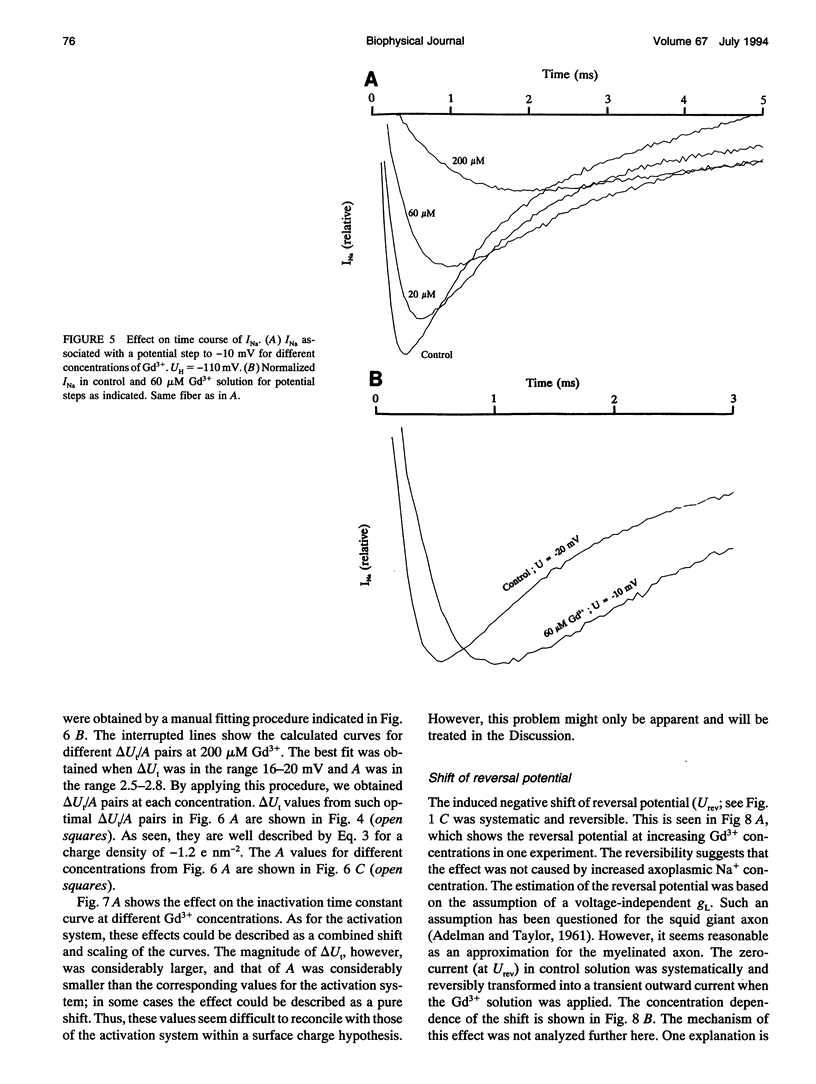
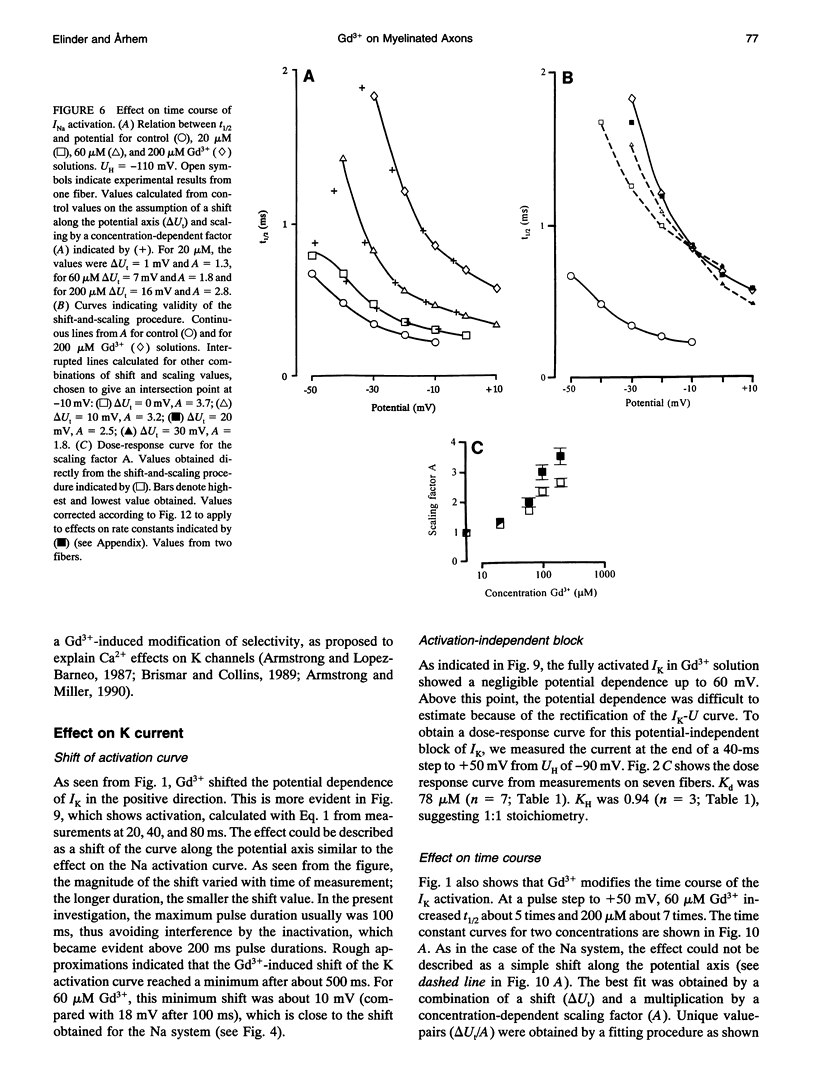
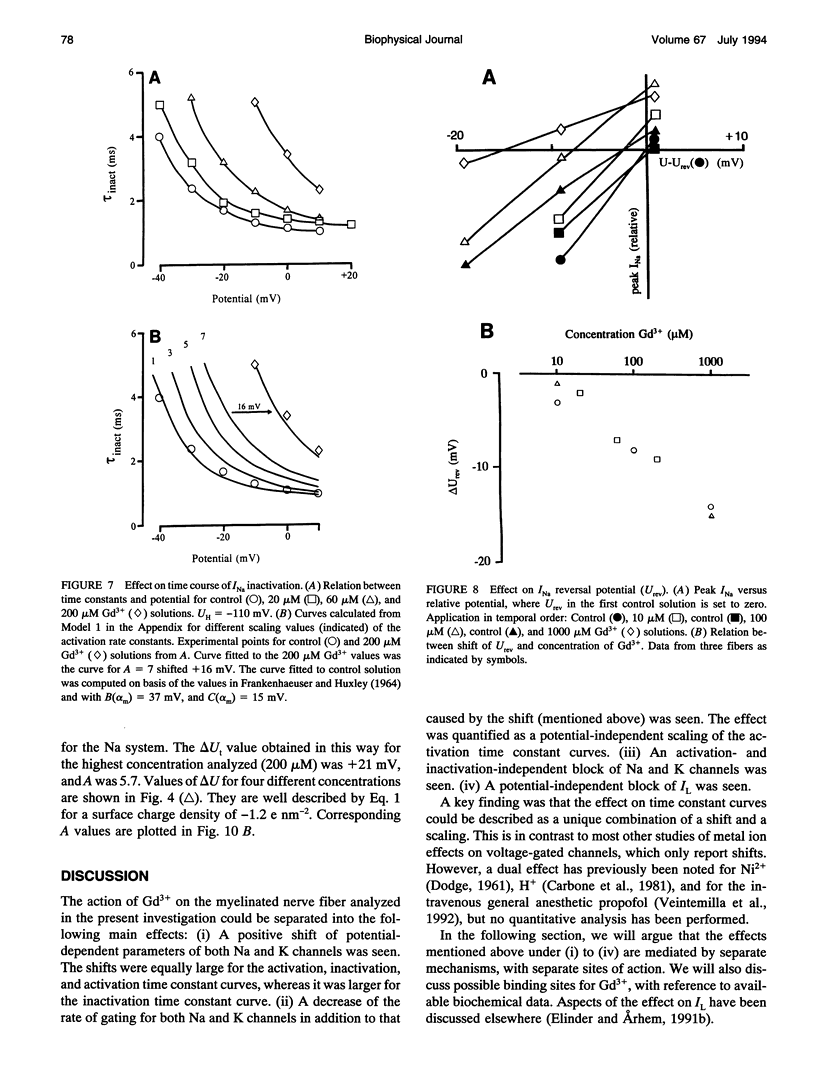
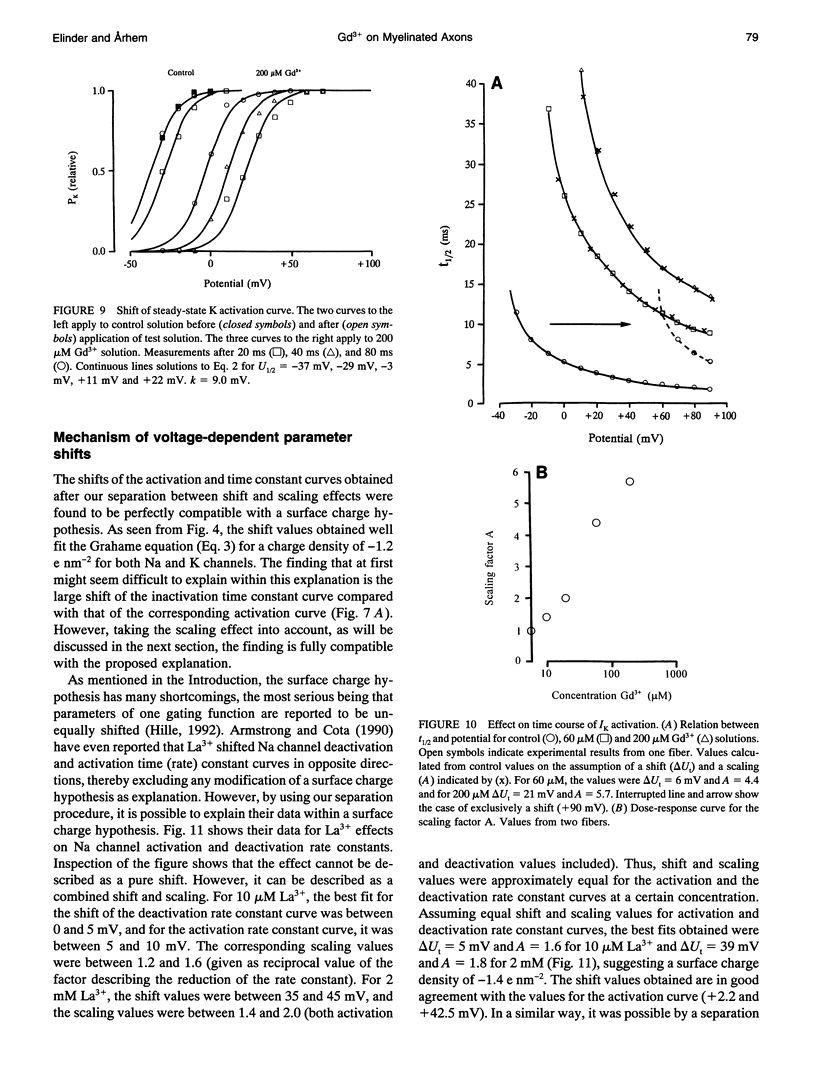
The action of gadolinium (Gd3+) on ion currents in myelinated axons of Xenopus laevis was investigated with the voltage clamp technique. The analysis revealed the following effects. (i) The potential-dependent parameters of both Na and K channels were shifted. The shift was equally large for activation, inactivation, and activation time constant curves (+9 mV for 100 microM Gd3+). The effects could be explained by screening of fixed surface charges at a density of -1.2 e nm-2. (ii) The rate of gating for both Na and K channels was reduced more than predicted from the shift. This effect could be quantified as a scaling (by a factor 3 and 5 respectively at 100 microM Gd3+) of the activation time constant curves. (iii) An activation- and inactivation-independent block of both Na and K channels, obeying 1:1 stoichiometry with a Kd value of about 70 microM potential-independent block of leakage current, obeying 1:2 stoichiometry with a Kd value of 600 microM. (iv) The analysis suggests separate binding sites for the effects, comprising high affinity modulatory and blocking sites on the channel proteins and low affinity receptors on phospholipids, associated with the effect on the leakage current.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELMAN W. J., TAYLOR R. E. Leakage current rectification in the squid giant axon. Nature. 1961 Jun 3;190:883–885. doi: 10.1038/190883a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agus Z. S., Dukes I. D., Morad M. Divalent cations modulate the transient outward current in rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C310–C318. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P. Effects of rubidium, caesium, strontium, barium and lanthanum on ionic currents in myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Jan;108(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P. Effects of some heavy metal ions on the ionic currents of myelinated fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:219–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P., Frankenhaeuser B., Moore L. E. Ionic currents at resting potential in nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. Potential clamp experiments. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Aug;88(4):446–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Cota G. Calcium ion as a cofactor in Na channel gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6528–6531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Cota G. Modification of sodium channel gating by lanthanum. Some effects that cannot be explained by surface charge theory. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Dec;96(6):1129–1140. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.6.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Lopez-Barneo J. External calcium ions are required for potassium channel gating in squid neurons. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):712–714. doi: 10.1126/science.2437654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Miller C. Do voltage-dependent K+ channels require Ca2+? A critical test employing a heterologous expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7579–7582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T., Collins V. P. Potassium and sodium channels in human malignant glioma cells. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 20;480(1-2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Effects of ionic concentration on permeability properties of nodal membrane in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Potential clamp experiments. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Apr;87(4):474–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. The effect of divalent and trivalent cations on the sodium permeability of myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Jan;108(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Testa P. L., Wanke E. Intracellular pH and ionic channels in the Loligo vulgaris giant axon. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):393–413. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84798-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Hille B., Neumcke B., Nonner W., Stämpfli R. Measurement of the conductance of the sodium channel from current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):699–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukierman S., Krueger B. K. Effects of internal divalent cations on the gating of rat brain Na+ channels reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Dec;419(6):559–565. doi: 10.1007/BF00370295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukierman S., Krueger B. K. Modulation of sodium channel gating by external divalent cations: differential effects on opening and closing rates. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):360–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00370741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE F. A., FRANKENHAEUSER B. Membrane currents in isolated frog nerve fibre under voltage clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):76–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE F. A., FRANKENHAEUSER B. Sodium currents in the myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis investigated with the voltage clamp technique. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:188–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J. Gadolinium selectively blocks a component of calcium current in rodent neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid (NG108-15) cells. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:33–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Bergman C. Conductance sodium de la membrane nodale: inhibition compétitive calcium-sodium. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Jun 7;272(23):2924–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M. Evidence for the existence of three types of potassium channels in the frog Ranvier node membrane. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:297–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakahany E., Lopez J. R., Richelson E. Lanthanum binding to murine neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 1983 Jun;40(6):1687–1691. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder F., Arhem P. Mechanisms of the tetrahydroaminoacridine effect on action potential and ion currents in myelinated axons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 12;208(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90044-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder F., Arhem P. Properties of the leakage current pathway: effects of the gadolinium ion on myelinated axons. Neuroreport. 1991 Nov;2(11):685–687. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199111000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder F., Arhem P. The modulatory site for the action of gadolinium on surface charges and channel gating. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80457-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HUXLEY A. F. THE ACTION POTENTIAL IN THE MYELINATED NERVE FIBER OF XENOPUS LAEVIS AS COMPUTED ON THE BASIS OF VOLTAGE CLAMP DATA. J Physiol. 1964 Jun;171:302–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY CHANGES IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:431–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. Potassium permeability in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:54–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Z., Hiraoka M. Depression of delayed outward K+ current by Co2+ in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):C23–C31. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.1.C23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. M., Rojas E., Stämpfli R. Blocking of sodium and potassium conductance by internal application of Zn++ in the node of Ranvier. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):271–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00586923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAME D. C. The electrical double layer and the theory of electrocapillarity. Chem Rev. 1947 Dec;41(3):441–501. doi: 10.1021/cr60130a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. L., Ehrenstein G. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: determination of surface charge. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86396-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Divalent cations and the activation kinetics of potassium channels in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):965–996. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Slowing of sodium channel opening kinetics in squid axon by extracellular zinc. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):935–964. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., STAMPFLI R. Direct determination of membrane resting potential and action potential in single myelinated nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):476–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanck D. A., Sheets M. F. Extracellular divalent and trivalent cation effects on sodium current kinetics in single canine cardiac Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:267–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Phillips M. C. Conformation of the lecithin polar group in charged vesicles. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):390–394. doi: 10.1038/261390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B. Blockade of current through single calcium channels by trivalent lanthanide cations. Effect of ionic radius on the rates of ion entry and exit. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Apr;95(4):679–696. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.4.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The electrostatic properties of membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Stämpfli R. Heterogeneity of external surface charges near sodium channels in the nodal membrane of frog nerve. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jun;401(2):125–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00583872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rack M., Drews G. Effects of a synthetic cationic polymer on sodium and potassium currents of frog nerve fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Apr;413(6):610–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00581810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. F., Hanck D. A. Mechanisms of extracellular divalent and trivalent cation block of the sodium current in canine cardiac Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:299–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The conductance of sodium channels under conditions of reduced current at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:131–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerup C., Purali N., Rydqvist B. Block of receptor response in the stretch receptor neuron of the crayfish by gadolinium. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991 Sep;143(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata M., Pickard W. F., Lettvin J. Y., Moore J. W. Ionic conductance changes in lobster axon membrane when lanthanum is substituted for calcium. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):461–471. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veintemilla F., Elinder F., Arhem P. Mechanisms of propofol action on ion currents in the myelinated axon of Xenopus laevis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 21;218(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90147-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W. Calcium and lanthanum effects at the nodal membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1974;350(1):25–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00586736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. C., Sachs F. Block of stretch-activated ion channels in Xenopus oocytes by gadolinium and calcium ions. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1068–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.2466333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. L., Stumpf M. A., Hoch H. C., Kung C. A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.1716786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


