Abstract
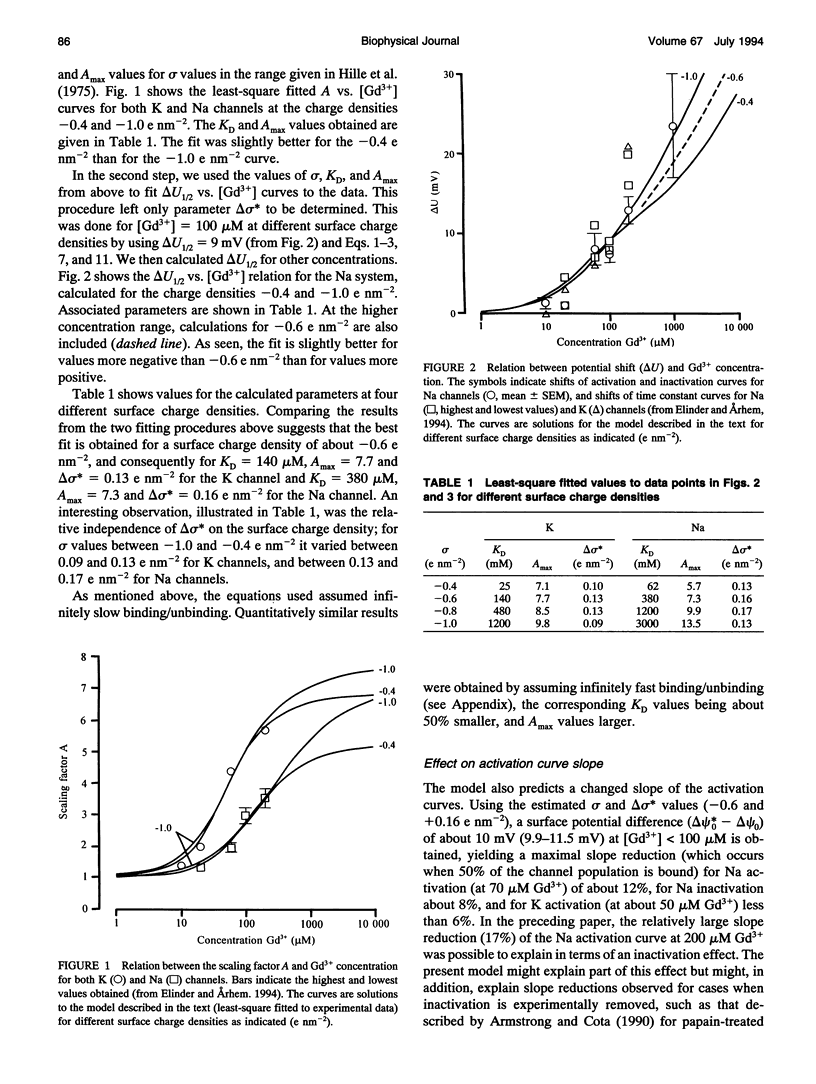
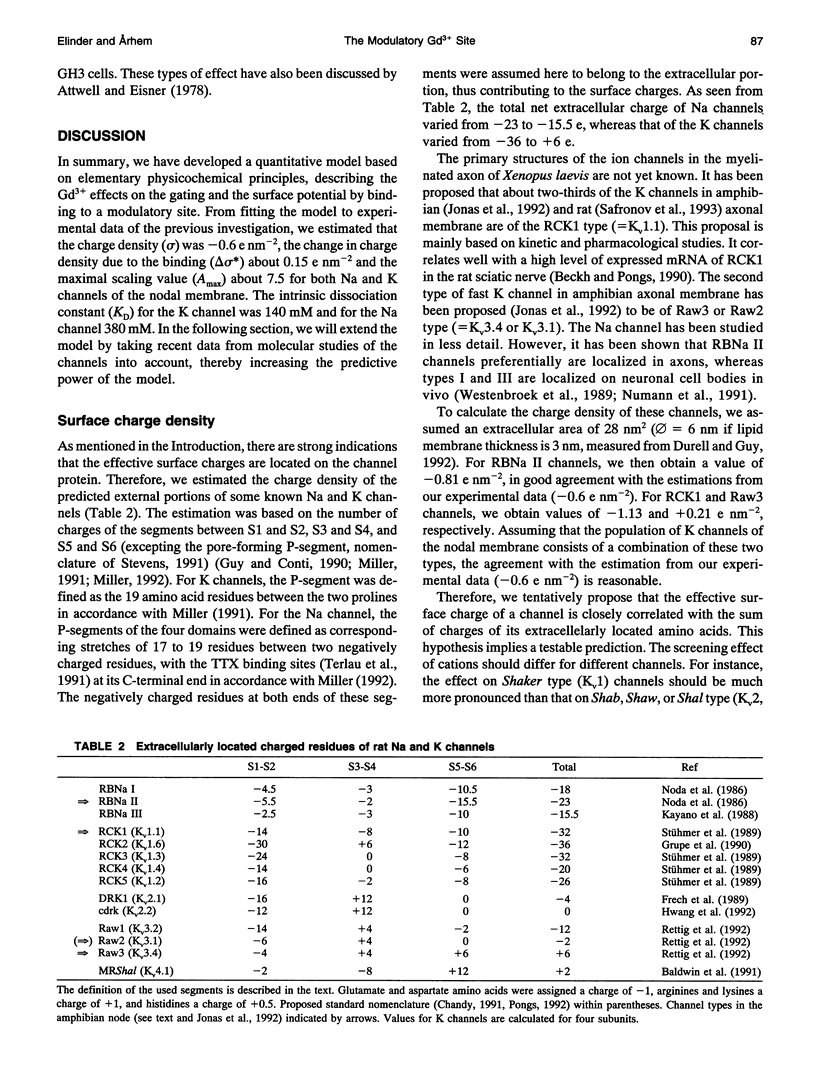
The gadolinium (Gd3+)-induced shift of potential dependence and modulated gating of Na and K channels were analyzed. In a previous investigation, we explained the shift in terms of pure screening (no binding) of fixed surface charges and the modulation by binding to modulatory sites on the channels. In the present paper, we have extended this model by including effects on the charge density of Gd3+ binding to the modulatory sites. From fitting the extended model to experimental data, the charge density was estimated to be -0.6 e nm-2, and the Gd(3+)-induced charge change to be +0.15 e nm-2, and the maximal scaling factor to be 7.5 for both Na and K channels. Intrinsic KD values for binding to the K and Na channels were estimated to be 140 and 380 mM, respectively. Estimations of the extracellular charge density, from primary structures of cloned channels, were found to be in agreement with estimations based on the present model. The modulatory site was suggested to be located at the cluster of negatively charged residues between the fifth transmembrane segment (S5) and the pore-forming region for both Na and K channels. These suggestions imply several testable predictions about different K channels.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arhem P. Effects of some heavy metal ions on the ionic currents of myelinated fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:219–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Cota G. Modification of sodium channel gating by lanthanum. Some effects that cannot be explained by surface charge theory. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Dec;96(6):1129–1140. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.6.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Eisner D. Discrete membrane surface charge distributions. Effect of fluctuations near individual channels. Biophys J. 1978 Dec;24(3):869–875. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85426-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Tsaur M. L., Lopez G. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Characterization of a mammalian cDNA for an inactivating voltage-sensitive K+ channel. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90299-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckh S., Pongs O. Members of the RCK potassium channel family are differentially expressed in the rat nervous system. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):777–782. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08173.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. E., Miller C. Effects of phospholipid surface charge on ion conduction in the K+ channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):279–287. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84154-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G. Simplified gene nomenclature. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):26–26. doi: 10.1038/352026b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukierman S., Zinkand W. C., French R. J., Krueger B. K. Effects of membrane surface charge and calcium on the gating of rat brain sodium channels in planar bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):431–447. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M. Evidence for the existence of three types of potassium channels in the frog Ranvier node membrane. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:297–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Guy H. R. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81809-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder F., Arhem P. Effects of gadolinium on ion channels in the myelinated axon of Xenopus laevis: four sites of action. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80456-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser B., Ryan K. J., Arhem P. The effects of neuraminidase and protamine chloride on potential clamp parameters of the node of Ranvier (Xenopus laevis). Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Apr;96(4):548–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., VanDongen A. M., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):642–645. doi: 10.1038/340642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAME D. C. The electrical double layer and the theory of electrocapillarity. Chem Rev. 1947 Dec;41(3):441–501. doi: 10.1021/cr60130a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. N., Weiss L. B., Andersen O. S. Batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in planar lipid bilayers. Ion permeation and block. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):841–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe A., Schröter K. H., Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Drewes T., Beckh S., Pongs O. Cloning and expression of a human voltage-gated potassium channel. A novel member of the RCK potassium channel family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1749–1756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Conti F. Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated channels. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Bredt D. S., Yellen G., Snyder S. H. A novel K+ channel with unique localizations in mammalian brain: molecular cloning and characterization. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90275-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayano T., Noda M., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Numa S. Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The electrostatic properties of membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Hughes H. Hunting for the pore of voltage-gated channels. Curr Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):115–118. doi: 10.1126/science.1656525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H., Yoshii M. Surface potential reflected in both gating and permeation mechanisms of sodium and calcium channels of the tunicate egg cell membrane. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):429–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Timpe L. C., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Alteration of voltage-dependence of Shaker potassium channel by mutations in the S4 sequence. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):305–310. doi: 10.1038/349305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O. Molecular biology of voltage-dependent potassium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S69–S88. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M. Divalent cations as probes for structure-function relationships of cloned voltage-dependent sodium channels. Eur Biophys J. 1990;18(6):327–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00196923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Thornhill W. B., Duch D. S., Levinson S. R., Urban B. W. Neuraminidase treatment modifies the function of electroplax sodium channels in planar lipid bilayers. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90221-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig J., Wunder F., Stocker M., Lichtinghagen R., Mastiaux F., Beckh S., Kues W., Pedarzani P., Schröter K. H., Ruppersberg J. P. Characterization of a Shaw-related potassium channel family in rat brain. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2473–2486. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safronov B. V., Kampe K., Vogel W. Single voltage-dependent potassium channels in rat peripheral nerve membrane. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:675–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammar M., Spira G., Meiri H. Depolarization exposes the voltage sensor of the sodium channels to the extracellular region. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jan;125(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00235793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spires S., Begenisich T. Chemical properties of the divalent cation binding site on potassium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Aug;100(2):181–193. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spires S., Begenisich T. Modification of potassium channel kinetics by amino group reagents. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jan;99(1):109–129. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Ion channels. Making a submicroscopic hole in one. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):657–658. doi: 10.1038/349657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlau H., Heinemann S. H., Stühmer W., Pusch M., Conti F., Imoto K., Numa S. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., Sigworth F. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Merrick D. K., Catterall W. A. Differential subcellular localization of the RI and RII Na+ channel subtypes in central neurons. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):695–704. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J., Pailthorpe B. A., Krueger B. K. Lipid surface charge does not influence conductance or calcium block of single sodium channels in planar bilayers. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1353–1363. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81942-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


