Abstract
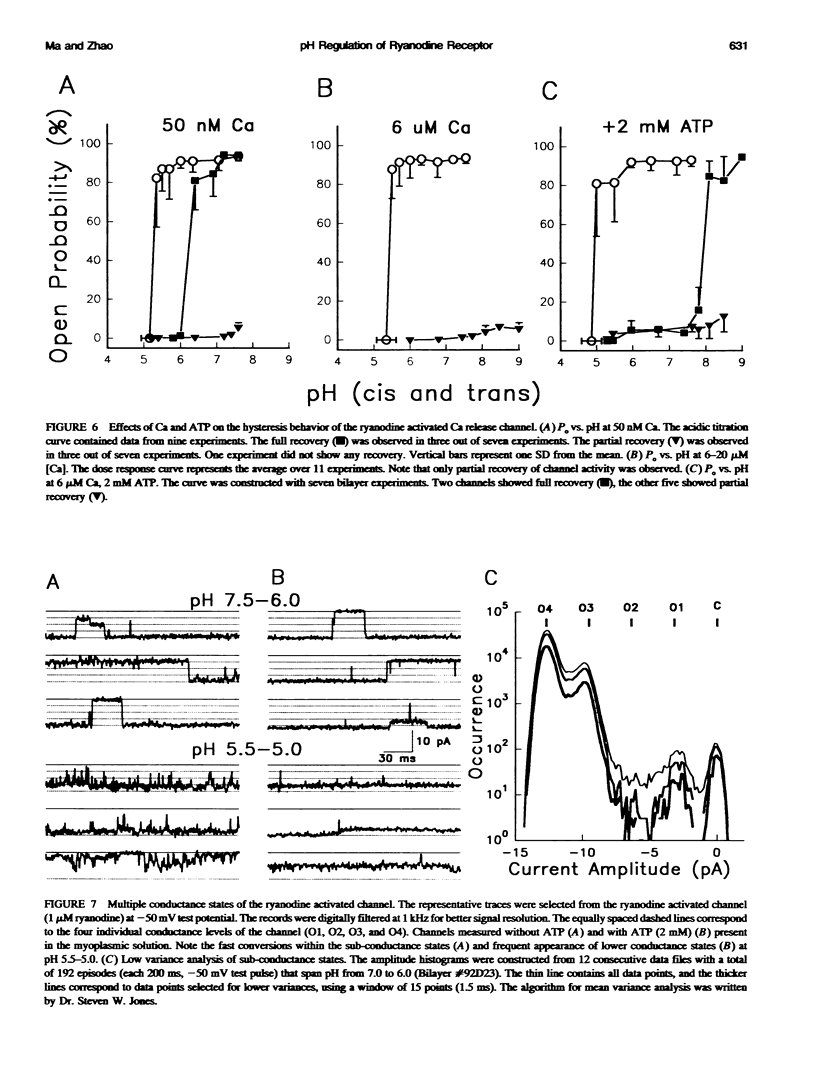
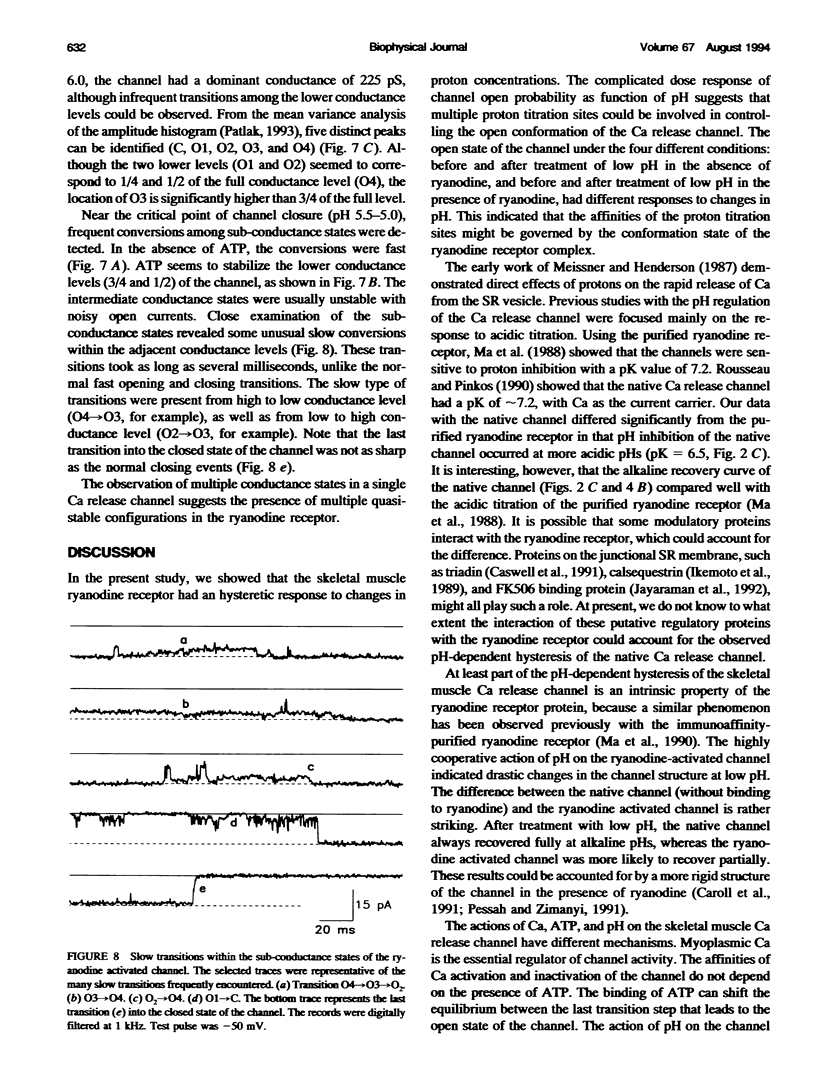
Ryanodine receptors are key molecules in excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle. They form the pore of the calcium release channel, which is regulated by Ca and ATP. Multiple proton titration sites are involved in controlling the different open states of the channel, as indicated by the following: i) the channel had a biphasic response to changes in proton concentrations around neutral pH; ii) the activities of the channel were inhibited by acidic pHs in a highly cooperative manner; and iii) the channel exhibited pronounced hysteresis to changes in pH. Four distinct conductance states can be identified in the single ryanodine-activated calcium release channel. The distribution of the multiple conductance states depends on the level of [Ca], ATP, and pH in the recording solution. The data are consistent with the multimeric structure of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman T., Brillantes A. M., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Marks A. R. FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9474–9477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenden D. J., Fairhurst A. S. The pharmacology of ryanodine. Pharmacol Rev. 1969 Mar;21(1):1–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Misra M., Xu L., Smith H. A., Meissner G. The ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for a cooperatively coupled, negatively charged homotetramer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16776–16785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. Block by ruthenium red of the ryanodine-activated calcium release channel of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Dec;102(6):1031–1056. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Fill M., Knudson C. M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle is a gap junction-type channel. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.2459777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S., Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Niidome T., Nishimura S., Adams B. A., Beam K. G. Molecular insights into excitation-contraction coupling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:1–7. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessah I. N., Zimanyi I. Characterization of multiple [3H]ryanodine binding sites on the Ca2+ release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal and cardiac muscle: evidence for a sequential mechanism in ryanodine action. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 May;39(5):679–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Ma J. J., González A. The mechanical hypothesis of excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Apr;12(2):127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01774031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G., Stefani E. Charge movement and the nature of signal transduction in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:109–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]