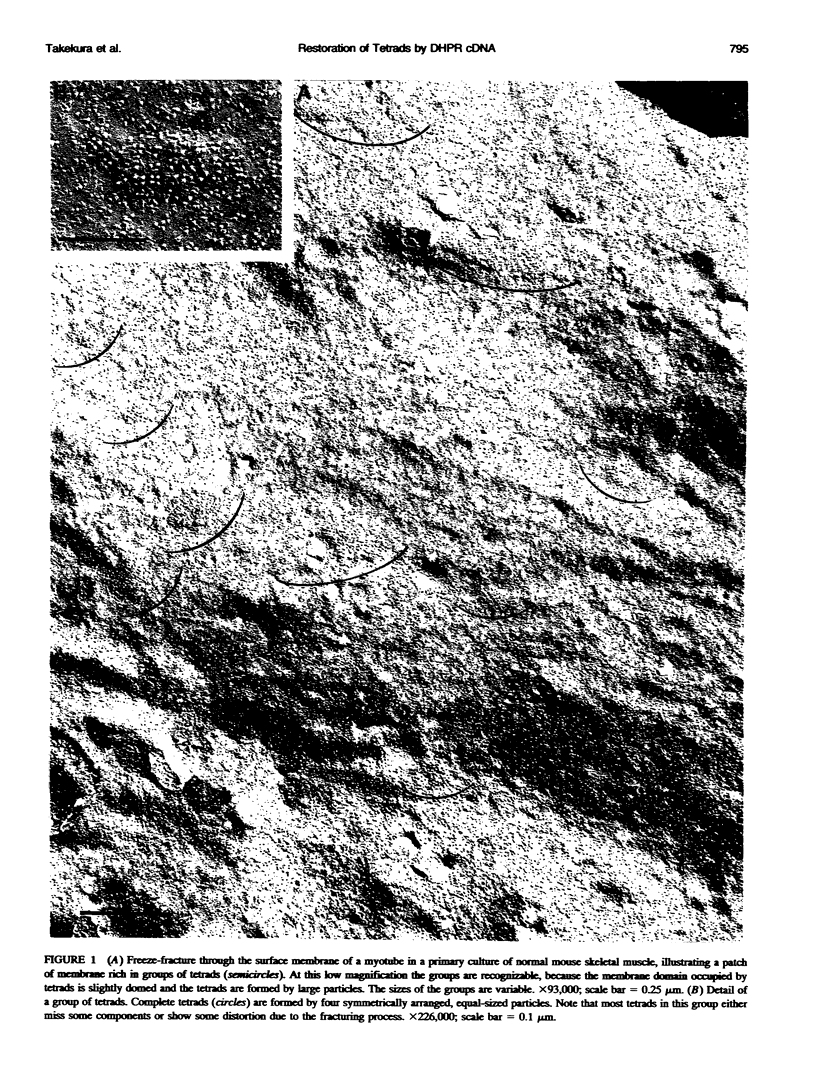
Abstract
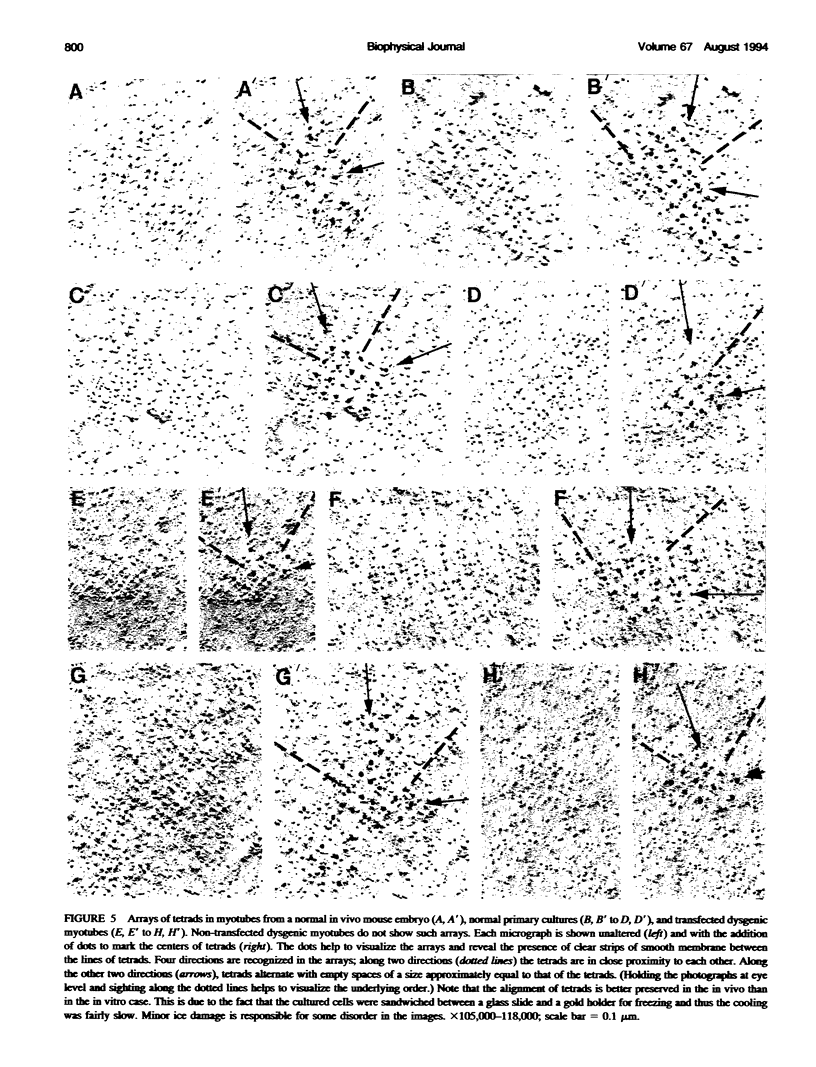
Excitation-contraction coupling was restored in primary cultures of dysgenic myotubes by transfecting the cells with an expression plasmid encoding the rabbit skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor. Dishes containing normal, dysgenic, and transfected myotubes were fixed, freeze-fractured, and replicated for electron microscopy. Numerous small domains in the surface membrane of normal myotubes contain ordered arrays of intramembrane particles in groups of four (tetrads). The disposition of tetrads in the arrays is consistent with alternate positioning of tetrads relative to the underlying feet of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Dysgenic myotubes have no arrays of tetrads. Some myotubes from successfully transfected cultures have arrays of tetrads with spacings equal to those found in normal myotubes. Thus the dihydropyridine receptor appears to be needed for the formation of tetrads and their association with the sarcoplasmic reticulum feet. This result is consistent with the hypothesis that each tetrad is composed of four dihydropyridine receptors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B. A., Beam K. G. A novel calcium current in dysgenic skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):429–444. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams B. A., Tanabe T., Mikami A., Numa S., Beam K. G. Intramembrane charge movement restored in dysgenic skeletal muscle by injection of dihydropyridine receptor cDNAs. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):569–572. doi: 10.1038/346569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Knudson C. M., Powell J. A. A lethal mutation in mice eliminates the slow calcium current in skeletal muscle cells. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):168–170. doi: 10.1038/320168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Stiffel V. M. Ratio of ryanodine to dihydropyridine receptors in cardiac and skeletal muscle and implications for E-C coupling. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 1):C1587–C1593. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.6.C1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari N. A single nucleotide deletion in the skeletal muscle-specific calcium channel transcript of muscular dysgenesis (mdg) mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25636–25639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
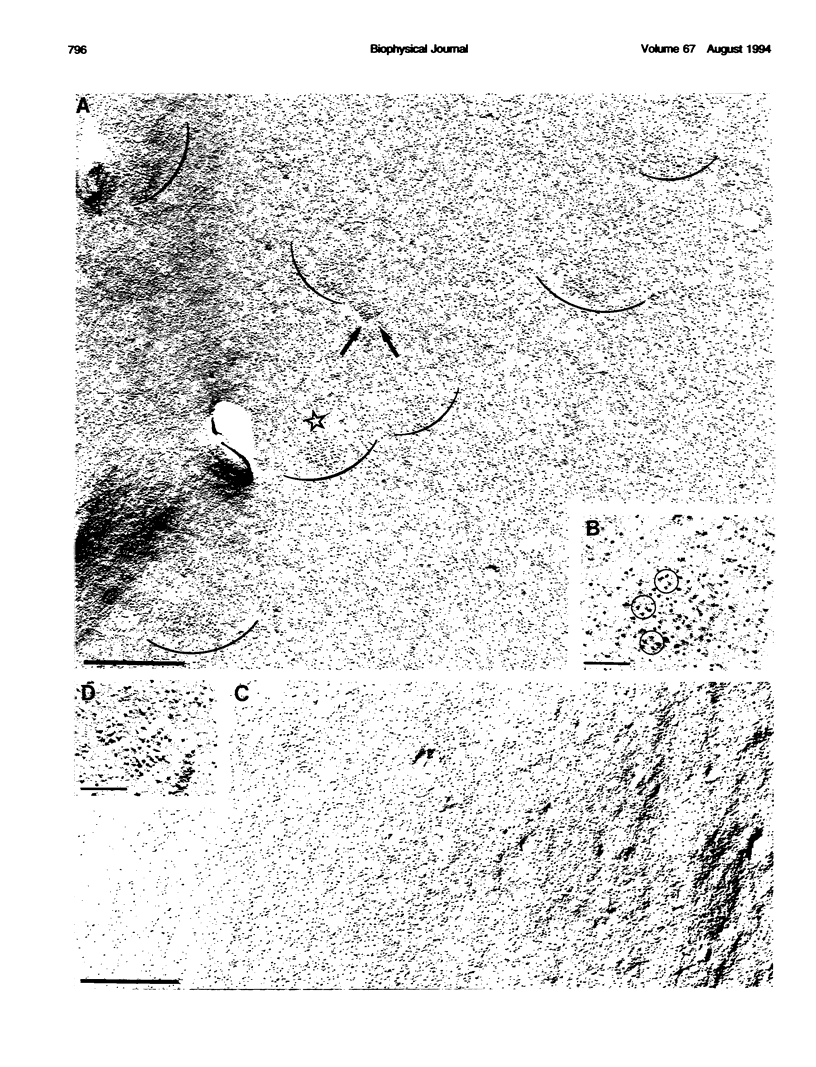
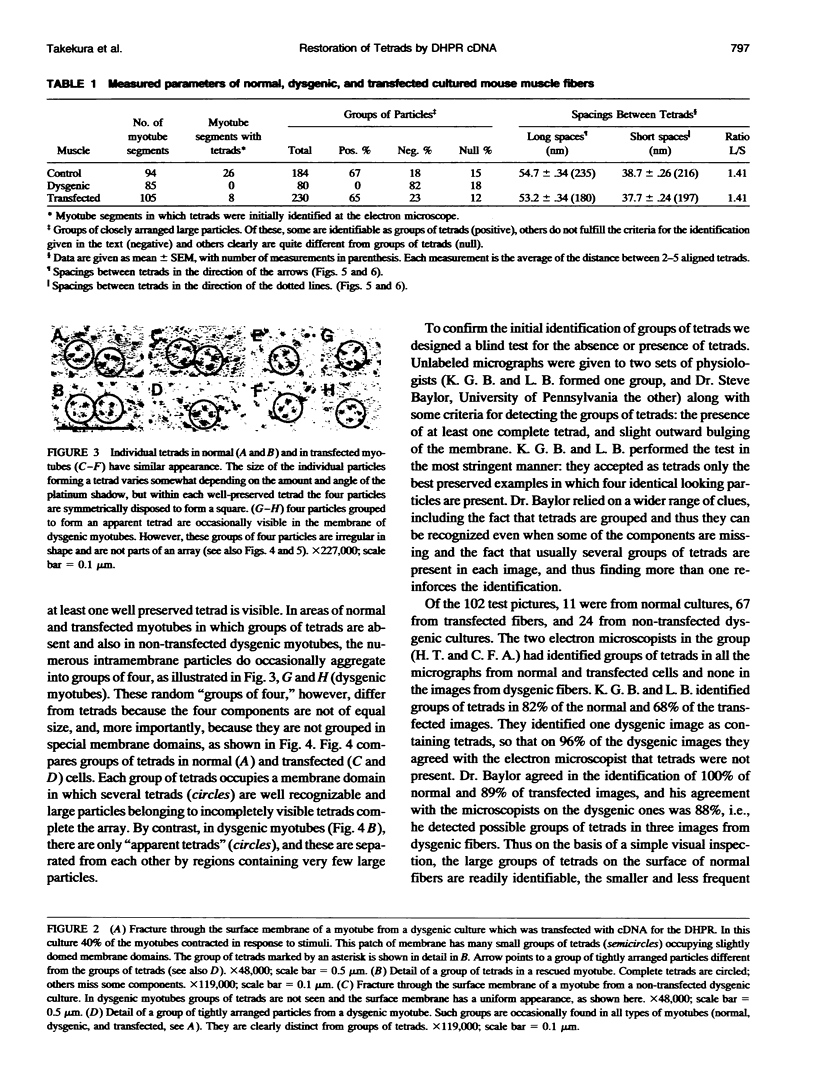
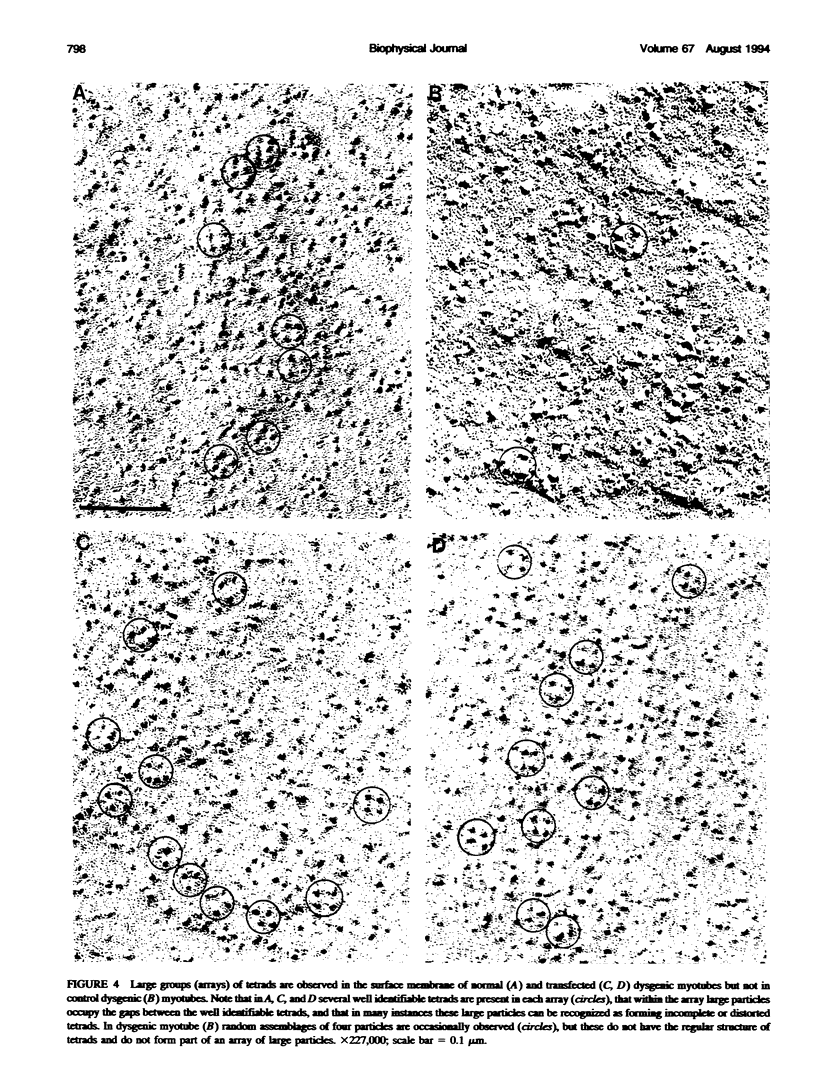
- Cohen S. A., Pumplin D. W. Clusters of intramembrane particles associated with binding sites for alpha-bungarotoxin in cultured chick myotubes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):494–516. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Junankar P. R., Stanhope C. Extra-junctional ryanodine receptors in the terminal cisternae of mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Jan 22;247(1318):69–75. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson D. G., Schwartz H. W., Franzini-Armstrong C. Subunit structure of junctional feet in triads of skeletal muscle: a freeze-drying, rotary-shadowing study. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1735–1742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flucher B. E., Morton M. E., Froehner S. C., Daniels M. P. Localization of the alpha 1 and alpha 2 subunits of the dihydropyridine receptor and ankyrin in skeletal muscle triads. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90170-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flucher B. E., Phillips J. L., Powell J. A. Dihydropyridine receptor alpha subunits in normal and dysgenic muscle in vitro: expression of alpha 1 is required for proper targeting and distribution of alpha 2. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1345–1356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. Membrane particles and transmission at the triad. Fed Proc. 1975 Apr;34(5):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Nunzi G. Junctional feet and particles in the triads of a fast-twitch muscle fibre. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):233–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00712033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Pincon-Raymond M., Rieger F. Muscle fibers from dysgenic mouse in vivo lack a surface component of peripheral couplings. Dev Biol. 1991 Aug;146(2):364–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. STUDIES OF THE TRIAD : I. Structure of the Junction in Frog Twitch Fibers. J Cell Biol. 1970 Nov 1;47(2):488–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Shen A. C., Arnold W., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P. Subcellular distribution of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor in rabbit skeletal muscle in situ: an immunofluorescence and immunocolloidal gold-labeling study. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):135–147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. C., Caswell A. H., Brunschwig J. P., Brandt N. R. Identification of a new subpopulation of triad junctions isolated from skeletal muscle; morphological correlations with intact muscle. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(3):221–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01870074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D. DHP receptors and excitation-contraction coupling. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Aug;13(4):394–405. doi: 10.1007/BF01738035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. D., Saito A., Palade P., Fleischer S. Morphology of isolated triads. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1017–1029. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli B., Weinstein R. S., Soble L. W., Alroy J. Freeze-fracture of monolayer cultures. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):763–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Inui M., Radermacher M., Frank J., Fleischer S. Ultrastructure of the calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):211–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]