Abstract
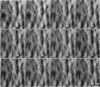
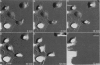
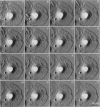
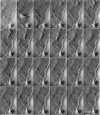
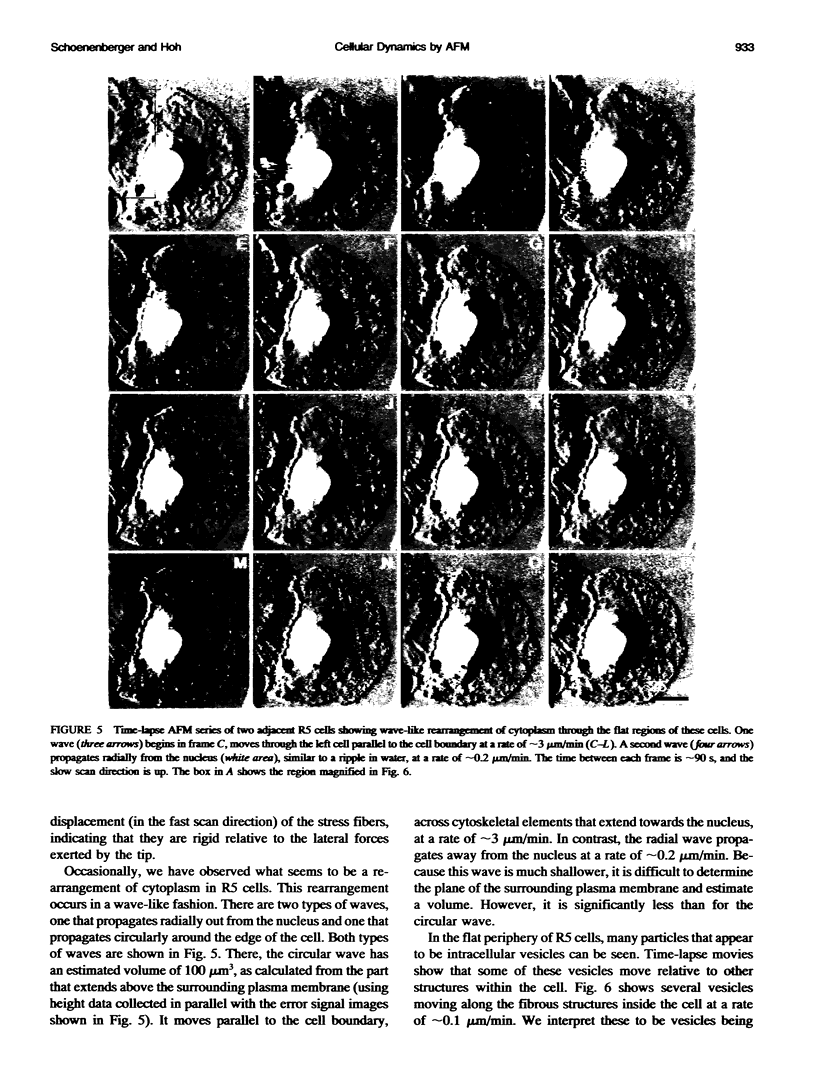
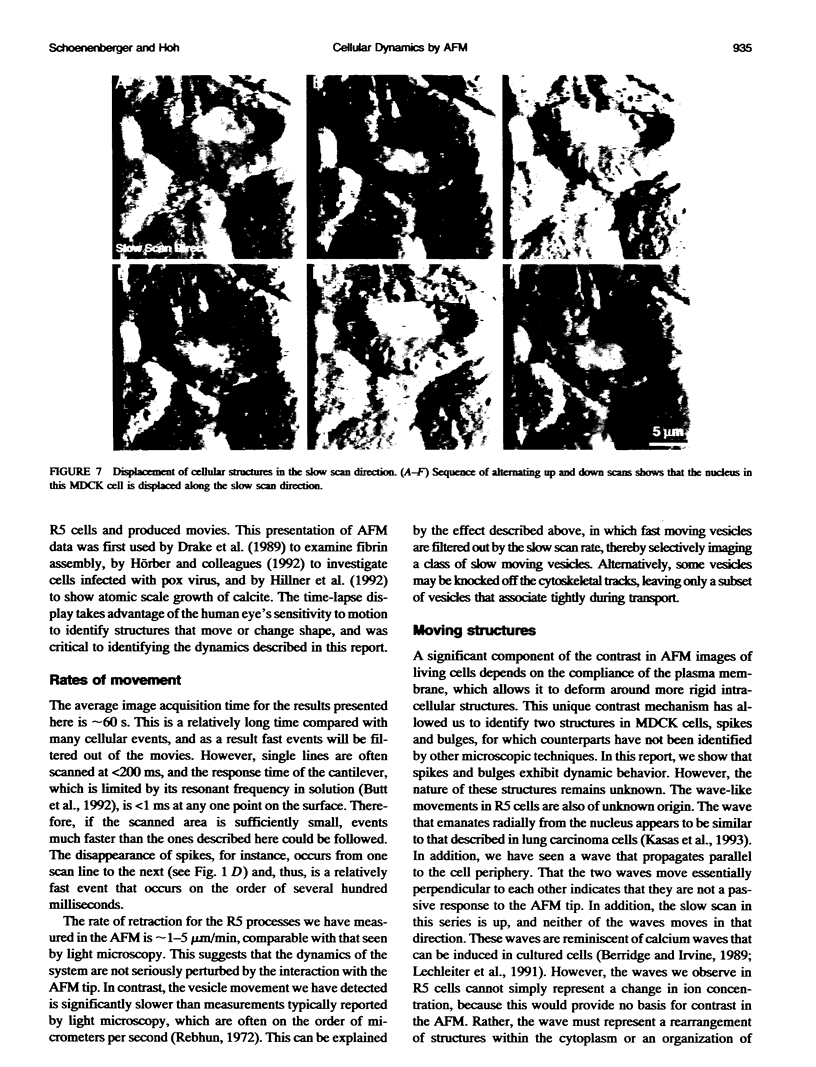
We have examined dynamic events that occur on a time scale of minutes in an epithelial monolayer of Madine-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells and in ras-transformed MDCK cells by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Cells were imaged under physiological conditions, and time-lapse movies representing approximately 60 s real time per frame were assembled. In normal MDCK cells, two types of protrusions in the apical plasma membrane exhibit dynamic behavior. First, smooth bulges formed transiently over the time scale of minutes to tens of minutes. Second, spike-like protrusions appear initially as bulges, extend well above the apical surface and, finally, seem to detach. R5, an oncogenic transformant derived from MDCK cells, grows very flat on glass. During AFM imaging, these cells sometimes round up and detach from the substrate. In light microscopic observations of parallel preparations, cells rarely detach, suggesting that this is an active response of these cells to irritation by the AFM tip. R5 cells often extend processes that are supported by actin stress fibers. During imaging with the AFM, these processes withdraw at a rate of 1-5 microns/min, similar to that observed by light microscopy. During the withdrawal, movement of the stress fibers can be clearly seen. In the flat periphery of these cells, the transport of intracellular particles along cytoskeletal elements was seen. In addition, we have observed two types of wave-like movements through the cell, which appear to be an organized rearrangement of cytoplasm. One type of wave moves radially out from center of the cell while the other moves circularly along the cell periphery.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang L., Kious T., Yorgancioglu M., Keller D., Pfeiffer J. Cytoskeleton of living, unstained cells imaged by scanning force microscopy. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1282–1286. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81493-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles A. C., Merrill J. E., Dirksen E. R., Sanderson M. J. Intercellular signaling in glial cells: calcium waves and oscillations in response to mechanical stimulation and glutamate. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90238-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz M., Radmacher M., Gaub H. E. In vitro activation of human platelets triggered and probed by atomic force microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Mar;205(1):187–190. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Haydon P. G., Sakaguchi D. S. Actin filament dynamics in living glial cells imaged by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1944–1946. doi: 10.1126/science.1411511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Hansma P. K. Atomic force microscopy for high-resolution imaging in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90248-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Schoenenberger C. A. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of MDCK monolayers by atomic force microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1994 May;107(Pt 5):1105–1114. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.5.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Sosinsky G. E., Revel J. P., Hansma P. K. Structure of the extracellular surface of the gap junction by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81074-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörber J. K., Häberle W., Ohnesorge F., Binnig G., Liebich H. G., Czerny C. P., Mahnel H., Mayr A. Investigation of living cells in the nanometer regime with the scanning force microscope. Scanning Microsc. 1992 Dec;6(4):919–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasas S., Gotzos V., Celio M. R. Observation of living cells using the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):539–544. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81396-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Girard S., Peralta E., Clapham D. Spiral calcium wave propagation and annihilation in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.2011747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L. Cellular and molecular adaptations to injurious mechanical stress. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;3(9):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90012-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpura V., Haydon P. G., Henderson E. Three-dimensional imaging of living neurons and glia with the atomic force microscope. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):427–432. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun L. I. Polarized intracellular particle transport: saltatory movements and cytoplasmic streaming. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;32:93–137. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenenberger C. A., Zuk A., Kendall D., Matlin K. S. Multilayering and loss of apical polarity in MDCK cells transformed with viral K-ras. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):873–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]