Abstract
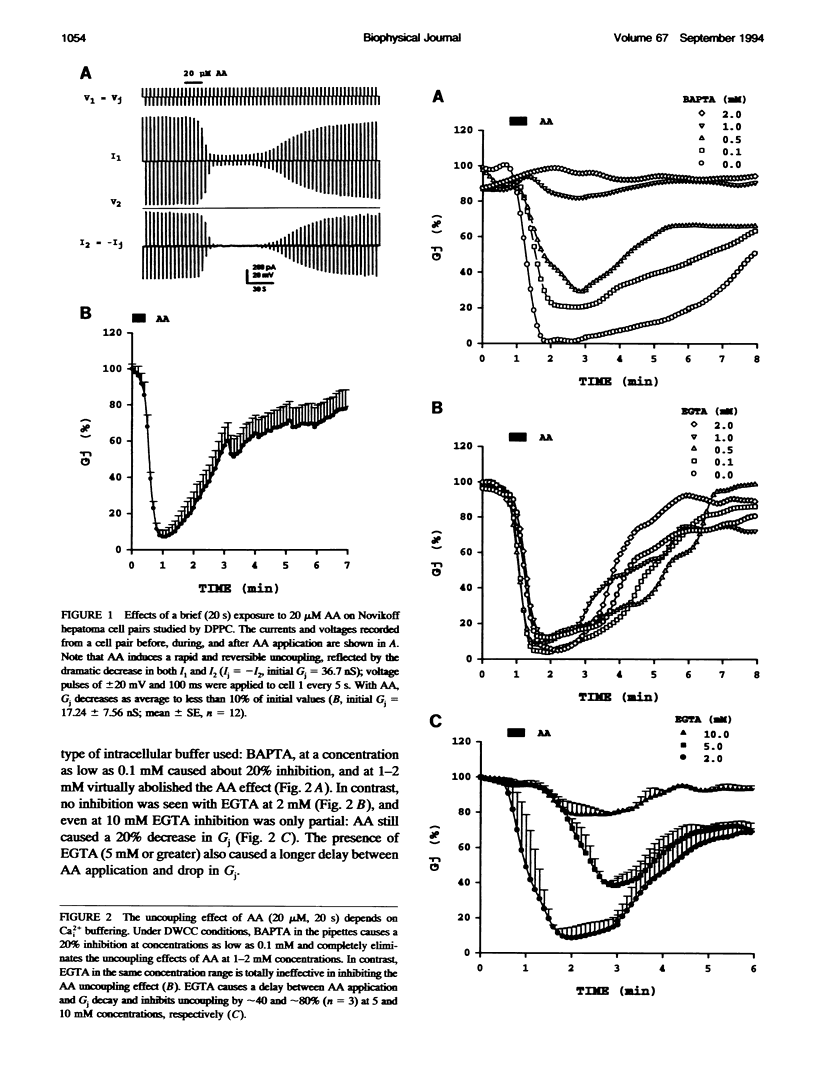
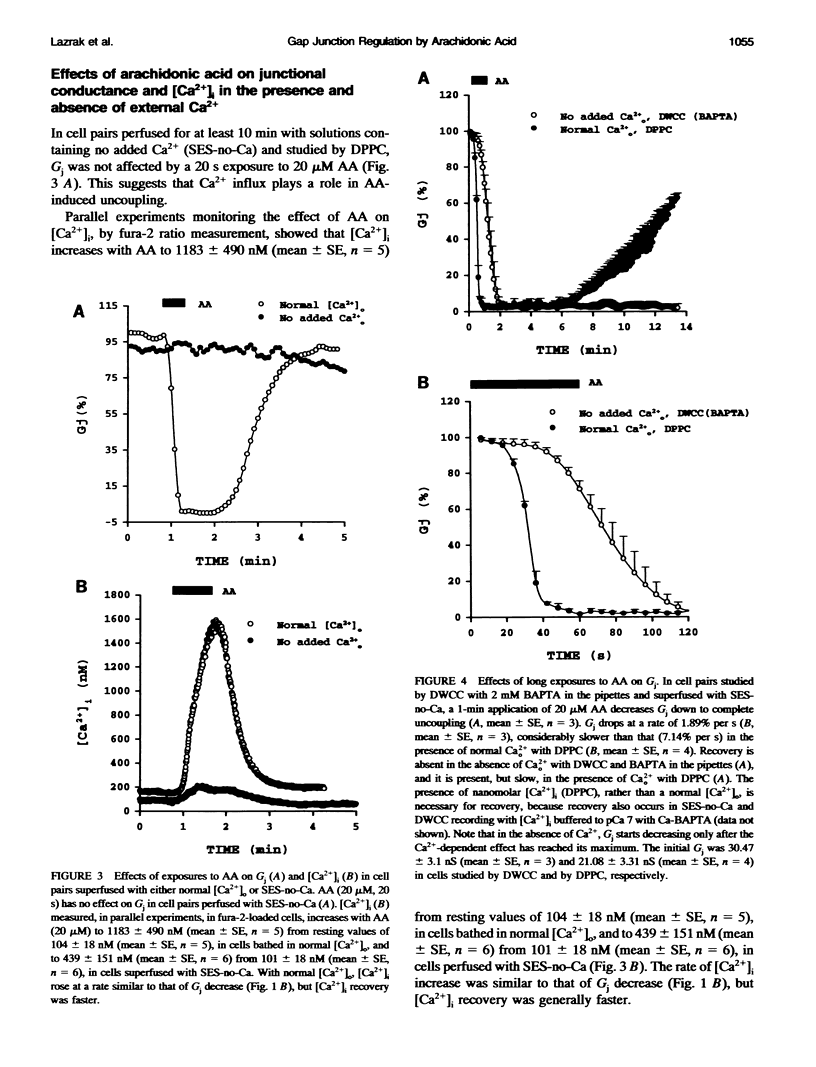
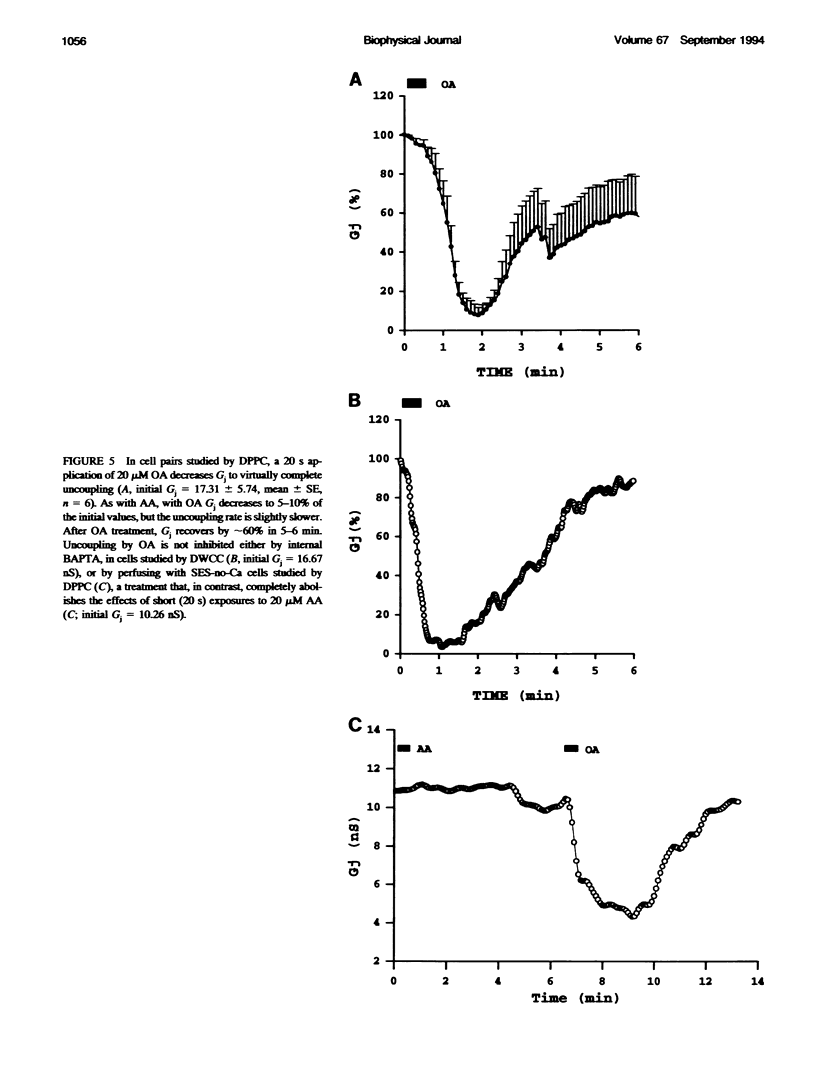
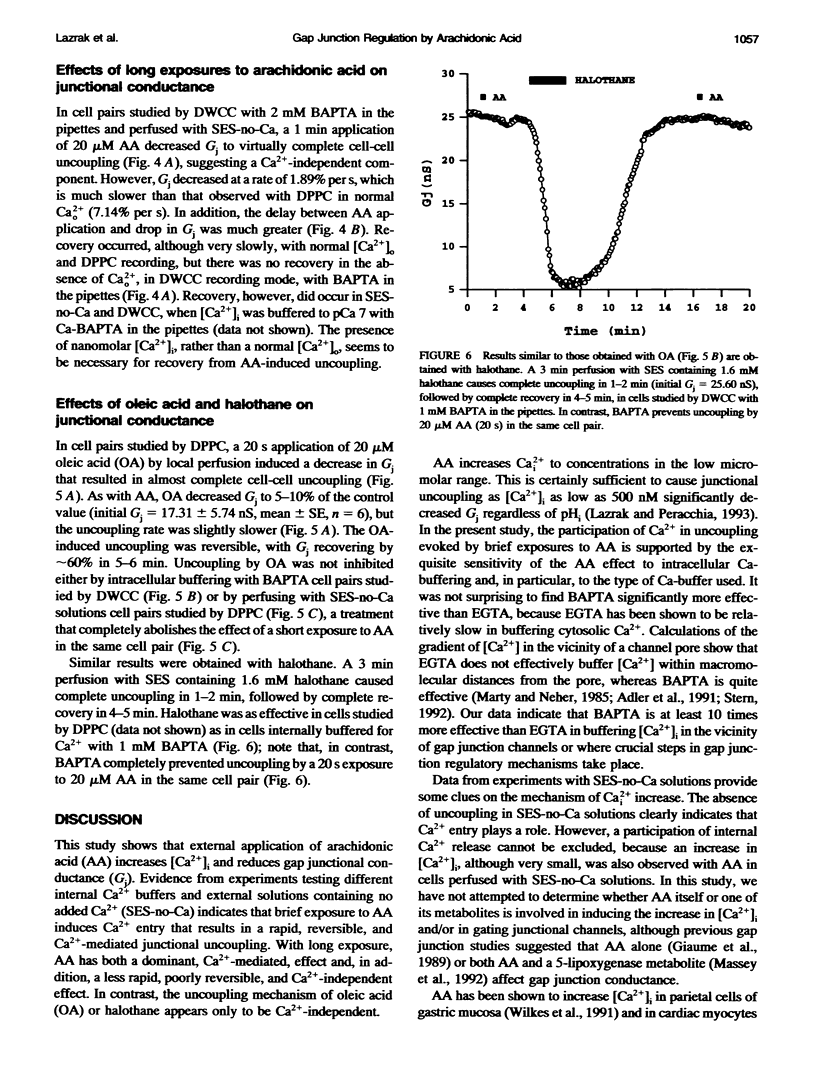
In Novikoff hepatoma cell pairs studied by double perforated patch clamp (DPPC), brief (20 s) exposure to 20 microM arachidonic acid (AA) induced a rapid and reversible uncoupling. In pairs studied by double whole-cell clamp (DWCC), uncoupling was completely prevented by effective buffering of Cai2+ with BAPTA. Similarly, AA (20 s) had no effect on coupling in cells perfused with solutions containing no added Ca2+ (SES-no-Ca) and studied by DPPC, suggesting that Ca2+ influx plays an important role. Parallel experiments monitoring [Ca2+]i with fura-2 showed that [Ca2+]i increases with AA to 0.7-1.5 microM in normal [Ca2+]o, and to approximately 400 nM in SES-no-Ca solutions. The rate of [Ca2+]i increase matched that of Gj decrease, but [Ca2+]i recovery was faster. In cells studied by DWCC with 2 mM BAPTA in the pipette solution and superfused with SES-no-Ca, long exposure (1 min) to 20 microM AA caused a slow and virtually irreversible uncoupling. This result suggests that AA has a dual mechanism of uncoupling: one dominant, fast, reversible, and Ca(2+)-dependent, the other slow, poorly reversible, and Ca(2+)-independent. In contrast, uncoupling by oleic acid (OA) or halothane was insensitive to internal buffering with BAPTA, suggesting a Ca(2+)-independent mechanism only.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler E. M., Augustine G. J., Duffy S. N., Charlton M. P. Alien intracellular calcium chelators attenuate neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1496–1507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01496.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J., Burch R. M., Jelsema C. L. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt J. M., Massey K. D., Minnich B. N. Uncoupling of cardiac cells by fatty acids: structure-activity relationships. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C439–C448. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damron D. S., Bond M. Modulation of Ca2+ cycling in cardiac myocytes by arachidonic acid. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):376–386. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. W., 2nd, Becker M. W. Thromboxane A2 stimulated signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Apr;265(1):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluri G. S., Rüdisüli A., Willi M., Rohr S., Weingart R. Effects of arachidonic acid on the gap junctions of neonatal rat heart cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Oct;417(2):149–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00370692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaume C., Randriamampita C., Trautmann A. Arachidonic acid closes gap junction channels in rat lacrimal glands. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jan;413(3):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00583541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R., Hammer M., Sheridan J., Revel J. P. Gap junction formation between reaggregated Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. C., Collins L. J., Schwerin F. T., Raychowdhury M. K., Ware J. A. Identification of functional PGH2/TxA2 receptors on human endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1993 May;72(5):958–965. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.5.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazrak A., Peracchia C. Gap junction gating sensitivity to physiological internal calcium regardless of pH in Novikoff hepatoma cells. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2002–2012. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81242-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Neher E. Potassium channels in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:117–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Laird D. W., Revel J. P., Johnson R. G. Inhibition of gap junction and adherens junction assembly by connexin and A-CAM antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki-Oda N., Negishi M., Mori K., Ito S. Arachidonic acid activates cation channels in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Nov;61(5):1882–1890. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb09830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Ito S., Hayaishi O. Arachidonic acid stimulates phosphoinositide metabolism and catecholamine release from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):773–779. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordway R. W., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr Direct regulation of ion channels by fatty acids. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Mar;14(3):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J., Daniel L. W., Waite M. Evidence of protein kinase C involvement in phorbol diester-stimulated arachidonic acid release and prostaglandin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5385–5393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peracchia C. Increase in gap junction resistance with acidification in crayfish septate axons is closely related to changes in intracellular calcium but not hydrogen ion concentration. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jan;113(1):75–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01869608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peres A., Racca C., Zippel R., Sturani E. Cytosolic calcium and membrane conductance in response to platelet-derived growth factor and bradykinin stimulation in single human fibroblasts. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;53(2):290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D., Shapiro E., Feinmark S. J., Schwartz J. H. Metabolites of arachidonic acid in the nervous system of Aplysia: possible mediators of synaptic modulation. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3675–3686. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03675.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M. Alteration of intracellular Fura-2 fluorescence by viscosity: a simple correction. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90062-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes J. L., Nava E., Namorado M. C. Receptor-mediated effect of a synthetic thromboxane-analogue on cytosolic calcium in isolated proximal tubules. Prostaglandins. 1992 Aug;44(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(92)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe M. W., Lemasters J. J., Herman B. Assessment of Fura-2 for measurements of cytosolic free calcium. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Wolfe L. S. Arachidonic acid cascade and signal transduction. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes J. M., Kajimura M., Scott D. R., Hersey S. J., Sachs G. Muscarinic responses of gastric parietal cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jun;122(2):97–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01872634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fay F. S. Intracellular calibration of the fluorescent calcium indicator Fura-2. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi T., Yanagisawa T., Taira N. Ca2+ influx induced by the agonist U46619 is inhibited by hyperpolarization induced by the K+ channel opener cromakalim in canine coronary artery. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;59(3):291–299. doi: 10.1254/jjp.59.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


