Abstract
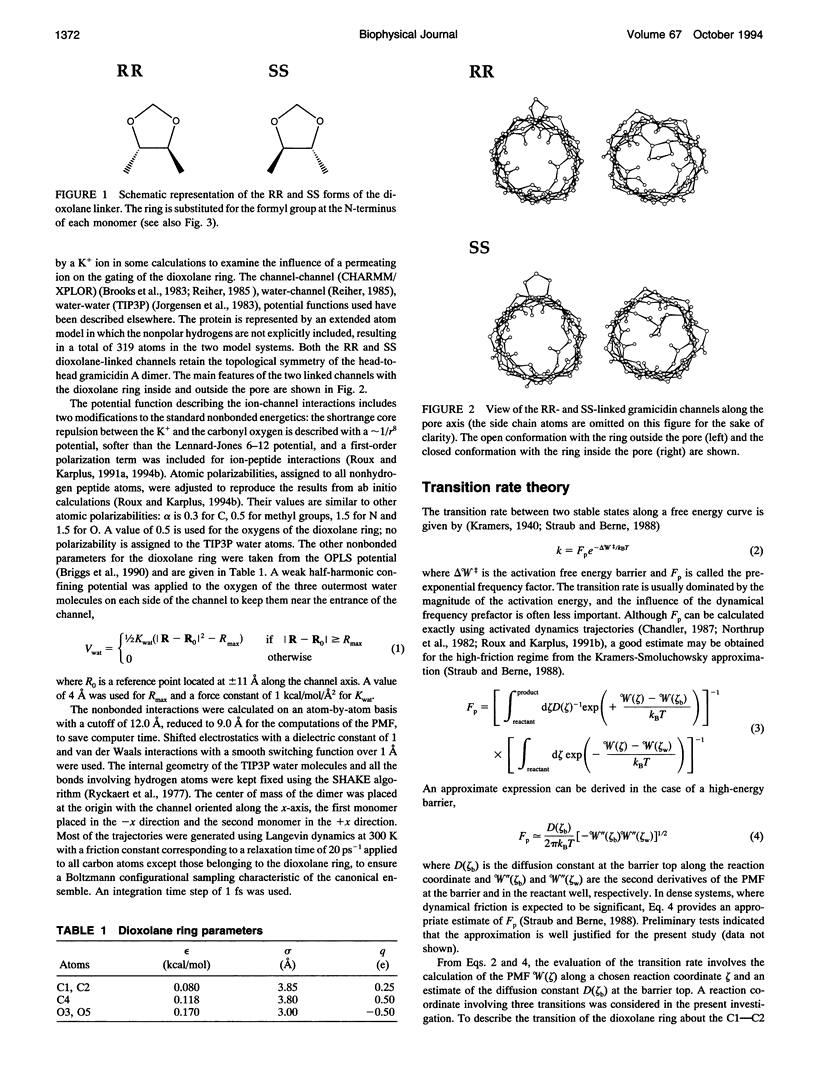
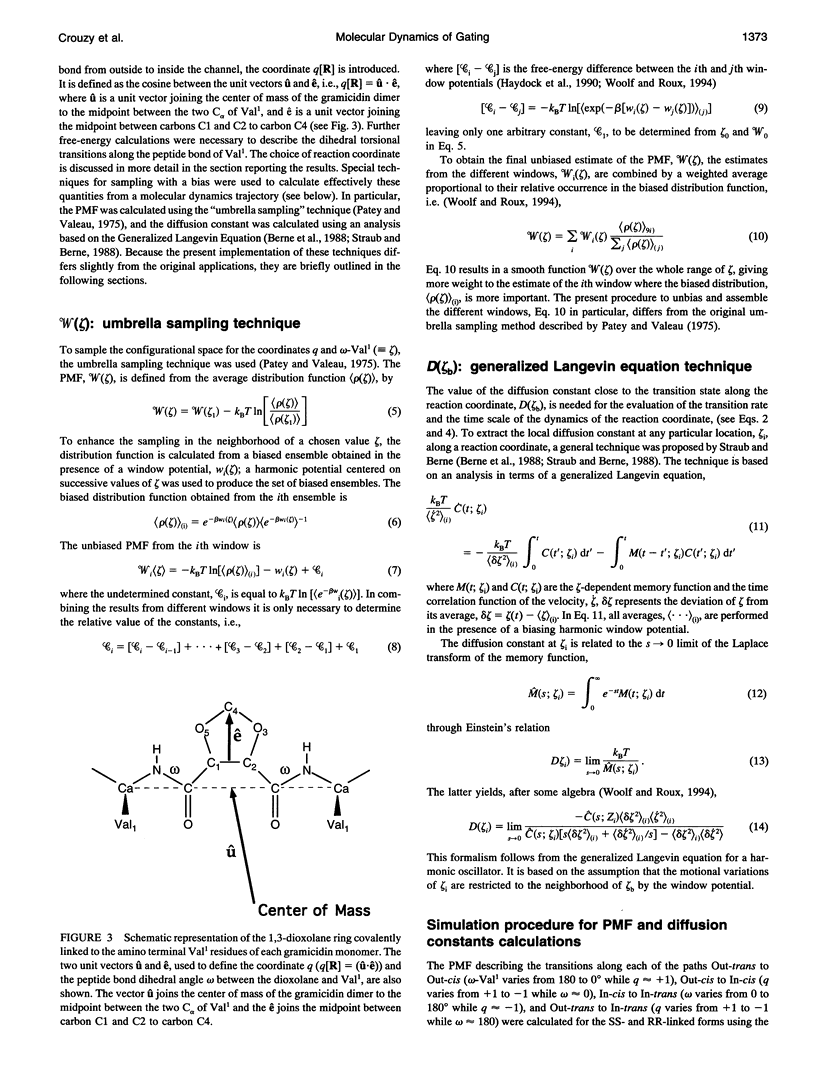
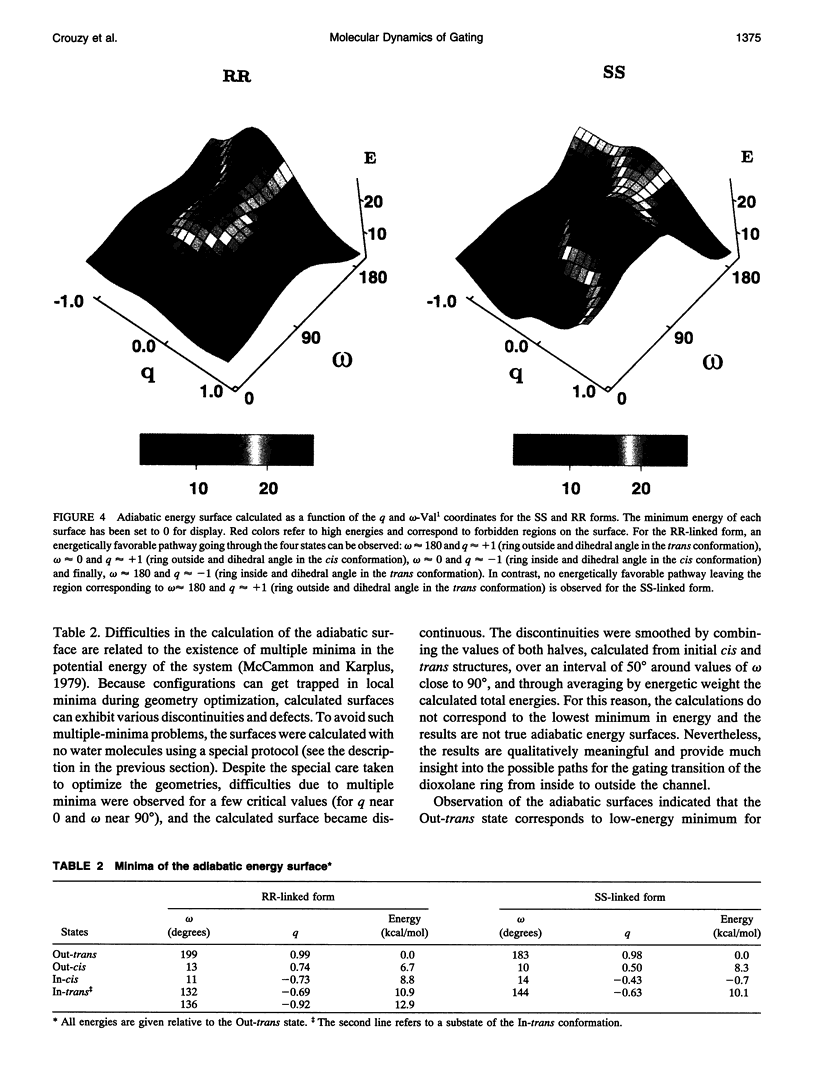
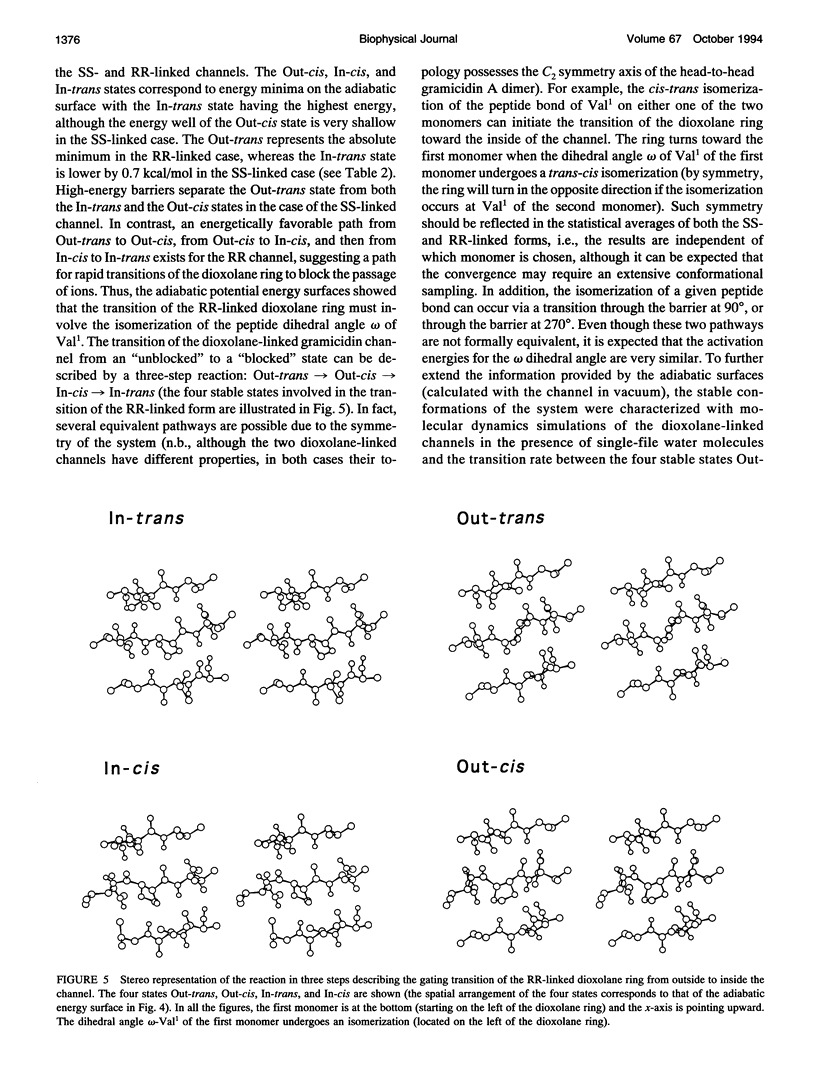
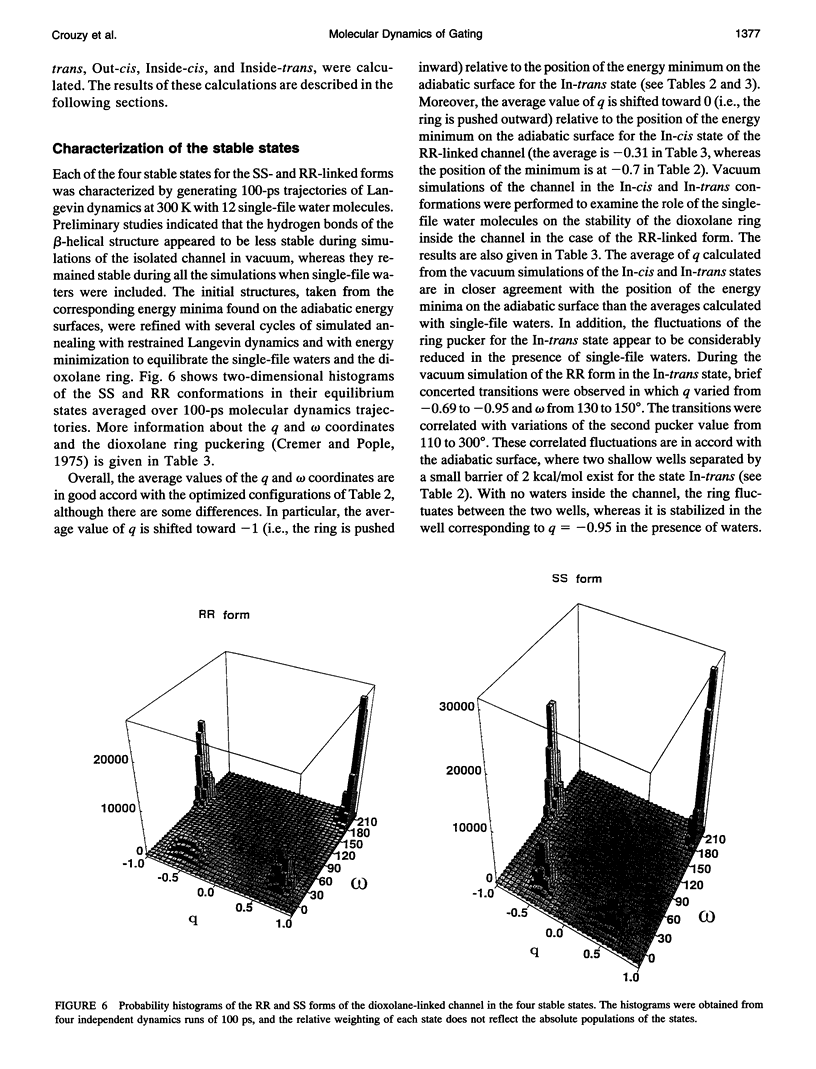
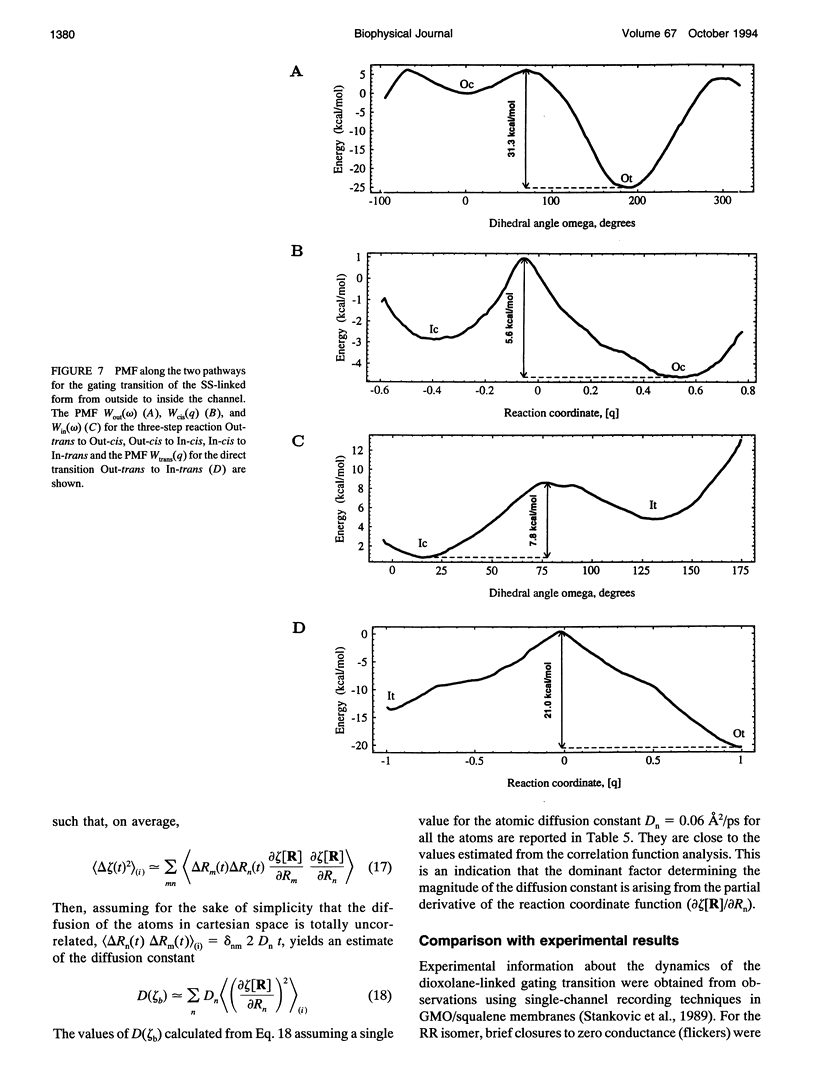
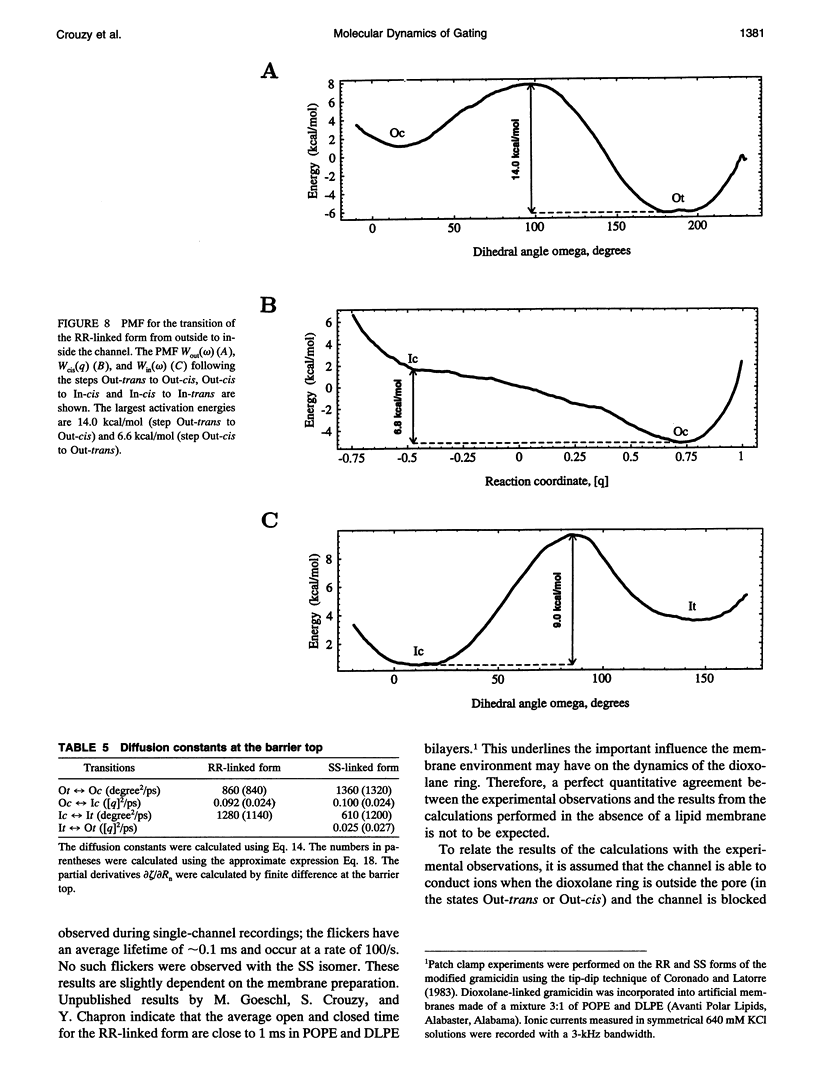
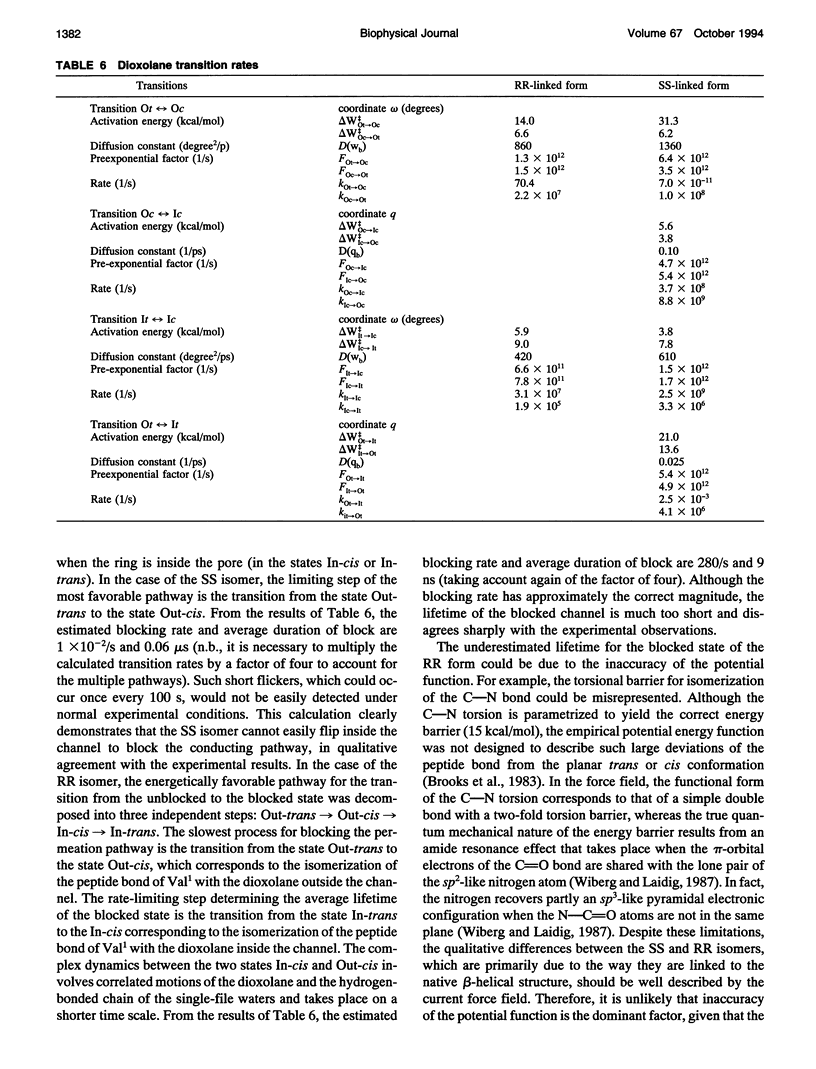
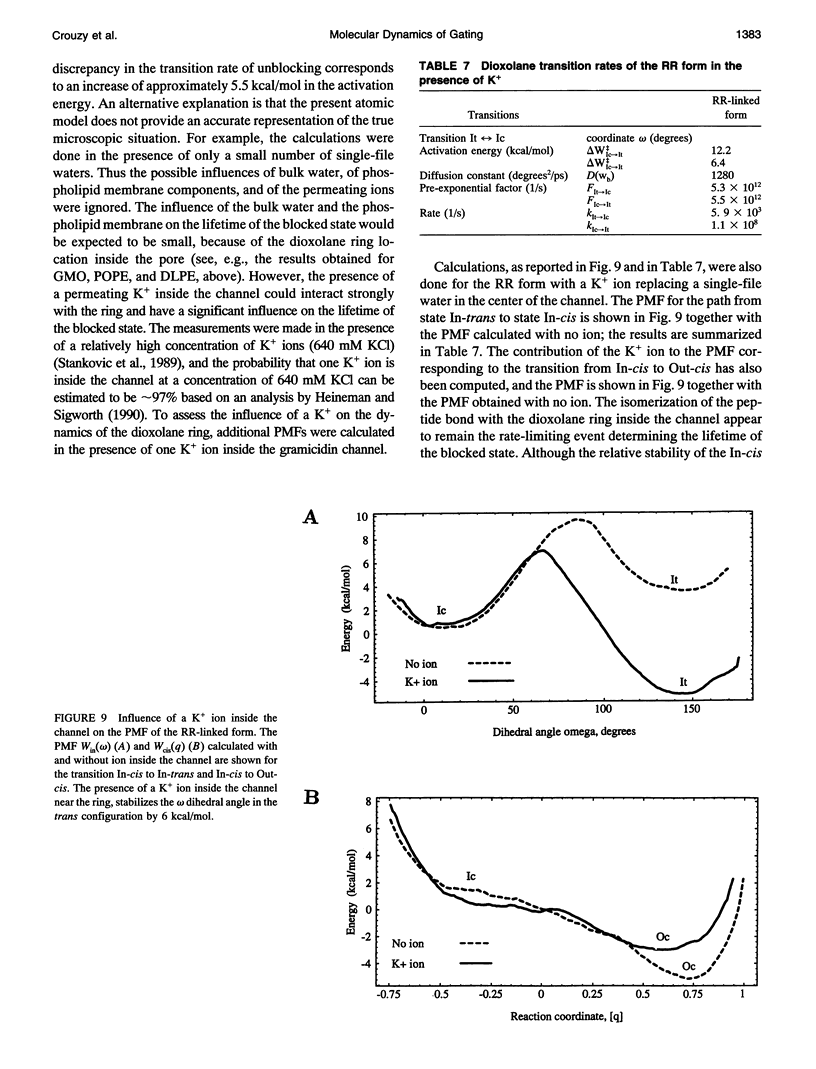
The gating transition of the RR and SS dioxolane ring-linked gramicidin A channels were studied with molecular dynamics simulations using a detailed atomic model. It was found that the probable reaction path, describing the transition of the ring from the exterior to the interior of the channel where it blocked the permeation pathway, involved several steps including the isomerization of the transpeptide plane dihedral angle of Val1. Reaction coordinates along this pathway were defined, and the transition rates between the stable conformers were calculated. It was found, in good accord with experimental observations, that the calculated blocking rate for the RR-linked channel was 280/s with a mean blocking time of 0.04 ms, whereas such blocking did not occur in the case of the SS-linked channel. An important observation is that the resulting lifetime for the blocked state of the RR-linked channel was in good accord with the experimental observations only when the calculations were performed in the presence of a potassium ion inside the channel.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Gramicidin channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:531–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Koeppe R. E., 2nd Molecular determinants of channel function. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S89–158. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Sodium channels and gating currents. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jul;61(3):644–683. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.3.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Swenson R. P., Jr, Taylor S. R. Block of squid axon K channels by internally and externally applied barium ions. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):663–682. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Voltage-dependent ion channels and their gating. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S5–13. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arseniev A. S., Barsukov I. L., Bystrov V. F., Lomize A. L., Ovchinnikov YuA 1H-NMR study of gramicidin A transmembrane ion channel. Head-to-head right-handed, single-stranded helices. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80702-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A. A statistical analysis of acetylcholine receptor activation in Xenopus myocytes: stepwise versus concerted models of gating. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:339–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Perozo E., Papazian D. M., Stefani E. Molecular basis of gating charge immobilization in Shaker potassium channels. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):679–683. doi: 10.1126/science.1948047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Jakobsson E., Subramaniam S., McCammon J. A. Time-correlation analysis of simulated water motion in flexible and rigid gramicidin channels. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):273–285. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82049-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Subramaniam S., Jakobsson E., McCammon J. A. Water and polypeptide conformations in the gramicidin channel. A molecular dynamics study. Biophys J. 1989 Aug;56(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82671-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Stühmer W. Quantal charge redistributions accompanying the structural transitions of sodium channels. Eur Biophys J. 1989;17(2):53–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00257102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Latorre R. Phospholipid bilayers made from monolayers on patch-clamp pipettes. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84343-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Guy H. R. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81809-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Conti F. Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated channels. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydock C., Sharp J. C., Prendergast F. G. Tryptophan-47 rotational isomerization in variant-3 scorpion neurotoxin. A combination thermodynamic perturbation and umbrella sampling study. Biophys J. 1990 Jun;57(6):1269–1279. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82645-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Sigworth F. J. Open channel noise. V. Fluctuating barriers to ion entry in gramicidin A channels. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):499–514. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82566-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchais D., Marty A. Interaction of permeant ions with channels activated by acetylcholine in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):9–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCammon J. A., Karplus M. Dynamics of activated processes in globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Latorre R., Reisin I. Coupling of voltage-dependent gating and Ba++ block in the high-conductance, Ca++-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Sep;90(3):427–449. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. K., Cross T. A. Gramicidin cation channel: an experimental determination of the right-handed helix sense and verification of beta-type hydrogen bonding. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9379–9385. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup S. H., Pear M. R., Lee C. Y., McCammon J. A., Karplus M. Dynamical theory of activated processes in globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4035–4039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Karplus M. Ion transport in a model gramicidin channel. Structure and thermodynamics. Biophys J. 1991 May;59(5):961–981. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82311-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Karplus M. Molecular dynamics simulations of the gramicidin channel. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:731–761. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seoh S. A., Busath D. D. Formamidinium-induced dimer stabilization and flicker block behavior in homo- and heterodimer channels formed by gramicidin A and N-acetyl gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1817–1827. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81239-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Voltage gating of ion channels. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 Feb;27(1):1–40. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic C. J., Heinemann S. H., Delfino J. M., Sigworth F. J., Schreiber S. L. Transmembrane channels based on tartaric acid-gramicidin A hybrids. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):813–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2471263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Toro L., Perozo E., Bezanilla F. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: I. Ionic and gating currents. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):996–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80881-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Jr, Armstrong C. M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):427–429. doi: 10.1038/291427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Urry D. W. N-acetyl gramicidin: single-channel properties and implications for channel structure. Science. 1979 Jan 5;203(4375):55–57. doi: 10.1126/science.83000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley G. A., Wallace B. A. Model ion channels: gramicidin and alamethicin. J Membr Biol. 1992 Aug;129(2):109–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00219508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]