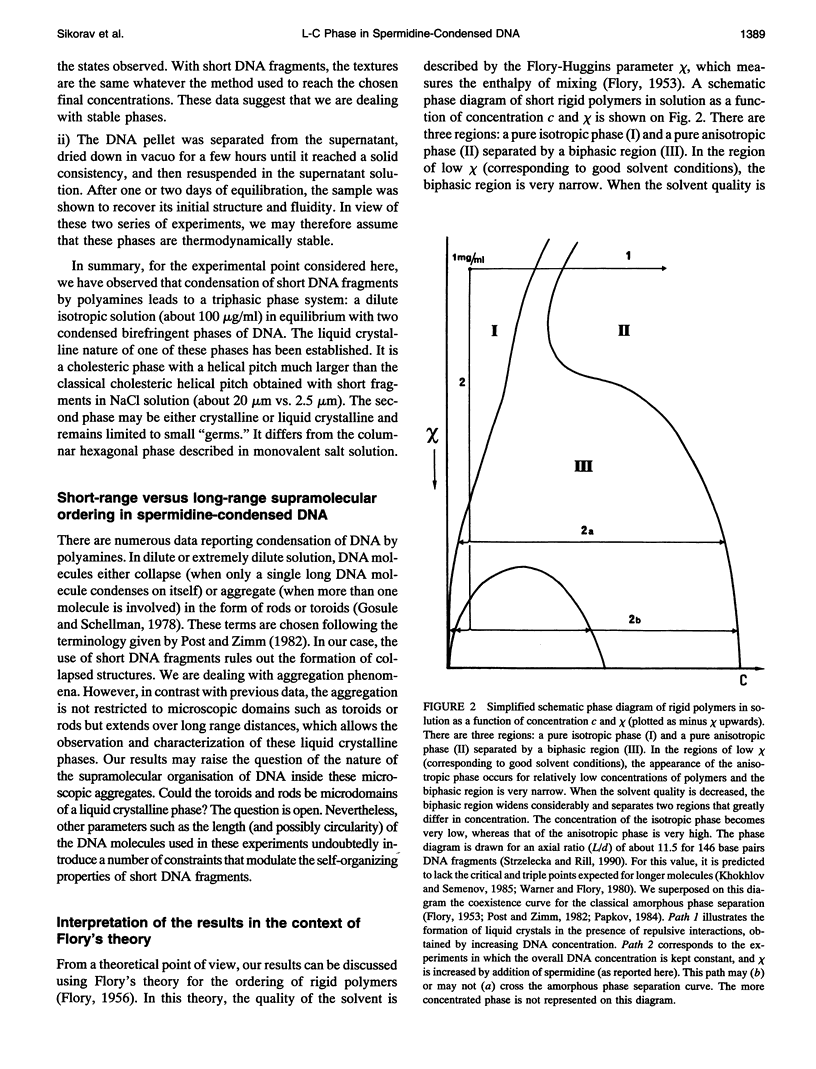
Abstract
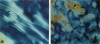
Over a large range of salt and spermidine concentrations, short DNA fragments precipitated by spermidine (a polyamine) sediment in a pellet from a dilute isotropic supernatant. We report here that the DNA-condensed phase consists of a cholesteric liquid crystal in equilibrium with a more concentrated phase. These results are discussed according to Flory's theory for the ordering of rigid polymers. The liquid crystal described here corresponds to an ordering in the presence of attractive interactions, in contrast with classical liquid crystalline DNA. Polyamines are often used in vitro to study the functional properties of DNA. We suggest that the existence of a liquid crystalline state in spermidine-condensed DNA is relevant to these studies.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeza I., Gariglio P., Rangel L. M., Chavez P., Cervantes L., Arguello C., Wong C., Montañez C. Electron microscopy and biochemical properties of polyamine-compacted DNA. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6387–6392. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeza I., Ibáez M., Wong C., Chávez P., Gariglio P., Oró J. Possible prebiotic significance of polyamines in the condensation, protection, encapsulation, and biological properties of DNA. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 1991;21(4):225–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01809858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M., Misselwitz R., Damaschun H., Damaschun G., Zirwer D. Spermine-DNA complexes build up metastable structures. Small-angle X-ray scattering and circular dichroism studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1297–1309. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield V. A. Condensation of DNA by multivalent cations: considerations on mechanism. Biopolymers. 1991 Nov;31(13):1471–1481. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Gosule L. C., Schellman A. DNA condensation with polyamines. II. Electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Baldwin R. L. Catalysis of DNA reassociation by the Escherichia coli DNA binding protein: A polyamine-dependent reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda D. K., Radding C. M. The mechanism of the search for homology promoted by recA protein. Facilitated diffusion within nucleoprotein networks. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13087–13096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Catenation of DNA rings by topoisomerases. Mechanism of control by spermidine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2687–2693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S. Chromosomal analogues: long-range order in psi-condensed DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:59–73. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Wilkerson L. S., Venable J. H., Jr, Robinson B. H. DNA packing in single crystals inferred from freeze-fracture-etch replicas. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):271–293. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livolant F., Levelut A. M., Doucet J., Benoit J. P. The highly concentrated liquid-crystalline phase of DNA is columnar hexagonal. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):724–726. doi: 10.1038/339724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestre M. F., Reich C. Contribution of light scattering to the circular dichroism of deoxyribonucleic acid films, deoxyribonucleic acid-polylysine complexes, and deoxyribonucleic acid particles in ethanolic buffers. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5214–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquet R., Houssier C. Thermodynamics of cation-induced DNA condensation. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Aug;9(1):159–167. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oller A. R., Vanden Broek W., Conrad M., Topal M. D. Ability of DNA and spermidine to affect the activity of restriction endonucleases from several bacterial species. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud A., Urbanke C., Alves J., Ehbrecht H. J., Zabeau M., Gualerzi C. Effect of polyamines and basic proteins on cleavage of DNA by restriction endonucleases. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5697–5703. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post C. B., Zimm B. H. Theory of DNA condensation: collapse versus aggregation. Biopolymers. 1982 Nov;21(11):2123–2137. doi: 10.1002/bip.360211104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau D. C., Parsegian V. A. Direct measurement of the intermolecular forces between counterion-condensed DNA double helices. Evidence for long range attractive hydration forces. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):246–259. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81831-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R., Weiner A., Kornberg A. Multienzyme systems of DNA replication. Science. 1974 Dec 13;186(4168):987–993. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4168.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A., Parthasarathy N. X-ray diffraction studies on cation-collapsed DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):313–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Church G. M. Complementary recognition in condensed DNA: accelerated DNA renaturation. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 20;222(4):1085–1108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90595-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivenugopal K. S., Wemmer D. E., Morris D. R. Aggregation of DNA by analogs of spermidine; enzymatic and structural studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2563–2580. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka T. E., Rill R. L. Phase transitions of concentrated DNA solutions in low concentrations of 1:1 supporting electrolyte. Biopolymers. 1990;30(1-2):57–71. doi: 10.1002/bip.360300108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Bloomfield V. A. Counterion-induced condesation of deoxyribonucleic acid. a light-scattering study. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2192–2196. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]