Abstract
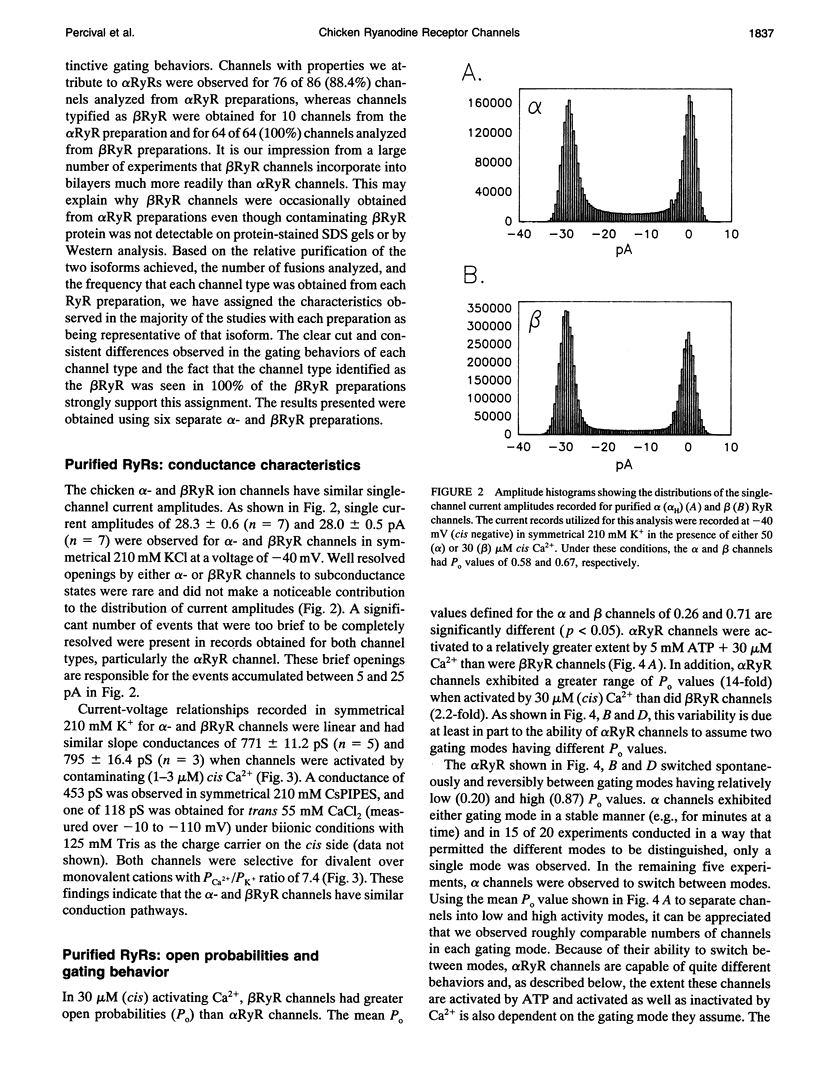
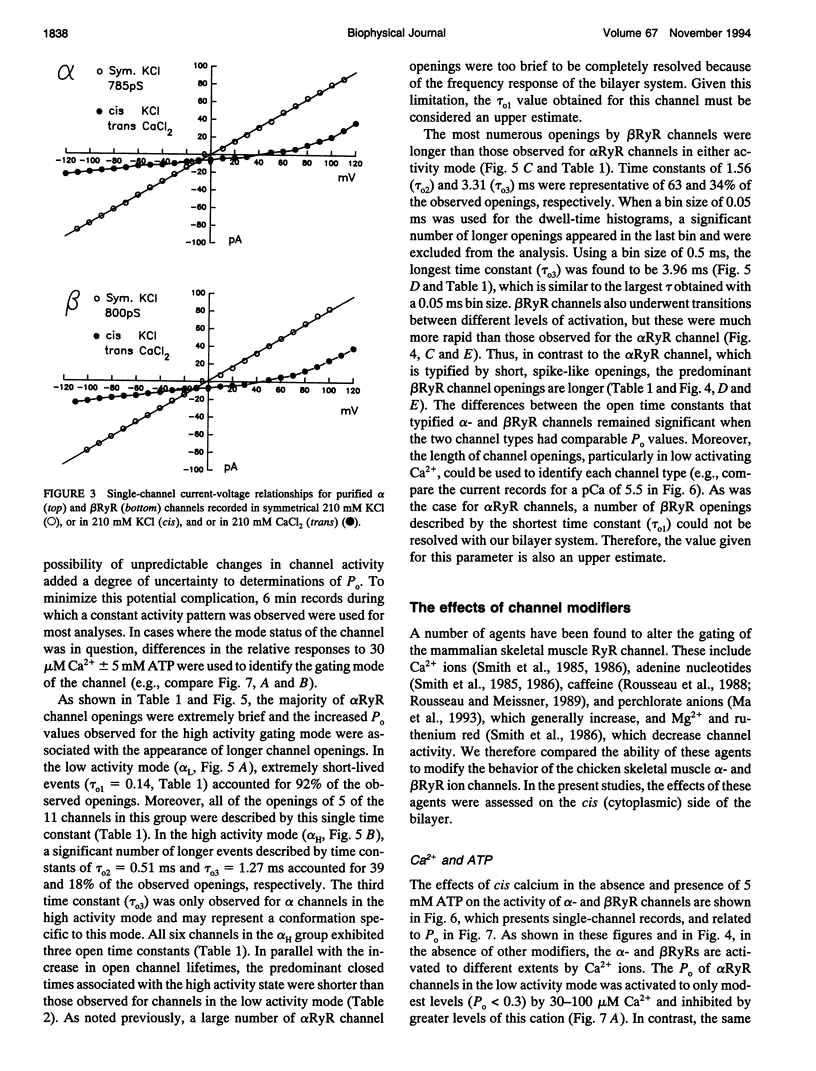
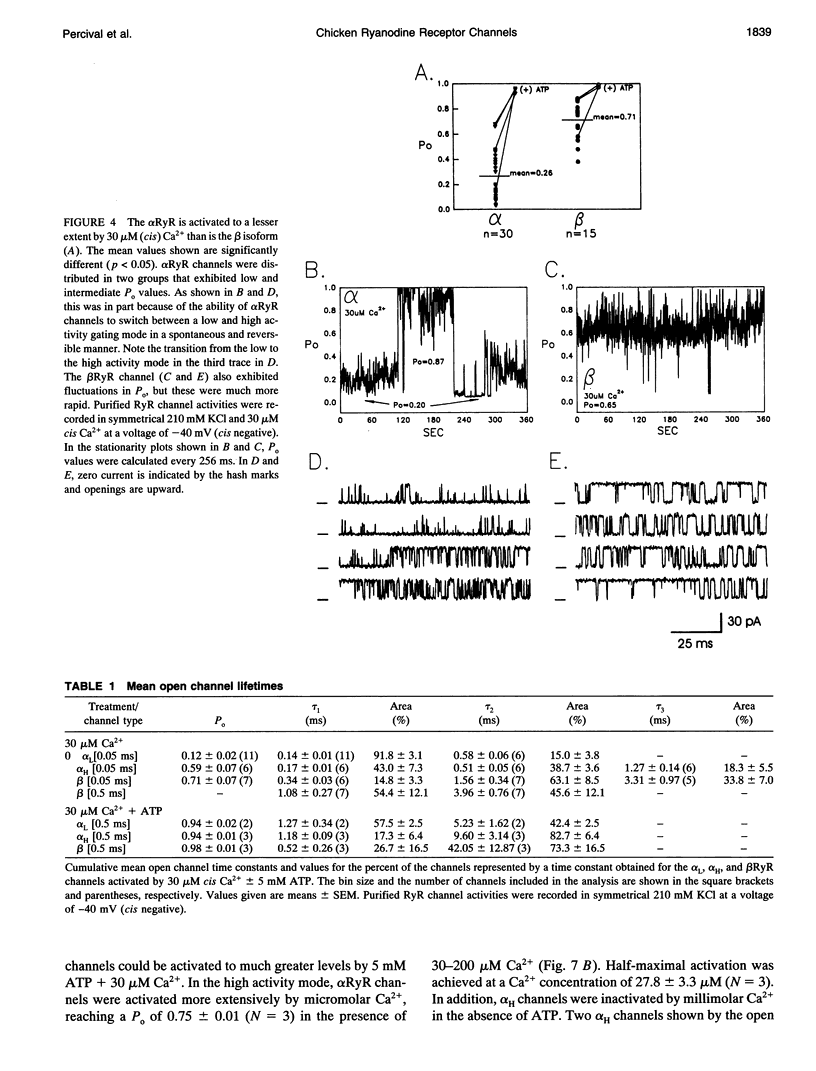
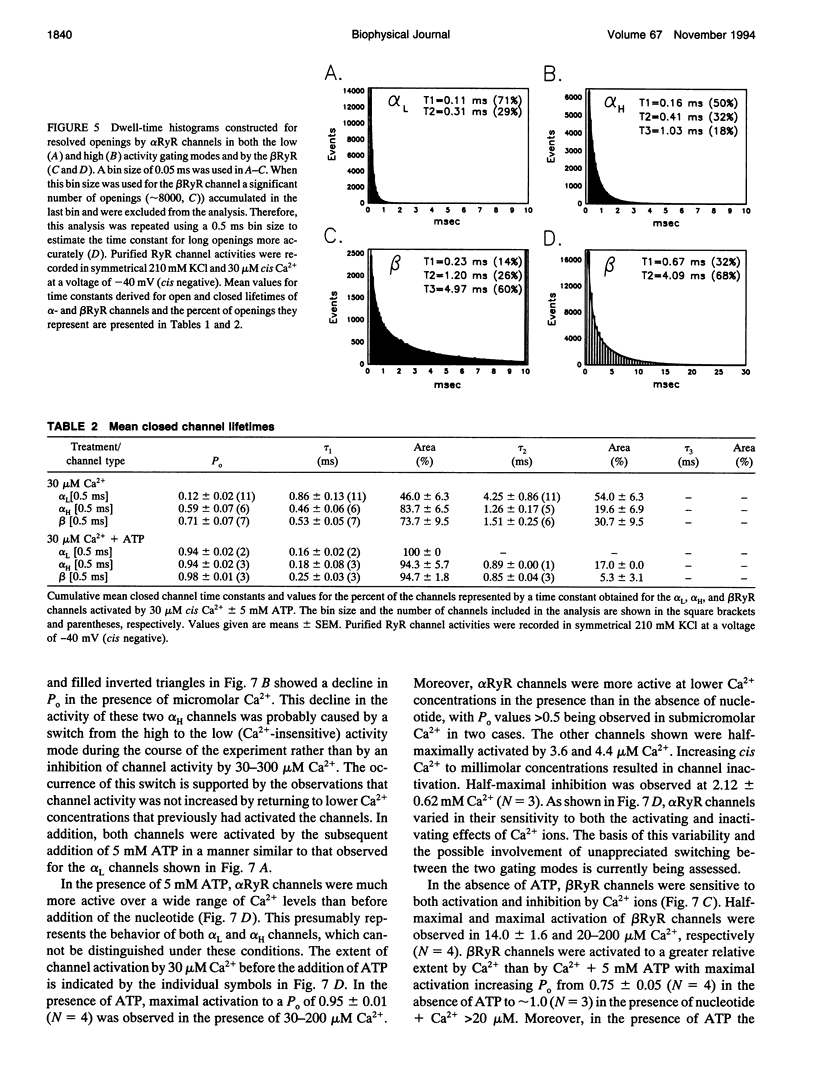
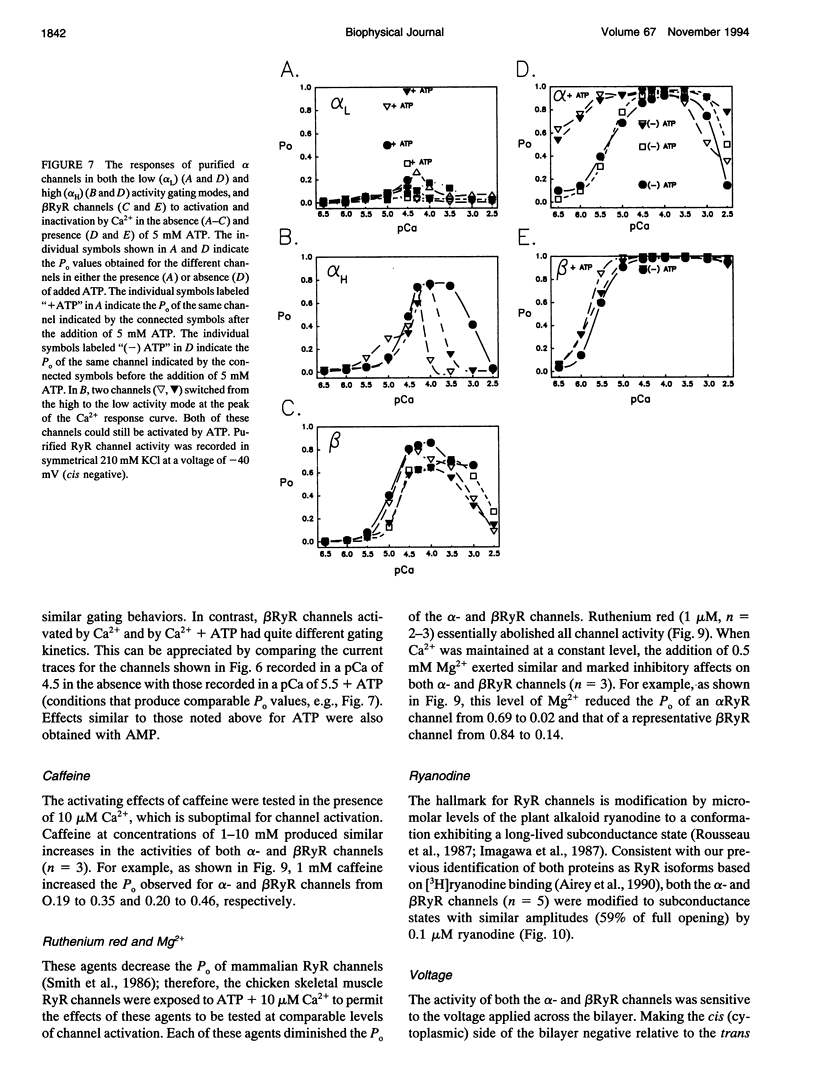
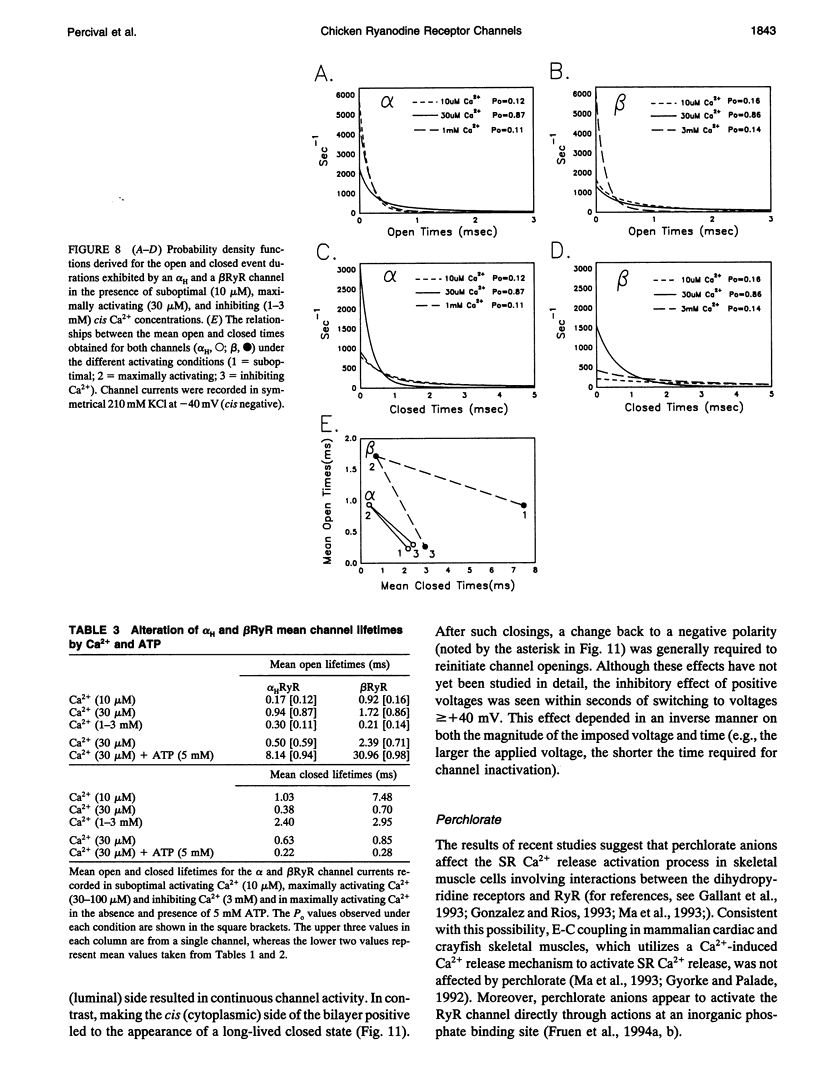
To define the roles of the alpha- and beta-ryanodine receptor (RyR) (sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel) isoforms expressed in chicken skeletal muscles, we investigated the ion channel properties of these proteins in lipid bilayers. alpha- and beta RyRs embody Ca2+ channels with similar conductances (792, 453, and 118 pS for K+, Cs+ and Ca2+) and selectivities (PCa2+/PK+ = 7.4), but the two channels have different gating properties. alpha RyR channels switch between two gating modes, which differ in the extent they are activated by Ca2+ and ATP, and inactivated by Ca2+. Either mode can be assumed in a spontaneous and stable manner. In a low activity mode, alpha RyR channels exhibit brief openings (tau o = 0.14 ms) and are minimally activated by Ca2+ in the absence of ATP. In a high activity mode, openings are longer (tau o1-3 = 0.17, 0.51, and 1.27 ms), and the channels are activated by Ca2+ in the absence of ATP and are in general less sensitive to the inactivating effects of Ca2+. beta RyR channel openings are longer (tau 01-3 = 0.34, 1.56, and 3.31 ms) than those of alpha RyR channels in either mode. beta RyR channels are activated to a greater relative extent by Ca2+ than ATP and are inactivated by millimolar Ca2+ in the absence, but not the presence, of ATP. Both alpha- and beta RyR channels are activated by caffeine, inhibited by Mg2+ and ruthenium red, inactivated by voltage (cytoplasmic side positive), and modified to a long-lived substate by ryanodine, but only alpha RyR channels are activated by perchlorate anions. The differences in gating and responses to channel modifiers may give the alpha- and beta RyRs distinct roles in muscle activation.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramcheck C. W., Best P. M. Physiological role and selectivity of the in situ potassium channel of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skinned frog skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jan;93(1):1–21. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airey J. A., Baring M. D., Beck C. F., Chelliah Y., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., Houenou L. J., McKemy D. D., Sutko J. L., Talvenheimo J. Failure to make normal alpha ryanodine receptor is an early event associated with the crooked neck dwarf (cn) mutation in chicken. Dev Dyn. 1993 Jul;197(3):169–188. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001970303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airey J. A., Beck C. F., Murakami K., Tanksley S. J., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., Sutko J. L. Identification and localization of two triad junctional foot protein isoforms in mature avian fast twitch skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14187–14194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airey J. A., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., Houenou L. J., Ivanenko A., Kenyon J. L., McKemy D. D., Sutko J. L. Crooked neck dwarf (cn) mutant chicken skeletal muscle cells in low density primary cultures fail to express normal alpha ryanodine receptor and exhibit a partial mutant phenotype. Dev Dyn. 1993 Jul;197(3):189–202. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001970304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airey J. A., Grinsell M. M., Jones L. R., Sutko J. L., Witcher D. Three ryanodine receptor isoforms exist in avian striated muscles. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 8;32(22):5739–5745. doi: 10.1021/bi00073a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K., Lai F. A., Liu Q. Y., Rousseau E., Erickson H. P., Meissner G. Structural and functional characterization of the purified cardiac ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1329–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull R., Marengo J. J. Sarcoplasmic reticulum release channels from frog skeletal muscle display two types of calcium dependence. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 4;331(3):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80341-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Knudson C. M., Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Sutko J. L., Kahl S. D., Raab C. R., Madson L. Identification and characterization of the high affinity [3H]ryanodine receptor of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6460–6463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell A. H., Brandt N. R. Does muscle activation occur by direct mechanical coupling of transverse tubules to sarcoplasmic reticulum? Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90265-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Tsien R. W. Altered prevalence of gating modes in neurotransmitter inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):980–984. doi: 10.1126/science.8094902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar A. L., Monck J. R., Fernandez J. M., Vergara J. L. Localization of the site of Ca2+ release at the level of a single sarcomere in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):739–741. doi: 10.1038/367739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M., Ma J. J., Knudson C. M., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Role of the ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle in excitation-contraction coupling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruen B. R., Mickelson J. R., Roghair T. J., Cheng H. L., Louis C. F. Anions that potentiate excitation-contraction coupling may mimic effect of phosphate on Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):C1729–C1735. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.6.C1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruen B. R., Mickelson J. R., Shomer N. H., Roghair T. J., Louis C. F. Regulation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor by inorganic phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):192–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant E. M., Taus N. S., Fletcher T. F., Lentz L. R., Louis C. F., Mickelson J. R. Perchlorate potentiation of excitation-contraction coupling in mammalian skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C559–C567. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini G., Clementi E., Ceci R., Marziali G., Sorrentino V. Expression of a ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ channel that is regulated by TGF-beta. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):91–94. doi: 10.1126/science.1320290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Ríos E. Perchlorate enhances transmission in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):373–421. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györke S., Palade P. Effects of perchlorate on excitation-contraction coupling in frog and crayfish skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:443–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakamata Y., Nakai J., Takeshima H., Imoto K. Primary structure and distribution of a novel ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel from rabbit brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann-Frank A., Varsányi M. Enhancement of Ca2+ release channel activity by phosphorylation of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 18;332(3):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80640-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Kurebayashi N., Konishi M., Baylor S. M. Excitation-contraction coupling in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers injected with mmolar concentrations of fura-2. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):224–234. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81599-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemond V., Csernoch L., Klein M. G., Schneider M. F. Voltage-gated and calcium-gated calcium release during depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):867–873. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82120-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman T., Brillantes A. M., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Marks A. R. FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9474–9477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong D. S., Pape P. C., Chandler W. K., Baylor S. M. Reduction of calcium inactivation of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release by fura-2 in voltage-clamped cut twitch fibers from frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Aug;102(2):333–370. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Liu Q. Y., Xu L., el-Hashem A., Kramarcy N. R., Sealock R., Meissner G. Amphibian ryanodine receptor isoforms are related to those of mammalian skeletal or cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C365–C372. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. R., Manning S. D., Williams A. J. Monovalent cation conductance in the ryanodine receptor-channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:463–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Functional characterisation of the ryanodine receptor purified from sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 26;1064(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Anderson K., Shirokov R., Levis R., González A., Karhanek M., Hosey M. M., Meissner G., Ríos E. Effects of perchlorate on the molecules of excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):423–448. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Ionic permeability of isolated muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum and liver endoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:417–437. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Rousseau E., Lai F. A. Structural and functional correlation of the trypsin-digested Ca2+ release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1715–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ogawa Y. Purification and characterization of two ryanodine-binding protein isoforms from sarcoplasmic reticulum of bullfrog skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1992 Oct;112(4):514–522. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Long-opening mode of gating of neuronal calcium channels and its promotion by the dihydropyridine calcium agonist Bay K 8644. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J., Meissner G., Block B. A. The fastest contracting muscles of nonmammalian vertebrates express only one isoform of the ryanodine receptor. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2418–2427. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81303-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivares E. B., Tanksley S. J., Airey J. A., Beck C. F., Ouyang Y., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., Sutko J. L. Nonmammalian vertebrate skeletal muscles express two triad junctional foot protein isoforms. Biophys J. 1991 Jun;59(6):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82331-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyamada H., Murayama T., Takagi T., Iino M., Iwabe N., Miyata T., Ogawa Y., Endo M. Primary structure and distribution of ryanodine-binding protein isoforms of the bullfrog skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17206–17214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape P. C., Jong D. S., Chandler W. K., Baylor S. M. Effect of fura-2 on action potential-stimulated calcium release in cut twitch fibers from frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Aug;102(2):295–332. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Ladine J., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Activation of the Ca2+ release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum by caffeine and related compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Meissner G. Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H328–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Henderson J. S., Meissner G. Single channel and 45Ca2+ flux measurements of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83543-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Karhanek M., Ma J., González A. An allosteric model of the molecular interactions of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Sep;102(3):449–481. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Vergara J. Modulation of Ca2+ transients by photorelease of caged nucleotides in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 1):C1291–C1300. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.5.C1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Klein M. G., Schneider M. F. Calcium dependence of inactivation of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Mar;97(3):437–471. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.3.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains adenine nucleotide-activated calcium channels. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):446–449. doi: 10.1038/316446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single-channel calcium and barium currents of large and small conductance from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):921–928. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83533-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutko J. L., Airey J. A., Murakami K., Takeda M., Beck C., Deerinck T., Ellisman M. H. Foot protein isoforms are expressed at different times during embryonic chick skeletal muscle development. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):793–803. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Isla B. A., Alcayaga C., Marengo J. J., Bull R. Activation of inositol trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ channels of sarcoplasmic reticulum from frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasago T., Imagawa T., Furukawa K., Ogurusu T., Shigekawa M. Regulation of the cardiac ryanodine receptor by protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation. J Biochem. 1991 Jan;109(1):163–170. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Ogunbumni E., Freund E., Wiederrecht G., Marks A. R., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506-binding protein. Dissociation and reconstitution of FKBP-12 to the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22992–22999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Best P. M. Inactivation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel by protein kinase. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):739–741. doi: 10.1038/359739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J. Ion conduction and discrimination in the sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor/calcium-release channel. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Feb;13(1):7–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01738423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witcher D. R., Kovacs R. J., Schulman H., Cefali D. C., Jones L. R. Unique phosphorylation site on the cardiac ryanodine receptor regulates calcium channel activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11144–11152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Takahashi M., Imagawa T., Shigekawa M., Takisawa H., Nakamura T. Phosphorylation of ryanodine receptors in rat myocytes during beta-adrenergic stimulation. J Biochem. 1992 Feb;111(2):186–190. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]