Abstract
In this study, we use fluorescent probes and proteolytic digestions to demonstrate structural coupling between distant regions of actin. We show that modifications of Cys-374 in the C-terminus of actin slow the rate of nucleotide exchange in the nucleotide cleft. Conformational coupling between the C-terminus and the DNasal loop in subdomain II is observed in proteolytic digestion experiments in which a new C-terminal cleavage site is exposed upon DNasel binding. The functional consequences of C-terminal modification are evident from S-1 ATPase activity and the in vitro motility experiments with modified actins. Pyrene actin, labeled at Cys-374, activates S-1 ATPase activity only half as well as control actin. This reduction is attributed to a lower Vmax value because the affinity of pyrene actin to S-1 is not significantly altered. The in vitro sliding velocity of pyrene actin is also decreased. However, IAEDANS labeling of actin (also at Cys-374) enhances the Vmax of acto-S-1 ATPase activity and the in vitro sliding velocity by approximately 25%. These results are discussed in terms of conformational coupling between distant regions in actin and the functional implications of the interactions of actin-binding proteins with the C-terminus of actin.
Full text
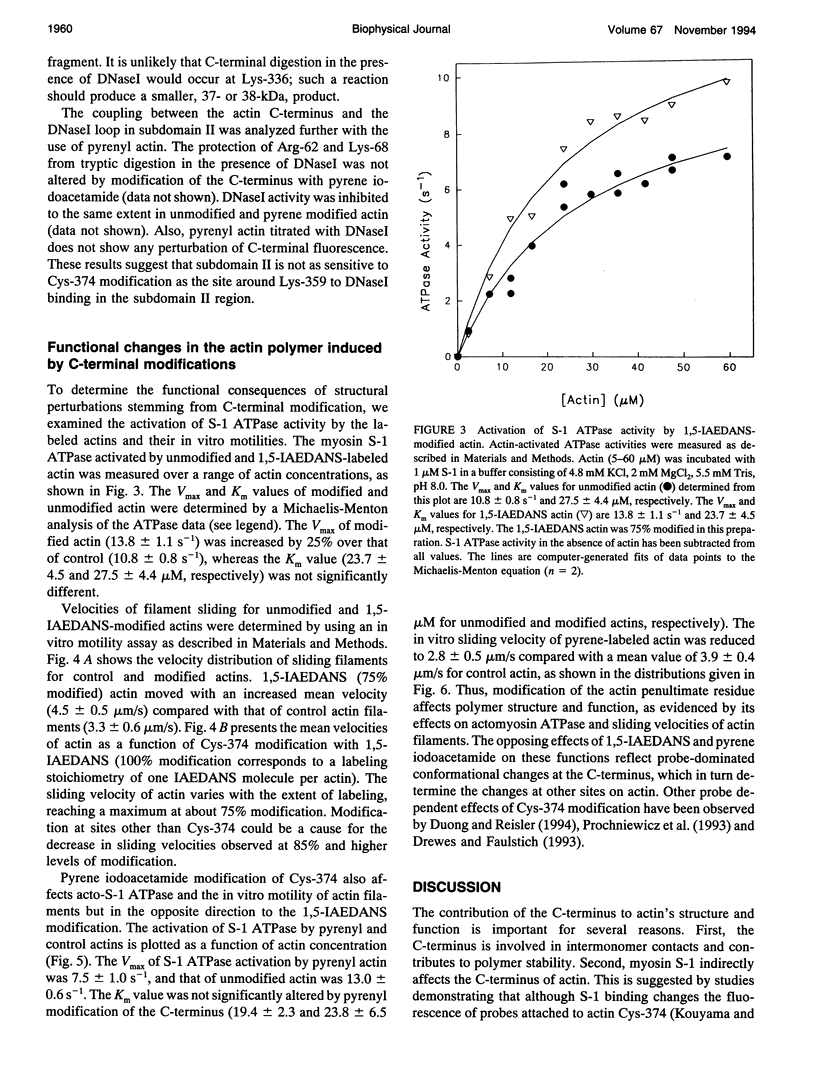
PDF

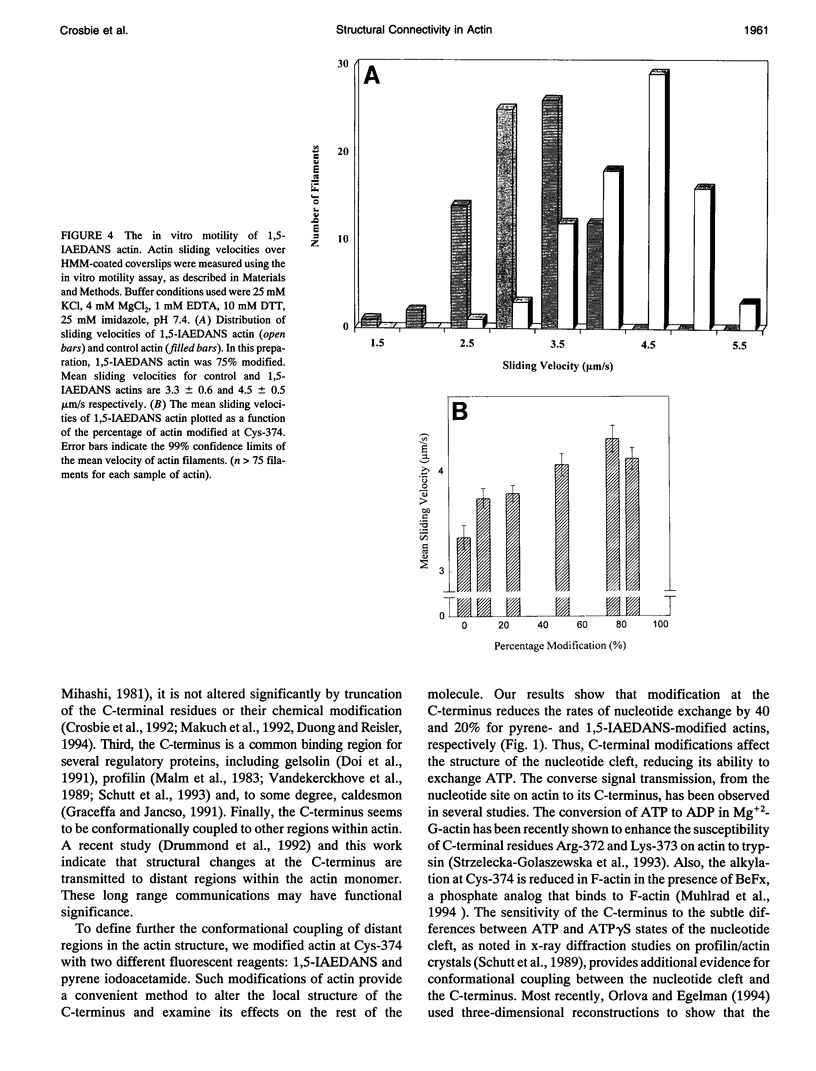


Images in this article
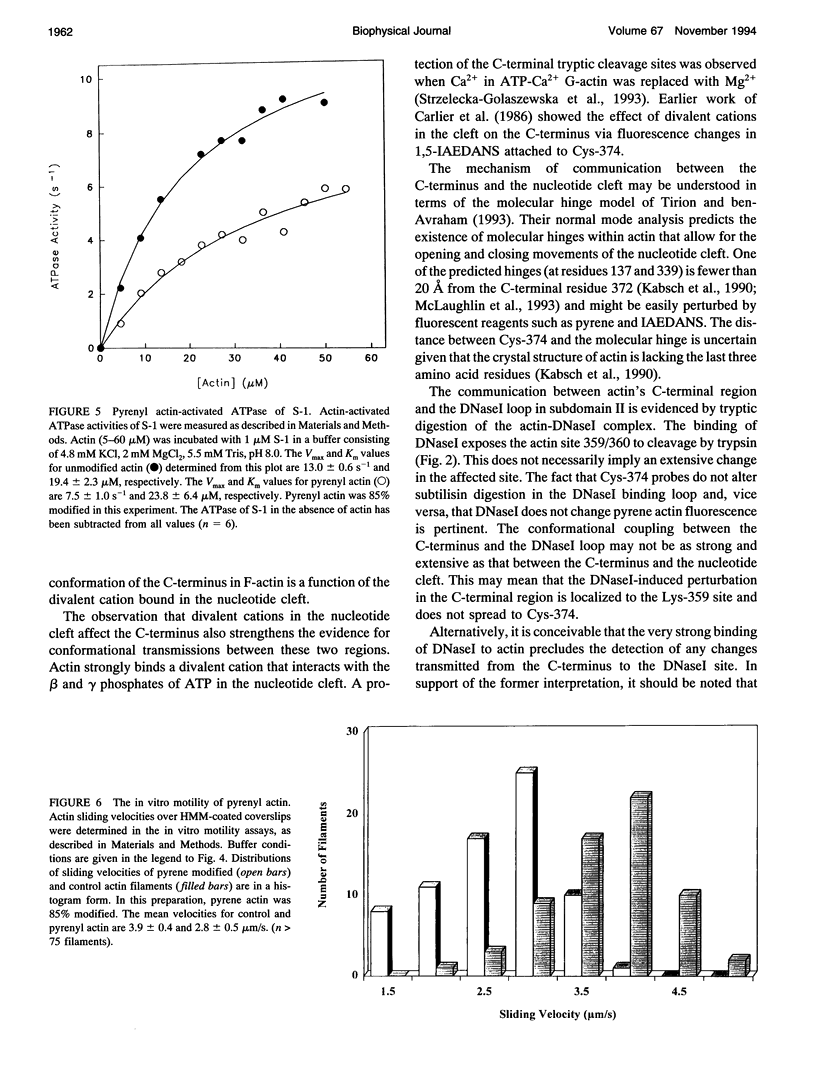
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulinski J. C., Kumar S., Titani K., Hauschka S. D. Peptide antibody specific for the amino terminus of skeletal muscle alpha-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtnick L. D., Chan K. W. Protection of actin against proteolysis by complex formation with deoxyribonuclease I. Can J Biochem. 1980 Dec;58(12):1348–1354. doi: 10.1139/o80-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. Fluorescence measurements of the binding of cations to high-affinity and low-affinity sites on ATP-G-actin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10778–10784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Walker S. B., Pollard T. D. Pyrene actin: documentation of the validity of a sensitive assay for actin polymerization. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):253–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00712034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criddle A. H., Geeves M. A., Jeffries T. The use of actin labelled with N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide to study the interaction of actin with myosin subfragments and troponin/tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):343–349. doi: 10.1042/bj2320343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosbie R. H., Chalovich J. M., Reisler E. Interaction of caldesmon and myosin subfragment 1 with the C-terminus of actin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91184-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Goch A., Gałazkiewicz B., Osińska H. The influence of caldesmon on ATPase activity of the skeletal muscle actomyosin and bundling of actin filaments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 27;842(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90295-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta G., Reisler E. Antibody against the amino terminus of alpha-actin inhibits actomyosin interactions in the presence of ATP. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):833–836. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Couet H. G. Studies on the antigenic sites of actin: a comparative study of the immunogenic crossreactivity of invertebrate actins. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Aug;4(4):405–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00711947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi Y. K., Banba M., Vertut-Doï A. Cysteine-374 of actin resides at the gelsolin contact site in the EGTA-resistant actin-gelsolin complex. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 11;30(23):5769–5777. doi: 10.1021/bi00237a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes G., Faulstich H. Cooperative effects on filament stability in actin modified at the C-terminus by substitution or truncation. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 15;212(1):247–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Hennessey E. S., Sparrow J. C. The binding of mutant actins to profilin, ATP and DNase I. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C., Patane K. Differences in G-actin containing bound ATP or ADP: the Mg2+-induced conformational change requires ATP. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4192–4196. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey J. E., Harrington W. F. Self-association in the myosin system at high ionic strength. I. Sensitivity of the interaction to pH and ionic environment. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):886–893. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graceffa P., Jancsó A. Disulfide cross-linking of caldesmon to actin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20305–20310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. ATP binding to a protease-resistant core of actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2742–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Fluorimetry study of N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide-labelled F-actin. Local structural change of actin protomer both on polymerization and on binding of heavy meromyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Fluorescent actin filaments move on myosin fixed to a glass surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6272–6276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Toyoshima Y. Y., Uyeda T. Q., Spudich J. A. Assays for actin sliding movement over myosin-coated surfaces. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:399–416. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebart M. C., Méjean C., Boyer M., Roustan C., Benyamin Y. Localization of a new alpha-actinin binding site in the COOH-terminal part of actin sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. I. Fluorimetric studies of actin labeled with dansyl aziridine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 30;185(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makuch R., Kołakowski J., Dabrowska R. The importance of C-terminal amino acid residues of actin to the inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by caldesmon and troponin I. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 10;297(3):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80546-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm B., Larsson H., Lindberg U. The profilin--actin complex: further characterization of profilin and studies on the stability of the complex. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Oct;4(5):569–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00712116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin P. J., Gooch J. T., Mannherz H. G., Weeds A. G. Structure of gelsolin segment 1-actin complex and the mechanism of filament severing. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):685–692. doi: 10.1038/364685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan R. A., Whittaker M., Safer D. Molecular structure of F-actin and location of surface binding sites. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):217–221. doi: 10.1038/348217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
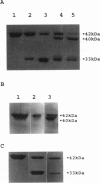
- Mornet D., Ue K. Proteolysis and structure of skeletal muscle actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossakowska M., Moraczewska J., Khaitlina S., Strzelecka-Golaszewska H. Proteolytic removal of three C-terminal residues of actin alters the monomer-monomer interactions. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):897–902. doi: 10.1042/bj2890897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlrad A., Cheung P., Phan B. C., Miller C., Reisler E. Dynamic properties of actin. Structural changes induced by beryllium fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11852–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méjean C., Lebart M. C., Boyer M., Roustan C., Benyamin Y. Localization and identification of actin structures involved in the filamin-actin interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):555–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue S. I., Miki M., dos Remedios C. G. Removing the two C-terminal residues of actin affects the filament structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 14;293(1):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E. Kinetic studies with synthetic myosin minifilaments show the equivalence of actomyosin and acto-HMM ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9541–9544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root D. D., Reisler E. The accessibility of etheno-nucleotides to collisional quenchers and the nucleotide cleft in G- and F-actin. Protein Sci. 1992 Aug;1(8):1014–1022. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt C. E., Lindberg U., Myslik J., Strauss N. Molecular packing in profilin: actin crystals and its implications. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90603-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt C. E., Myslik J. C., Rozycki M. D., Goonesekere N. C., Lindberg U. The structure of crystalline profilin-beta-actin. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):810–816. doi: 10.1038/365810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosiński J., Szpacenko A., Dabrowska R. Potentiation of actomyosin ATPase activity by filamin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Dec 10;178(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80623-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka-Gołaszewska H., Moraczewska J., Khaitlina S. Y., Mossakowska M. Localization of the tightly bound divalent-cation-dependent and nucleotide-dependent conformation changes in G-actin using limited proteolytic digestion. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 1;211(3):731–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirion M. M., ben-Avraham D. Normal mode analysis of G-actin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):186–195. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Myosin step size. Estimation from slow sliding movement of actin over low densities of heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90287-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Ranc C., Carlier M. F. Evidence for the direct interaction between tightly bound divalent metal ion and ATP on actin. Binding of the lambda isomers of beta gamma-bidentate CrATP to actin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20871–20880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J. S., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D. Acanthamoeba actin and profilin can be cross-linked between glutamic acid 364 of actin and lysine 115 of profilin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):129–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]