Abstract
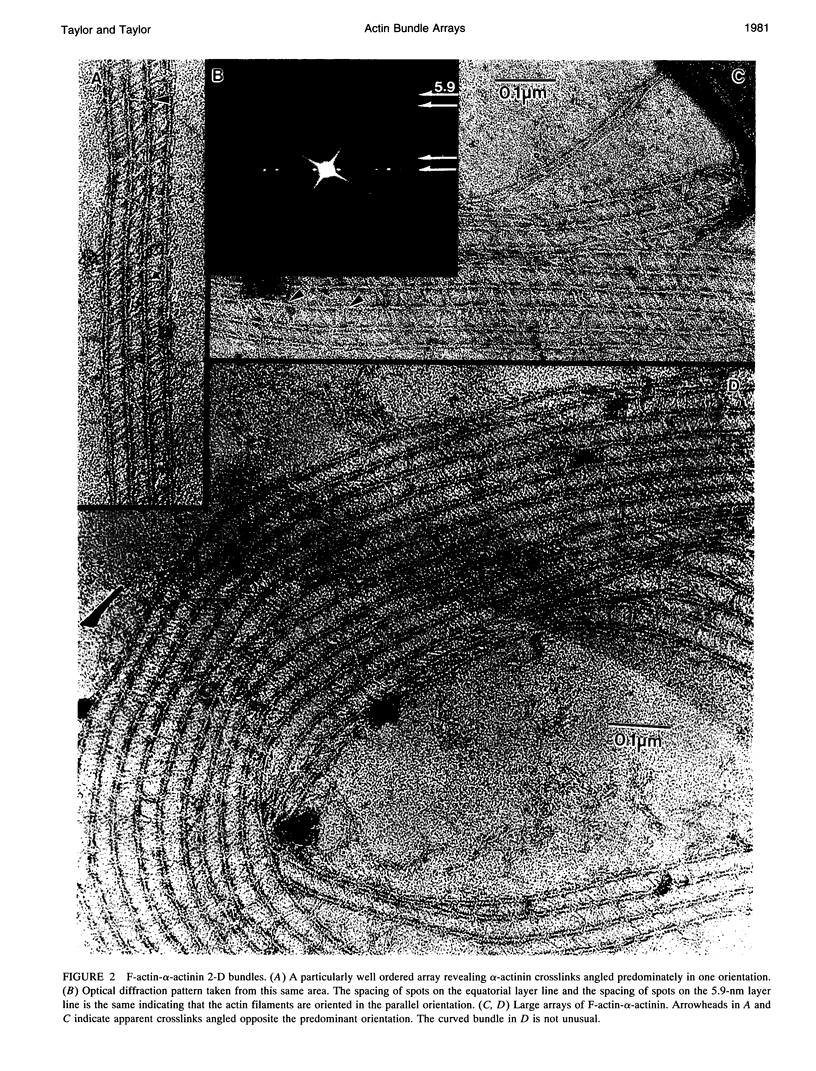
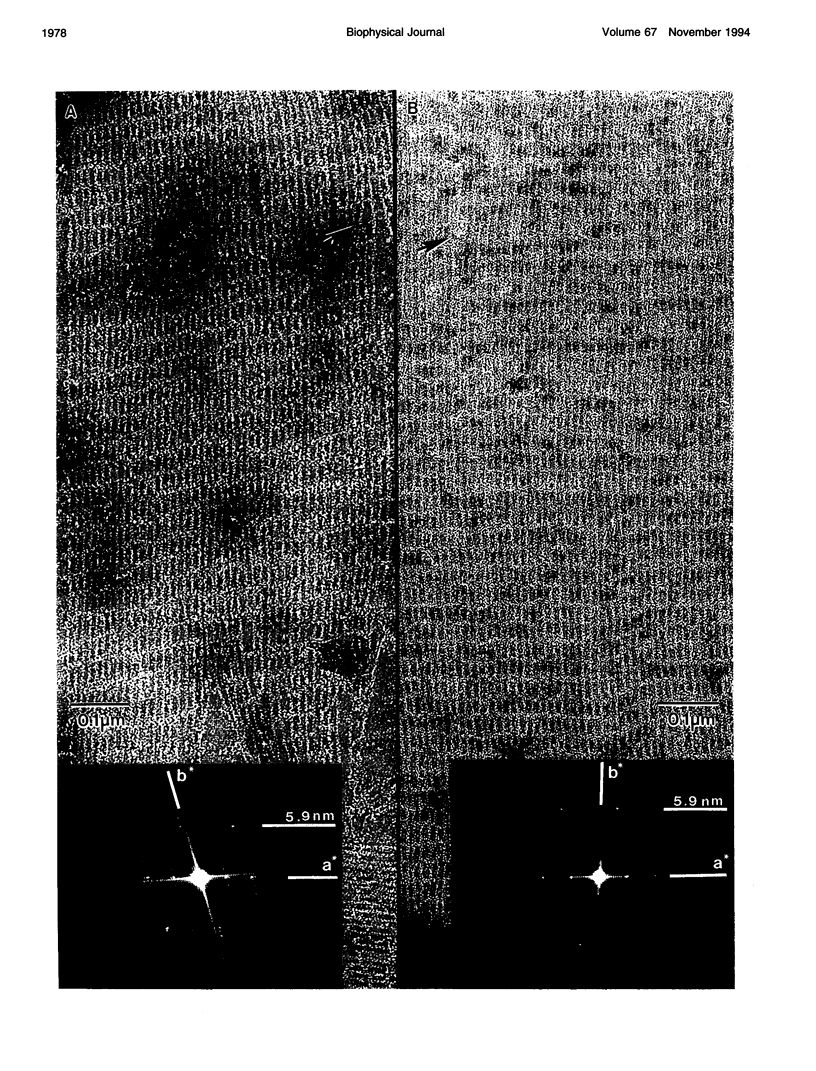
A method is described for forming two-dimensional (2-D) paracrystalline complexes of F-actin and bundling/gelation proteins on positively charged lipid monolayers. These arrays facilitate detailed structural studies of protein interactions with F-actin by eliminating superposition effects present in 3-D bundles. Bundles of F-actin have been produced using the glycolytic enzymes aldolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, the cytoskeletal protein erythrocyte adducin as well as smooth muscle alpha-actinin from chicken gizzard. All of the 2-D bundles formed contain F-actin with a 13/6 helical structure. F-actin-aldolase bundles have an interfilament spacing of 12.6 nm and a superlattice arrangement of actin filaments that can be explained by expression of a local twofold axis in the neighborhood of the aldolase. Well ordered F-actin-alpha-actinin 2-D bundles have an interfilament spacing of 36 nm and contain crosslinks 33 nm in length angled approximately 25-35 degrees to the filament axis. Images and optical diffraction patterns of these bundles suggest that they consist of parallel, unipolar arrays of actin filaments. This observation is consistent with an actin crosslinking function at adhesion plaques where actin filaments are bound to the cell membrane with uniform polarity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold H., Pette D. Binding of aldolase and triosephosphate dehydrogenase to F-actin and modification of catalytic properties of aldolase. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):360–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg D. A., Rodewald R., Rebhun L. I. The visualization of actin filament polarity in thin sections. Evidence for the uniform polarity of membrane-associated filaments. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):846–852. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond M., Somlyo A. V. Dense bodies and actin polarity in vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):403–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Fimbrin, a new microfilament-associated protein present in microvilli and other cell surface structures. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Feramisco J. R. Non-muscle alpha actinins are calcium-sensitive actin-binding proteins. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):565–567. doi: 10.1038/294565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Morton D. J. Aldolase binding to actin-containing filaments. Formation of paracrystals. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):797–798. doi: 10.1042/bj1590797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Ribi H. O., Pierce D. W., Kornberg R. D. Two-dimensional crystals of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme on positively charged lipid layers. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Masaki T. Molecular properties and functions in vitro of chicken smooth-muscle alpha-actinin in comparison with those of striated-muscle alpha-actinins. J Biochem. 1982 Nov;92(5):1457–1468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Voter W. A., Leonard K. Image reconstruction in electron microscopy: enhancement of periodic structure by optical filtering. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:39–63. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Burridge K. A rapid purification of alpha-actinin, filamin, and a 130,000-dalton protein from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. R., Waterston R. H. Muscle organization in Caenorhabditis elegans: localization of proteins implicated in thin filament attachment and I-band organization. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1532–1549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis N. R., DeRosier D. J. A polymorphism peculiar to bipolar actin bundles. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):771–776. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82419-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami A., Adachi K. A new method of preparation of a self-perforated micro plastic grid and its application. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1965;14(2):112–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamblin S. J., Cooper B., Millar J. R., Davies G. J., Littlechild J. A., Watson H. C. The crystal structure of human muscle aldolase at 3.0 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80211-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner K., Bennett V. A new erythrocyte membrane-associated protein with calmodulin binding activity. Identification and purification. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1339–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner K., Bennett V. Modulation of spectrin-actin assembly by erythrocyte adducin. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):359–362. doi: 10.1038/328359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Dutton A. H., Tokuyasu K. T., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscope studies of membrane-microfilament interactions: distributions of alpha-actinin, tropomyosin, and vinculin in intestinal epithelial brush border and chicken gizzard smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):614–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goli D. E., Suzuki A., Temple J., Holmes G. R. Studies on purified -actinin. I. Effect of temperature and tropomyosin on the -actinin-F-actin interaction. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):469–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. R., Goll D. E., Suzuki A. Effect of -actinin on actin viscosity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 2;253(1):240–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C., Popp D., Gebhard W., Kabsch W. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):44–49. doi: 10.1038/347044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi R., Bennett V. Mapping the domain structure of human erythrocyte adducin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13130–13136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi R., Gilligan D. M., Otto E., McLaughlin T., Bennett V. Primary structure and domain organization of human alpha and beta adducin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):665–675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M. Thermodynamical aspect of G-F transformations of actin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 24;180(2):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Granger B. L. Fluorescent localization of membrane sites in glycerinated chicken skeletal muscle fibers and the relationship of these sites to the protein composition of the Z disc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamud D., Drysdale J. W. Isoelectric points of proteins: a table. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;86(2):620–647. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90790-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Endo M., Ebashi S. Localization of 6S component of a alpha-actinin at Z-band. J Biochem. 1967 Nov;62(5):630–632. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Modular organization of actin crosslinking proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., Aebi U. Bundling of actin filaments by alpha-actinin depends on its molecular length. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2013–2024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mische S. M., Mooseker M. S., Morrow J. S. Erythrocyte adducin: a calmodulin-regulated actin-bundling protein that stimulates spectrin-actin binding. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2837–2845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Clarke F. M., Masters C. J. An electron microscope study of the interaction between fructose diphosphate aldolase and actin-containing filaments. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser G., Ravanat C., Freyssinet J. M., Brisson A. Sub-domain structure of lipid-bound annexin-V resolved by electron image analysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 20;217(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90538-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R., Tucker A., Ferguson C., Tsernoglou D., Leonard K., Crumpton M. J. Crystallization of p68 on lipid monolayers and as three-dimensional single crystals. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Spudich J. A. Purification of muscle actin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):164–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlubnaya Z. A., Tskhovrebova L. A., Zaalishtsbvili M. M., Stefanenko G. A. Electron microscopic study of alpha-actinin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):357–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi H. O., Ludwig D. S., Mercer K. L., Schoolnik G. K., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of cholera toxin penetrating a lipid membrane. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1272–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.3344432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. P., Schmid M. F., Morgan D. G., Chiu W. Three-dimensional structural analysis of tetanus toxin by electron crystallography. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Ford G. C., Watson H. C., Banaszak L. J. Molecular symmetry of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Mittal B., Sanger J. M. Analysis of myofibrillar structure and assembly using fluorescently labeled contractile proteins. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):825–833. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnyder T., Cyrklaff M., Fuchs K., Wallimann T. Crystallization of mitochondrial creatine kinase on negatively charged lipid layers. J Struct Biol. 1994 Mar-Apr;112(2):136–147. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1994.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V. Geometry of actin-membrane attachments in the smooth muscle cell: the localisations of vinculin and alpha-actinin. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):45–49. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Isenberg G., Celis J. E. Polarity of actin at the leading edge of cultured cells. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):638–639. doi: 10.1038/272638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Morton D. J., Clarke F. M. Interaction of aldolase with actin-containing filaments. Structural studies. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):99–104. doi: 10.1042/bj1860099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. L., Fuller S. D., Burnett R. M. Difference imaging of adenovirus: bridging the resolution gap between X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2589–2599. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sygusch J., Beaudry D., Allaire M. Molecular architecture of rabbit skeletal muscle aldolase at 2.7-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7846–7850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sygusch J., Boulet H., Beaudry D. Structure of rabbit muscle aldolase at low resolution. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15286–15290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Taylor D. W. Formation of 2-D paracrystals of F-actin on phospholipid layers mixed with quaternary ammonium surfactants. J Struct Biol. 1992 Mar-Apr;108(2):140–147. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90013-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Taylor D. W. Projection image of smooth muscle alpha-actinin from two-dimensional crystals formed on positively charged lipid layers. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):196–205. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidball J. G. Alpha-actinin is absent from the terminal segments of myofibrils and from subsarcolemmal densities in frog skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jun;170(2):469–482. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Bonder E. M., DeRosier D. J. Actin filaments elongate from their membrane-associated ends. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):485–494. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Tsukita S., Ishikawa H. Association of actin and 10 nm filaments with the dense body in smooth muscle cells of the chicken gizzard. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;229(2):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00214972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzgiris E. E., Kornberg R. D. Two-dimensional crystallization technique for imaging macromolecules, with application to antigen--antibody--complement complexes. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):125–129. doi: 10.1038/301125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Filamin, a new high-molecular-weight protein found in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4483–4486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Arruda M. V., Watson S., Lin C. S., Leavitt J., Matsudaira P. Fimbrin is a homologue of the cytoplasmic phosphoprotein plastin and has domains homologous with calmodulin and actin gelation proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1069–1079. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




