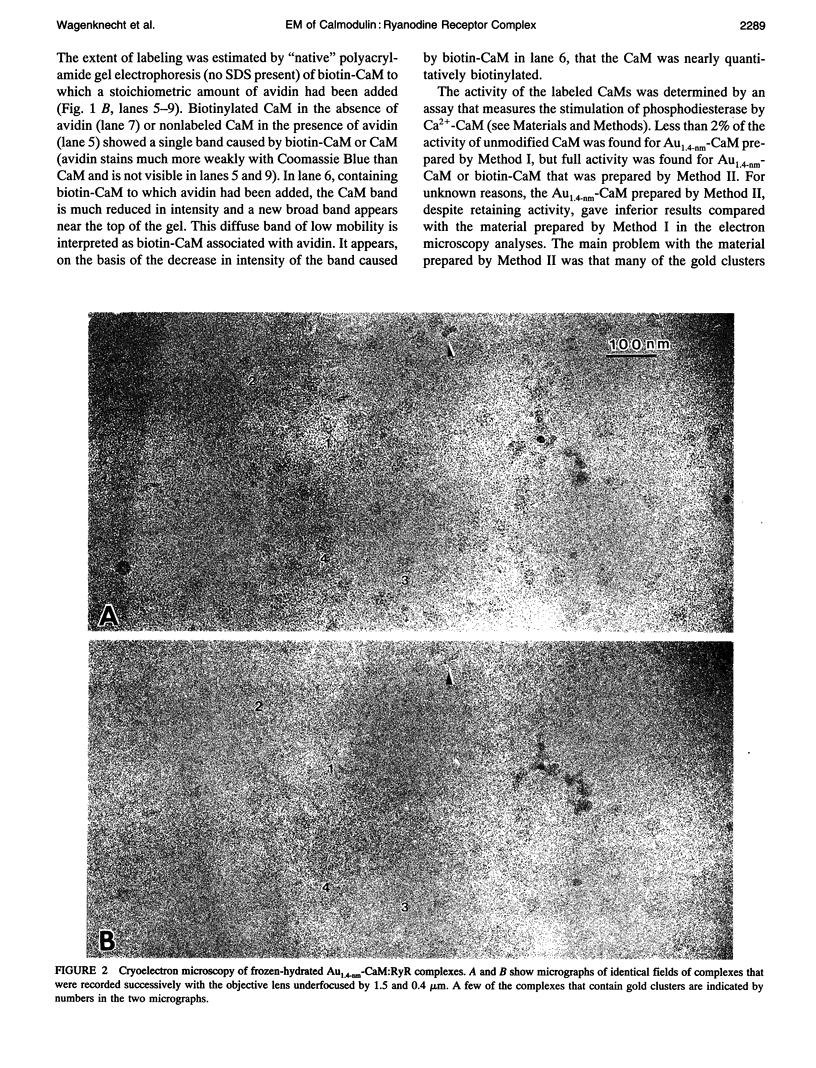
Abstract
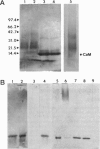
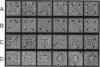
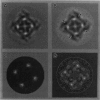
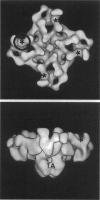
Calmodulin (CaM) is a regulator of the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) of the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscle. The locations where CaM binds on the surface of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor were determined by electron microscopy. Wheat germ CaM was labeled specifically at Cys-27 with a maleimide derivative of a 1.4-nm-diameter gold cluster, and the gold-cluster-labeled CaM was bound to the purified ryanodine receptor. The complexes were imaged in the frozen-hydrated state by cryoelectron microscopy with no stains or fixatives present. In the micrographs, gold clusters were frequently observed near the corners of the square-shaped images of the ryanodine receptors. In some images, all four corners of the receptor were occupied by gold clusters. Image averaging allowed the site of CaM binding to be determined in two dimensions with an estimated precision of 4 nm. No changes were apparent in the quaternary structure of the ryanodine receptor upon binding CaM to the resolution attained, about 3 nm. Side views of the ryanodine receptor, in which the receptor is oriented approximately perpendicular to the much more frequent fourfold symmetric views, were occasionally observed, and showed that the CaM binding site is most likely on the surface of the receptor that faces the cytoplasm. We conclude that the CaM binding site is at least 10 nm from the transmembrane channel of the receptor and, consequently, that long-range conformational changes are involved in the modulation of the calcium channel activity of the receptor by CaM.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braig K., Simon M., Furuya F., Hainfeld J. F., Horwich A. L. A polypeptide bound by the chaperonin groEL is localized within a central cavity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Evidence for and properties of a protein activator. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2859–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu W. What does electron cryomicroscopy provide that X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy cannot? Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:233–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A., Sumbilla C., Inesi G., Jay S. D., Campbell K. P. Specific association of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and related substrates with the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5899–5905. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyrklaff M., Adrian M., Dubochet J. Evaporation during preparation of unsupported thin vitrified aqueous layers for cryo-electron microscopy. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1990 Dec;16(4):351–355. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Adrian M., Chang J. J., Homo J. C., Lepault J., McDowall A. W., Schultz P. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Q Rev Biophys. 1988 May;21(2):129–228. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Inui M. Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Nunzi G. Junctional feet and particles in the triads of a fast-twitch muscle fibre. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):233–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00712033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. Structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Fed Proc. 1980 May 15;39(7):2403–2409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainfeld J. F., Furuya F. R. A 1.4-nm gold cluster covalently attached to antibodies improves immunolabeling. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Feb;40(2):177–184. doi: 10.1177/40.2.1552162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann-Frank A., Varsányi M. Enhancement of Ca2+ release channel activity by phosphorylation of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 18;332(3):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80640-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura M., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Zhu G., Klee C. B., Bax A. Solution structure of a calmodulin-target peptide complex by multidimensional NMR. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):632–638. doi: 10.1126/science.1585175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasturi R., Vasulka C., Johnson J. D. Ca2+, caldesmon, and myosin light chain kinase exchange with calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7958–7964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P. S., Campbell K. P. The ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13765–13768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Modulation of calmodulin plasticity in molecular recognition on the basis of x-ray structures. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1718–1721. doi: 10.1126/science.8259515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Target enzyme recognition by calmodulin: 2.4 A structure of a calmodulin-peptide complex. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1251–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1519061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Evidence of a role for calmodulin in the regulation of calcium release from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):244–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Henderson J. S. Rapid calcium release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles is dependent on Ca2+ and is modulated by Mg2+, adenine nucleotide, and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3065–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu K., Willard H. F., Khanna V. K., Zorzato F., Green N. M., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13472–13483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penczek P., Radermacher M., Frank J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of single particles embedded in ice. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jan;40(1):33–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher M., Rao V., Grassucci R., Frank J., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Wagenknecht T. Cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction of the calcium release channel/ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):411–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher M., Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Inui M., Chadwick C., Fleischer S. Cryo-EM of the native structure of the calcium release channel/ryanodine receptor from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):936–940. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81900-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohringer R., Holden D. W. Protein blotting: detection of proteins with colloidal gold, and of glycoproteins and lectins with biotin-conjugated and enzyme probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Inui M., Radermacher M., Frank J., Fleischer S. Ultrastructure of the calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):211–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler S., Wegener A. D., Whang D. D., Hathaway D. R., Jones L. R. High molecular weight proteins in cardiac and skeletal muscle junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles bind calmodulin, are phosphorylated, and are degraded by Ca2+-activated protease. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8550–8557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Rousseau E., Meissner G. Calmodulin modulation of single sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channels from cardiac and skeletal muscle. Circ Res. 1989 Feb;64(2):352–359. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasburg G. M., Hogan M., Birmachu W., Thomas D. D., Louis C. F. Site-specific derivatives of wheat germ calmodulin. Interactions with troponin and sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):542–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suko J., Maurer-Fogy I., Plank B., Bertel O., Wyskovsky W., Hohenegger M., Hellmann G. Phosphorylation of serine 2843 in ryanodine receptor-calcium release channel of skeletal muscle by cAMP-, cGMP- and CaM-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jan 17;1175(2):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90023-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Ogunbumni E., Freund E., Wiederrecht G., Marks A. R., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506-binding protein. Dissociation and reconstitution of FKBP-12 to the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22992–22999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Berkowitz J., Forneris C. Configuration of interdomain linkers in pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli as determined by cryoelectron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Jul-Aug;109(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90069-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Best P. M. Inactivation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel by protein kinase. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):739–741. doi: 10.1038/359739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkens S., Capaldi R. A. Monomaleimidogold labeling of the gamma subunit of the Escherichia coli F1 ATPase examined by cryoelectron microscopy. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 15;299(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90250-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witcher D. R., Kovacs R. J., Schulman H., Cefali D. C., Jones L. R. Unique phosphorylation site on the cardiac ryanodine receptor regulates calcium channel activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11144–11152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. C., Reedy M. M., Burke C. L., Strasburg G. M. Calmodulin interaction with the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel protein. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 18;33(2):518–525. doi: 10.1021/bi00168a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Minowa O., Yagi K. Divalent cation binding to wheat germ calmodulin. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):1925–1933. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]