Abstract
1. A new preparation of mouse skeletal muscle, prepared from pectoral muscles, is described.
2. The sorbitol space of this muscle, both in vivo and in vitro, has been measured with dynamic loading of the muscle in vitro as an experimental variable.
3. The Na+ and K+ contents of the muscle have been determined and the apparent intracellular concentration for these ions calculated both in vivo and after incubation in vitro.
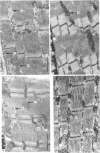
4. Histological studies on the incubated muscle have been made so as to permit comparison of the changes in the chemical measurements with changes in the ultrastructure of the muscle.
5. The results of these experiments show that there is an increase in the apparent extracellular space of the muscle following incubation. This increase is constant, and independent of the load, with the important exception that unloaded muscles do not reach an equilibrium during the period of incubation and have a much greater apparent extracellular space.
6. Intracellular Na+ and K+ concentrations are consistent with the sorbitol being restricted to an extracellular phase in the loaded muscle; but the evidence implies that sorbitol in the unloaded muscle penetrates into a space from which Na+ is excluded.
7. The total water content of the muscle per unit weight is unchanged by incubation, indicating that the apparent change in sorbitol space is in the ratio of intracellular space to extracellular space rather than by addition of water to the extracellular space.
The significance of these results is discussed with reference to the use of such preparations for in vitro studies.
Full text
PDF



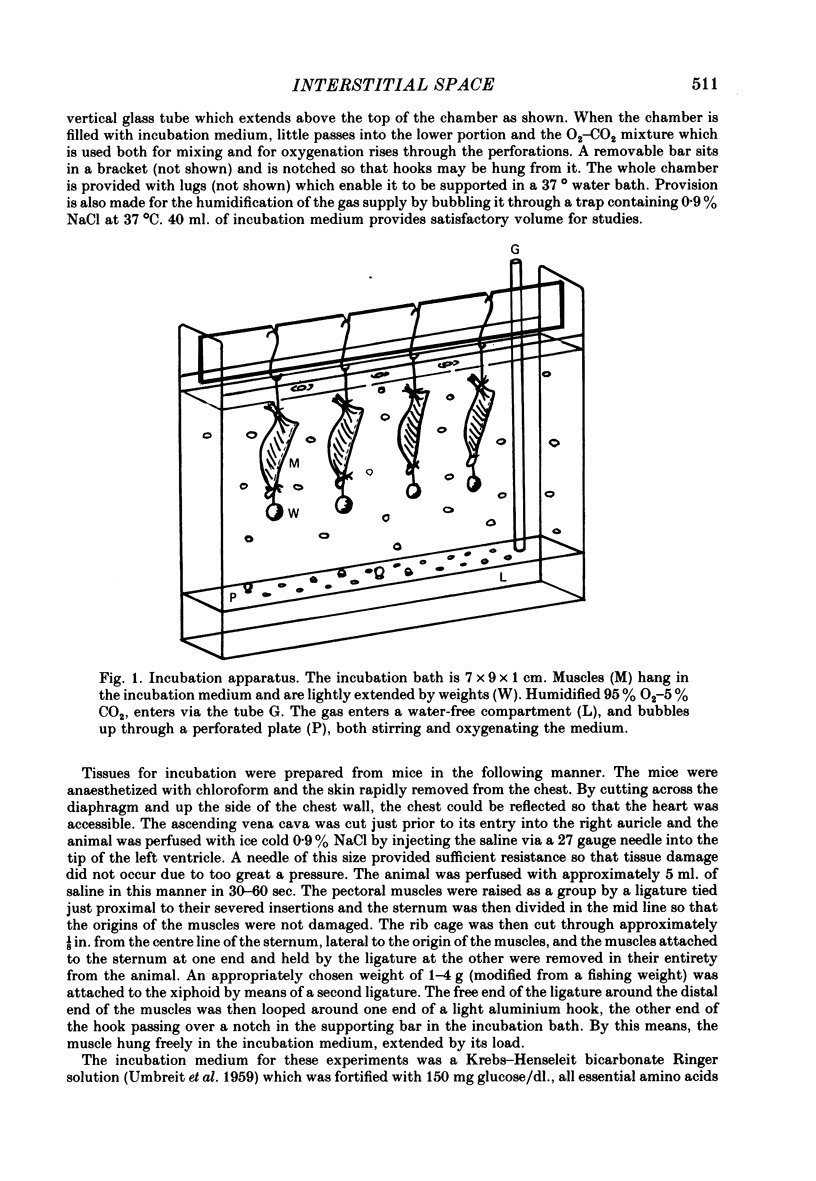






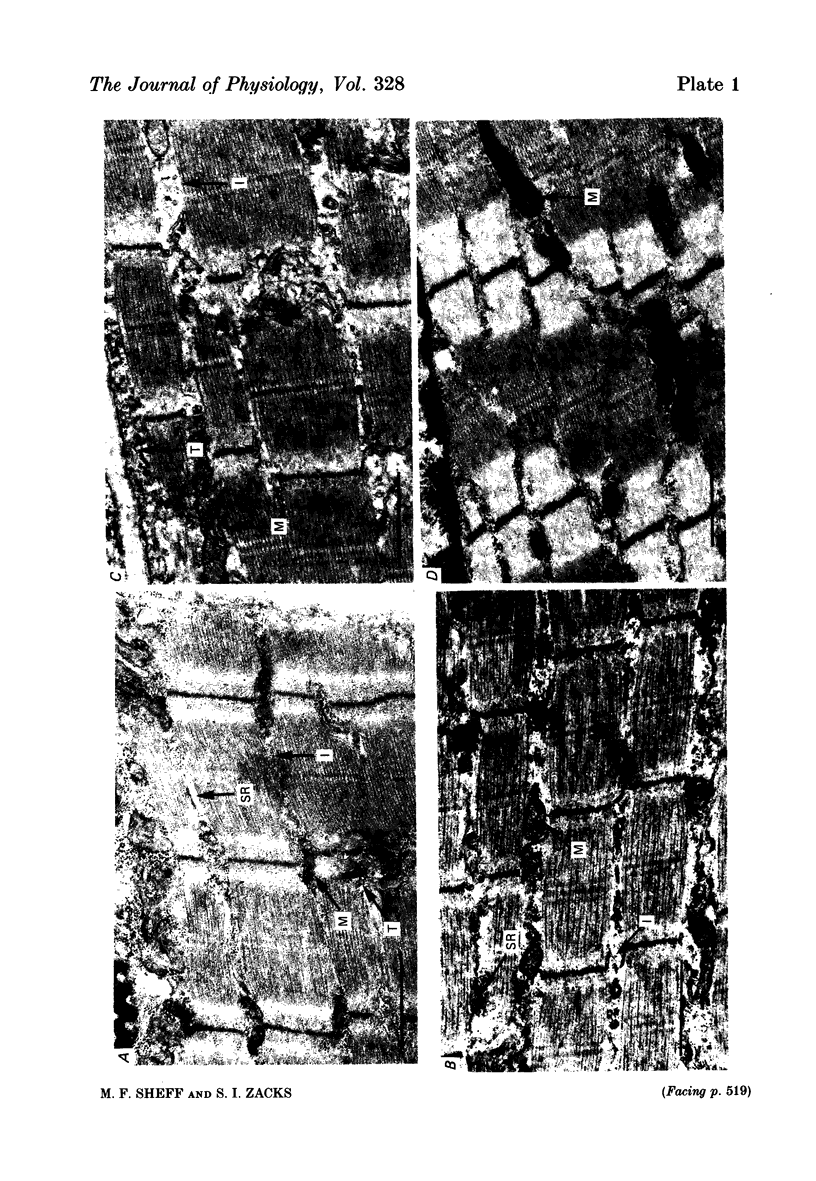

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aukland K., Nicolaysen G. Interstitial fluid volume: local regulatory mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jul;61(3):556–643. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.3.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I., Davey D. F. Osmotic responses demonstrating the extracellular character of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):171–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J., Kane F., O'reilly H. L. Volume of interfibre spaces in frog muscle and the calculation of concentrations in the fibre water. J Physiol. 1941 Jun 30;99(4):401–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F., Jones A. W. Distribution and kinetics of CoEDTA in smooth muscle, and its use as an extracellular marker. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):387–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns K. F., De Lannoy C. W., Jr Compendium of normal blood values of laboratory animals with indication of variations. I. Random-sexed populations of small animals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1966 May;8(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(66)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J. Distribution and movement of muscle chloride. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:87–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Fern E. B., London D. R. Identification in skeletal muscle of a distinct extracellular pool of amino acids, and its role in protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):817–827. doi: 10.1042/bj1210817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchia D. D., Page E., Polimeni P. I. Interstitial anion distribution in striated muscle determined with [35S]sulfate and [3H]sucrose. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):C125–C130. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.3.C125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. C., Mathias R. T. The extracellular compartments of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:45–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. C., White S. Extracellular space of frog skeletal muscle in vivo and in vitro: relation to proton magnetic resonance relaxation times. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:71–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole-Wilson P. A., Cameron I. R. ECS, intracellular pH, and electrolytes of cardiac and skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1299–1304. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogus E., Zierler K. L. Sodium and water contents of sarcoplasm and sarcoplasmic reticulum in rat skeletal muscle: effects of anisotonic media, ouabain and external sodium. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):227–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS J. M. Mitochondrial changes induced by potassium and sodium in the duodenal absorptive cell as studied with the electron microscope. J Exp Med. 1955 Dec 1;102(6):783–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.6.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]