Abstract
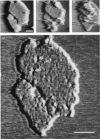
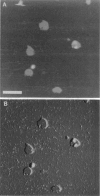
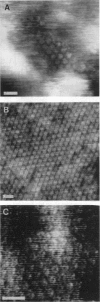
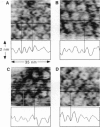
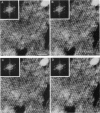
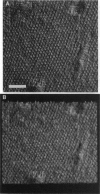
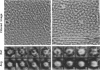
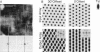
The extracellular surface of the gap junction cell-to-cell channels was imaged in phosphate-buffered saline with an atomic force microscope. The fully hydrated isolated gap junction membranes adsorbed to mica were irregular sheets approximately 1-2 microns across and 13.2 (+/- 1.3) nm thick. The top bilayer of the gap junction was dissected by increasing the force applied to the tip or sometimes by increasing the scan rate at moderate forces. The exposed extracellular surface revealed a hexagonal array with a center-to-center spacing of 9.4 (+/- 0.9) nm between individual channels (connexons). Images of individual connexons with a lateral resolution of < 3.5 nm, and in the best case approximately 2.5 nm, were reliably and reproducibly obtained with high-quality tips. These membrane channels protruded 1.4 (+/- 0.4) nm from the extracellular surface of the lipid membrane, and the atomic force microscope tip reached up to 0.7 nm into the pore, which opened up to a diameter of 3.8 (+/- 0.6) nm on the extracellular side.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. S., Caspar D. L., Hollingshead C. J., Goodenough D. A. Gap junction structures. IV. Asymmetric features revealed by low-irradiation microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):204–216. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. S., Sosinsky G. E., Caspar D. L., Gall C., Goodenough D. A. Gap junction structures. VII. Analysis of connexon images obtained with cationic and anionic negative stains. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90045-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti E. L., Emmelot P. Hexagonal array of subunits in tight junctions separated from isolated rat liver plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):15–24. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Barrio L. C., Bargiello T. A., Spray D. C., Hertzberg E., Sáez J. C. Gap junctions: new tools, new answers, new questions. Neuron. 1991 Mar;6(3):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90241-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Goodenough D. A. Gap junctions, electrotonic coupling, and intercellular communication. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1978 Sep;16(3):1–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Steinberg T. H. Evidence that the gap junction protein connexin-43 is the ATP-induced pore of mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):7971–7974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Downing K. H., Hansma P. K. Imaging the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82492-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspar D. L., Goodenough D. A., Makowski L., Phillips W. C. Gap junction structures. I. Correlated electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):605–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Amos L. A. Harmonic analysis of electron microscope images with rotational symmetry. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVries S. H., Schwartz E. A. Hemi-gap-junction channels in solitary horizontal cells of the catfish retina. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:201–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermietzel R., Hwang T. K., Spray D. S. The gap junction family: structure, function and chemistry. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1990;182(6):517–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00186458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaud G., Furcinitti P. S., Fleming J. C., Lyon M. K., Douglas K. Direct observation of defect structure in protein crystals by atomic force and transmission electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Sep;63(3):630–638. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81651-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. Biological applications of scanning probe microscopes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M., Yancey S. B., Johnson R., Revel J. P. Independent lines of evidence suggesting a major gap junctional protein with a molecular weight of 26,000. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):970–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogol E., Unwin N. Organization of connexons in isolated rat liver gap junctions. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82935-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough D. A., Gilula N. B. The splitting of hepatocyte gap junctions and zonulae occludentes with hypertonic disaccharides. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):575–590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough D. A., Stoeckenius W. The isolation of mouse hepatocyte gap junctions. Preliminary chemical characterization and x-ray diffraction. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):646–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Vesenka J., Siegerist C., Kelderman G., Morrett H., Sinsheimer R. L., Elings V., Bustamante C., Hansma P. K. Reproducible imaging and dissection of plasmid DNA under liquid with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1180–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma P. K., Elings V. B., Marti O., Bracker C. E. Scanning tunneling microscopy and atomic force microscopy: application to biology and technology. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):209–216. doi: 10.1126/science.3051380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Eibl H., Weber K. Structure and biochemistry of mouse hepatic gap junctions. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 5;132(2):193–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. Imaging and nanodissection of individual supercoiled plasmids by atomic force microscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):445–447. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Heuser J. The inside and outside of gap-junction membranes visualized by deep etching. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Hansma P. K. Atomic force microscopy for high-resolution imaging in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90248-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Lal R., John S. A., Revel J. P., Arnsdorf M. F. Atomic force microscopy and dissection of gap junctions. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1405–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.1910206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. A., Revel J. P. Connexon integrity is maintained by non-covalent bonds: intramolecular disulfide bonds link the extracellular domains in rat connexin-43. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1312–1318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91037-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makowski L., Caspar D. L., Phillips W. C., Goodenough D. A. Gap junction structures. II. Analysis of the x-ray diffraction data. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):629–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malewicz B., Kumar V. V., Johnson R. G., Baumann W. J. Lipids in gap junction assembly and function. Lipids. 1990 Aug;25(8):419–427. doi: 10.1007/BF02538083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjunath C. K., Goings G. E., Page E. Detergent sensitivity and splitting of isolated liver gap junctions. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(2):147–155. doi: 10.1007/BF01869201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Laird D. W., Revel J. P., Johnson R. G. Inhibition of gap junction and adherens junction assembly by connexin and A-CAM antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B. J., Revel J. P. Gap junctions in liver: isolation, morphological analysis, and quantitation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:519–537. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L., Ebihara L., Takemoto L. J., Swenson K. I., Goodenough D. A. Connexin46, a novel lens gap junction protein, induces voltage-gated currents in nonjunctional plasma membrane of Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1077–1089. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman S., Evans W. H. Topography of connexin32 in rat liver gap junctions. Evidence for an intramolecular disulphide linkage connecting the two extracellular peptide loops. J Cell Sci. 1991 Nov;100(Pt 3):567–578. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel J. P., Hoh J. H., John S. A., Laird D. W., Puranam K., Yancey S. B. Aspects of gap junction structure and assembly. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;3(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel J. P., Karnovsky M. J. Hexagonal array of subunits in intercellular junctions of the mouse heart and liver. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):C7–C12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.c7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. O., Baumeister W. The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein. J Microsc. 1982 Aug;127(Pt 2):127–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikerwar S. S., Unwin N. Three-dimensional structure of gap junctions in fragmented plasma membranes from rat liver. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82936-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosinsky G. E., Baker T. S., Caspar D. L., Goodenough D. A. Correlation analysis of gap junction lattice images. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82462-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosinsky G. E. Image analysis of gap junction structures. Electron Microsc Rev. 1992;5(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(92)90005-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosinsky G. E., Jésior J. C., Caspar D. L., Goodenough D. A. Gap junction structures. VIII. Membrane cross-sections. Biophys J. 1988 May;53(5):709–722. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83152-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unser M., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. A new resolution criterion based on spectral signal-to-noise ratios. Ultramicroscopy. 1987;23(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(87)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Ennis P. D. Two configurations of a channel-forming membrane protein. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):609–613. doi: 10.1038/307609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Zampighi G. Structure of the junction between communicating cells. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):545–549. doi: 10.1038/283545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenka J., Guthold M., Tang C. L., Keller D., Delaine E., Bustamante C. Substrate preparation for reliable imaging of DNA molecules with the scanning force microscope. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1243–1249. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90430-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenhorn AL, Maivald P, Butt H, Hansma PK. Measuring adhesion, attraction, and repulsion between surfaces in liquids with an atomic-force microscope. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1992 May 15;45(19):11226–11232. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.45.11226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]