Abstract
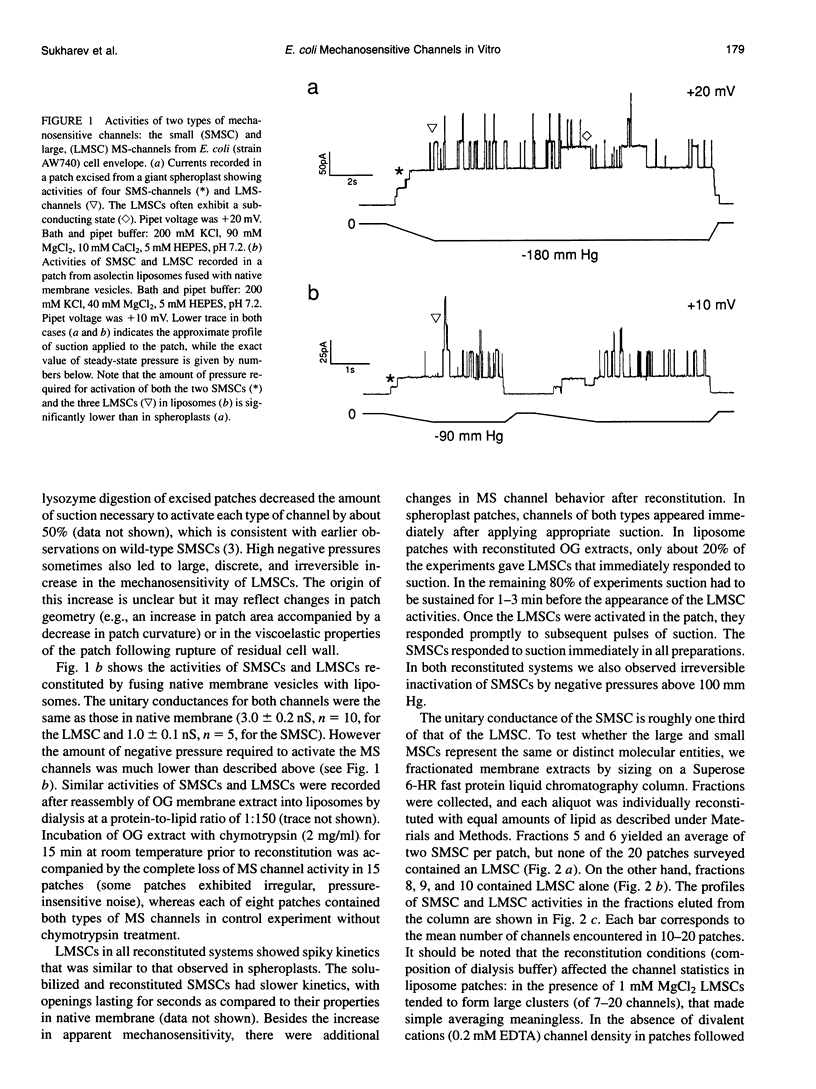
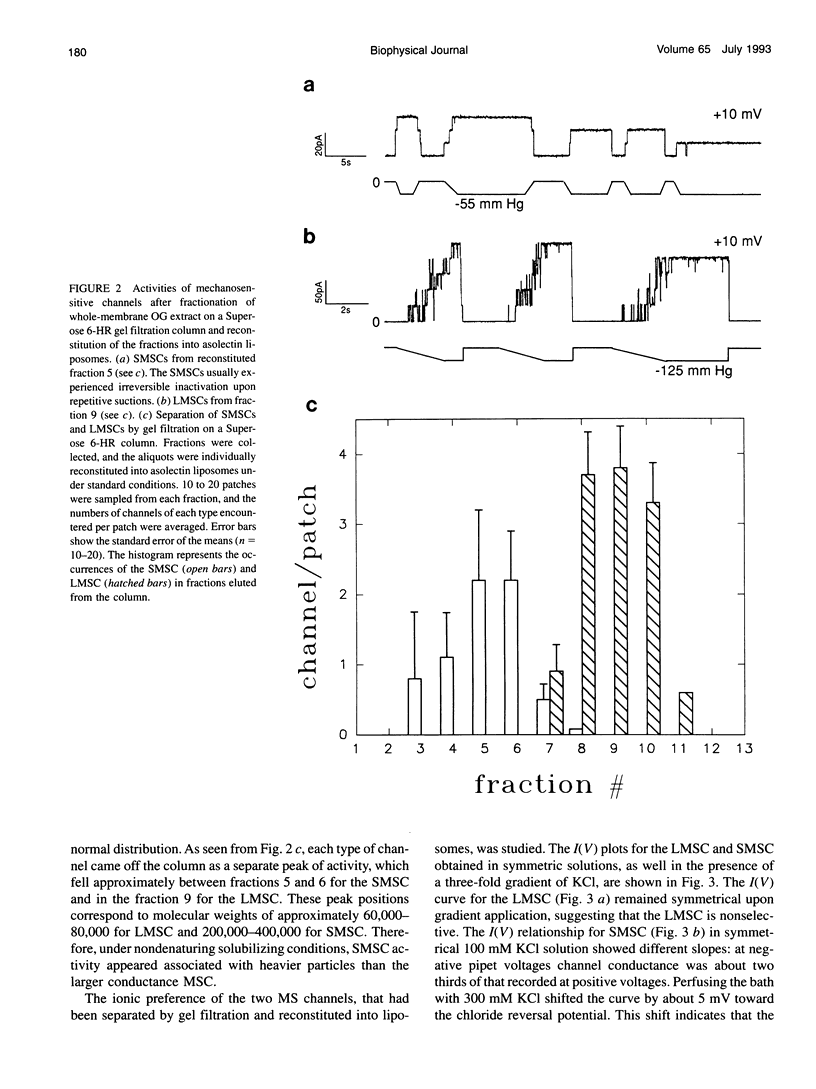
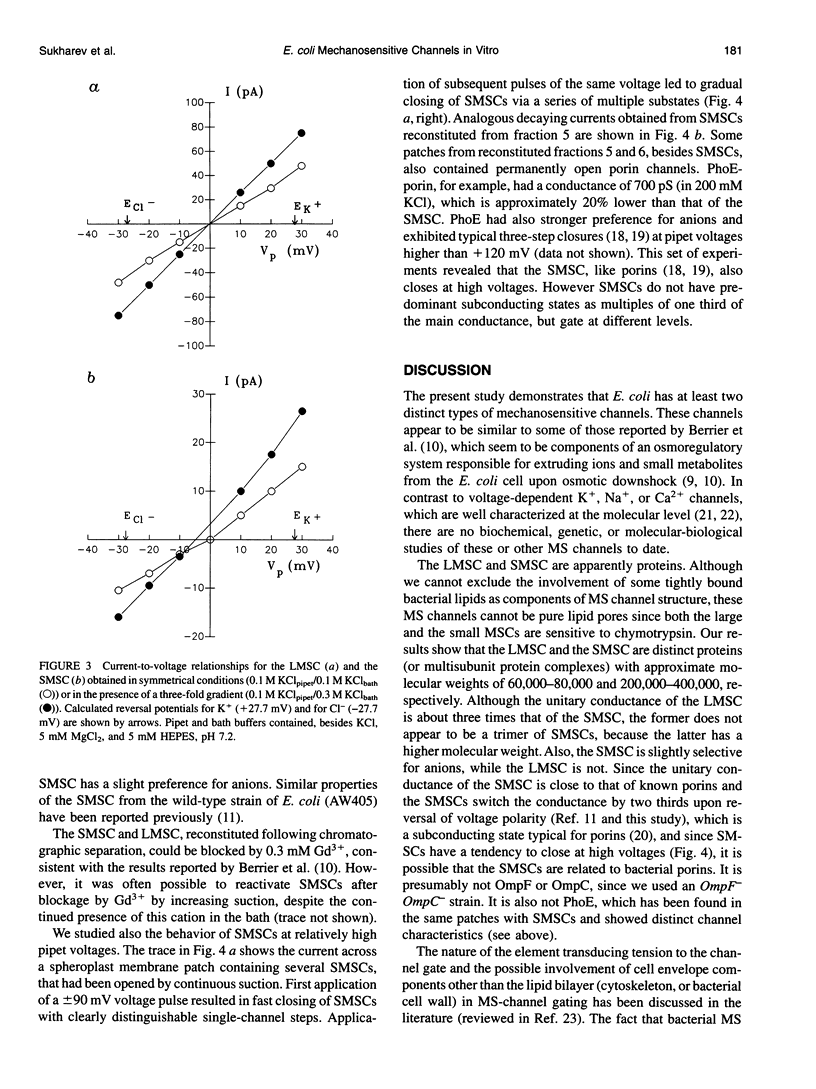
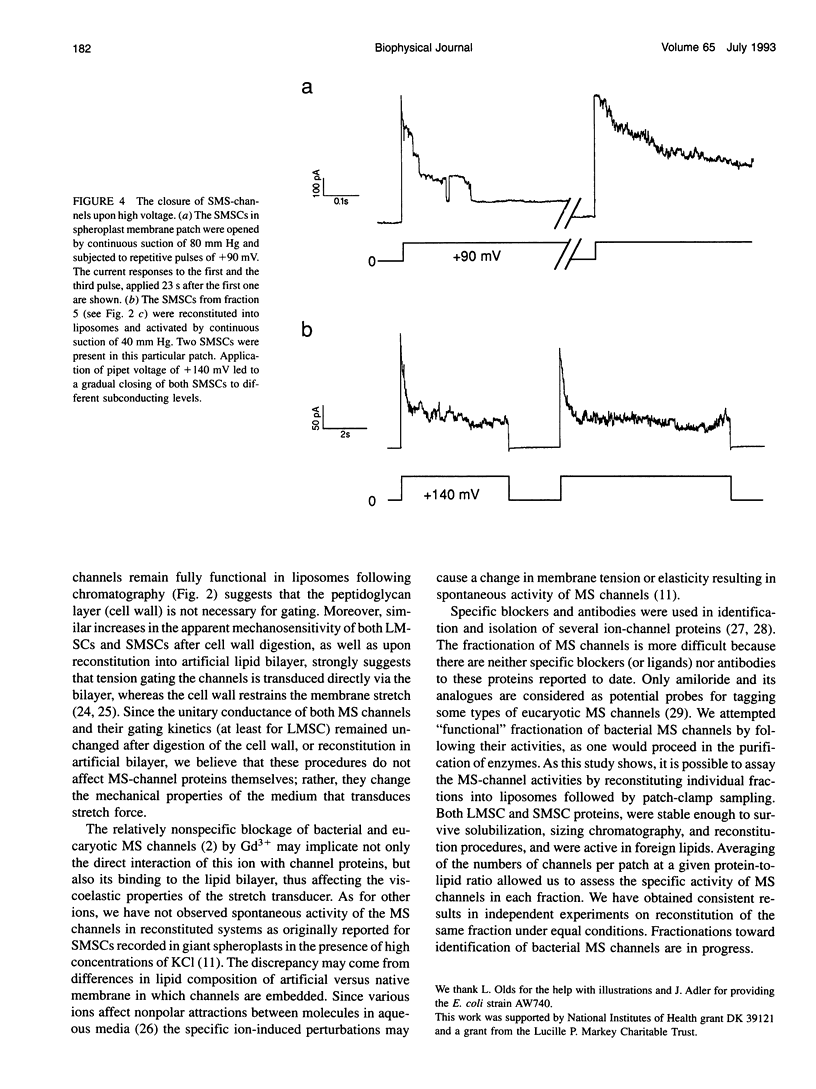
Mechanosensitive ion channels (MSCs) which could provide for fast osmoregulatory responses in bacteria, remain unidentified as molecular entities. MSCs from Escherichia coli (strain AW740) were examined using the patch-clamp technique, either (a) in giant spheroplasts, (b) after reconstitution by fusing native membrane vesicles with asolectin liposomes, or (c) by reassembly of octylglucoside-solubilized membrane extract into asolectin liposomes. MSC activities were similar in all three preparations, consisting of a large nonselective MSC of 3-nS conductance (in 200 mM KCl) that was activated by high negative pressures, and a small weakly anion-selective MSC of 1 nS activated by lower negative pressures. Both channels appeared more sensitive to suction in liposomes than in spheroplasts. After gel filtration of the solubilized membrane extract and reconstituting the fractions, both large MSC and small MSC activities were retrieved in liposomes. The positions of the peaks of channel activity in the column eluate, assayed by patch sampling of individual fractions reconstituted in liposomes, showed an apparent molecular mass under nondenaturing conditions of about 60-80 kDa for the large and 200-400 kDa for the small MSC. We conclude that (a) the large MSC and the small MSC are distinct molecular entities, (b) the fact that both MSCs were functional in liposomes following chromatography strongly suggests that these channels are gated by tension transduced via lipid bilayer, and (c) chromatographic fractionation of detergent-solubilized membrane proteins with subsequent patch sampling of reconstituted fractions can be used to identify and isolate these MS channel proteins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrier C., Coulombe A., Houssin C., Ghazi A. A patch-clamp study of ion channels of inner and outer membranes and of contact zones of E. coli, fused into giant liposomes. Pressure-activated channels are localized in the inner membrane. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81486-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrier C., Coulombe A., Szabo I., Zoratti M., Ghazi A. Gadolinium ion inhibits loss of metabolites induced by osmotic shock and large stretch-activated channels in bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):559–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechner M., Delcour A. H., Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Ion channel activities in the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Hanson A. D. Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:569–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargent B., Hofmann W., Pattus F., Rosenbusch J. P. The selectivity filter of voltage-dependent channels formed by phosphoporin (PhoE protein) from E. coli. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):773–778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Modified reconstitution method used in patch-clamp studies of Escherichia coli ion channels. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):631–636. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82710-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erxleben C. Stretch-activated current through single ion channels in the abdominal stretch receptor organ of the crayfish. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Dec;94(6):1071–1083. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Lane J. W., McBride D. W., Jr Amiloride: a molecular probe for mechanosensitive channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90115-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. Purification of the saxitoxin receptor of the sodium channel from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J., Roberts W. M., Hudspeth A. J. Mechanoelectrical transduction by hair cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:99–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham C., Buechner M., Adler J. Effect of outer membrane permeability on chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3577–3583. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3577-3583.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K. Toward an understanding of structure and function of ion channels. FASEB J. 1989 Jun;3(8):1906–1914. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.8.2470631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markin V. S., Martinac B. Mechanosensitive ion channels as reporters of bilayer expansion. A theoretical model. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1120–1127. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82147-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinac B., Buechner M., Delcour A. H., Adler J., Kung C. Pressure-sensitive ion channel in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2297–2301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. E. Mechanosensitive ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(2):93–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01872883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruthe H. J., Adler J. Fusion of bacterial spheroplasts by electric fields. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 25;819(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F. Mechanical transduction in biological systems. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 1988;16(2):141–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein from Escherichia coli outer membranes forms voltage-controlled channels in lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3751–3755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. L., Stumpf M. A., Hoch H. C., Kung C. A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.1716786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoratti M., Petronilli V. Ion-conducting channels in a gram-positive bacterium. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 21;240(1-2):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



