Abstract
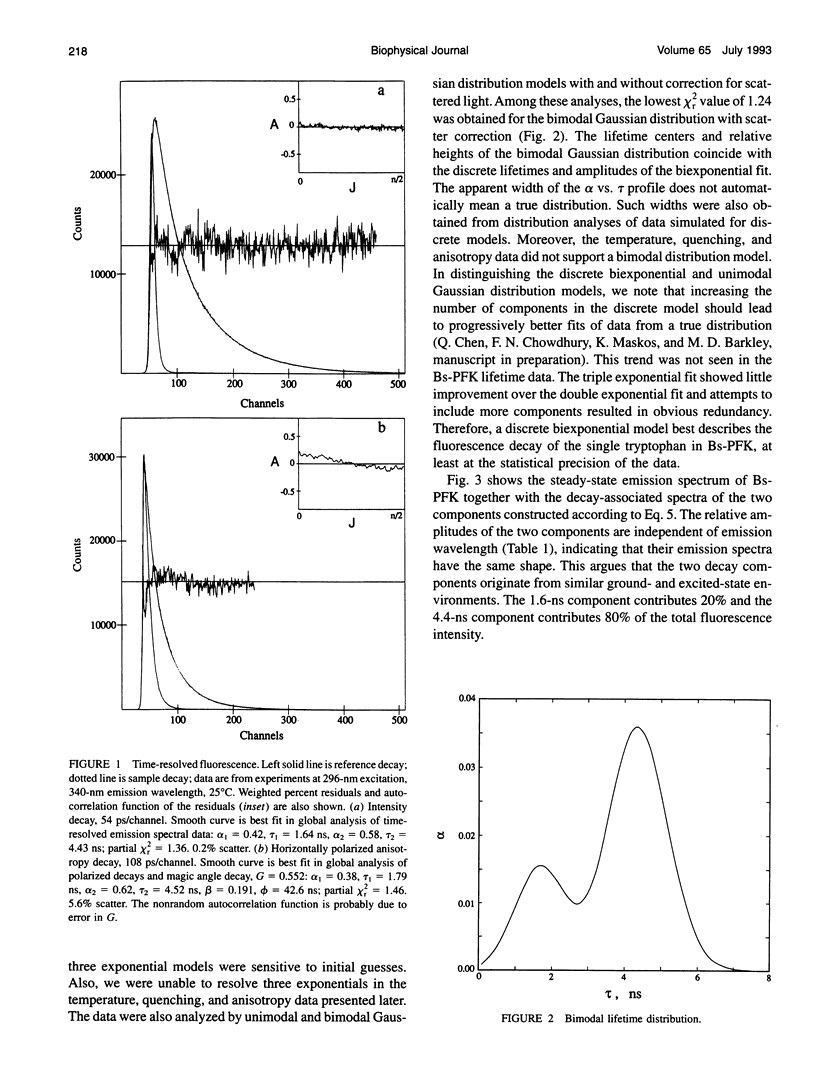
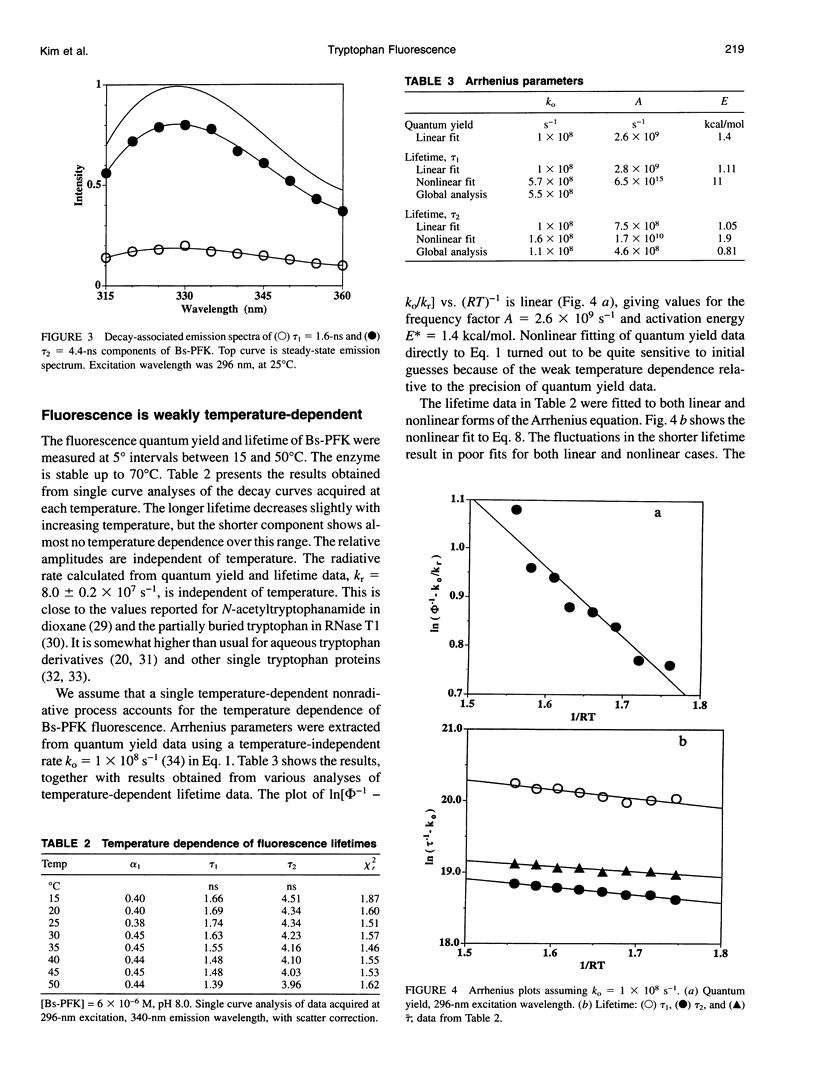
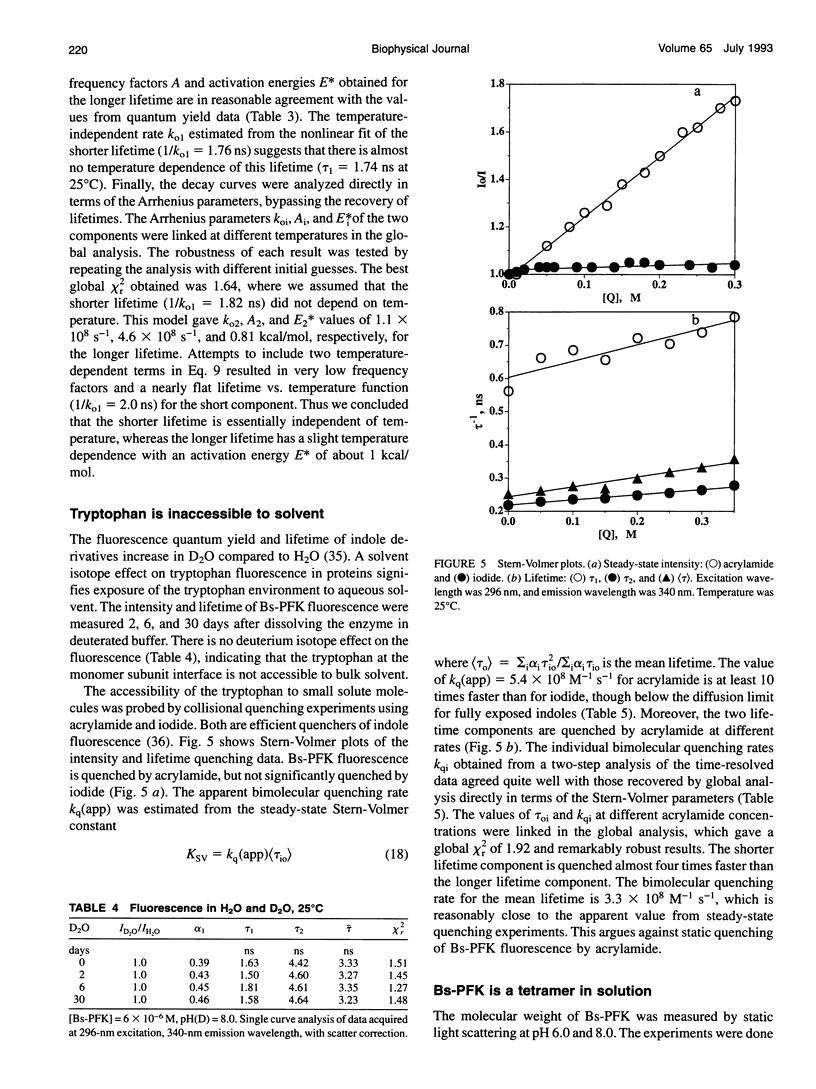
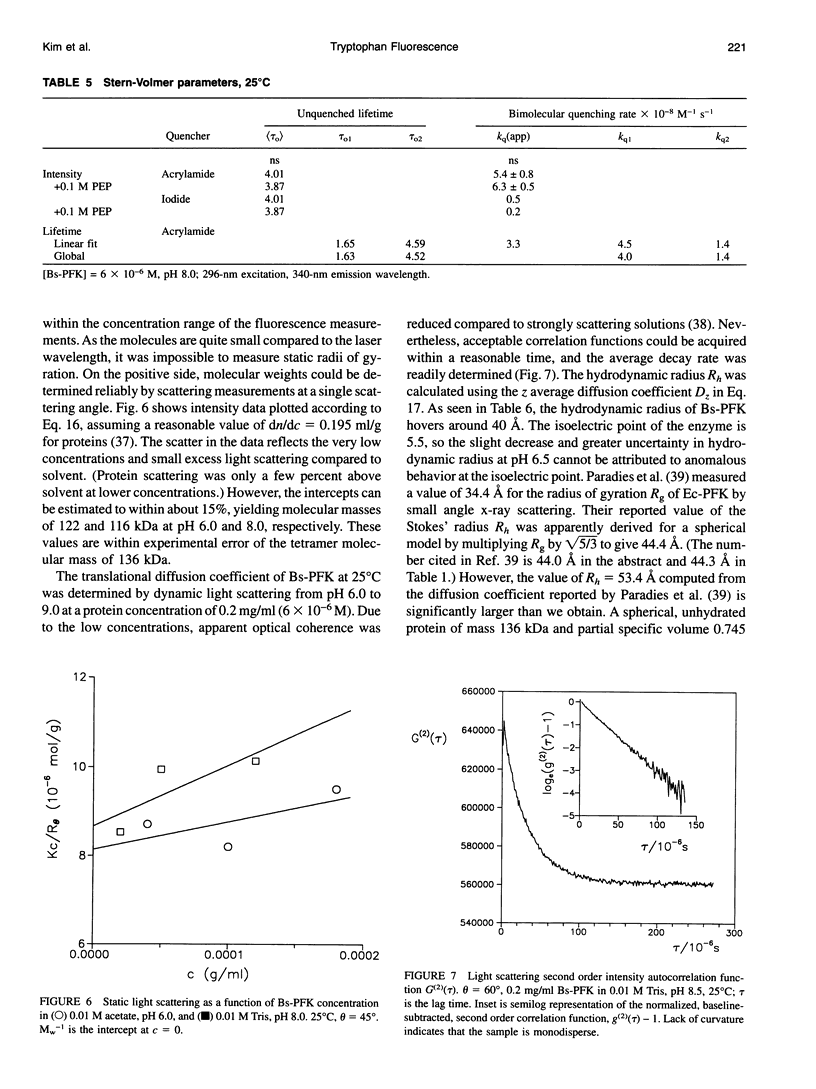
The fluorescence of the single tryptophan in Bacillus stearothermophilus phosphofructokinase was characterized by steady-state and time-resolved techniques. The enzyme is a tetramer of identical subunits, which undergo a concerted allosteric transition. Time-resolved emission spectral data were fitted to discrete and distributed lifetime models. The fluorescence decay is a double exponential with lifetimes of 1.6 and 4.4 ns and relative amplitudes of 40 and 60%. The emission spectra of both components are identical with maxima at 327 nm. The quantum yield is 0.31 +/- 0.01. The shorter lifetime is independent of temperature; the longer lifetime has weak temperature dependence with activation energy of 1 kcal/mol. The fluorescence intensity and decay are the same in H2O and D2O solutions, indicating that the indole ring is not accessible to bulk aqueous solution. The fluorescence is not quenched significantly by iodide, but it is quenched by acrylamide with bimolecular rate constant of 5 x 10(8) M-1 s-1. Static and dynamic light scattering measurements show that the enzyme is a tetramer in solution with hydrodynamic radius of 40 A. Steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence anisotropies indicate that the tryptophan is immobile. The allosteric transition has little effect on the fluorescence properties. The fluorescence results are related to the x-ray structure.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcala J. R., Gratton E., Prendergast F. G. Interpretation of fluorescence decays in proteins using continuous lifetime distributions. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):925–936. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83420-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins W. M., Stayton P. S., Villafranca J. J. Time-resolved fluorescence studies of genetically engineered Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Effects of ATP on the tryptophan-57 loop. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3406–3416. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechem J. M. A second generation global analysis program for the recovery of complex inhomogeneous fluorescence decay kinetics. Chem Phys Lipids. 1989 Jun;50(3-4):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(89)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boens N., Janssens L. D., De Schryver F. C. Simultaneous analysis of single-photon timing data for the one-step determination of activation energies, frequency factors and quenching rate constants. Application to tryptophan photophysics. Biophys Chem. 1989 Mar;33(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(89)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. B., Englander S. W., Wright W. W., Vanderkooi J. M. Quenching of room temperature protein phosphorescence by added small molecules. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8466–8474. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. X., Longworth J. W., Fleming G. R. Picosecond time-resolved fluorescence of ribonuclease T1. A pH and substrate analogue binding study. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):865–873. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83414-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowgill R. W. Fluorescence and protein structure. XVII. On the mechanism of peptide quenching. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 20;200(1):18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Ghiron C. A. Fluorescence quenching studies with proteins. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 1;114(2):199–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90474-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. R., Hudson P. J. Structure and control of phosphofructokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):500–504. doi: 10.1038/279500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French B. A., Chang S. H. Nucleotide sequence of the phosphofructokinase gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus and comparison with the homologous Escherichia coli gene. Gene. 1987;54(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French B. A., Valdez B. C., Younathan E. S., Chang S. H. High-level expression of Bacillus stearothermophilus 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhammer A. R., Paradies H. H. Phosphofructokinase: structure and function. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:109–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. E., Longworth J. W., Fleming G. R. Photophysics of metalloazurins. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7329–7338. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Hudson B. S. Photophysics of tryptophan in bacteriophage T4 lysozymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5276–5285. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellinga H. W., Evans P. R. Nucleotide sequence and high-level expression of the major Escherichia coli phosphofructokinase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):363–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutnik C. M., MacManus J. P., Szabo A. G. A calcium-specific conformational response of parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7318–7328. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. R., Demmer D. R., Steer R. P., Verrall R. E. Fluorescence lifetime quenching and anisotropy studies of ribonuclease T1. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5517–5526. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb E., Hudson P. J., Harris J. I. Phosphofructokinase: complete amino-acid sequence of the enzyme from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):587–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolber Z. S., Barkley M. D. Comparison of approaches to the instrumental response function in fluorescence decay measurements. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jan;152(1):6–21. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlarz D., Buc H. Phosphofructokinases from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):60–70. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundrot C. E., Evans P. R. Designing an allosterically locked phosphofructokinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1478–1484. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Cherek H. Dipolar relaxation in proteins on the nanosecond timescale observed by wavelength-resolved phase fluorometry of tryptophan fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Maliwal B. P., Cherek H., Balter A. Rotational freedom of tryptophan residues in proteins and peptides. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1741–1752. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luther M. A., Cai G. Z., Lee J. C. Thermodynamics of dimer and tetramer formations in rabbit muscle phosphofructokinase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7931–7937. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradies H. H., Vettermann W., Werz G. Shape of phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli in solution. Protoplasma. 1977;92(1-2):43–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01280199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrich J. W., Longworth J. W., Fleming G. R. Internal motion and electron transfer in proteins: a picosecond fluorescence study of three homologous azurins. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2711–2722. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privat J. P., Wahl P., Auchet J. C. Rates of deactivation processes of indole derivatives in water-organic solvent mixtures--application to tryptophyl fluorescence of proteins. Biophys Chem. 1979 Mar;9(3):223–233. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(79)85005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci R. W. Deuterium-isotope effect on the fluorescence yields and lifetimes of indole derivatives--including tryptophan and tryptamine. Photochem Photobiol. 1970 Jul;12(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1970.tb06039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer C. A., Gardner J. A., Beechem J. M., Brochon J. C., Matthews K. S. Resolution of the fluorescence decay of the two tryptophan residues of lac repressor using single tryptophan mutants. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):363–378. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82383-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rypniewski W. R., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of unliganded phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):805–821. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer T., Evans P. R. Structural basis of the allosteric behaviour of phosphofructokinase. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):140–145. doi: 10.1038/343140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakihara Y., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the complex of phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli with its reaction products. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):973–994. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stayton P. S., Sligar S. G. Structural microheterogeneity of a tryptophan residue required for efficient biological electron transfer between putidaredoxin and cytochrome P-450cam. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1845–1851. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. F., Kirby E. P. The interaction of the ground and excited states of indole derivatives with electron scavengers. J Phys Chem. 1969 Dec;73(12):4130–4135. doi: 10.1021/j100846a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdez B. C., French B. A., Younathan E. S., Chang S. H. Site-directed mutagenesis in Bacillus stearothermophilus fructose-6-phosphate 1-kinase. Mutation at the substrate-binding site affects allosteric behavior. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeur B., Weber G. Resolution of the fluorescence excitation spectrum of indole into the 1La and 1Lb excitation bands. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 May;25(5):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb09168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Brochon J. C., Merola F., Jordi W., Gallay J. Nanosecond dynamics of horse heart apocytochrome c in aqueous solution as studied by time-resolved fluorescence of the single tryptophan residue (Trp-59). Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8752–8761. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


