Abstract
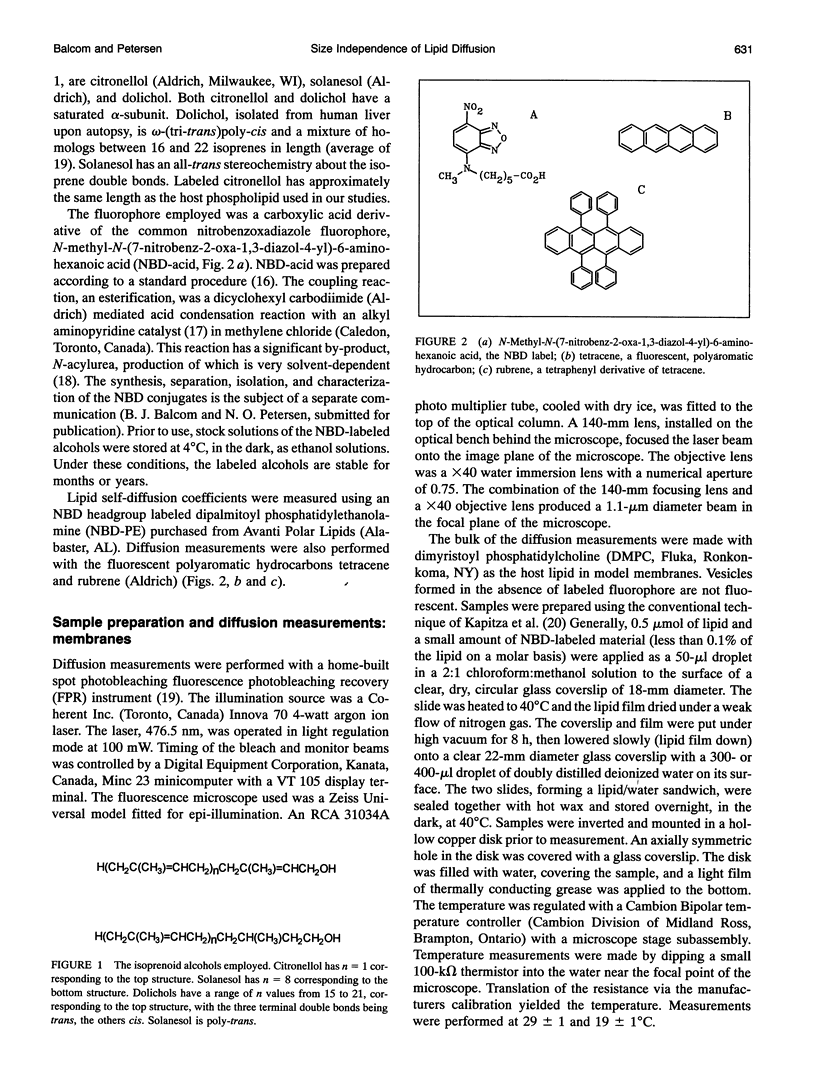
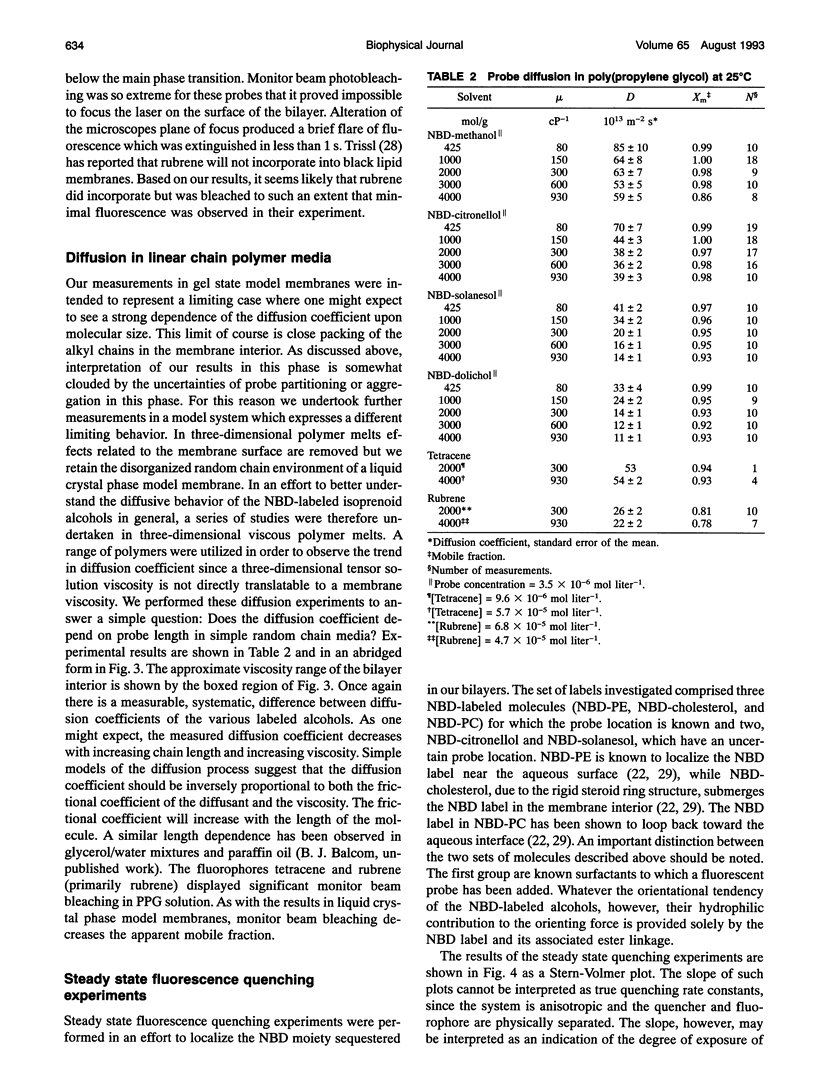
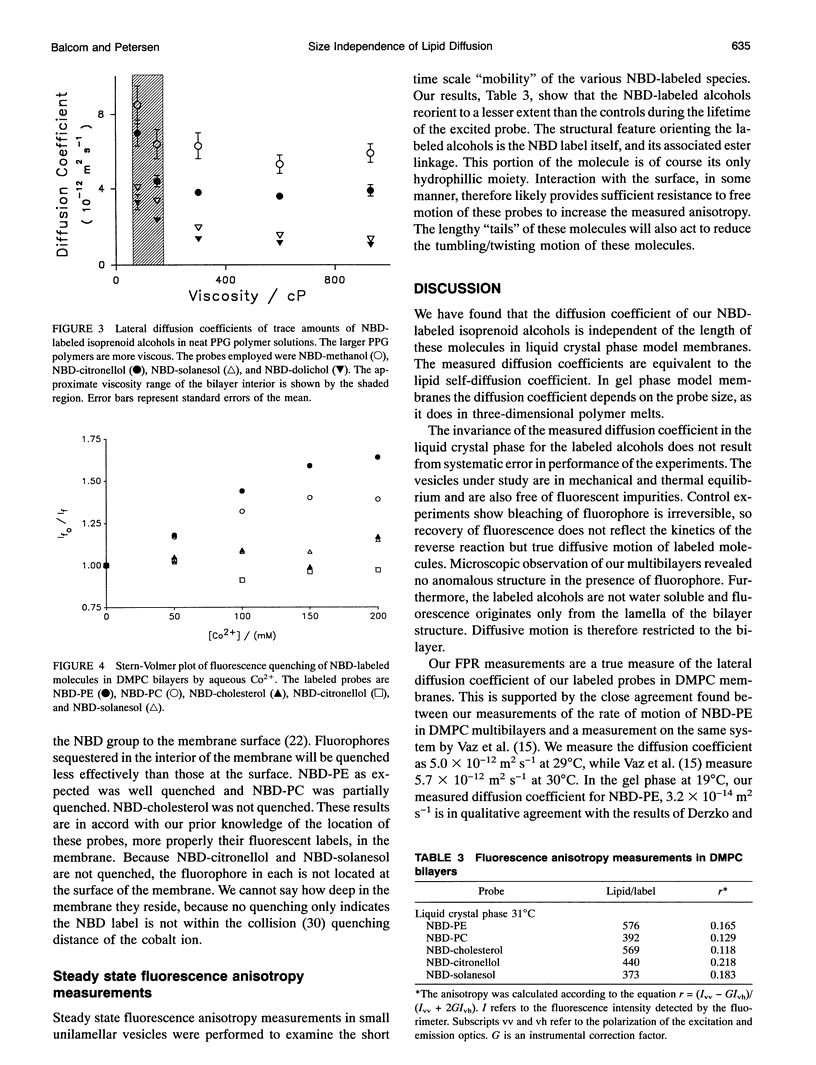
We have systematically investigated the probe size and shape dependence of lateral diffusion in model dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine membranes. Linear hydrophobic polymers, which differ in length by an order of magnitude, were used to explore the effect on the lateral diffusion coefficient of hydrodynamic restrictions in the bilayer interior. The polymers employed are isoprenoid alcohols--citronellol, solanesol, and dolichol. Tracer lateral diffusion coefficients were measured by fluorescence photobleaching recovery. Despite the large difference in lengths, the nitrobenzoxadiazole labelled alcohols all diffuse at the rate of lipid self-diffusion (5.0 x 10(-12) m2 s-1, 29 degrees C) in the liquid crystal phase. Companion measurements in isotropic polymer solution, in gel phase lipid membranes and with nonpolar fluorescent polyaromatic hydrocarbons, show a marked dependence of the lateral diffusion coefficient on the probe molecule size. Our results in the liquid crystal phase are in accord with free area theory which asserts that lateral diffusion in the membrane is restricted by the surface-free area. Probe molecules which are significantly longer than the host phospholipid, seven times longer in the case of dolichol, are still restricted in their lateral motion by the surface properties of the bilayer in the liquid crystal phase. Fluorescence quenching experiments indicate that the nitrobenzoxadiazole label does not reside at the aqueous interface, although it must reside in close proximity according to the diffusion measurements.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chattopadhyay A., London E. Parallax method for direct measurement of membrane penetration depth utilizing fluorescence quenching by spin-labeled phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):39–45. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay A., London E. Spectroscopic and ionization properties of N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)-labeled lipids in model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 8;938(1):24–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derzko Z., Jacobson K. Comparative lateral diffusion of fluorescent lipid analogues in phospholipid multibilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6050–6057. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Stryer L. Surface density determination in membranes by fluorescence energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5241–5248. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupte S., Wu E. S., Hoechli L., Hoechli M., Jacobson K., Sowers A. E., Hackenbrock C. R. Relationship between lateral diffusion, collision frequency, and electron transfer of mitochondrial inner membrane oxidation-reduction components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitza H. G., Rüppel D. A., Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Lateral diffusion of lipids and glycophorin in solid phosphatidylcholine bilayers. The role of structural defects. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):577–587. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84195-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion of phospholipids in a vesicle membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2564–2568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo A. L., Wade C. G. Lipid lateral diffusion by pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2300–2308. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. J., Bradley D., Blumenthal R. The use of cobalt ions as a collisional quencher to probe surface charge and stability of fluorescently labeled bilayer vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 10;818(3):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Theory of lipid monolayer and bilayer chain-melting phase transitions. Faraday Discuss Chem Soc. 1986;(81):151–162. doi: 10.1039/dc9868100151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M. Rapid lateral diffusion of functional A Ch receptors in embryonic muscle cell membrane. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):332–334. doi: 10.1038/295332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajarathnam K., Hochman J., Schindler M., Ferguson-Miller S. Synthesis, location, and lateral mobility of fluorescently labeled ubiquinone 10 in mitochondrial and artificial membranes. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3168–3176. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter P., Rogers M. J. Apparent dependence of interactions between cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase upon translational diffusion in dimyristoyl lecithin liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2658–2661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl H. W. Studies on the incorporation of fluorescent pigments into bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 15;367(3):326–337. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Clegg R. M., Hallmann D. Translational diffusion of lipids in liquid crystalline phase phosphatidylcholine multibilayers. A comparison of experiment with theory. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):781–786. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


