Abstract
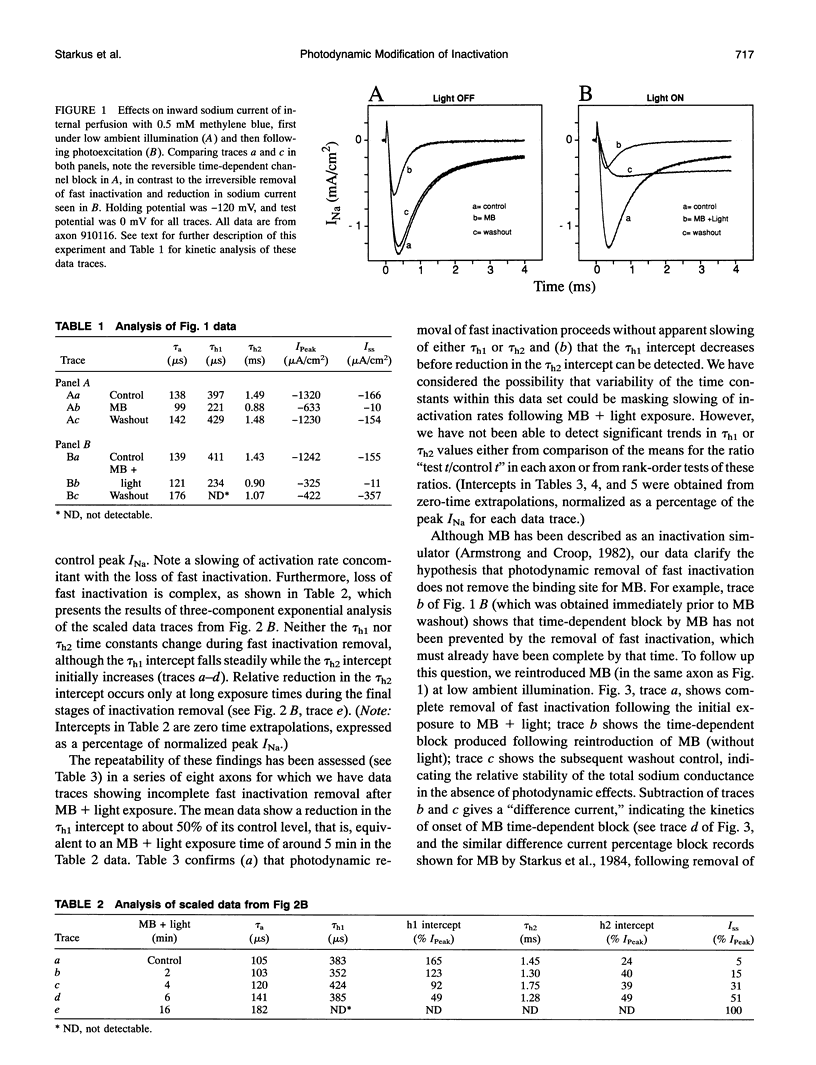
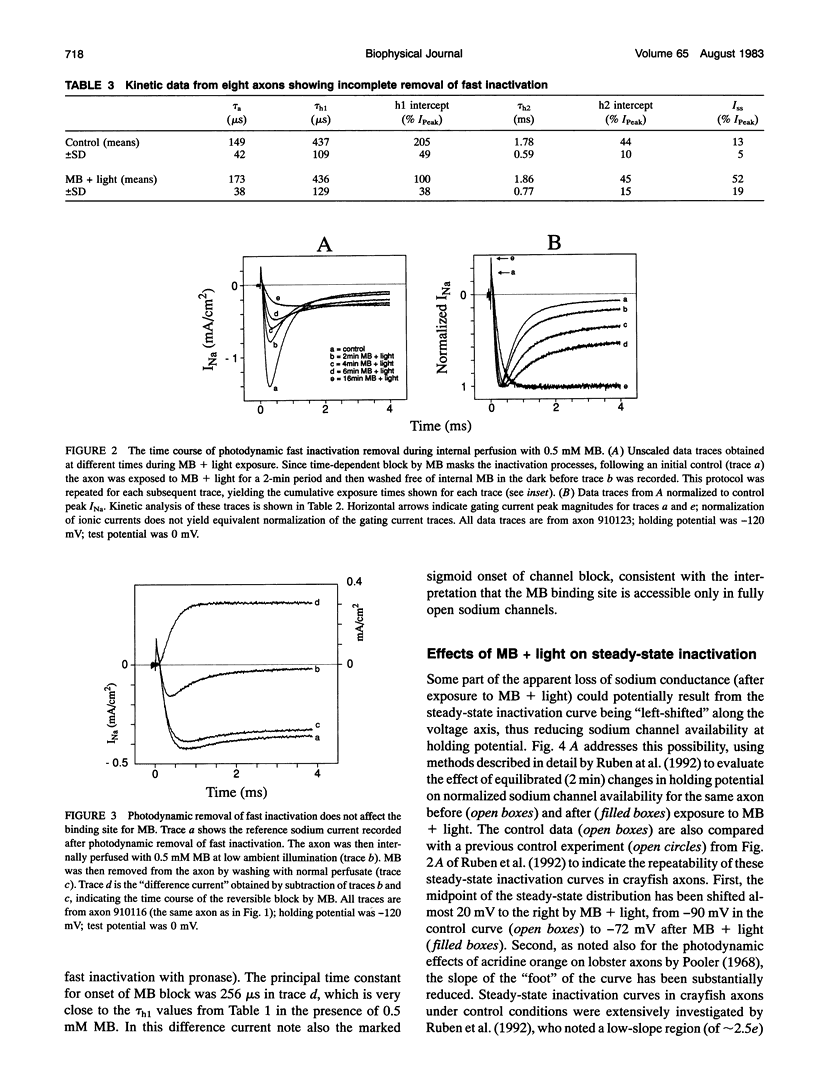
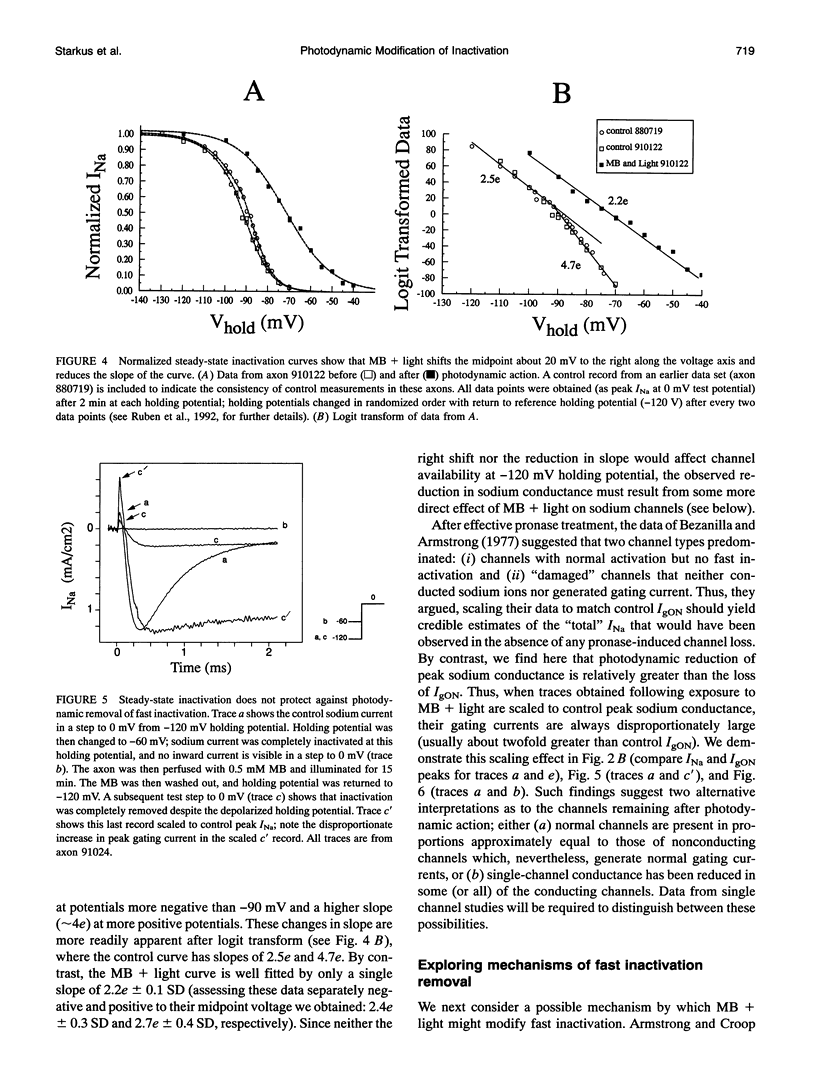
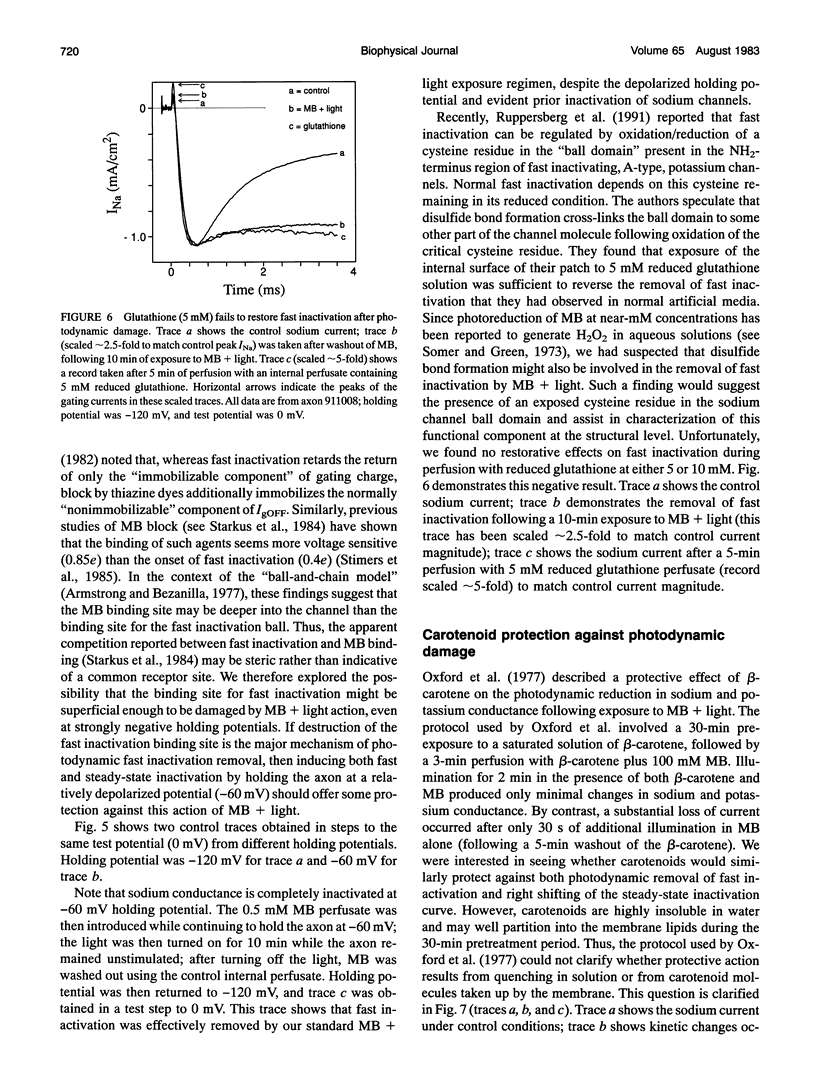
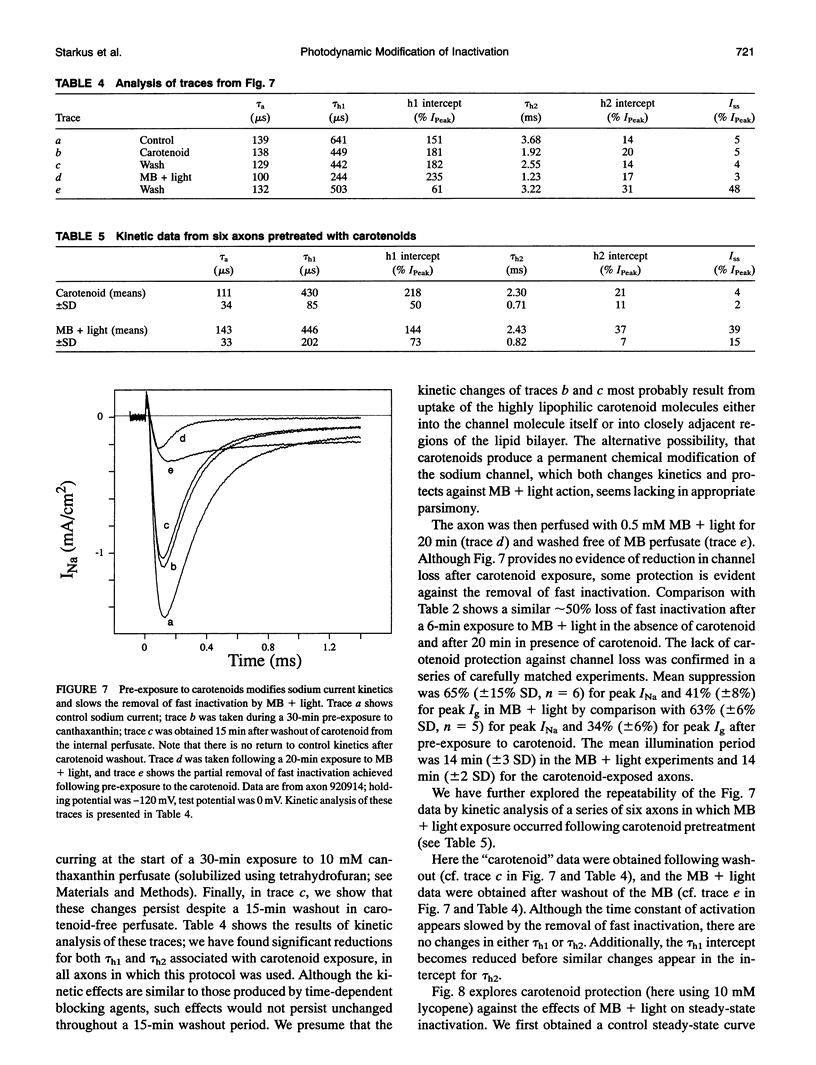
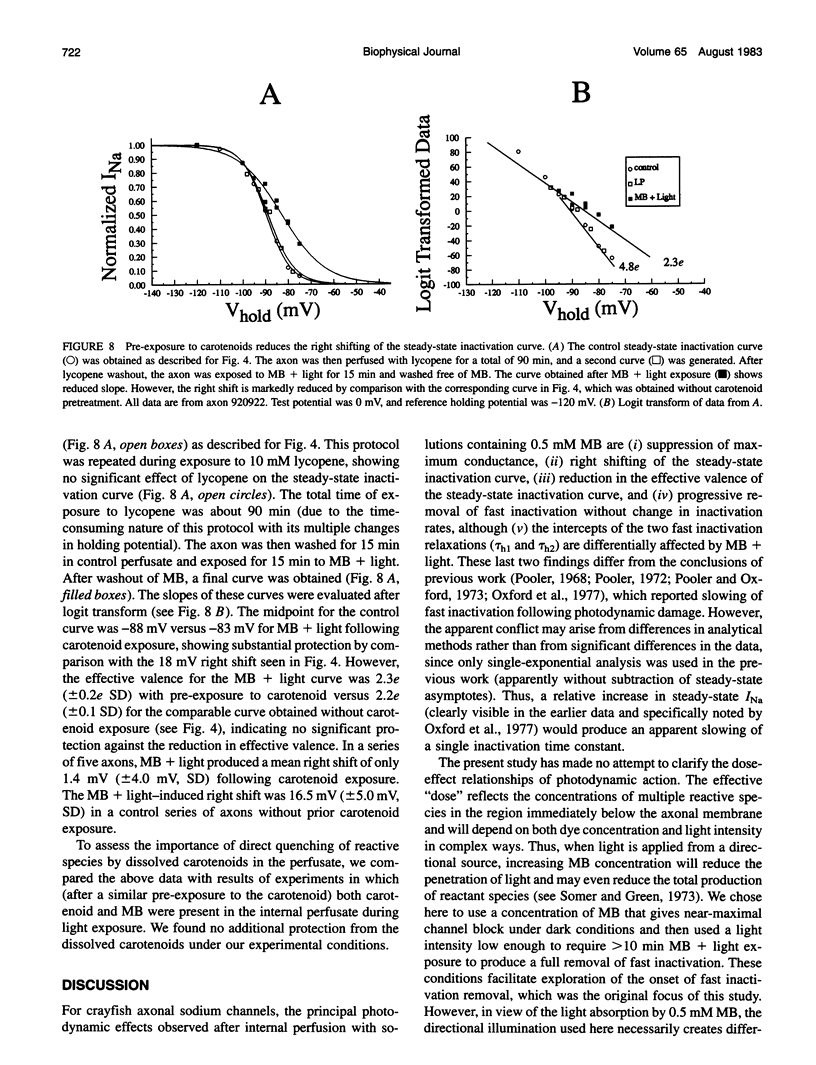
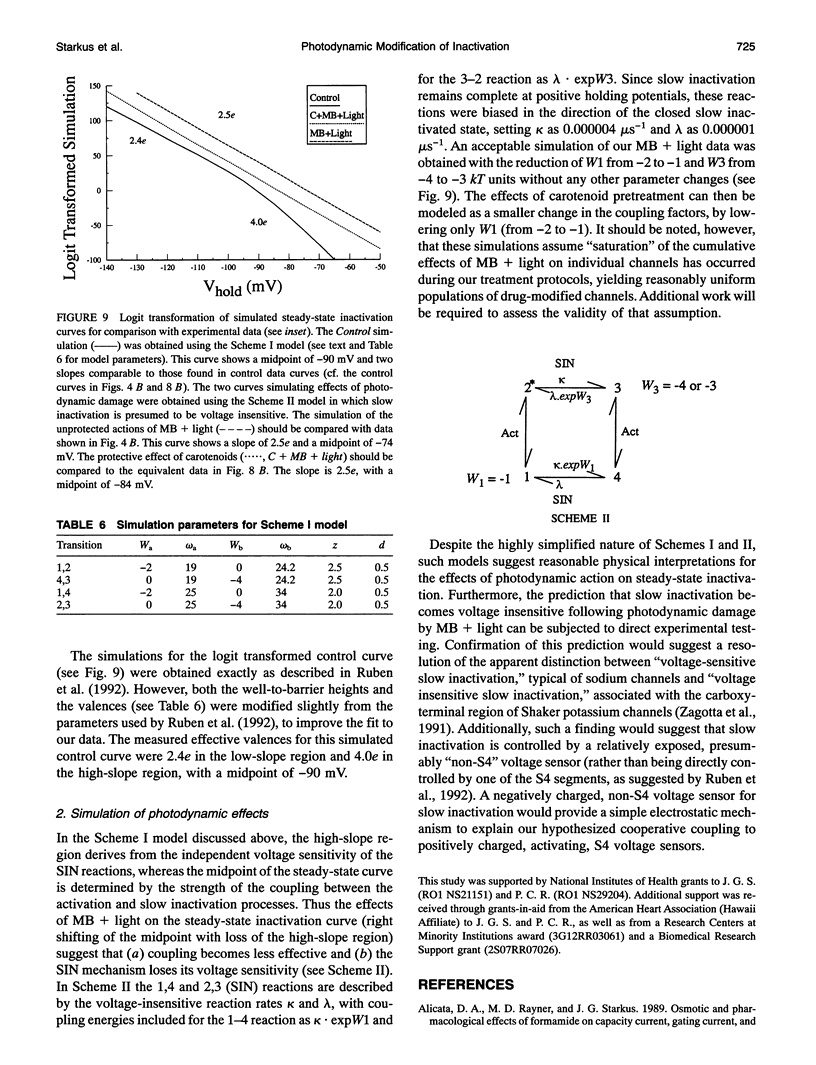
Illumination of crayfish giant axons, during internal perfusion with 0.5 mM methylene blue (MB), produces photodynamic effects that include (i) reduction in total sodium conductance, (ii) shifting of the steady-state inactivation curve to the right along the voltage axis, (iii) reduction in the effective valence of steady-state inactivation and, (iv) potentially complete removal of fast inactivation. Additionally, the two kinetic components of fast inactivation in crayfish axons are differentially affected by MB+light. The intercept of the faster component (tau h1) is selectively reduced at shorter MB+light exposure times. Neither tau h1 nor the slower (tau h2) process was protected from MB+light by prior steady-state inactivation of sodium channels. However, carotenoids provide differing degrees of protection against each of the photodynamic actions listed above, suggesting that the four major effects of MB+light are mediated by changes occurring within different regions of the sodium channel molecule.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alicata D. A., Rayner M. D., Starkus J. G. Osmotic and pharmacological effects of formamide on capacity current, gating current, and sodium current in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82811-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Croop R. S. Simulation of Na channel inactivation by thiazine dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):641–662. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E., Fernández J. M. Distribution and kinetics of membrane dielectric polarization. 1. Long-term inactivation of gating currents. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):21–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness S. T., Starkus J. G. Saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin. Electrostatic effects on sodium channel gating current in crayfish axons. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):629–643. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83690-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., VanDongen A. M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Fast and slow gating of sodium channels encoded by a single mRNA. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Pooler J. P., Narahashi T. Internal and external application of photodynamic sensitizers on squid giant axons. J Membr Biol. 1977 Sep 14;36(2-3):159–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01868149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooler J. Light-induced changes in dye-treated lobster giant axons. Biophys J. 1968 Sep;8(9):1009–1026. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86535-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooler J., Oxford G. S. Photodynamic alteration of lobster giant axons in calcium-free and calcium-rich media. J Membr Biol. 1973 Aug 3;12(4):339–348. doi: 10.1007/BF01870009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooler J. Photodynamic alteration of sodium currents in lobster axons. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Oct;60(4):367–387. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner M. D., Starkus J. G. The steady-state distribution of gating charge in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82775-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben P. C., Starkus J. G., Rayner M. D. Holding potential affects the apparent voltage-sensitivity of sodium channel activation in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1169–1181. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82458-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben P. C., Starkus J. G., Rayner M. D. Steady-state availability of sodium channels. Interactions between activation and slow inactivation. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):941–955. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81901-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Pongs O., Heinemann S. H., Frank R., Koenen M. Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):711–714. doi: 10.1038/352711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Ionic conductance changes in voltage clamped crayfish axons at low pH. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Dec;64(6):666–690. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.6.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Heggeness S. T., Rayner M. D. Kinetic analysis of sodium channel block by internal methylene blue in pronased crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):205–218. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84014-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Rayner M. D. Gating current "fractionation" in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1101–1119. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82146-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Shrager P. Modification of slow sodium inactivation in nerve after internal perfusion with trypsin. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):C238–C244. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.5.C238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimers J. R., Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E. Sodium channel activation in the squid giant axon. Steady state properties. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):65–82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


