Abstract
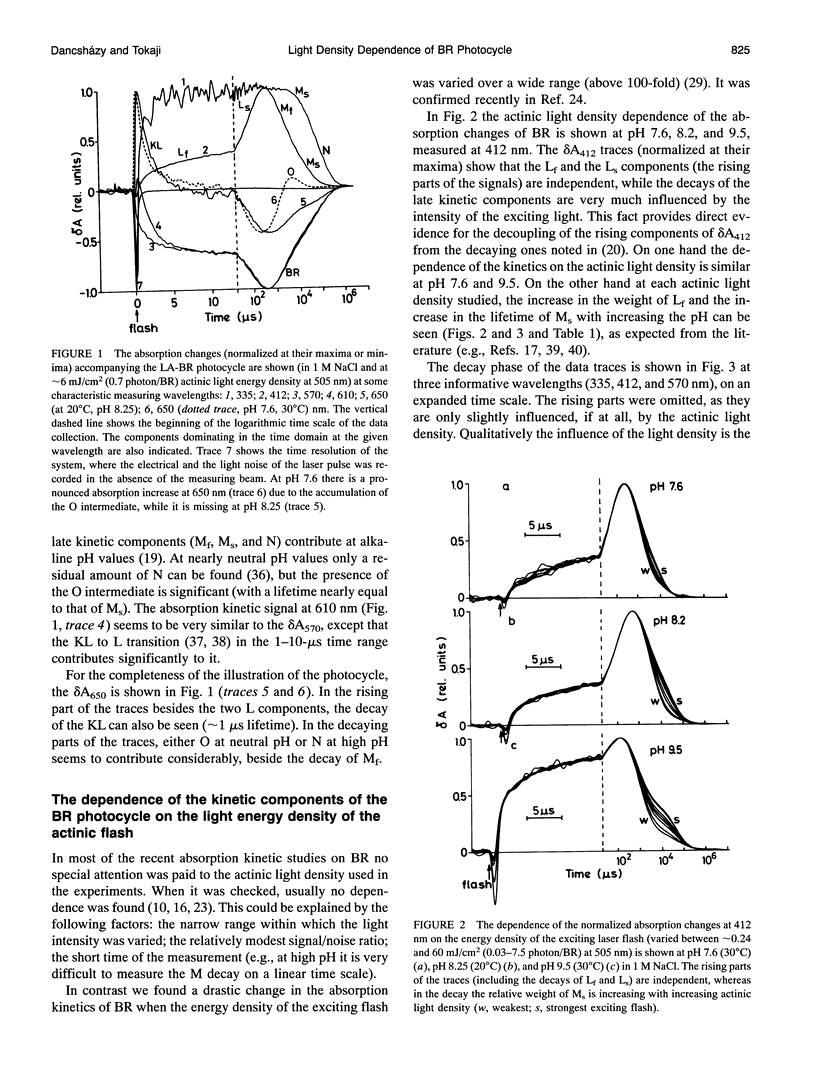
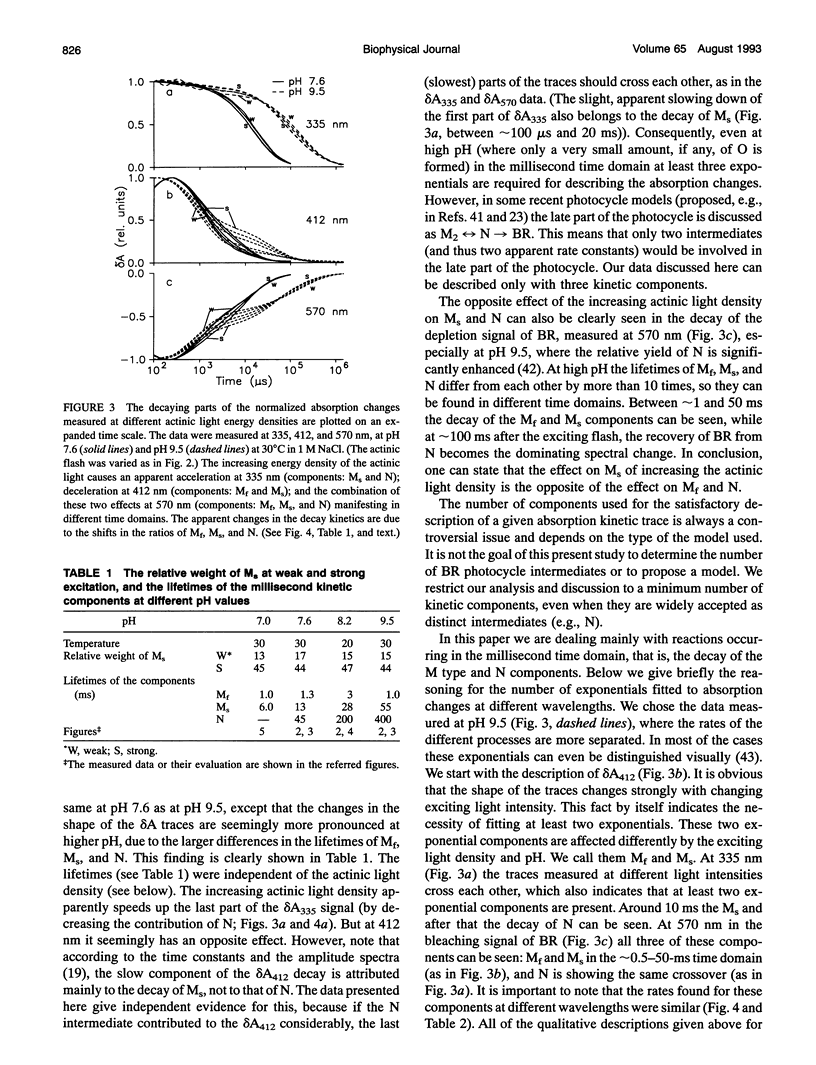
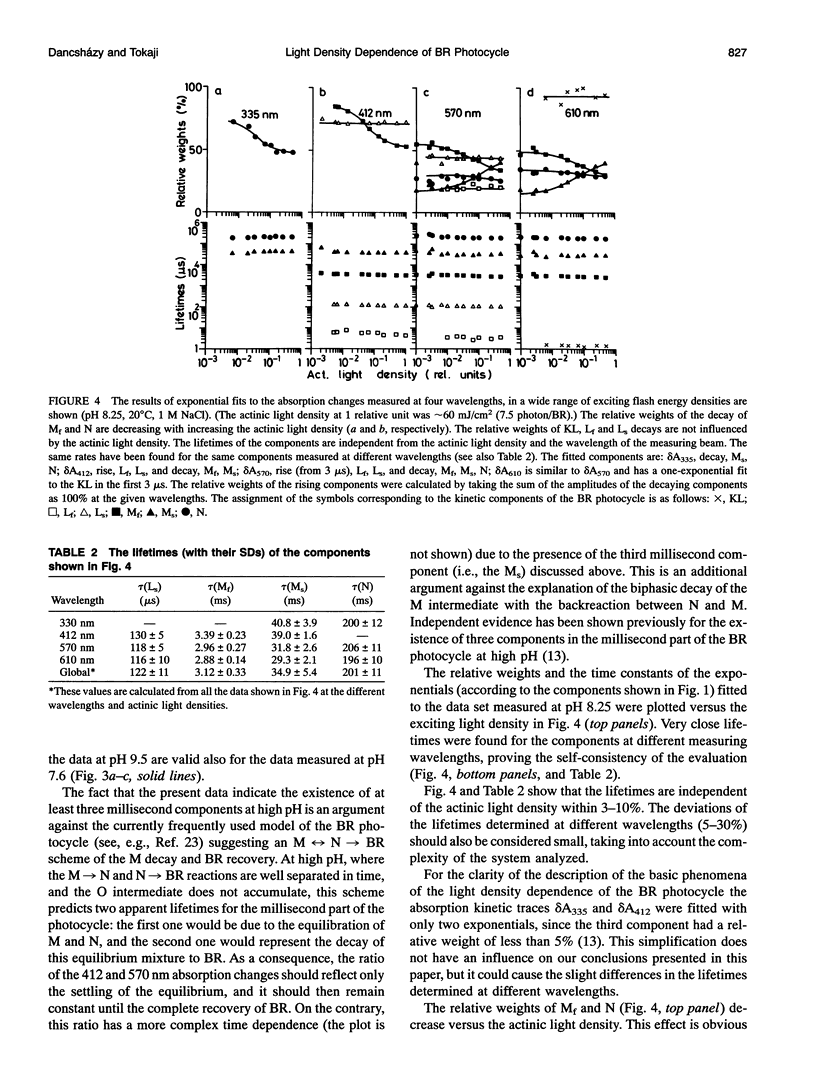
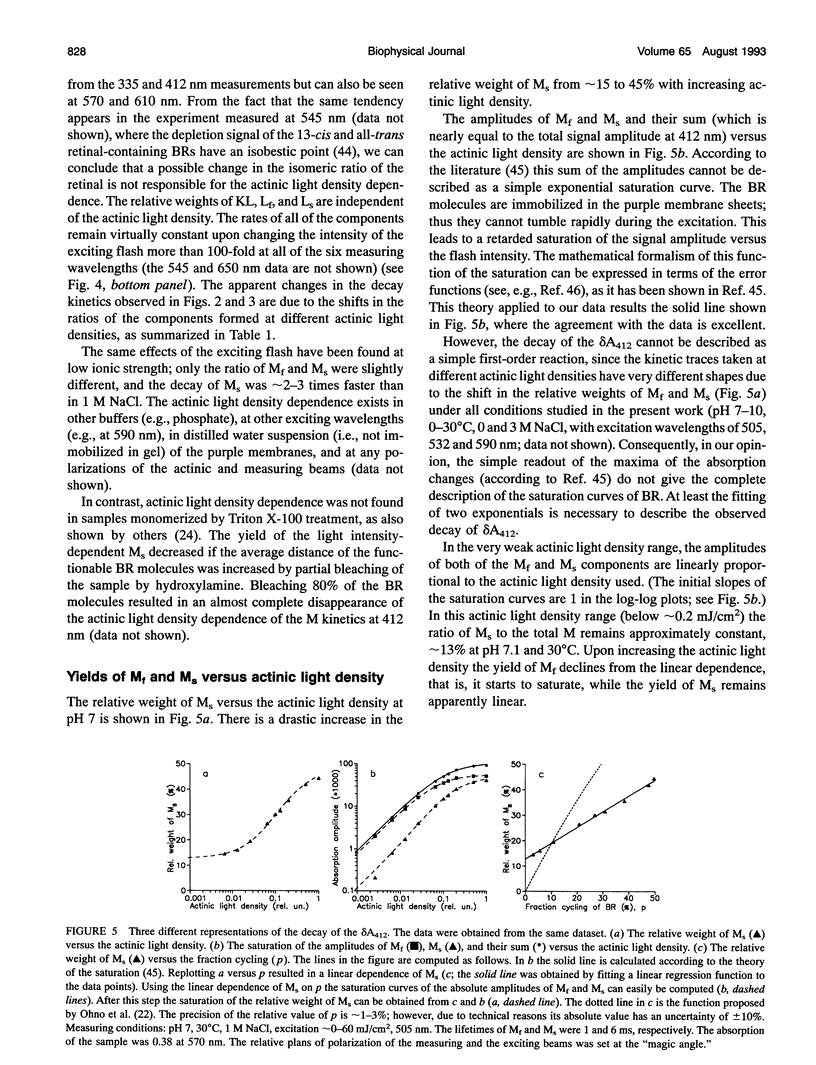
The photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin (BR) was studied in the 0.3 microsecond to 10 s time interval after excitation, using a wide range of actinic light intensities (10 ns half-duration, 0.06-60 mJ/cm2), at neutral and alkaline pH values. The relative weights of the rapidly and the slowly decaying components of the M intermediate (Mf and M(s), respectively) and the yield of the third millisecond component, N(R,P), are the function of the exciting light intensity (density), while their lifetimes are not. The relative weight of M(s) is found to be a linear function of the portion of the BR molecules undergoing the photocycle. This suggests the existence of a cooperative interaction of the BR molecules arranged in the crystalline purple membrane sheets. Another source of M(s) is also found, which results a nonvanishing relative weight of M(s) even at very weak actinic light density values. The explanation for this may be a branching, or the heterogeneity of BR itself or with its environment. It is shown that the relative weights of the rising and decaying components of the M form(s) do not correlate directly with each other.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahl P. L., Cone R. A. Light activates rotations of bacteriorhodopsin in the purple membrane. Biophys J. 1984 Jun;45(6):1039–1049. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84251-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames J. B., Mathies R. A. The role of back-reactions and proton uptake during the N----O transition in bacteriorhodopsin's photocycle: a kinetic resonance Raman study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7181–7190. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balashov S. P., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. Redshift of the purple membrane absorption band and the deprotonation of tyrosine residues at high pH: Origin of the parallel photocycles of trans-bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1991 Aug;60(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82074-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. R. Nature of the primary photochemical events in rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):293–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernavskii D. S., Chizhov I. V., Lozier R. H., Murina T. M., Prokhorov A. M., Zubov B. V. Kinetic model of bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: pathway from M state to bR. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 May;49(5):649–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb08437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancsházy Z., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. Independent photocycles of the spectrally distinct forms of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6358–6361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N., Wilms M. Flash photometric experiments on the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys Struct Mech. 1975 May 30;1(3):259–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00535760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dér A., Hargittai P., Simon J. Time-resolved photoelectric and absorption signals from oriented purple membranes immobilized in gel. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1985 Mar;10(5-6):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(85)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrey T. G., Becher B., Mao B., Kilbride P., Honig B. Exciton interactions and chromophore orientation in the purple membrane. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):377–397. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kouyama T. Photoreaction of bacteriorhodopsin at high pH: origins of the slow decay component of M. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11740–11747. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Balashov S. P., Ebrey T. G. Quantum efficiency of the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):597–608. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82403-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groma G. I., Dancshazy Z. How Many M Forms are there in the Bacteriorhodopsin Photocycle? Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83469-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanamoto J. H., Dupuis P., El-Sayed M. A. On the protein (tyrosine)-chromophore (protonated Schiff base) coupling in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B., Kuschmitz D. Branching reactions in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Nasuda-Kouyama A., Ikegami A., Mathew M. K., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin photoreaction: identification of a long-lived intermediate N (P,R350) at high pH and its M-like photoproduct. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5855–5863. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Xie A., Hofrichter J., Clore G. M. Reversible steps in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3610–3614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T. Nonproton ion release by purple membranes exhibits cooperativity as shown by determination of the optical cross-section. Biophys J. 1988 Aug;54(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82948-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder S. J., Kliger D. S. A time-resolved spectral study of the K and KL intermediates of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):465–468. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83124-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Parodi L. A., Lozier R. H. Procedure for testing kinetic models of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1982 May;38(2):161–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84543-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J. Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. Flash-induced volume changes of bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments and their relationship to proton movements and absorbance transients. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Lindau M., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Aspartic acid-96 is the internal proton donor in the reprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokaji Z., Dancsházy Z. Kinetics of the N intermediate and the two pathways of recovery of the ground-state of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 26;311(3):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokaji Z., Dancsházy Z. Light-induced, long-lived perturbation of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80385-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Pathways of the rise and decay of the M photointermediate(s) of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2241–2250. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie A. H., Nagle J. F., Lozier R. H. Flash spectroscopy of purple membrane. Biophys J. 1987 Apr;51(4):627–635. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83387-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Keszthelyi L., Lanyi J. K. Transient spectroscopy of bacterial rhodopsins with an optical multichannel analyzer. 1. Comparison of the photocycles of bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5165–5172. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


