Abstract
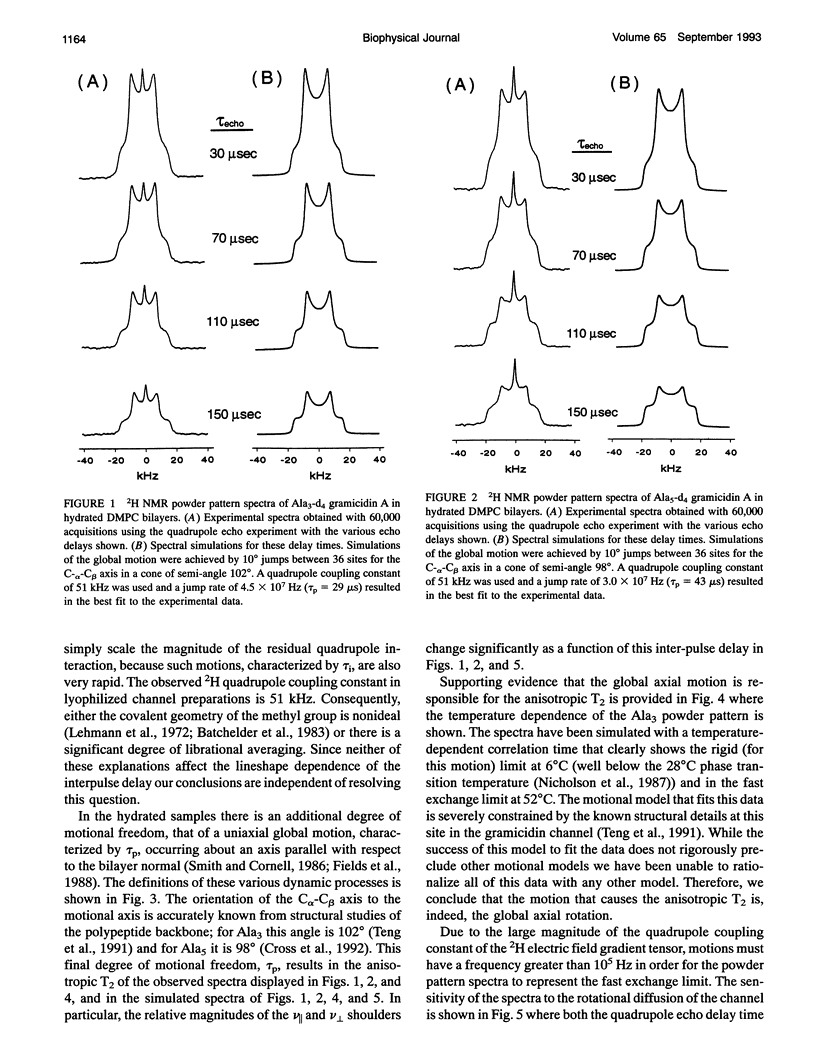
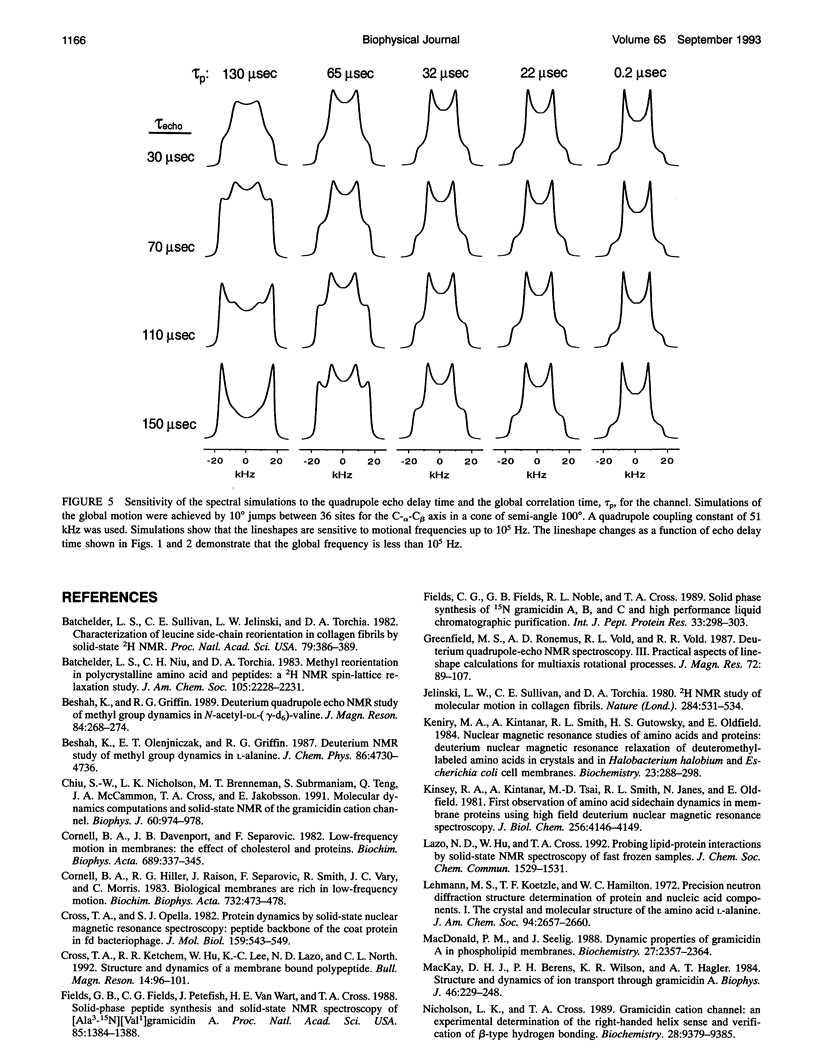
A detailed experimental description of molecular dynamics requires an accurate description of the global correlation time. For the gramicidin cation-selective channel the local dynamics of the polypeptide backbone are thought to play a very significant role in the functional process of this channel which occurs on the 10-100-ns time scale. By solid-state NMR spectroscopy an experimental description of the local dynamics including a description of the axis about which the motions occur, the amplitude of the motions, whether they are diffusional or discontinuous and the frequency of the motions is possible. Initial interpretations of the NMR data for this polypeptide backbone in fully hydrated lipid bilayers suggests that the time scale for the local motions is the same as the kinetic time scale (North and Cross, 1993). Here the global correlation time is found from d4-Ala3 and d4-Ala5-gramicidin A powder pattern spectra to be 36 microseconds at 309 K. This surprisingly long correlation time may reflect the high viscosity of the peptide environment or possibly the higher molecular weight of a peptide-lipid aggregate. Furthermore, this reassessment of the global correlation time supports the initial interpretation of relaxation data for the local motions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batchelder L. S., Sullivan C. E., Jelinski L. W., Torchia D. A. Characterization of leucine side-chain reorientation in collagen-fibrils by solid-state 2H NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):386–389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Nicholson L. K., Brenneman M. T., Subramaniam S., Teng Q., McCammon J. A., Cross T. A., Jakobsson E. Molecular dynamics computations and solid state nuclear magnetic resonance of the gramicidin cation channel. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):974–978. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82131-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Davenport J. B., Separovic F. Low-frequency motion in membranes. The effect of cholesterol and proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 28;689(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Hiller R. G., Raison J., Separovic F., Smith R., Vary J. C., Morris C. Biological membranes are rich in low-frequency motion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross T. A., Opella S. J. Protein dynamics by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Peptide backbone of the coat protein in fd bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90301-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields C. G., Fields G. B., Noble R. L., Cross T. A. Solid phase peptide synthesis of 15N-gramicidins A, B, and C and high performance liquid chromatographic purification. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Apr;33(4):298–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1989.tb01285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields G. B., Fields C. G., Petefish J., Van Wart H. E., Cross T. A. Solid-phase peptide synthesis and solid-state NMR spectroscopy of [Ala3-15N][Val1]gramicidin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1384–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinski L. W., Sullivan C. E., Torchia D. A. 2H NMR study of molecular motion in collagen fibrils. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):531–534. doi: 10.1038/284531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keniry M. A., Kintanar A., Smith R. L., Gutowsky H. S., Oldfield E. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of amino acids and proteins. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation of deuteriomethyl-labeled amino acids in crystals and in Halobacterium halobium and Escherichia coli cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):288–298. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsey R. A., Kintanar A., Tsai M. D., Smith R. L., Janes N., Oldfield E. First observation of amino acid side chain dynamics in membrane proteins using high field deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4146–4149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann M. S., Koetzle T. F., Hamilton W. C. Precision neutron diffraction structure determination of protein and nucleic acid components. I. The crystal and molecular structure of the amino acid L-alanine. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Apr 19;94(8):2657–2660. doi: 10.1021/ja00763a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Seelig J. Dynamic properties of gramicidin A in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2357–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay D. H., Berens P. H., Wilson K. R., Hagler A. T. Structure and dynamics of ion transport through gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):229–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84016-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. K., Cross T. A. Gramicidin cation channel: an experimental determination of the right-handed helix sense and verification of beta-type hydrogen bonding. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9379–9385. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. K., Moll F., Mixon T. E., LoGrasso P. V., Lay J. C., Cross T. A. Solid-state 15N NMR of oriented lipid bilayer bound gramicidin A'. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6621–6626. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. K., Teng Q., Cross T. A. Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance derived model for dynamics in the polypeptide backbone of the gramicidin A channel. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):621–637. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90706-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng J. W., Wagner G. Mapping of the spectral densities of N-H bond motions in eglin c using heteronuclear relaxation experiments. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8571–8586. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Z. Y., Simplaceanu V., Dowd S. R., Ho C. Effects of cholesterol or gramicidin on slow and fast motions of phospholipids in oriented bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8758–8762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Z. Y., Simplaceanu V., Lowe I. J., Ho C. Rotating-frame relaxation studies of slow motions in fluorinated phospholipid model membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):81–95. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82933-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Karplus M. The normal modes of the gramicidin-A dimer channel. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):297–309. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83107-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Cornell B. A. The dynamics of the intrinsic membrane polypeptide gramicidin a in phospholipid bilayers: a solid state carbon-13 NMR study. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):117–118. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83617-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng Q., Nicholson L. K., Cross T. A. Experimental determination of torsion angles in the polypeptide backbone of the gramicidin A channel by solid state nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):607–619. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90705-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



