Abstract
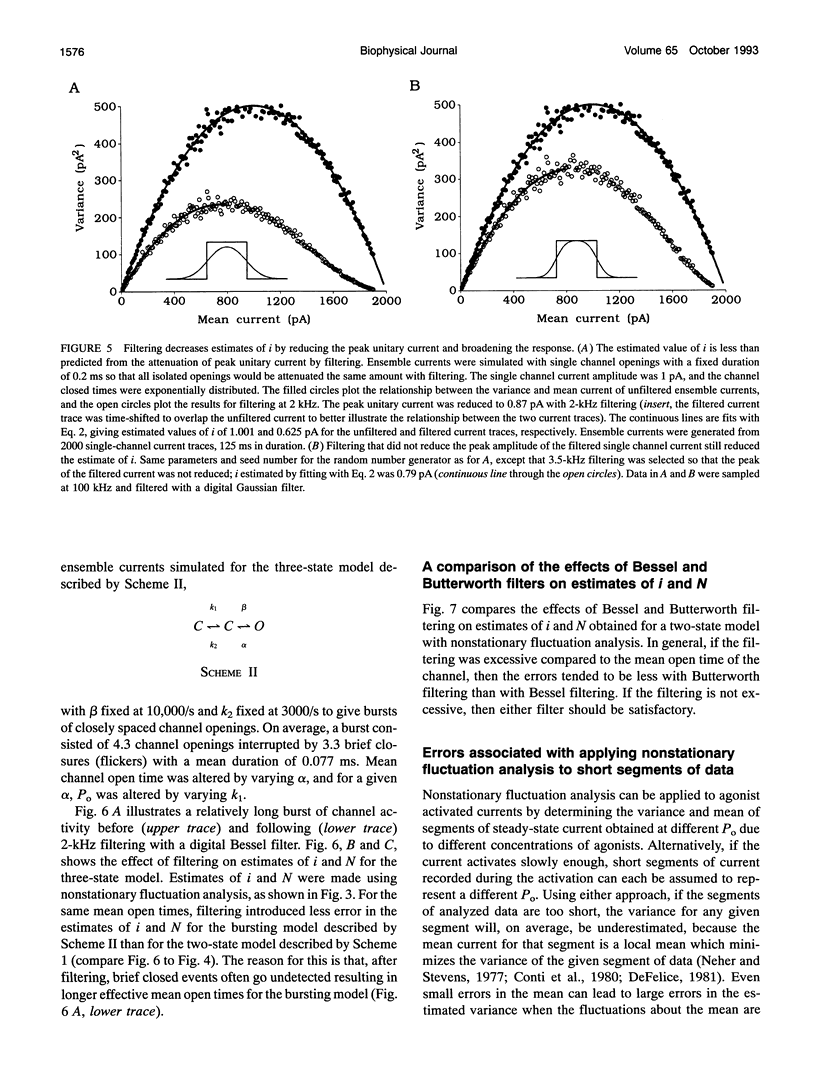
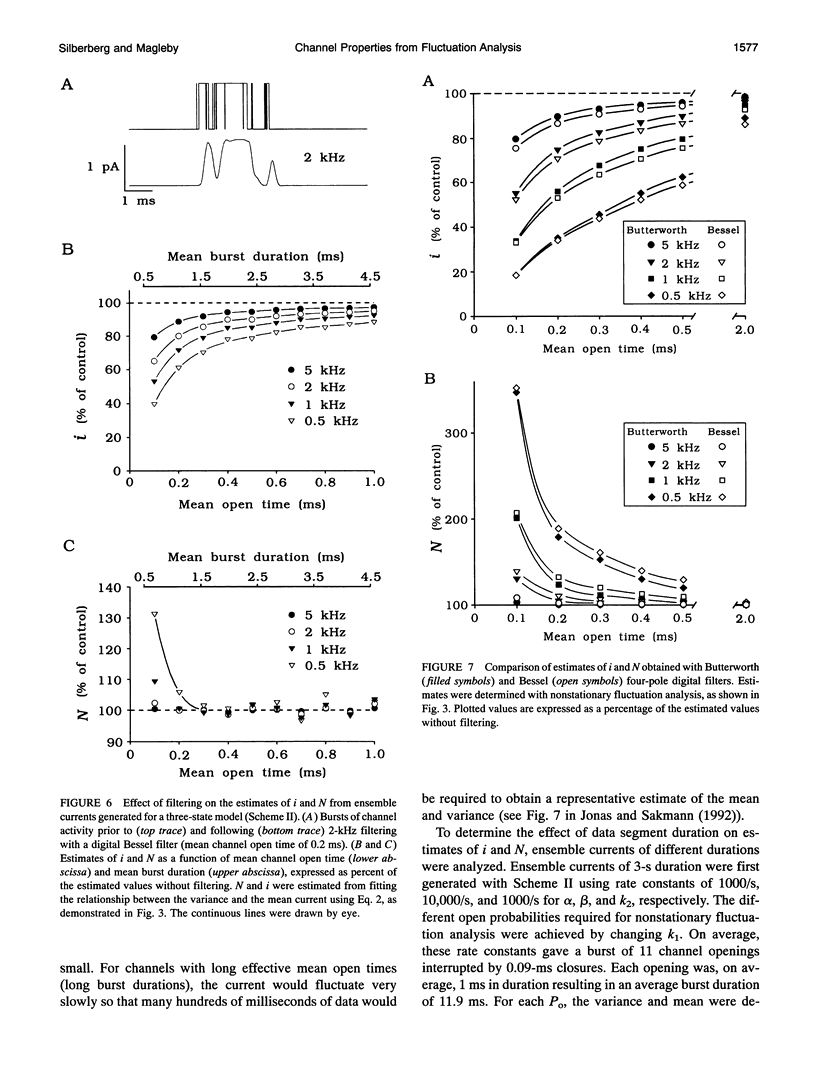
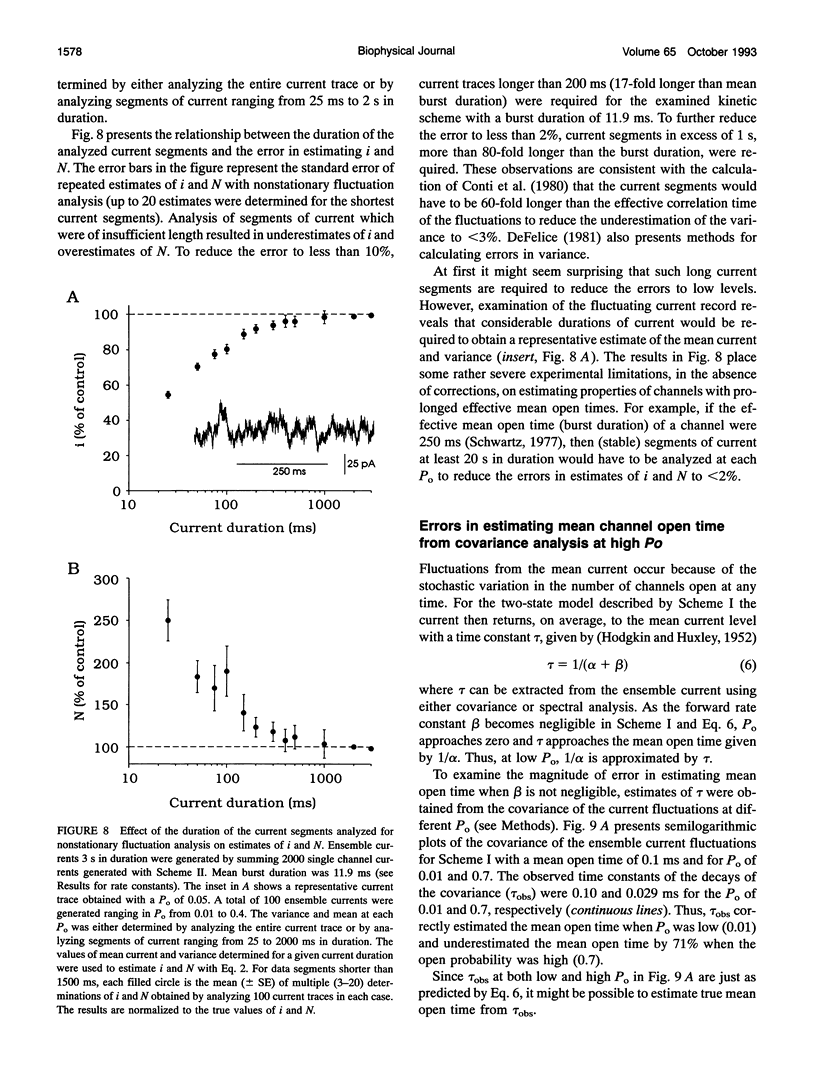
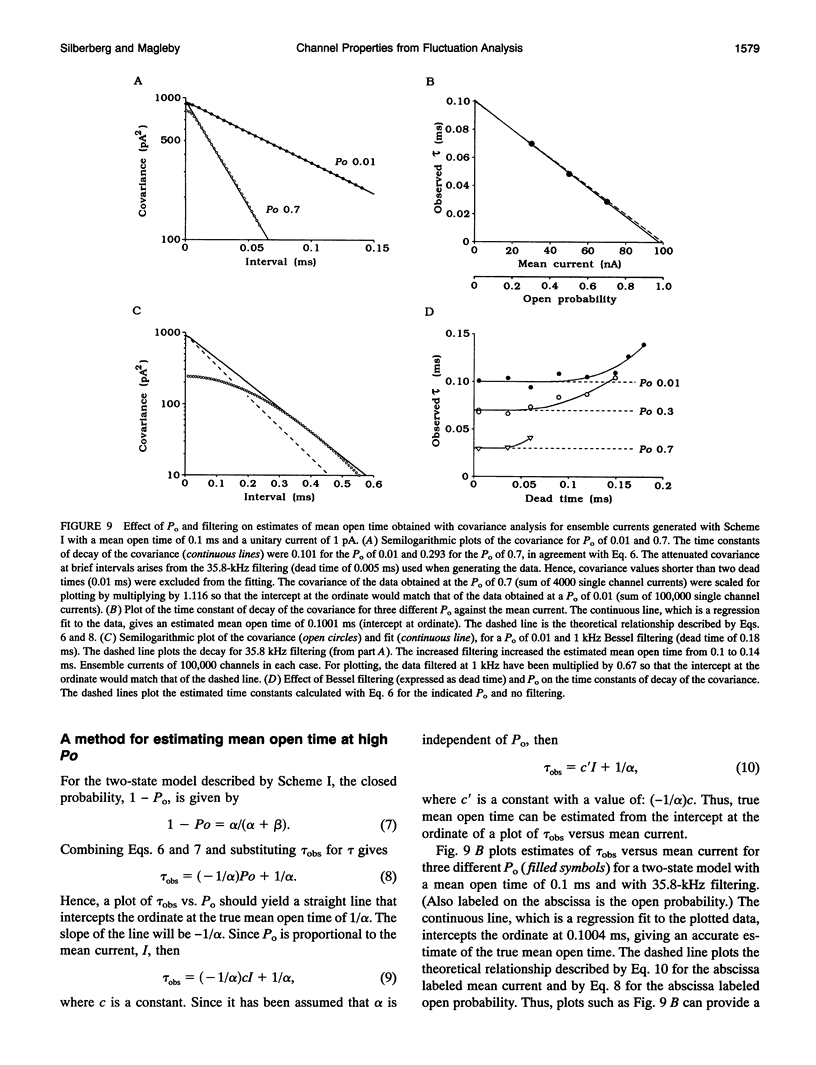
The conductance, number, and mean open time of ion channels can be estimated from fluctuations in membrane current. To examine potential errors associated with fluctuation analysis, we simulated ensemble currents and estimated single channel properties. The number (N) and amplitude (i) of the underlying single channels were estimated using nonstationary fluctuation analysis, while mean open time was estimated using covariance and spectral analysis. Both excessive filtering and the analysis of segments of current that were too brief led to underestimates of i and overestimates of N. Setting the low-pass cut-off frequency of the filter to greater than five times the inverse of the effective mean channel open time (burst duration) and analyzing segments of current that were at least 80 times the effective mean channel open time reduced the errors to < 2%. With excessive filtering, Butterworth filtering gave up to 10% less error in estimating i and N than Bessel filtering. Estimates of mean open time obtained from the time constant of decay of the covariance, tau obs, at low open probabilities (Po) were much less sensitive to filtering than estimates of i and N. Extrapolating plots of tau obs versus mean current to the ordinate provided a method to estimate mean open time from data obtained at higher Po, where tau obs no longer represents mean open time. Bessel filtering gave the least error when estimating tau obs from the decay of the covariance function, and Butterworth filtering gave the least error when estimating tau obs from spectral density functions.
Full text
PDF
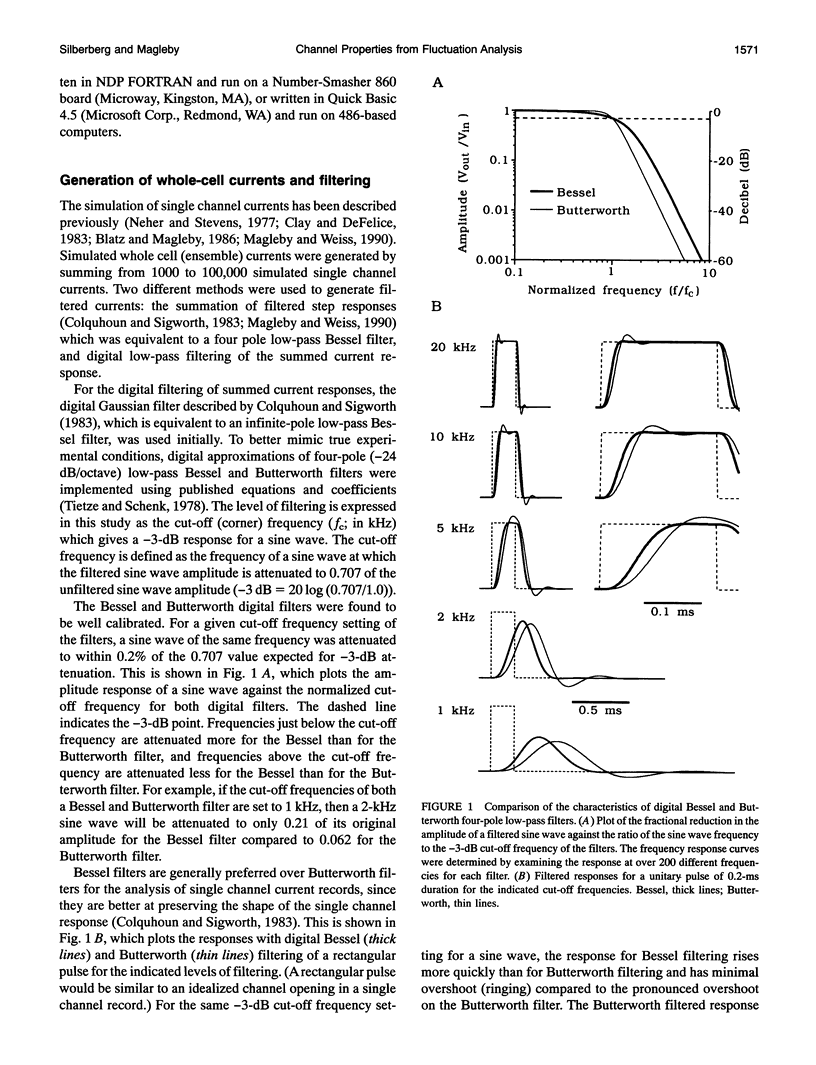

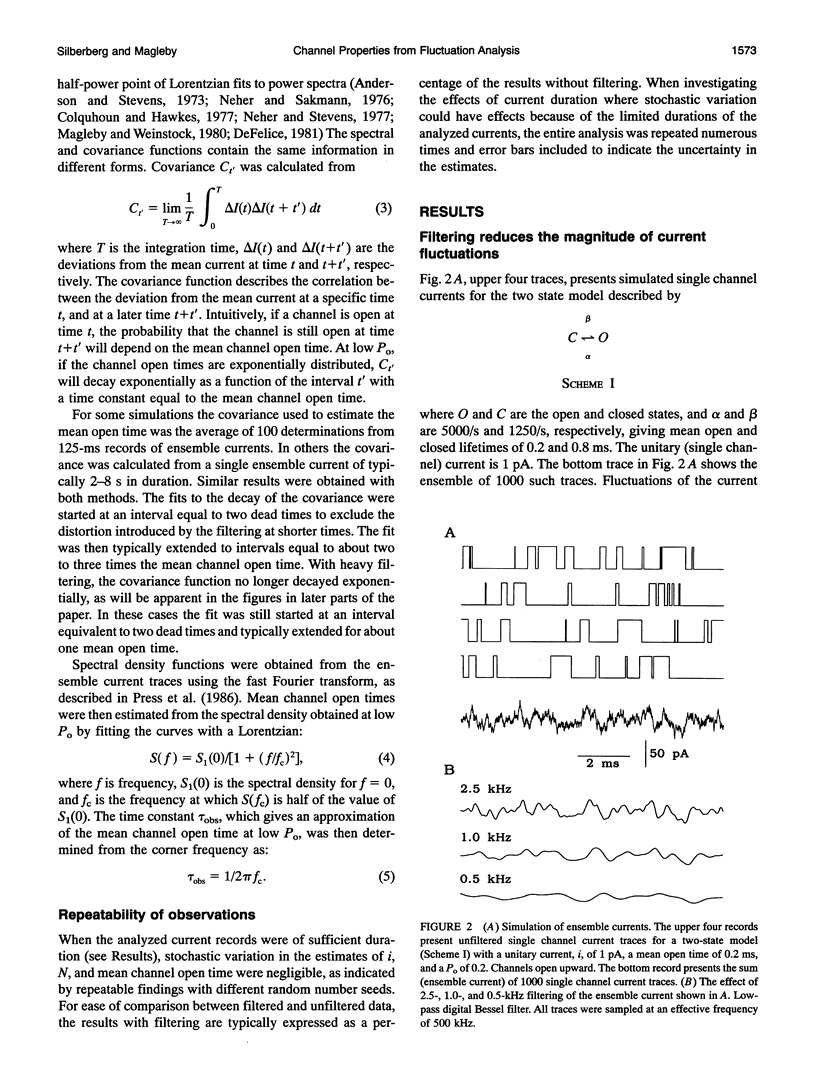
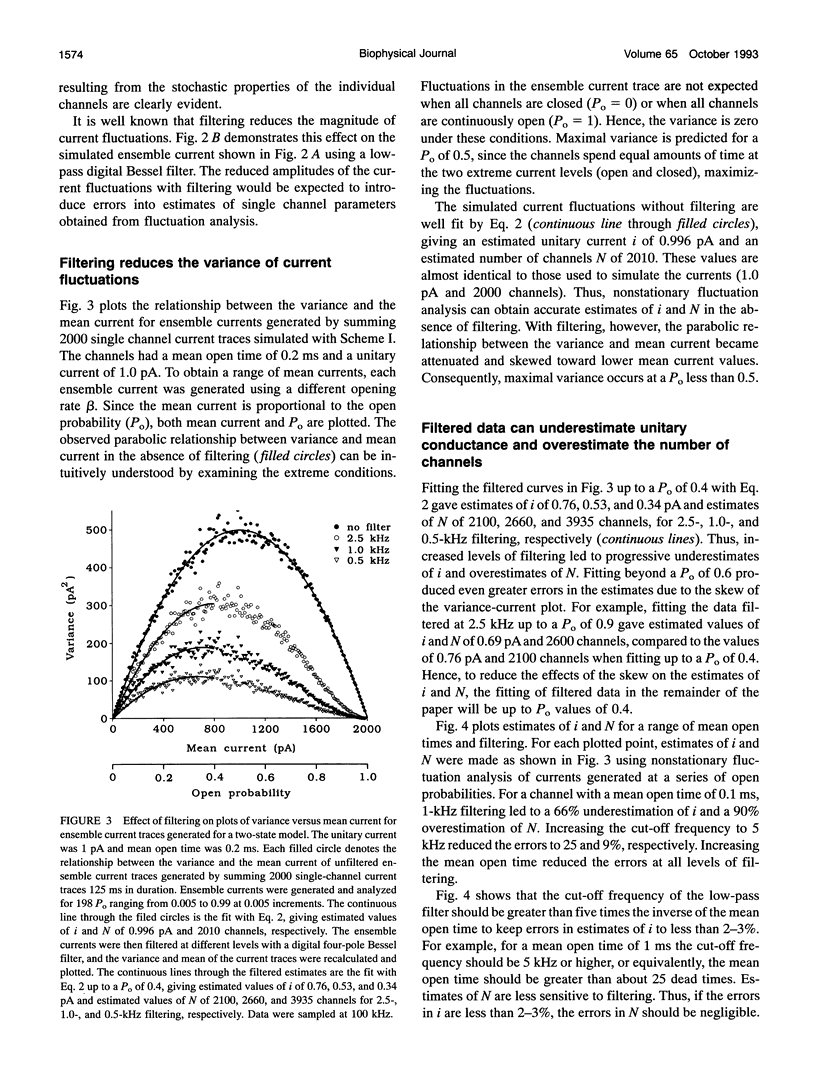
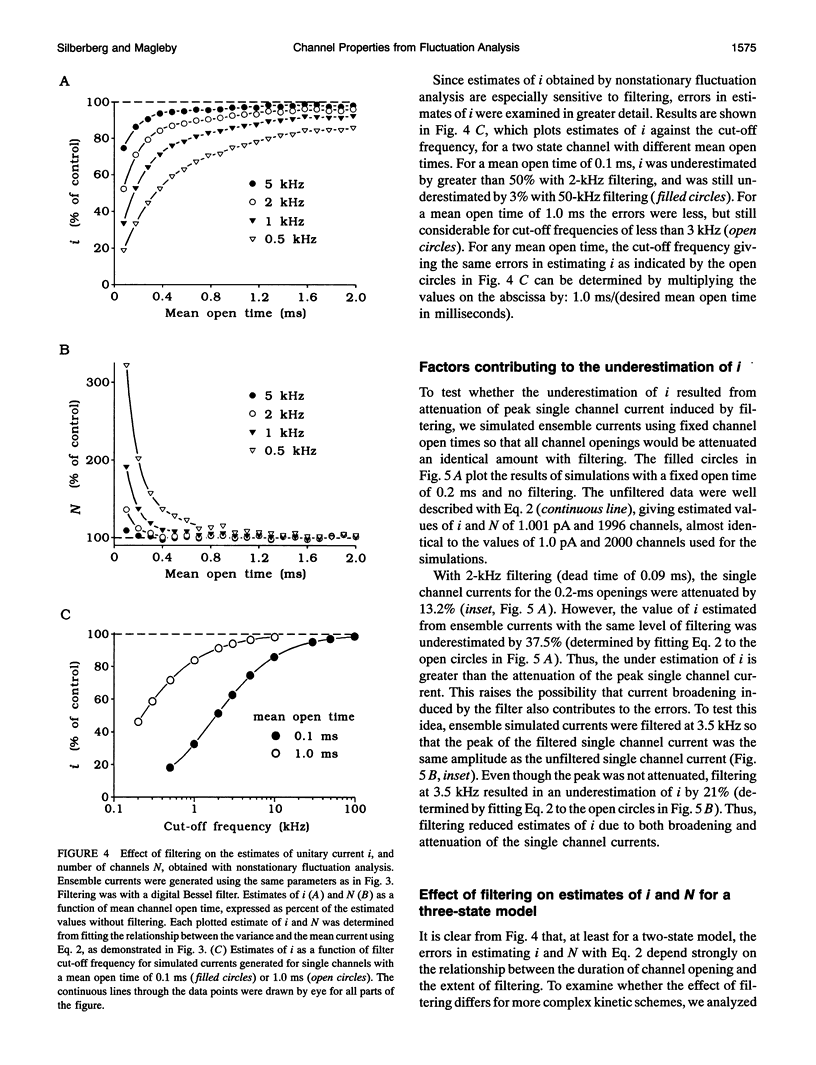




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. B., Kass R., Begenisich T. Nonstationary fluctuation analysis of the delayed rectifier K channel in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Actions of norepinephrine on single-channel current. Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):731–738. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82872-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Correcting single channel data for missed events. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):967–980. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83725-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Osterrieder W., Trautwein W. Beta-adrenergic increase in the calcium conductance of cardiac myocytes studied with the patch clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jun;401(2):111–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00583870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay J. R., DeFelice L. J. Relationship between membrane excitability and single channel open-close kinetics. Biophys J. 1983 May;42(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84381-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Hille B., Nonner W. Non-stationary fluctuations of the potassium conductance at the node of ranvier of the frog. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:199–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Neumcke B., Nonner W., Stämpfli R. Conductance fluctuations from the inactivation process of sodium channels in myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:217–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P., Ogden D. C., Colquhoun D. Conductances of single ion channels opened by nicotinic agonists are indistinguishable. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):160–162. doi: 10.1038/309160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grissmer S., Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in human leukemic T cells. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jan;99(1):63–84. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton T., Hudspeth A. J. The transduction channel of hair cells from the bull-frog characterized by noise analysis. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:195–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E. Glutamate receptor channels in rat DRG neurons: activation by kainate and quisqualate and blockade of desensitization by Con A. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):255–266. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90163-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Sakmann B. Glutamate receptor channels in isolated patches from CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:143–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimitsuki T., Mitsuiye T., Noma A. Maximum open probability of single Na+ channels during depolarization in guinea-pig cardiac cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jul;416(5):493–500. doi: 10.1007/BF00382681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Brown A. M. Patch and whole cell calcium currents recorded simultaneously in snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1984 May;83(5):727–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Weinstock M. M. Nickel and calcium ions modify the characteristics of the acetylcholine receptor-channel complex at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Weiss D. S. Estimating kinetic parameters for single channels with simulation. A general method that resolves the missed event problem and accounts for noise. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1411–1426. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82487-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon D. G., Knapp A. G., Dowling J. E. Horizontal cell gap junctions: single-channel conductance and modulation by dopamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7639–7643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Noise analysis of drug induced voltage clamp currents in denervated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):705–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Stevens C. F. Conductance fluctuations and ionic pores in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:345–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Marsh S. J., Brown D. A. M-current noise and putative M-channels in cultured rat sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:269–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. P., Sahara Y., Kawai N. Nonstationary fluctuation analysis and direct resolution of single channel currents at postsynaptic sites. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82223-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L. The kinetics of local anesthetic blockade of end-plate channels. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):625–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Voltage noise observed in rods of the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Covariance of nonstationary sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):111–133. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84840-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Open channel noise. I. Noise in acetylcholine receptor currents suggests conformational fluctuations. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):709–720. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83968-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


