Abstract
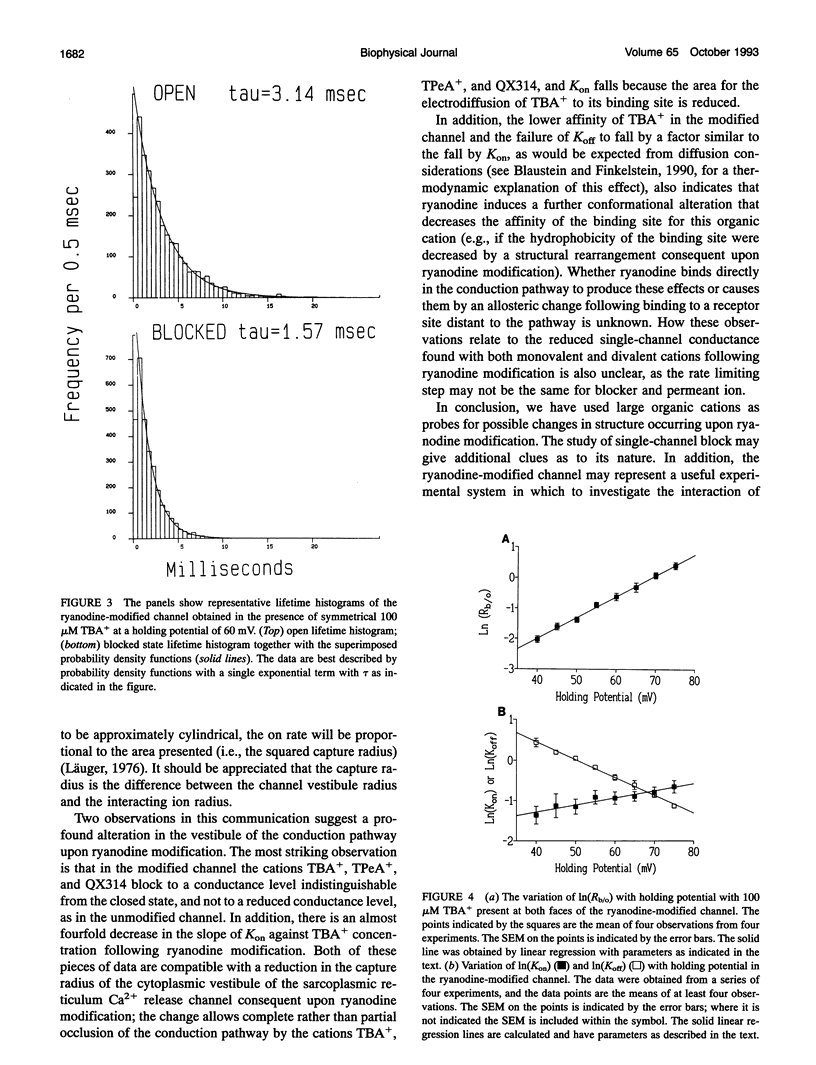
We have reported that the large impermeant organic cations tetrabutyl ammonium (TBA+), tetrapentyl ammonium, and the charged local anesthetic QX314 produce unique reduced conductance states in the purified sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel when present at the cytoplasmic face of the channel. We have interpreted this as a form of partial occlusion by the blocking cation in wide vestibules of the conduction pathway. Following modification with ryanodine, which causes the channel to enter a reduced conductance state with long open dwell time, these cations block the receptor channel to a level that is indistinguishable from the closed state. The voltage dependence of TBA+'s interaction with the Ca2+ release channel is the same before and after ryanodine modification. The concentration dependence is different, in that the ryanodine-modified channel has one-third the affinity for TBA+, which is accounted for predominantly by changes in the TBA+ on rate. The data are compatible with a structural change in the vestibule of the conduction pathway consequent upon ryanodine binding that reduces the capture radius for blocking ion entry.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertl A., Blumwald E., Coronado R., Eisenberg R., Findlay G., Gradmann D., Hille B., Köhler K., Kolb H. A., MacRobbie E. Electrical measurements on endomembranes. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):873–874. doi: 10.1126/science.1439795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Quantitative description of three modes of activity of fast chloride channels from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:141–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein R. O., Finkelstein A. Diffusion limitation in the block by symmetric tetraalkylammonium ions of anthrax toxin channels in planar phospholipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Nov;96(5):943–957. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.5.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa A. M., Latorre R., Bezanilla F. Ion permeation in normal and batrachotoxin-modified Na+ channels in the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Mar;97(3):605–625. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Ogunbunmi E. M., Dixon M. C., Fleer E. A. Localization of Ca2+ release channels with ryanodine in junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7256–7259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I. Batrachotoxin as a tool to study voltage-sensitive sodium channels of excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;45(2):57–148. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J. Single sodium channels from rat brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):172–175. doi: 10.1038/303172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattanzio F. A., Jr, Schlatterer R. G., Nicar M., Campbell K. P., Sutko J. L. The effects of ryanodine on passive calcium fluxes across sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2711–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. R., Manning S. D., Williams A. J. Monovalent cation conductance in the ryanodine receptor-channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:463–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Functional characterisation of the ryanodine receptor purified from sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 26;1064(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Diffusion-limited ion flow through pores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):493–509. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90320-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):401–411. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Garber S. S., Miller C. Batrachotoxin-activated Na+ channels in planar lipid bilayers. Competition of tetrodotoxin block by Na+. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):665–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessah I. N., Francini A. O., Scales D. J., Waterhouse A. L., Casida J. E. Calcium-ryanodine receptor complex. Solubilization and partial characterization from skeletal muscle junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8643–8648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitsapesan R., Williams A. J. Mechanisms of caffeine activation of single calcium-release channels of sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:425–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Block of the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-release channel by tetra-alkyl ammonium cations. J Membr Biol. 1992 Apr;127(2):149–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00233287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Large tetraalkyl ammonium cations produce a reduced conductance state in the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-release channel. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1122–1132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81922-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Williams A. J. Charged local anesthetics block ionic conduction in the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release channel. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):852–864. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81104-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins B., Harding S. E., Kirby M. S., Poole-Wilson P. A., Williams A. J. Contamination of a cardiac sarcolemmal preparation with endothelial plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


